Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Stitch Diary Ebook Defects Part 2
Încărcat de
Rafael CuicapuzaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Stitch Diary Ebook Defects Part 2
Încărcat de
Rafael CuicapuzaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CLASSIFY THE FAULT
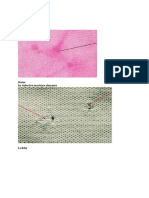
Defects in Woven Fabric
After the knit defects post, we will talk about the defects found in woven fabrics. Defects found in fabric ruin the aesthetic appeal and quality of
the final garment, making it really important to identify and take corrective measures at the right time.
Defects in woven fabric can be a result of yarn imperfections, incorrect weaving process or errors in the finishing process. They can be catego-
rized into 3 groups: yarn related defects, defects occurring in warp direction and defects in the filling direction.
Yarn Related Defects:
1. Mixed End/ Thick End: It can be identified as the warp end having larger diameter than the other warps.
Cause Remedies
Occurrence of excessive count variation Conduct frequent inspection to make sure
count mixing does not happen
Accidentally missing up of counts in winding
and warping
Piecing up of broken ends with wrong count
thread
Defects in woven fabric 17
2. Slub Or Slug: Abnormally thick place occurring in the yarn that affects the fabric’s appearance.
Cause Remedies
Occurrence of undrafted portions or sections in Ensure proper yarn spinning and yarn cleaning
the yarn during the winding processes
Warp Direction Defects:
1. Reedy Fabric Marks: Appearance of fine cracks across the fabric between warp end groups which resemble denting pattern in the reed.
Cause Remedies
High warp tension Ensure warp tension as required
Insufficient shade toughing Early shed timing
Late shed timing that causes tension imbalance Back rest should be raised by around 2 cms
at beat-up above the front rest level
Defects in woven fabric 18
2. Warp Streaks: Warp streaks can be identified as the warp way stripes of shade variations occurring between groups of threads.
Cause Remedies
Uneven reed dents spacing Use of good quality warp thread
Variations in warp Periodic checking of the reed’s condition
Coarse count and tight ends spacing appear Metal reeds give better results than the pitch
lighter in shade, whereas, finer count and bound reeds
wider spaced appear darker in shade
Ensuring proper material handling and
storage will help us avoid any yarn count
mixing
3. Misdraws / Wrong Draw: Design or stripes in the final fabric being damaged due to drawing of incorrect ends.
Cause Remedies
The fault in drawing-in of beam or drawing-in of Proper training of the drawing-in
the broken-ends by the weaving operator operator is necessary
End of different colour than needed being drawn Fabric inspection on the loom
Defects in woven fabric 19
4. Broken / Missing End: It can be identified as the space created in the fabric when a yarn partially or completely is missing from the fabric
Cause Remedies
Weaver fails to attend the warp breaks Use spare ends on the loom to
immediately substitute missing ends
The warp stop motion isn’t working properly in Instruct the weaver to attend to the warp
the machine breakages attentively and fast
Check the warp stop motion assembly before
weaving starts
Inspect the drop pins and replace any
defective ones when putting on a new beam
Weft Direction Defects:
1. Starting Marks: Thick or thin places occurring in fabric due to pick density variation when starting the loom, causing starting marks.
Cause Remedies
Anti-crack motion not functioning Training of the weaver to follow the correct
properly procedure
Fell of the fabric is very close to the reed due Ensure take-up motion is working correctly
to faulty take-up motion
Defects in woven fabric 20
2. Filling/Weft Bars:
Cause Remedies
Periodic variation in the count of the weft yarn Incorporate count identification and rectifica-
due to spinning defect tion processes
Mixing of different counts or different twist Properly segregate yarn to avoid lot mix-up of
yarns weft during weaving
3. Broken Pick: Broken Pick defect can be identified as the weft inserted to only a partial portion of the pick.
Cause Remedies
Weft breaks in ordinary looms Inspect the shuttle for any loose fitting
pirn or any form of roughness of
Faulty weft fork mechanism on surfaces, as friction might cause
automatic looms weft breakages
Check the shuttle and shuttle box for
settings and surface smoothness to
prevent weft cuts
Ensure weft fork mechanism is running
smoothly
Check for any loose picks before
starting the loom
Defects in woven fabric 21
4. Broken Pattern: This defect occurs on drop box looms for fabrics that have patterns. If the sequence of weft yarn colour breaks or pattern
width of particular colour is distorted, broken pattern defect appears.
