Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Imax MM
Încărcat de
SanghamitraDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Imax MM
Încărcat de
SanghamitraDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
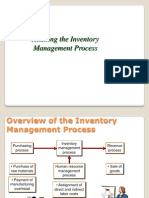
Materials Management (MM)
The grouping of management functions supporting the complete cycle of material flow,
from the purchase and internal control of production materials to the planning and
control of work in process to the warehousing, shipping, and d
distribution
istribution of the finished
product.
Introduction to ERP – SAP R/3 system
Working with System.
IMG (Implementation Guide)
Project implementation.
MM overview.
1. Material Master Organizational Levels
Material type and Industrial Sector.
Number assignment for material.
Valuation classes.
Views, editing material master.
2. Service Master
Maintaining the service master
Vendor master
Organization levels
Account group
Partner functions / Roles views
Editing vendor master
3. Materials planning and forecasting.
MRP rates in material, Master MRP profiles.
Planning methods. Net requirements, calculations, scheduling procedures, Lot
size procedures.
Processing planning run, planning file, Planning level, storage location MRP.
Fixing and rescheduling check, planning hor
horizon.
MRP list and current requirements / stock list, eelements
lements of MRP list and current
requirement / stock list, exception message.
4. Purchasing generals.
Item category.
Account assignment category, procurement for stock / consumption,
procurement for exte
external, account assignment.
Release procedure.
Fundamental structure of purchasing documents
5. Purchase requisitions.
MRP sources.
General structure.
Overall release of purchase requisitions.
6. Request for Quotation.
Business process integration.
Fundamental structure.
Price compassion list.
7. Purchase order.
Fundamental structure, sources / references.
Purchase order history.
8. Lean process for procurement of consumables and services
services.
Blanket purchase order.
Invoicing plan.
Outline agreement.
Quality / value contracts, scheduling agreements
Release order history.
Automatic generation of delivery schedule lines / automatic delivery
schedule update.
Aggregation of schedule lines.
9. Supply source determination and optimized purchasing
Purchasing information recor
record, source list, quota arrangements.
Assigning and editing purchase requisition, automatic purchase order generation
Optimization of the procurement process.
Pricing and message printing.
Output medium.
10. Reports.
Purchase order and contract monitoring, pur
purchase reports.
Logistics Information Systems (LIST)
11. Inventor Management Goods Movements, Stocks.
Movement types.
Goods receipts (referencing purchase orders, referencing production orders /
reservations, other GR)
Inventory management levels, stock types, special stocks, quality inspection.
lanned / Unplanned movements, reservations.
Goods issue.
Transfer postings and stock transfers.
Reverse postings (Reverse posting movement, document reversals), return
deliveries.
Integration, effects of inventory management postings, quality / value, control
data (Eg. Field control, Inspection indicator, Tolerances)
Message determination.
Analysis / Inventory controlling.
12. Special processing forms.
Negative stocks.
Stocks under split valuation.
Subcontracting (Purchase
rchase and Inventory management)
Vendor consignment, zero value stocks, non valued GR,
Quantity / value.
13. Simplification of procurement stock.
Consignment (Info record for consignment)
Automatic generation of purchase order for goods receipt.
One step procedure
ocedure for stock transport orders.
14. Physical Inventory.
Physical inventory methods.
Physical inventory procedures.
15. Invoice verification.
Procedure and forms of invoice verification.
Referencing on purchase order or goods receipt / delivery note.
Purchase
se orders with account assignment, valuated / non
non-valuated
valuated goods
receipt.
Gross and net posting, Cash discount.
Planned and unplanned delivery cost.
Taxes.
Variances blocking reasons.
Preliminary posting.
Posting transactions, value, and price control.
16. Release procedure.
Blocking reasons.
Individual and collective release.
Automatic release.
17. Special processing forms.
Credit memos and cancellations.
Subsequent debits / credits.
Invoices in foreign currency.
Invoices in consignment stock.
