Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
What Is Volcano
Încărcat de
leizlDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
What Is Volcano
Încărcat de
leizlDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
What is Volcano ?
An opening in the Earth's crust from which lava, ash, and hot gases flow or are ejected during an eruption.
A usually cone-shaped mountain formed by the materials issuing from such an opening. Volcanoes are
usually associated with plate boundaries but can also
occur within the interior areas of a tectonic plate.
Mount Binuluan (also known as Ambalatungan) is a
remote volcano in the Kalinga province of the Cordillera
Administrative Region of the Philippines. The 2,329-
metre-high (7,641 ft) mountain is part of the Cordillera
Central mountain range on Luzon island, the largest
island in the country. Binuluan exhibits active
volcanism through
numerous fumarole fields, solfataras and hot springs on
its slope. There were reports of possible eruptions in
1952 and 1986 (or 1987), but they are unverified.
Babuyan Claro Volcano, also known as Mount Pangasun, is
a potentially active volcano located on Babuyan Island, the
northernmost of the Babuyan group of islands in Luzon Strait,
north of the main island of Luzon in the Philippines. It is
classified as one of the active volcanoes of the country with the
last confirmed eruption in 1860.[2]
The volcano is politically located in the similarly-
named Barangay of Babuyan Claro, in the Municipality of
Calayan, Cagayan province, in the Cagayan
Valley Region (Region II) of the country.
Mount Banahaw (alternative
spelling: Banahao or Banájao) is a potentially active
volcano on Luzon in the Philippines. The three-
peaked volcano complex is located between
the provinces of Laguna and Quezon and is the tallest
mountain in the CALABARZON region dominating
the landscape for miles around
Smith Volcano, also known as Mount Babuyan, is
a cinder cone on Babuyan Island, the northernmost of
the Babuyan group of islands on Luzon Strait, north of the
main island of Luzon in the Philippines. The mountain is
one of the active volcanoes in the Philippines, which last
erupted in 1924.
The volcano is politically located in the Municipality of
Calayan, Cagayan province, the town that has jurisdiction
over the Babuyan Islands except Fuga Island.
The Mayon Volcano, also known as Mount Mayon, is an
active volcano in the province of Albay, on Luzon island in the
Philippines. It is a part of the Pacific Ring of Fire. It is one the
most active and dangerous volcanoes in the Philippines.
Apo volcano is the highest mountain in the Philippines, and
its name means "Master" or "Grandfather". There are no
known historic eruptions, but the volcano is considered still
active.
Balatukan (also known as Balingoan or Balatocan) is a
massive compound stratovolcano on the SW shore of
Gingoog Bay, 15 km SW of Gingoog city in north-central
Mindanao
Kalatungan volcano (also known as Catatungan), is the second highest
volcano in the Philippines and located 47 km east of Lake Lana on
Mindanao Island.
The dominantly basaltic volcano forms a broad E-W trending ridge.
The age of its last activity is unknown.
Makaturing is a stratovolcano at the shore of Illana Bay located about 40
km South of Marawi city, in central Mindanao, Philippines.
It is part of the Central Mindanao Arc.
Matutum is a symmetrical stratovolcano located in southern
Mindanao, NW of Sarangani Bay and 30 km NNW of General
Santos City.
What are the three main volcanoes?
There are three main types of volcano - composite or strato, shield and dome.
Composite Volcanoes
Composite volcanoes, sometimes known as strato volcanoes, are steep sided cones
formed from layers of ash and [lava] flows. The eruptions from these volcanoes may be
a pyroclastic flow rather than a flow of lava. A pyroclastic flow is a superheated mixture
of hot steam, ash, rock and dust. A pyroclastic flow can travel down the side of a
volcano at very high speeds with temperatures over 400 degrees celsius. Composite
volcanoes can rise over 8000 feet.
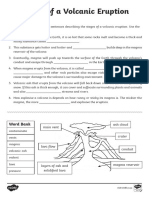
A simple cross section through a composite volcano
When composite volcanoes erupt they are explosive
and pose a threat to nearby life and
property. Eruptions are explosive due to the
thick, highly viscous lava that is produced by
composite cone volcanoes. This viscous lava
has a lot to do with why they are shaped the
way they are. The thick lava cannot travel far
down the slope of the volcano before it cools.