Cause Remedies
The pattern cards or lattices are not Train the weaver to be vigilant regarding the
properly adjusted design needs and to find picks before
restarting the loom
Weaver fails to adjust the pattern chain
after mending or break The pattern cards should be checked and
adjusted as needed at the start of the beam
Pick being inserted in wrong shed when
mending a break
5. Double Pick: This defect happens when more than one pick is inserted in the single shed.
Cause Remedies
In ordinary looms, when restarting the loom, Pick finding every time the loom is restarted
weaver might fail to find out the correct shed for
inserting the pick Proper pirn change with weft feeder mechanism
On automatic looms, if the pirn change gets
affected by the weft form then double pick
defect appears
Defects in woven fabric 22
6. Gout: Appearance of foreign matter or contamination like lint, waste, etc woven into the fabric.
Cause Remedies
Waste disposed off randomly by the weaver Ensure the machine’s and shed’s
maintenance and cleaning
Foreign matter or waste getting into the
weaving shed
7. Sloughing off: When a bunch of or coil of yarn slips from the pirn during weaving then thick yarn bunches or coils appear on the fabric.
Cause Remedies
Pirn winding done without the proper tension Maintaining proper tension during pirn winding
being maintained during the winding process
Check the picking mechanisms
Due to harsh picking Condition the weft yarn appropriately before
using it
The humidity settings in the pirn
storage or shed are not set as required
Defects in woven fabric 23
8. Snarl: When yarn doubles back on itself especially because of high twist yarn, then snarling appears. It can be found randomly spread across
fabric width or only in a region nearby the selvedge.
Cause Remedies
Use of high twist weft yarn Weft conditioning before using it
Keeping the weft tension extremely low Ensuring needed drag in the shuttle
The weft fork is not set correctly Propel shuttle and weft fork setting
monitoring
Shuttle rebounds between its way
Now we know some of the common defects that can appear in woven fabric that can hamper the quality of the final garment produced out of it.
With the knowledge of what causes these defects and how we can avoid them during the weaving process, we can ensure the fabric produced is
as per the quality and appearance intended.
Image sources:
• http://textilelearner.blogspot.in/
• http://tohproblemkyahai.com/
• http://www.garmentsmerchandising.com/
• http://www.slideshare.net/hiteshhobbit/
• http://opticalengineering.spiedigitallibrary.org/
Defects in woven fabric 24
CLASSIFY THE FAULT
Defects in knit fabric
Defects spoil the aesthetics of the fabric and hence causes a gigantic quality issue. In this series of articles, we are going to discuss various
defects that can occur in knit and woven fabrics, the embroidery defects encountered and also the dyeing and printing ones.
Defects in knits are caused due to the faulty raw material, faulty knitting elements, wrong machine settings or faulty dyeing and finishing
processes.
Raw Material (yarn) Related defects:
There is a simple way to identify yarn related defects: these defects mostly appear in the horizontal direction in the fabric.
Some of the major yarn related knit fabric defects are:
• Barriness: Horizontal Stripes or streaks of uniform or uneven width, visible in the fabric.
Cause Remedies
Barriness occurs when the yarn is at high Make sure that there is a limited count
tension or there is a high level of variation in variation in every lot: not higher than +/- 0.3.
the thread count in the fabric. This happens For this, ensure yarns being used belong to
when many yarn lots get mixed the same lot and there is a consistent yarn
tension across all the feeders* in the
machine
*Feeder: helps to feed the yarn through the machine
Defects in knit fabric 25
• Imperfections: Imperfections are the occurrence of knots, slubs, thick or thin yarns, and neps in the fabric.
Cause Remedies
If the yarn being used has knots, slubs or neps or is Use good quality yarn to control these imperfec-
thick or thin at places tions and so, convey quality parameters clearly to
the yarn supplier
• Contaminations: When foreign matter like dead or dyed fibres or husk, etc appear in the fabric.
Cause Remedies
Caused due to the presence of dead fibres Using yarns with rich fibre mixing leads to
or other foreign elements being present in the occurrence of a lesser number of dead
the staple spun yarn like dyed fibres, or fibres in the fabric
husk, etc.
In the blow room, tight control in cotton
Sometimes adjacent machine’s fibres can mixing needs to be ensured to prevent any
fly to the fabric and get foreign matter mixing. Also,
embedded in it partitioning machines specially spinning
and knitting with plastic curtains can
prevent contamination
Defects in knit fabric 26
• Snarling: Snarls are big twisted yarn loops on the fabric surface.
