Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
DCN NetworkTopologies
Încărcat de
SeanDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
DCN NetworkTopologies
Încărcat de
SeanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
2. What is network topology ? Explain the different network topologies.
The term physical topology refers to the way in which a network is laid out physically:
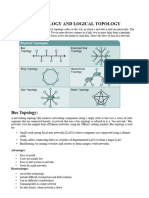
I/O or more devices connect to a link; two or more links form a topology. There are four basic topologies possible: mesh, star, bus, and ring.
Advantages Disadvantages
Bus Topology • Bus topology includes ease of • Difficult reconnection and fault
installation. isolation.
• A bus uses less cabling than mesh or • A fault or break in the bus cable stops
star topologies. all transmission, even between devices
The preceding examples all describe point-to- on the same side of the problem.
point connections.
A bus topology, on the other hand, is
multipoint.
One long cable acts as a backbone to link all
the devices in a network.
Ring Topology • A ring is relatively easy to install and • Unidirectional traffic can be a
reconfigure. Fault isolation is disadvantage.
simplified. • In a simple ring, a break in the ring
(such as a disabled station) can
disable the entire network.
In a ring topology, each device has a dedicated
point-to-point connection with only the two
devices on either side of it.
A signal is passed along the ring in one
direction, from device to device, until it reaches
its destination.
Advantages Disadvantages
Mesh Topology • The use of dedicated links guarantees • Amount of cabling and the number of
that each connection can carry its own I/O ports required.
data load, thus eliminating the traffic • The sheer bulk of the wiring can be
problems that can occur when links greater than the available space (in
must be shared by multiple devices. walls, ceilings, or floors) can
• A mesh topology is robust. If one link accommodate.
Mesh In a mesh topology, every device has a becomes unusable, it does not • The hardware required to connect each
dedicated point-to-point link to every other incapacitate the entire system. link (I/O ports and cable) can be
device. • There is the advantage of privacy or prohibitively expensive.
The term dedicated means that the link carries security. When every message travels
traffic only between the two devices it along a dedicated line, only the
connects. intended recipient sees it.
Node 1 must be connected to n - 1nodes, node • Point-to-point links make fault
2 must be connected to n – 1 nodes, and identification and fault isolation easy.
finally node n must be connected to n - 1
nodes. We need n (n - 1) physical links.
Star Topology • A star topology is less expensive than a • The dependency of the whole topology
mesh topology. bon one single point, the hub. If the hub
goes down, the whole system is dead.
• In a star, each device needs only one
link and one I/O port to connect it to • Although a star requires far less cable
any number of others. This factor also than a mesh, each node must be linked
In a star topology, each device has a dedicated makes it easy to install and to a central hub.
point-to-point link only to a central controller, reconfigure.
usually called a hub. • Far less cabling needs to be housed,
The devices are not directly linked to one and additions, moves, and deletions
another. Unlike a mesh topology, a star involve only one connection: between
topology does not allow direct traffic between that device and the hub.
devices. • Other advantages include robustness.
If one link fails, only that link is
The controller acts as an exchange: If one affected. All other links remain active.