Composite volcanoes are usually found at
destructive plate margins. Examples of composite volcanoes include Mount Fuji
(Japan), Mount St Helens (USA) and Mount Pinatubo (Philippines).
zShield Volcanoes
Shield volcanoes are low with gently sloping sides and
are formed from layers of lava. Eruptions are typically
non-explosive. Shield volcanoes produce fast flowing
fluid [lava] that can flow for many miles. Eruptions tend
to be frequent but relatively gentle. Although these
eruptions destroy property, death or injury to humans
rarely occurs
Dome (Acid Lava
Cones)
Acid [lava] is much thicker than [lava] which flows from
shield volcanoes. Dome volcanoes have much steeper sides
than shield volcanoes. This is because the lava is thick and
sticky. It cannot flow very far before ot cools and hardens.
An example is Puy de Dome in the Auvergne region of
France which last erupted over 1 million years ago.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Active VolcanoDocument6 paginiActive Volcanoexcelle reyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- VolcanoesDocument14 paginiVolcanoesSHANNEL ANN VILLUGAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcanoes ProjDocument20 paginiVolcanoes ProjKristyl Joy AnasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active and Inactive VolcanoDocument21 paginiActive and Inactive VolcanoRosiabell CoroniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Active Volcano in MindanaoDocument3 paginiList of Active Volcano in MindanaoVikki AmorioÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Active Volcanoes of Luzon IslandDocument3 paginiThe Active Volcanoes of Luzon IslandLawrence DelacruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- GabsDocument11 paginiGabsApriljane CanjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DrrreDocument3 paginiDrrreLaika LaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth Tone Multipurpose Visual Charts Diagram PresentationDocument16 paginiEarth Tone Multipurpose Visual Charts Diagram PresentationFrancine DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcanoes of The PhilippinesDocument5 paginiVolcanoes of The PhilippinesBogart MacatangayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Additional Activity 1.it's More Fun Near Philippine VolcanoesDocument5 paginiAdditional Activity 1.it's More Fun Near Philippine VolcanoesAngel Baldueza100% (2)
- Philippine Institute of Volcanology and SeismologyDocument3 paginiPhilippine Institute of Volcanology and SeismologyMyrna jalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PrayerDocument14 paginiPrayerJaypee CarlÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Active Volcanoes in The PhilipphinesDocument8 pagini10 Active Volcanoes in The PhilipphinesJustine TatontiloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active VolcanoesDocument2 paginiActive VolcanoesJay TimtimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name That Volcanoes: Activity 1Document39 paginiName That Volcanoes: Activity 1Brezel EñateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Activity-DRRMDocument15 paginiResearch Activity-DRRMJacinthe Angelou D. PeñalosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LandDocument2 paginiLandGol Den DeeksÎncă nu există evaluări
- VolcanoesDocument5 paginiVolcanoesJV PadernaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exploring Volcanoes Earth Science Education Presentation Organic Semi-Lined StyleDocument2 paginiExploring Volcanoes Earth Science Education Presentation Organic Semi-Lined StyleDantes, AndhreiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active VolcanoesDocument7 paginiActive VolcanoesMargie Torregosa-Sabunod ValdonÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Top 10 Provinces That at Risk To Volcanic EruptionDocument26 paginiThe Top 10 Provinces That at Risk To Volcanic Eruptionjohnmarc albiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taal VolcanoDocument12 paginiTaal VolcanoFernando AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anyong Lupa: Mount Apo, at 9,692 Feet (2,954 Metres), Is An Active Volcano inDocument4 paginiAnyong Lupa: Mount Apo, at 9,692 Feet (2,954 Metres), Is An Active Volcano inNight dreamer CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mayon VolcanoDocument12 paginiMayon VolcanoJuan UnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dormant VolcanoesDocument2 paginiDormant VolcanoesCharis Marie Urgel100% (1)