Cause Remedies
High twist in the yarn being used for knitting The yarn twist should be as per
causes appearance of snarls predefined TPM (twist per metre)
• Spirality: Spirality is when after washing garment gets twisted, and the seams of the garment get displaced from the sides of front and back of
the garment.
Cause Remedies
Using high TPM (twist per metre) hosiery yarn The yarn twist should be as per
or uneven fabric tension on the machine predefined twist per metre (TPM)
causes spirality
If the feeding of fabric at stenter,
calendar and compactor are on
uneven rates
Defects in knit fabric 27
Knitting Elements Related Defects
These defects appear vertically in the fabric. There are two main defects that come under this categorization:
• Needle and Sinker Lines: Prominent or feeble vertical lines across the fabric.
Cause Remedies
Needle lines are caused due to bent Replacing bent or worn out sinkers and
needles, i.e. bent latches, needle hooks or defective needles, along with cleaning of
needle stems that form distorted stitches the sinker grooves by removing fibres
Sinker lines are formed due to bent or
worn-out sinkers, or if the sinkers are set
too tight
• Drop Stitches (or holes): Appearance of small or big random holes in the fabric.
Cause Remedies
Caused due to high yarn tensions; yarn over or To ensure holes free knit fabric, make sure
under feed, or due to the that there is a uniform yarn
incorrect gap between the dial and cylinder tension on all the feeders and the gap
rings while knitting between cylinder and dial should be accurate-
ly adjusted to suit the loop size
Malfunctioning needles might also cause drop
stitches
Defects in knit fabric 28
Knitting Machine Settings Related Defects
The defects that appear due to wrong machine settings or faulty machine parts come under this category:
• Yarn streaks: Thin horizontal lines that appear at irregularly spaced intervals and are of various sizes.
Cause Remedies
If the winding of the yarn packages is not When yarn packages are being
done properly, i.e. when winding the yarn wounded, ensure that the yarn runs
runs out of the belt on the pulley on the belt around the pulley
• Fabric Press off: Appearance of holes in the fabric due to an interruption in a loop formation.
Cause Remedies
If some or all needles on the machine fail to Before starting a lot, inspect for broken
function, then the fabric falls off the needles and replace them
machine and the design gets
distorted, this is known as for press off. It Maintain a consistent yarn tension across
can happen due to interruption in loop all feeders and check, set needle detectors
forming process due to yarn properly
breakage or needle hooks being closed
Defects in knit fabric 29
• Broken Ends: a bunch of ends knitted at a point.
Cause Remedies
When the end of the yarn breaks, the loose end Ensure consistent yarn tension and avoid using
strays in the fabric into yarn with thick and thin places. Hence, manage
another area. It can be due to high tension in the the quality of the yarn being used
yarn or if a cone gets finished in between
Unlike woven fabric, yarn strength in knit fabric is of secondary importance in the quality management of the fabric, as the load that the yarn
undergoes during knitting is lower than that in weaving. But knit fabric yarn must have elasticity and should be even with no thick and thin places
to ensure quality and prevent frequent needle breaks. Yarns with low friction and even moisture content are hence the preferred choices. When
using knit fabrics or when involved in knitting process, keep in mind the above-described defects with their causes and remedies to ensure
required parameters are being met, and the fabric thus obtained is of the demanded quality.
Image sources:
•http://www.slideshare.net/OliyadEbba/faults-remediespreventive-measures-in-knitted-fabric-dyeing
http://www.slideshare.net/88azmir/fault-of-knitted-fabrics
•http://www.slideshare.net/sheshir/an-investigation-on-the-inspection-of-grey-finished-knit-fabric-in-wet-processinge
•http://textilecollection.blogspot.in/
•https://shosh101.files.wordpress.com/
Defects in knit fabric 30
CLASSIFY THE FAULT
Defects in garment manufacturing
In our defects blog series, we have so far covered the defects occurring in knitted and woven fabrics and also in embroidery. Now, we are going to
take up the defects that occur in our final garments, and how can we control or correct them.
Garment defects can be caused due to the use of defective fabric, workmanship defects, and handling defects, and due to the defects in the
trims and accessories being used in the garment.