device wants to send data to another, it sends
the data to the controller, which then relays the
data to the other connected device.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P1 MarkschemeDocument21 paginiPhysics H2 9749 Specimen P1 MarkschemeSeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 2 AnswersDocument4 paginiPaper 2 AnswersSean100% (1)
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P3Document25 paginiPhysics H2 9749 Specimen P3SeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P3Document25 paginiPhysics H2 9749 Specimen P3SeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P2Document24 paginiPhysics H2 9749 Specimen P2SeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P2Document24 paginiPhysics H2 9749 Specimen P2SeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coll. - Success One HSC Physics 2017 (2017, Pascal Press)Document546 paginiColl. - Success One HSC Physics 2017 (2017, Pascal Press)Sean100% (2)
- FortiNAC Quiz - Attempt ReviewDocument3 paginiFortiNAC Quiz - Attempt Reviewullianjnathan0% (1)
- TopologyDocument6 paginiTopologyHaruhi SuzumiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P1 MarkschemeDocument21 paginiPhysics H2 9749 Specimen P1 MarkschemeSeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syc Ale Jan, Mar & Jul Fee Structure 2019Document1 paginăSyc Ale Jan, Mar & Jul Fee Structure 2019SeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologyDocument15 paginiNetwork TopologyKritika TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-1 (Part-B)Document158 paginiUnit-1 (Part-B)LEKHAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Concepts of Computer Networks and Communications Network TopologyDocument21 paginiBasic Concepts of Computer Networks and Communications Network Topologydanding aganonÎncă nu există evaluări
- NetworktopologyDocument35 paginiNetworktopologyAkshay ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect1 Network BasicsDocument28 paginiLect1 Network BasicsVibhav ChhabraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Concepts of Computer Networks and Communications Network TopologyDocument21 paginiBasic Concepts of Computer Networks and Communications Network TopologyGen Pantaleon Garcia ShsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Concepts of Computer Networks and Communications Network TopologyDocument18 paginiBasic Concepts of Computer Networks and Communications Network TopologyVijay KambleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topology (Avdesh)Document14 paginiTopology (Avdesh)Avdesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- TopologyDocument17 paginiTopologyPiush SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition of Network Topology Types of Network Topology Differentiation Between The Types of Network TopologyDocument25 paginiDefinition of Network Topology Types of Network Topology Differentiation Between The Types of Network Topologykritagya chandra100% (3)
- Basic Concepts of Computer Networks and Communications Network TopologyDocument21 paginiBasic Concepts of Computer Networks and Communications Network TopologyHiba MoussaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologiesDocument43 paginiNetwork TopologiesKunal Sah100% (1)
- Network Topologies: 1-Bus TopologyDocument4 paginiNetwork Topologies: 1-Bus TopologyIqra KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 307 Lab3Document33 pagini307 Lab3Thohith ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topology Mind-MapDocument1 paginăTopology Mind-Mapmitchlovemore2Încă nu există evaluări
- Topology ProjectDocument14 paginiTopology ProjectAbhishek Gupta33% (3)
- Network TopologiesDocument43 paginiNetwork Topologiesayunik615Încă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks: Network TopologiesDocument8 paginiComputer Networks: Network Topologiesharshit suriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologiesDocument24 paginiNetwork TopologiesArslanKamranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 2.1 Network Topology Pros & ConsDocument15 paginiLec 2.1 Network Topology Pros & ConsSuman JyotiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Networking TopologiesDocument4 paginiNetworking Topologiessamriti100% (6)
- Network TopologyDocument18 paginiNetwork TopologyArchanaa PadmavathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 CCNDocument17 paginiLecture 2 CCNNoor UddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classrom PPT For TopologiesDocument8 paginiClassrom PPT For TopologiesdarshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of TopologiesDocument17 paginiTypes of Topologiesgwapogi0320Încă nu există evaluări
- Network Hardware:: Transmission Technology and ScaleDocument8 paginiNetwork Hardware:: Transmission Technology and Scalemoon iqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologiesDocument11 paginiNetwork TopologiesYashfa ShafiqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologyDocument26 paginiNetwork Topologyvijaysingh100% (25)
- Different Types of Topologies.Document23 paginiDifferent Types of Topologies.Fernando TanginÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Network TopologiesDocument18 pagini2 Network TopologiesPRO GAMERÎncă nu există evaluări