Invoices without reference. (Posting to material or G/L account)
Evaluated receipt settlement (ERS)
GR/IR account maintenance.
Posting transactions, value, and price control.
18. Enhancements in Invoice verification Account determination.
Account determination controlling, needed dates and customizing settings
valuation grouping. Account grouping, General reconciliation account / value
string, posting keys.
Account determination for stock movements and invoice verification.
Automatic postings.
19. Valuation in the Fiscal year.
Price control and effects for valuation / account determination.
Valuation of goods receipt and invoice verification.
Valuation levels, quality / value, split valuation.
Zero – value stocks, Non – valuated gross receipt.
Revaluation.
Integration, posting transactions / postings keys, field control, control /
reconciliation account, cost element.
20. Classification / Batch management.
Basics in classification.
Batch management.
21. Integration.
Cross company procurement.
MM processes with modules FI, SD, PP.
Basis
sis in integration (Project experience or participation in case study)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- SAP PR Release Strategy Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyDe la EverandSAP PR Release Strategy Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (6)
- Domesticity and Power in The Early Mughal WorldDocument17 paginiDomesticity and Power in The Early Mughal WorldUjjwal Gupta100% (1)
- Supply Chain Management ProcurementDocument3 paginiSupply Chain Management ProcurementKirola SanjayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auditing The Inventory Management ProcessDocument15 paginiAuditing The Inventory Management ProcessGohar Mahmood100% (1)
- TCSiON Cloud ERP Modules DescriptionDocument3 paginiTCSiON Cloud ERP Modules DescriptionDexÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP Training Courses in Lahore: Finance and AccountingDocument2 paginiSAP Training Courses in Lahore: Finance and Accountingnaeemabbas.skpÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP MM (Materials Management) Is A Module of The SAP ERP Software Package From SAP AG That Is Used ForDocument9 paginiSAP MM (Materials Management) Is A Module of The SAP ERP Software Package From SAP AG That Is Used ForBoppineti Naga RajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP MM SkillsDocument2 paginiSAP MM SkillsRahul100% (1)
- Sap Fundamental Guide Procurement ProcessDocument39 paginiSap Fundamental Guide Procurement Processvmyreddy80% (5)
- Raman MittalDocument2 paginiRaman MittalSuresh BabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Purchase CycleDocument3 paginiPurchase Cyclenikku115Încă nu există evaluări
- L12 ProcureDocument32 paginiL12 ProcureMRASSASINÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2011-1-Training Manual On Material ManagementDocument119 pagini2011-1-Training Manual On Material ManagementPrudhvikrishna GurramÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP MM Online Training CurriculumDocument2 paginiSAP MM Online Training Curriculumdudhmogre23Încă nu există evaluări
- SAP MM Course Curriculum: Day-1: Overview of SAP, MM, and Procurement ProcessDocument4 paginiSAP MM Course Curriculum: Day-1: Overview of SAP, MM, and Procurement ProcessAbcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Canias System Analysis TemplateDocument17 paginiCanias System Analysis TemplateDickson AllelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chiranjeet - Das - SAP MMDocument7 paginiChiranjeet - Das - SAP MMshanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP MM SyllabusDocument3 paginiSAP MM SyllabusVinod JunjuÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP MM Overview & Course ContentDocument5 paginiSAP MM Overview & Course ContentVasavi AcuteSoftÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reddy, Sravani - SAP-UpdatedDocument6 paginiReddy, Sravani - SAP-UpdatedMadhu ITÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sap MM Creating ExpertsDocument4 paginiSap MM Creating Expertstrishul100% (1)
- NaukDocument1 paginăNaukEash WarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Naukri Jnagaraja (8y 5m)Document5 paginiNaukri Jnagaraja (8y 5m)ANUSHA K SÎncă nu există evaluări
- B W Retail Con Ten Supply Chan ADocument69 paginiB W Retail Con Ten Supply Chan As.zeraoui1595Încă nu există evaluări