1. Fabric defects: Part of the defects occurring in the final garment could be caused due to the defects in the fabric being used. In our previous
articles, we have discussed the defects in knitted fabric and defects in woven fabric, their causes and possible remedies in depth.
2. Workmanship & handling defects: Garment manufacturing is a long process compromising of various stages, pattern making, spreading,
cutting, sewing and finishing. Hence, defects can creep in any of or all of these stages, so we need to stay vigilant at each of these stages to
ensure the desired quality of the final garment.
There is a variety of workmanship and handling defects that occur commonly in garments:
Pattern stage: There are various defects in patterns that mark the garment quality. At times patterns or parts of the patterns can be missing from
the marker, or if the marker wasn’t correctly labeled, we can end up with mixed garment parts, which can lead to garments with the wrong size of
parts. In napped fabrics, if patterns are not facing the right direction, garment design can be compromised.
Pattern not properly aligned to fabric’s grain line, or poor line definition can lead to inaccurate cutting. Skimpy marking to better utilize the fabric
by not using the patterns’ outside edge for cutting, or moving pattern to squeeze into smaller spaces, can lead to patterns with worn out edges or
faulty and wrong sized parts, which leads to puckering or pleating when the garment parts are sewn together as they are not of correct sizes.
Missing or displaced notches and drill marks, not enough knife clearance, wrong check matching, or wrong check boxing, all can hamper the quality
of the final garment.
Spreading stage: Narrow fabric lay, misaligned plies, or not enough plies, all can lead to missing bits in the garment parts. Incorrect ply tension
Defects in garment manufacturing 31
leads to size variations in the parts. Also, while spreading, incorrect ply direction, splicing errors, distortion in lay due to static between plies can
lead to incorrect cutting, especially if the fabric has checks or stripes.
Cutting Stage: Failure to precisely follow the marker lines, leaning straight knife while cutting, using round knife on a considerably high speed,
misplaced or incorrect notches and drill marks, frayed or fused edges due to blunt knife, faulty marker placement, etc. lead to distorted garment
parts or missing bits which leads to quality issues at later stages.
Some of the defects that occur due to faulty workmanship and handling are:
• Shade variation:
Causes Remedies
Shade variation in fabric Fabric inspection and quality monitoring
Parts mixing Proper numbering and bundling
processes
• Seam puckering: Bunching of fabric in a seam is seam puckering.
Causes Remedies
High thread tension Maintain proper thread tension while sewing
Faulty fabric feeding Fabric should be fed through the machine at a
constant rate
Using wrong thread and/or needle
Choosing appropriate needle and thread thickness
as per the fabric requirements
Defects in garment manufacturing 32
• Open or broken seams: Openings or unstitched parts in seams.
Causes Remedies
Faulty sewing practices Ensuring the garments are folded
properly and pressure is not being applied on
seams
Proper sewing operator training
• Broken stitches:
Causes Remedies
Improper thread feed to machine Training workers to handle the garment properly
Incorrect thread tension Thread trimming should not be done aggres-
sively
Abrasive handling of the piece
Manage the thread feed and tension
Defects in garment manufacturing 33
• Skipped stitches: Irregular stitches along the seam.
Causes Remedies
Use of bent needles Use reinforced needles
Incorrect tension in sewing and bobbin thread Set the needle guard to ensure needle clearance
Manage thread tension
Select proper thread twist and thickness
• Wavy seam: Wavy Seam occurs when the seam is not straight.
Causes Remedies
Rough handling when cutting and sewing Ensure proper material handling
Tension applied on part while sewing is high Train operator to not pull excessively while
cutting or sewing
Wrong Needle size
Choose the correct needle size
Defects in garment manufacturing 34
• Misaligned buttons and buttonholes:
Causes Remedies
Error made by the machine operator Internal QC checks
Operators should be aware of the design and dimension
specifications
‘
• Untrimmed threads: Extra lose thread appearing along the seam.
Causes Remedies
Tail ends left untrimmed post sewing Trim the threads using clipper or
trimmer
Defects in garment manufacturing 35
• Out of tolerance sizing: The dimensions or measurements of the garment parts are not within the tolerance limits defined by the buyer.
Causes Remedies
Cutting and Sewing operators having incorrect Ensure the operators have the
information dimension specifications.
Ensure correct pattern making
Inspect first piece form every size in
an order
‘
3. Trims & Accessory defects: At times the use of wrong color or size of trims or embroidery or wrong placement of the same can also make the
garment defective.