- VolcanoDocument59 paginiVolcanoJhanna Mae HicanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: Balita, Nikko J. Date: - Course/Section: ACT 2D SubjectDocument5 paginiName: Balita, Nikko J. Date: - Course/Section: ACT 2D SubjectMau AcusaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active Volcanoes in The PhilippinesDocument2 paginiActive Volcanoes in The PhilippinesPlaza IdeasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group VolcanicDocument1 paginăGroup VolcanicGianna ManabatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20 Volcanoes in PhilippinesDocument5 pagini20 Volcanoes in Philippinesset netÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active VolcanoDocument6 paginiActive VolcanoKàtrįńá Jøÿ ÅgùśtïńÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mountaineering Guide Trifold Brochure in Pink White Modern Minimalist Style 20231025 214117 0000Document2 paginiMountaineering Guide Trifold Brochure in Pink White Modern Minimalist Style 20231025 214117 0000Cyrus PascualÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philippine VolcanoesDocument4 paginiPhilippine VolcanoesCamille SalasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure in ScienceDocument2 paginiBrochure in SciencePauline Joy AligwayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cancajanag: Victoria IslandDocument6 paginiCancajanag: Victoria Islandevelyn godinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHIL GEO LESSON 1 2 THC 2Document18 paginiPHIL GEO LESSON 1 2 THC 2prencessmaeyaon02Încă nu există evaluări
- Mga BulkanDocument5 paginiMga BulkanRenelynn SiloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcaanoes Found in VisayasDocument6 paginiVolcaanoes Found in VisayasJohan Yousef0% (1)
- Research Activity-DRRMDocument6 paginiResearch Activity-DRRMJacinthe Angelou D. PeñalosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active Ang Inactive Volcanoes in PhilippinesDocument2 paginiActive Ang Inactive Volcanoes in PhilippinesRegina Mae MegrenioÎncă nu există evaluări
- BROCHURE in Science Even BetterDocument2 paginiBROCHURE in Science Even BetterPauline Joy AligwayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Province Active Volcano Interesting Facts 1. Batangas Taal VolcanoDocument2 paginiProvince Active Volcano Interesting Facts 1. Batangas Taal VolcanoMA. CINDERELLA DE GUZMANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment in GeologyDocument10 paginiAssignment in GeologyNeisha Kwane PuglayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcanoes of The Central PhilippinesDocument3 paginiVolcanoes of The Central PhilippinesLawrence DelacruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Most Active Volcanoes in The PhilippinesDocument9 pagini6 Most Active Volcanoes in The PhilippinesYollyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tle Water and Land FomsDocument4 paginiTle Water and Land FomsJermaine Marcus DeleonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distribution of Active VolcanoesDocument15 paginiDistribution of Active VolcanoesJoan MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Albay: Bicol RegionDocument3 paginiAlbay: Bicol RegionGerica AgustinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 1Document8 paginiScience 1Leomar CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brown and Cream Delicate Organic Freelance Writer Marketing PresentationDocument8 paginiBrown and Cream Delicate Organic Freelance Writer Marketing PresentationELIJAH GABRIELÎncă nu există evaluări
- VolcanoesDocument4 paginiVolcanoesnightslayer1722Încă nu există evaluări
- Taal Volcano and Lake Are Wholly Located in TheDocument17 paginiTaal Volcano and Lake Are Wholly Located in TheAliah GombioÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Volcano's in PhilippinesDocument9 paginiList of Volcano's in PhilippinesJeric Fernandez CayabyabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disaster Risk Reduction and Readiness: Volcanic HazardsDocument34 paginiDisaster Risk Reduction and Readiness: Volcanic HazardsanneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bulusan: Alert !Document28 paginiBulusan: Alert !Janice Cara-atÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 10 1.1 Distribution of Active VolcanoesDocument18 paginiScience 10 1.1 Distribution of Active VolcanoesKenneth CorpesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philippine Popular CultureDocument40 paginiPhilippine Popular CultureMylene Rocaberte33% (3)