- Technical ProposalDocument7 paginiTechnical ProposalMD ABUL KHAYERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bestow ERP General 2Document14 paginiBestow ERP General 2M. MUBASHARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Executive SummaryDocument4 paginiExecutive Summaryanon_590527118Încă nu există evaluări
- CV Coverletter11Document2 paginiCV Coverletter11sulabh1Încă nu există evaluări
- SAP MM Having 8 Years of ExperienceDocument5 paginiSAP MM Having 8 Years of Experiencejagadishwas09Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4Document57 paginiChapter 4mÎncă nu există evaluări
- 29953bos19569 3 PDFDocument7 pagini29953bos19569 3 PDFKALPANA R KHADLOYAÎncă nu există evaluări
- ERP Design & Implementation: Purchase-to-Pay Processing in SAP ERP Organizational Levels TransactionsDocument27 paginiERP Design & Implementation: Purchase-to-Pay Processing in SAP ERP Organizational Levels TransactionsM Aamir AsgharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sap MM Q&aDocument26 paginiSap MM Q&abeema197750% (2)
- Procurement Module Requirements GatheringDocument2 paginiProcurement Module Requirements GatheringKirui KimutaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Audit Process Coreia - Com GoodDocument11 paginiInternal Audit Process Coreia - Com Goodsarvjeet_kaushalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview of Logistics Execution: ContentsDocument34 paginiOverview of Logistics Execution: ContentsSaikiran81100% (1)
- Sales and Distribution ModuleDocument14 paginiSales and Distribution Modulearnold6123Încă nu există evaluări
- Procure To PayDocument14 paginiProcure To PaymeegunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inventory Management: Subhani ShaikDocument31 paginiInventory Management: Subhani ShaikJagadish JAGANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pom Unit 4-1Document16 paginiPom Unit 4-1Rakesh ChebroluÎncă nu există evaluări
- P2P Interview Questions and Answer 3Document13 paginiP2P Interview Questions and Answer 3Raju Bothra100% (2)
- Expenditure CycleDocument5 paginiExpenditure Cyclengkqd29fsyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 4 - Materials Management (2nd Sem, C2 AY 2021-2022) FinalDocument46 paginiModule 4 - Materials Management (2nd Sem, C2 AY 2021-2022) FinalJayron NonguiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erp Practitioner Session Write Up 2jdDocument4 paginiErp Practitioner Session Write Up 2jdSiddharth SamantakurthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCM Mod3Document25 paginiSCM Mod3Amir RajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bin Card System Stock ControlDocument2 paginiBin Card System Stock ControlYobsanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Controlling and Costing MaterialsDocument70 paginiControlling and Costing Materialstotongop100% (1)
- ZameerSupply Chain AnalystDocument3 paginiZameerSupply Chain Analystmohammed ghouse aazminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Audit of Inventory and CGSDocument9 paginiChapter 4 Audit of Inventory and CGSminichelÎncă nu există evaluări
- SI0020 SAP Fundamental: Logistics - ProcurementDocument20 paginiSI0020 SAP Fundamental: Logistics - ProcurementBinsar WilliamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit V: Materials Management-ObjectivesDocument8 paginiUnit V: Materials Management-ObjectivesSunkeswaram Deva PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOP 10 General Questions For SAP MM InterviewDocument2 paginiTOP 10 General Questions For SAP MM InterviewabhishekÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Procurement ProcessDocument32 paginiThe Procurement ProcessRahul RaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- S/4 HANA Certification GuideDocument18 paginiS/4 HANA Certification GuideSubhasis Sikdar0% (1)
- Business Intelligent: Unit 14: Unit TitleDocument8 paginiBusiness Intelligent: Unit 14: Unit TitlekevinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Purchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsDe la EverandPurchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Supply Chain and Procurement Quick Reference: How to navigate and be successful in structured organizationsDe la EverandSupply Chain and Procurement Quick Reference: How to navigate and be successful in structured organizationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logistics in Manufacturing, Supply Chain, and DistributionDe la EverandLogistics in Manufacturing, Supply Chain, and DistributionÎncă nu există evaluări