The defects that can appear in embroidery have been discussed in depth in our previous blog of this series “Embroidery Defects” (LINK). Other
than embroidery defects some of the other commonly occurring trim defects are:
• Broken Trim: Use of broken or inoperable trim or if the trim is insecure.
Causes Remedies
Rough trim handling Internal QC checks
Rushing through production process Good quality trims
Defects in garment manufacturing 36
• Wrong trim: The trim used differs in color or size, or might be missing when compared against the buyer’s specification.
Causes Remedies
Rough trim handling Internal QC checks
Rushing through production process Good quality trims
• Trim Bleeding:
Causes Remedies
Trim quality not as per specification Internal QC checks
Garment finishing not appropriate Good quality trims
Garment label should contain care instruc-
tions
Garment finishing should follow the manu-
facturer’s care instructions
for trim
Defects in garment manufacturing 37
With the knowledge of the commonly occurring defects and their causes and remedies, we can take measures to alleviate the risks of quality
fallouts in our orders. Keeping the above pointers in mind, we can align the quality inspection process in our factories to produce quality output.
Image Sources:
• http://www.impactiva.com/blog/apparel-the-importance-of-performing-materials-qc-before-starting-production/
• http://en.renataperito.com/
• http://www.onlineclothingstudy.com/
• http://www.slideshare.net/hiteshhobbit/fabric-defects-11884107
• http://www.slideshare.net/InTouchQuality/garment-defects-58264246
• http://textilelearner.blogspot.com/
• http://ehow.com
Defects in garment manufacturing 38
LOOKING TO TAKE YOUR APPAREL
KNOWLEDGE TO THE NEXT LEVEL?
Subscribe now on www.stitchdiary.com
http://stitchdiary.com/
http://stitchdiary.com/
Blog
http://stitchdiary.com/ Vlog
https://www.youtube.com/stitchdiary
Powered by ThreadSol
Established in 2012, Threadsol softwares Pvt. Ltd. is an organization with a unique combination of apparel production experts and
software professionals working together to bring innovative technologies to the manufacturing sector to enhance efficiency,
profitability and sustainability.
ThreadSol is helping over 150 customers across 16 countries to plan 1.5 billion garments per year.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Warp Way DefectsDocument11 paginiWarp Way Defectsharshal52855Încă nu există evaluări
- Sewing Defect Types, Causes and SolutionsDocument11 paginiSewing Defect Types, Causes and SolutionsVeverley CarupoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fabric Defects GuideDocument15 paginiFabric Defects GuidehirenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knitted Fabric Defect Identification and SolutionsDocument11 paginiKnitted Fabric Defect Identification and SolutionsPawan Kumar100% (1)
- Women Denim Shorts Defect Analysis Case StudyDocument11 paginiWomen Denim Shorts Defect Analysis Case Studyshalu singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1) Count Variation: 2) Unevenness or Irregularity: 3) Frequently Occurring FaultsDocument40 pagini1) Count Variation: 2) Unevenness or Irregularity: 3) Frequently Occurring FaultsshaifaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fabric DefectsDocument5 paginiFabric Defectsalibaqar74100% (5)
- Fabric Defect Reading MaterialDocument6 paginiFabric Defect Reading MaterialAnoop Singh100% (1)
- 1.fabric Defects and IdentificationDocument16 pagini1.fabric Defects and IdentificationRuhi gnextÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fabric Quality Assessment Assignment - 1: National Institute of Fashion TechnologyDocument19 paginiFabric Quality Assessment Assignment - 1: National Institute of Fashion TechnologyAyushi ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warp Vs Weft KnittingDocument5 paginiWarp Vs Weft KnittingLinh NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Defects in Denim Jeans SewingDocument10 paginiCommon Defects in Denim Jeans SewingShaaban NoamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Các loại lỗi trên vảiDocument17 paginiCác loại lỗi trên vảiTrangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Utkarsh SinghDocument9 paginiUtkarsh Singhgopica3448Încă nu există evaluări
- Top 10 Fabric DefectsDocument3 paginiTop 10 Fabric DefectsAbhiraj SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Major Defects in Woven FabricDocument15 paginiMajor Defects in Woven FabricTuan Nguyen MinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Seam Types and Quality IssuesDocument53 paginiIntroduction to Seam Types and Quality IssuesYetana WubnehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yarn Defect-Final - ReadyDocument47 paginiYarn Defect-Final - Readyparash rajÎncă nu există evaluări