- Volcano HazardsDocument5 paginiVolcano HazardsMaria ClaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pagini6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Product Creation and DevelopmentDocument3 paginiProduct Creation and DevelopmentleizlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inca Civilization Aztec CivilizationDocument7 paginiInca Civilization Aztec CivilizationleizlÎncă nu există evaluări
- RPH Final Reviewer PDFDocument4 paginiRPH Final Reviewer PDFleizlÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Recreational ActivitiesDocument7 paginiWhat Is Recreational ActivitiesleizlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apostles Creed: Article 5 PDFDocument15 paginiApostles Creed: Article 5 PDFleizl50% (2)
- Site of The First MassDocument7 paginiSite of The First Massleizl100% (1)
- Handouts Acctg 1Document11 paginiHandouts Acctg 1leizlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of VolcanoesDocument33 paginiTypes of VolcanoesJerrald Meyer L. BayaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 1Document17 paginiScience: Quarter 3 - Module 1NRIZA MAE CACHOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geol 122 Lab NotesDocument5 paginiGeol 122 Lab NotesColeen Loise NavarroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stages of Volcaning EruptionDocument2 paginiStages of Volcaning EruptionLily Anne Cerillo0% (1)
- Volcanoes Grade 9 Third QuarterDocument50 paginiVolcanoes Grade 9 Third QuarterChelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Province Active Volcano Interesting Facts 1. Batangas Taal VolcanoDocument2 paginiProvince Active Volcano Interesting Facts 1. Batangas Taal VolcanoMA. CINDERELLA DE GUZMANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcanoes in The Philippines: (Some)Document14 paginiVolcanoes in The Philippines: (Some)Ash ʕっ•ᴥ•ʔっÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dacite Rock (Igneous Rock) ExtrusiveDocument6 paginiDacite Rock (Igneous Rock) ExtrusiveDewanshu VikramÎncă nu există evaluări
- VolvanoDocument6 paginiVolvanoZarinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Types of VolcanoesDocument9 pagini5 Types of VolcanoesQasim IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 9, Quarter 3Document51 paginiGrade 9, Quarter 3Marfe MontelibanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 9 Quarter 3 - Module 1Document9 paginiScience 9 Quarter 3 - Module 1HPLaptop ReymarkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Volcanoes Fact FileDocument2 paginiTypes of Volcanoes Fact FileLily Anne CerilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diliman TuffDocument21 paginiDiliman TuffCo ConÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcano Review With AnswersDocument3 paginiVolcano Review With Answersduncanpatti100% (4)
- List of Volcanoes in The PhilippinesDocument3 paginiList of Volcanoes in The PhilippinesVictor FajardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is VolcanoDocument4 paginiWhat Is VolcanoleizlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pacific Ring of Fire WSDocument6 paginiPacific Ring of Fire WSBilly STOJANOVSKIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 6 PosterDocument1 paginăYear 6 PosterHifsa batoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soal Bahasa InggrisDocument22 paginiSoal Bahasa InggrisMadrasah Aliyah Al-RaudlahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcanoes of The PhilippinesDocument5 paginiVolcanoes of The PhilippinesBogart MacatangayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dark Gray and Orange Textured Illustrative Science Volcanoes Presentation 20240204 075942 0000Document19 paginiDark Gray and Orange Textured Illustrative Science Volcanoes Presentation 20240204 075942 0000jaeloceralbo47Încă nu există evaluări
- What Are The Different Types of VolcanoesDocument3 paginiWhat Are The Different Types of VolcanoesBenes Salamanca BolascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcano QuizDocument3 paginiVolcano QuizGrasya Catacutan78% (9)
- Distribution of Active VolcanoesDocument15 paginiDistribution of Active VolcanoesJoan MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LeaP Science G9 Week 1 Q3Document4 paginiLeaP Science G9 Week 1 Q3Christine Marquez RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcanoes, Magma & PlutonsDocument37 paginiVolcanoes, Magma & Plutonswonder-chef-4677100% (1)
- Sci19 - Q3 - M1 - Types of VolcanoDocument18 paginiSci19 - Q3 - M1 - Types of VolcanoJoanne Apduhan BorjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VolcanoesDocument36 paginiVolcanoesjhoms8Încă nu există evaluări
- Volcanoes and The Interior of The EarthDocument5 paginiVolcanoes and The Interior of The EarthJelly AnnÎncă nu există evaluări