- JEE Mains Paper 1 (12 Apr 2019 Shift 2) EnglishDocument131 paginiJEE Mains Paper 1 (12 Apr 2019 Shift 2) EnglishRudraksha KushwahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concise Selina Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 15 Construction of PolygonsDocument31 paginiConcise Selina Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 15 Construction of Polygonsbhaskar51178Încă nu există evaluări
- 2010 Information ExchangeDocument15 pagini2010 Information ExchangeAnastasia RotareanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing Errors and ExceptionDocument12 paginiManaging Errors and ExceptionShanmuka Sreenivas100% (1)
- Army Aviation Digest - Apr 1971Document68 paginiArmy Aviation Digest - Apr 1971Aviation/Space History LibraryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bagian AwalDocument17 paginiBagian AwalCitra Monalisa LaoliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris TranslateDocument14 paginiMakalah Bahasa Inggris TranslatevikaseptideyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 95-03097 Ballvlv300350 WCB PDFDocument26 pagini95-03097 Ballvlv300350 WCB PDFasitdeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessing Apical PulseDocument5 paginiAssessing Apical PulseMatthew Ryan100% (1)
- Dist - Propor.danfoss PVG32Document136 paginiDist - Propor.danfoss PVG32Michal BujaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- S-Sapfico-Satyanarayanamaterial 121212Document183 paginiS-Sapfico-Satyanarayanamaterial 121212mpsing1133Încă nu există evaluări
- SY22-23+Annual+Report FinalDocument47 paginiSY22-23+Annual+Report FinalNorus LizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Actron Vismin ReportDocument19 paginiActron Vismin ReportSirhc OyagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 2 HORSEPOWER EFFICIENCY GEAR RATIO AND SPEED RATIODocument10 paginiExperiment 2 HORSEPOWER EFFICIENCY GEAR RATIO AND SPEED RATIOJake Polo SantiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retail Branding and Store Loyalty - Analysis in The Context of Reciprocity, Store Accessibility, and Retail Formats (PDFDrive)Document197 paginiRetail Branding and Store Loyalty - Analysis in The Context of Reciprocity, Store Accessibility, and Retail Formats (PDFDrive)Refu Se ShitÎncă nu există evaluări
- ManualDocument50 paginiManualspacejung50% (2)
- Auditing Principles and Practices-IDocument8 paginiAuditing Principles and Practices-IMoti BekeleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To MavenDocument18 paginiIntro To MavenDaniel ReckerthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norman, K. R., Pali Philology & The Study of BuddhismDocument13 paginiNorman, K. R., Pali Philology & The Study of BuddhismkhrinizÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1Document2 pagini1TrầnLanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 30 - HypertensionDocument70 paginiChapter 30 - HypertensionSakaC.TanayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formato MultimodalDocument1 paginăFormato MultimodalcelsoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glossary of Blasting TermsDocument13 paginiGlossary of Blasting TermsNitesh JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer: C: Exam Name: Exam Type: Exam Code: Total QuestionsDocument26 paginiAnswer: C: Exam Name: Exam Type: Exam Code: Total QuestionsMohammed S.GoudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abas Drug Study Nicu PDFDocument4 paginiAbas Drug Study Nicu PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vest3000mkii TurntableDocument16 paginiVest3000mkii TurntableElkin BabiloniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter1 Intro To Basic FinanceDocument28 paginiChapter1 Intro To Basic FinanceRazel GopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- DL Manual - Com Vs Controller Gs Driver p100 Operating ManualDocument124 paginiDL Manual - Com Vs Controller Gs Driver p100 Operating ManualThiago Teixeira PiresÎncă nu există evaluări
- French Cuisine RecipeDocument6 paginiFrench Cuisine RecipeJimmy AchasÎncă nu există evaluări