- DefectsDocument31 paginiDefectsKawsar HamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common faults in weaving and remediesDocument8 paginiCommon faults in weaving and remediesManish KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- UAQ 2nd Assignment (Pooja Kumari)Document14 paginiUAQ 2nd Assignment (Pooja Kumari)Reena VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fig: Various Garment DefectsDocument11 paginiFig: Various Garment DefectsNitin VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faults in The Knitted FabricsDocument11 paginiFaults in The Knitted FabricsShwetaLoonkarPitliya100% (2)
- ..Knitting Defects and Remedies..: Made By: Raisa GuptaDocument39 pagini..Knitting Defects and Remedies..: Made By: Raisa Guptalovelife_gupta83% (6)
- ABUJEDIDDocument5 paginiABUJEDIDyenesew mulluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sewing Needles Used in Sewing MachineDocument6 paginiSewing Needles Used in Sewing MachineKhandaker Sakib Farhad100% (1)
- Fabric Bowing & Skewing - Textile SchoolDocument5 paginiFabric Bowing & Skewing - Textile Schoolmithun77Încă nu există evaluări
- Weaving Faults: 1. Horizontal LinesDocument4 paginiWeaving Faults: 1. Horizontal LinesRosheen RahatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surigao Del Sur State University-Main CampusDocument5 paginiSurigao Del Sur State University-Main Campusjemuel cinso0% (1)
- garDocument33 paginigarAmor ELHAJAHMEDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Apparel Quality: Abhinav Krishna Bft/18/1044 Amisha Sahu Bft/18/734Document10 paginiUnderstanding Apparel Quality: Abhinav Krishna Bft/18/1044 Amisha Sahu Bft/18/734kashorina AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Garment Defect AnalysisDocument21 paginiGarment Defect AnalysisIndranil Saha100% (10)
- Gar 2Document31 paginiGar 2Nit VictorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apuntes ParametriaDocument5 paginiApuntes ParametriaPEPAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment On Different Kinds of Knitting Faults Causes and Their RemediesDocument4 paginiAssignment On Different Kinds of Knitting Faults Causes and Their RemediesRaihan Moner Manush0% (2)
- Seam PuckeringDocument16 paginiSeam PuckeringIshika100% (2)
- Textiles Quality Management (QTEX-4021) Online Class MaterialsDocument7 paginiTextiles Quality Management (QTEX-4021) Online Class MaterialsRakibul HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- A&estitchseamdefectsDocument5 paginiA&estitchseamdefectsTee CeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sewing Faults and RemediesDocument16 paginiSewing Faults and RemediesRomanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knitting Defects and RemediesDocument13 paginiKnitting Defects and RemediesKomal ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fabric Defect TypesDocument23 paginiFabric Defect TypesJubayer Uddin100% (1)
- 23 Fabric Defects To Look Out For During Fabric InspectionDocument5 pagini23 Fabric Defects To Look Out For During Fabric Inspectionudi969100% (1)
- Perform Basic MaintenanceDocument3 paginiPerform Basic MaintenancejessafesalazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sadia Mam... PPDocument11 paginiSadia Mam... PPsazzad alaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knitted Fabric DefectsDocument13 paginiKnitted Fabric DefectssimranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prevention of BarreDocument5 paginiPrevention of BarreKavi DhingraÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRI 3015 Guide To Evaluating and Reducing Holes in Knitted FabricsDocument14 paginiTRI 3015 Guide To Evaluating and Reducing Holes in Knitted FabricsLong VuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of Fabric DefectsDocument7 paginiClassification of Fabric DefectsAdnan HameedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knitting FaultsDocument8 paginiKnitting FaultsSara TariqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Defects - Faults and Remedies of Warping - Textile LearnerDocument4 paginiDefects - Faults and Remedies of Warping - Textile LearnerGOWTHAM CHANDRUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knit Fabric FaultDocument9 paginiKnit Fabric FaultLucas HillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Textiles and Garment Production GuideDocument29 paginiTextiles and Garment Production Guidezeeshan_220Încă nu există evaluări