- MD AMANULLAH PPT - PPT-1Document19 paginiMD AMANULLAH PPT - PPT-1zeeshan2001md0Încă nu există evaluări
- Presentation Types of Topologies 1487157223 247536Document9 paginiPresentation Types of Topologies 1487157223 247536Priyam TripathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISO-8859-1 - Network TopologiesDocument13 paginiISO-8859-1 - Network TopologiesMithicher BaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologiesDocument18 paginiNetwork TopologiesAkshita GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 5 Mesh TopologyDocument12 paginiGroup 5 Mesh Topologymarivic itongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Topology and Logical TopologyDocument3 paginiPhysical Topology and Logical TopologyNO NameÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Network TopologyDocument26 paginiTypes of Network TopologyRoyan HabibieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document29 paginiChapter 1muhammedsuhailch7Încă nu există evaluări
- TopologyDocument13 paginiTopologyhadirehman488Încă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologyDocument25 paginiNetwork TopologySSB WORLDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologyDocument25 paginiNetwork Topology421 Rushikesh Bhavsar IFÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Network Topology 10Document11 paginiComputer Network Topology 10家星Încă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologyDocument36 paginiNetwork TopologySai NarayananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologyDocument24 paginiNetwork TopologyVahough BhielhattÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 4-Network TopologiesDocument17 paginiLecture 4-Network TopologiesNikhil GaddamÎncă nu există evaluări
- TopologyDocument33 paginiTopologyRanjan Dwivedi100% (1)
- TopologyDocument37 paginiTopologyMahbubul Islam KoushickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Networking 1.2Document7 paginiNetworking 1.2Echo greenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Communication and Networks: Course: BBA Subject: Introduction To Computer Unit: 4Document27 paginiData Communication and Networks: Course: BBA Subject: Introduction To Computer Unit: 4220479Încă nu există evaluări
- Topologyies by SyedDocument19 paginiTopologyies by SyedSyed hasan haiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- NetworkDocument14 paginiNetworkfifen pokaro ousseniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blue Computer Icon Background Technology PresentationDocument13 paginiBlue Computer Icon Background Technology Presentationmarivic itongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks Lecture - 2-: Dr. Abbas A. AbdulazeezDocument25 paginiComputer Networks Lecture - 2-: Dr. Abbas A. AbdulazeezDimitris TheodoropoulosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Neha Gulati Assistant Professor University Business School Panjab University, ChandigarhDocument11 paginiDr. Neha Gulati Assistant Professor University Business School Panjab University, ChandigarhNavneet NandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CN - Assignment2Document14 paginiCN - Assignment2WhatsApp statusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic NetworkingDocument8 paginiBasic NetworkingDavid Atoroyo SikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Chapter 2 Network TopologyDocument9 pagini2 Chapter 2 Network TopologyDivina Labuguen TurquezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CN Lab2Document10 paginiCN Lab2AmaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)De la EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)Încă nu există evaluări
- Challenge 2021 - Smart Car SystemDocument8 paginiChallenge 2021 - Smart Car SystemSeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsDocument6 paginiSolution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsSeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAIE 9709 03 ComplexNumber M/J2008/Q5Document1 paginăCAIE 9709 03 ComplexNumber M/J2008/Q5SeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6093 - w18 - w21 - QP - 03 - Question 2Document18 pagini6093 - w18 - w21 - QP - 03 - Question 2SeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021 Kedah Fizik MPAT Paper 1Document5 pagini2021 Kedah Fizik MPAT Paper 1SeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 964 QP 2 STPM Biology 2012 Section BDocument2 pagini964 QP 2 STPM Biology 2012 Section BSeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsDocument5 paginiSolution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsSeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsDocument10 paginiSolution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsSeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsDocument10 paginiSolution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsSeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- UCSI University 33RD CONVOCATION CEREMONY YEAR 2021 - Convocation Details - 31.12.2020Document21 paginiUCSI University 33RD CONVOCATION CEREMONY YEAR 2021 - Convocation Details - 31.12.2020SeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Co Co: U-Trac U-TracDocument18 paginiCo Co: U-Trac U-TracSeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 6Document53 paginiSPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 6Sean75% (4)
- Tutorial - Lesson 7 Solution PDFDocument5 paginiTutorial - Lesson 7 Solution PDFSeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Co Co: U-Trac U-TracDocument25 paginiCo Co: U-Trac U-TracSeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homeostasis: S14.1 Structure of The LiverDocument5 paginiHomeostasis: S14.1 Structure of The LiverSeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Document22 paginiSPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Sean71% (7)
- Syc Ausmat Sept Fee Structure 2019Document1 paginăSyc Ausmat Sept Fee Structure 2019SeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM Add Maths 2019 P2Document28 paginiSPM Add Maths 2019 P2SeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- H218c Notes Tutorial - A Primer of Quantum MechanicsDocument21 paginiH218c Notes Tutorial - A Primer of Quantum MechanicsSeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM Add Maths 2019 P1Document32 paginiSPM Add Maths 2019 P1Sean100% (1)
- XHD6801+ Broadcast Quality Up/Cross/Downconverter: Installation and Operation ManualDocument94 paginiXHD6801+ Broadcast Quality Up/Cross/Downconverter: Installation and Operation ManualHernan QuinterosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Precision Measurement Overview TdcsDocument3 paginiPrecision Measurement Overview Tdcsअमरेश झाÎncă nu există evaluări
- ToP MonitoringDocument52 paginiToP MonitoringEd MulÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0 Export Solution 5th Version 20170619Document5 pagini0 Export Solution 5th Version 20170619Hary Anugrah100% (1)
- DH-IPC-HFW2531S-S-S2: 5MP Lite IR Fixed-Focal Bullet Network CameraDocument3 paginiDH-IPC-HFW2531S-S-S2: 5MP Lite IR Fixed-Focal Bullet Network CameraguestisorÎncă nu există evaluări
- PScell ChangeDocument7 paginiPScell ChangevabfouzdarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Country Network Name PrefixesDocument3 paginiCountry Network Name Prefixesوليد خالدÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Linear EditingDocument25 paginiNon-Linear EditingVikram Aditya ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceragon FibeAir 2500 Product Description V3.3.30 RevADocument127 paginiCeragon FibeAir 2500 Product Description V3.3.30 RevAEloy AndrésÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADT406-AP Technical ManualDocument55 paginiADT406-AP Technical ManualALEXANDER ROBLESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inter-Frequency Cell Re-Selection: SsearchhcsDocument3 paginiInter-Frequency Cell Re-Selection: SsearchhcsGiotbuonkhongtenToiÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAB 1-PE-LabDocument10 paginiLAB 1-PE-LabLovely JuttÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sanet - st-5g Networks Background Issues and SecurityDocument432 paginiSanet - st-5g Networks Background Issues and SecurityodoanthonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMARI LTE Callbox: The Portable LTE NetworkDocument6 paginiAMARI LTE Callbox: The Portable LTE NetworkluisisidoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Citycell AllDocument90 paginiCitycell AllChayan ArdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blue Print IP XII 2023-24Document1 paginăBlue Print IP XII 2023-24Naren Kumar0% (1)
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsDocument4 pagini1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsRicardo Aguilar20% (5)
- Module4 Problems: 2. Five Channels, Each With A 100-Khz Bandwidth, Are To Be Multiplexed Together. WhatDocument5 paginiModule4 Problems: 2. Five Channels, Each With A 100-Khz Bandwidth, Are To Be Multiplexed Together. WhatKeerthi RajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Samsung A02 SchematicsDocument30 paginiSamsung A02 SchematicsAuto repair diagnostic cars / trucksÎncă nu există evaluări
- SoundDocument25 paginiSoundRamesh BscÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Networks: Architecture, Protocols and ProceduresDocument202 paginiGSM Networks: Architecture, Protocols and Proceduresbulls1234Încă nu există evaluări
- 28.1.4 Lab - Use Netconf To Access A Ios Xe Device - IlmDocument21 pagini28.1.4 Lab - Use Netconf To Access A Ios Xe Device - IlmAndrei Petru PârvÎncă nu există evaluări
- BE AM Users Manual 71686Document320 paginiBE AM Users Manual 71686Edgar NunesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5G Ecosystem: The Digital Haven of OpportunitiesDocument40 pagini5G Ecosystem: The Digital Haven of OpportunitiesOguzhan Demirdogen (Student)Încă nu există evaluări
- Noticesittinglistbom 20220128144646Document5 paginiNoticesittinglistbom 20220128144646Yash AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Begin: Choose An All-In-The-Cloud Solution or Bring Your Own Telephony Carrier To Office 365Document1 paginăHow To Begin: Choose An All-In-The-Cloud Solution or Bring Your Own Telephony Carrier To Office 365akdreamscapeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Trends in Indian TelevisionDocument8 paginiCurrent Trends in Indian Televisionthe_f0rsak3nÎncă nu există evaluări
- V236BJ1 LE1 CHIMEIInnolux PDFDocument33 paginiV236BJ1 LE1 CHIMEIInnolux PDFジ气覀 气亠亠Încă nu există evaluări