- Dyeing or Finishing DefectsDocument1 paginăDyeing or Finishing DefectsMianAbrarAnjumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applique Petal Party: A Bouquet of 16 Blocks & Flowering BorderDe la EverandApplique Petal Party: A Bouquet of 16 Blocks & Flowering BorderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macraweave: Macrame Meets Weaving with 18 Stunning Home Decor ProjectsDe la EverandMacraweave: Macrame Meets Weaving with 18 Stunning Home Decor ProjectsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sewing Knits from Fit to Finish: Proven Methods for Conventional Machine and SergerDe la EverandSewing Knits from Fit to Finish: Proven Methods for Conventional Machine and SergerEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (3)
- Veritrade Resumen UPC - (Pcmemama) US E 20220628172031Document36 paginiVeritrade Resumen UPC - (Pcmemama) US E 20220628172031Juan MartinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knit Packer - The Bobbin TreeDocument4 paginiKnit Packer - The Bobbin TreeJenn HoeggÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lets Knit Issue 172-July 2021Document102 paginiLets Knit Issue 172-July 2021Gavril Bogdan100% (1)
- Yarn HairinessDocument11 paginiYarn HairinessEngr Parvez Hasan0% (3)
- Weaving 1Document96 paginiWeaving 1jayrock574765100% (2)
- Milk Dreams - Knitted Blanket With Lace Pattern For Baby. Piece Is Knitted in DROPS BabyMerino. Theme - Baby Blanket - Free Pattern by DROPS DesignDocument4 paginiMilk Dreams - Knitted Blanket With Lace Pattern For Baby. Piece Is Knitted in DROPS BabyMerino. Theme - Baby Blanket - Free Pattern by DROPS DesignIonelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bungee Kurve Klassisk UsDocument6 paginiBungee Kurve Klassisk UsLőrinczi FanniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machine Settings For Sewing Knit Fabrics ChartDocument1 paginăMachine Settings For Sewing Knit Fabrics ChartUTKARSH UPADHYAY100% (1)
- Assessment and Technological Forecasting in The Textile Industry: From First Industrial Revolution To The Industry 4.0Document10 paginiAssessment and Technological Forecasting in The Textile Industry: From First Industrial Revolution To The Industry 4.0Rizqi Sausan SalsabilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knit Kimono TooDocument8 paginiKnit Kimono TooInterweave50% (8)
- Fibre Tech TestsDocument12 paginiFibre Tech TestsMohsin SaeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uk Cardigan Lace Flounce BookletDocument6 paginiUk Cardigan Lace Flounce BookletadinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enzian EnglDocument2 paginiEnzian EnglAna Giulia100% (1)
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 paginiMultiple Choice QuestionsRuma GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buksh IndustriesDocument3 paginiBuksh IndustriesM Yasir AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Woven Fabrics PDFDocument304 paginiWoven Fabrics PDFJuan Cubas100% (4)
- Forensics - PowerPoint Notes - Chapter 6 - FibersDocument7 paginiForensics - PowerPoint Notes - Chapter 6 - FibersKrithika NaiduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Major Defects Causing Process Non-ConformanceDocument3 paginiMajor Defects Causing Process Non-ConformanceMd.Rasel RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SmoothFox Jubilee Square 6x6Document3 paginiSmoothFox Jubilee Square 6x6Jill KrahlingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3x3 A Shawl For Anita by Lolita AndradaDocument5 pagini3x3 A Shawl For Anita by Lolita AndradaAllan Cesario Abad100% (7)
- Amigurumi Bee Doll Free Crochet PatternDocument7 paginiAmigurumi Bee Doll Free Crochet PatternFruzsina KovácsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of HandicraftsDocument3 paginiTypes of HandicraftsAdrian Contillo100% (4)
- Final Project of 4 P's 1Document105 paginiFinal Project of 4 P's 1Er Bikramjit Singh100% (1)
- Mrs Kare's extra place at the tableDocument41 paginiMrs Kare's extra place at the tableTafadzwa ChagwizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- B ' N T M: With Dust Bunnies!Document6 paginiB ' N T M: With Dust Bunnies!cordial100% (1)
- Unit-5 Cutting of Synthetic MaterialsDocument7 paginiUnit-5 Cutting of Synthetic MaterialsumidgrtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lace Leaf HatDocument2 paginiLace Leaf HatLaura ToddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knitting Sub Contract All in OneDocument1.118 paginiKnitting Sub Contract All in OneMd FaridujjamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free Online Cabaret Moss Stitch - p2Document3 paginiFree Online Cabaret Moss Stitch - p2adinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1412 Instruction ManualDocument60 pagini1412 Instruction ManualBet RomeÎncă nu există evaluări