Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
FDNMARK Reviewer
Încărcat de
Trish Bernabe100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
94 vizualizări3 paginiTitlu original
FDNMARK_reviewer
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
94 vizualizări3 paginiFDNMARK Reviewer
Încărcat de
Trish BernabeDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
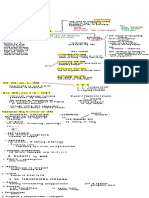
FDNMARK PRODUCT
Marketing Elements of Product Planning for Goods & Services
more than just selling and advertising
performance of activities that aims to 1. Product Idea
accomplish a firm’s objectives through - physical good or service
satisfying the customer’s needs – for profit - experience, benefits and features
begins w potential customer’s needs
2. Branding
Marketing Discrepancies & Separations - creating a name, symbol or design that
- Discrepancies of Quantity identifies and differentiates a product from
- Discrepancies of Assortment other products 5L of Brand Familiarity
- Spatial Separation
- Separation in time Manufacturer –
- Separation of information national brand owned
- Separation in values by producers
- Separation of ownership Dealer – private brands
owned by
Marketing Functions intermediaries
- Buying
- Selling 3. Packaging
- Transporting Protecting
- Storing Promoting
- Standardization & grading Enhancing
- Financing
- Risk taking 4. Warranty
- Market information - what sellers promise about the product
Limited Warranty – specified scope
Marketing Concept Full Warranty – repair or replacement of a
- Customer satisfaction product for a certain time period
- Total company effort
- Profit 5. Product Classes
- depends on the type of customer
Marketing Orientation – from a firm 1. Consumer Products – final consumer
Production Orientation – from a customer a. Convenience – purchased quickly
with little effort staple impulse emrgn
Customer Value – benefits vs costs obtaining the b. Shopping – worthy to compare
benefits c. Specialty – no substitutes
d. Unsought – not normally bought
Micro-macro dilemma – economic phenomenon 2. Business Products – how products will be
results in negative social consequences used
a. Installations – major facilities
Marketing Management Process b. Accessories – short-lived capital item
1. Planning c. Raw materials – becomes part of the
2. Implementation physical good
3. Controlling d. Components – processed and
becomes a part of the final product
4Ps of Marketing e. Maintenance, repair & operations
1. Product – Customer’s needs; goods/services Supplies - not directly related to
2. Place – Convenience; channel of distrib making a finished product but are
3. Promotion – Communication necessary to keep their operation
4. Price – Cost going
f. Professional Services – supports a
Product Life Cycle firm’s operations
1. Introduction
2. Growth
3. Maturity
4. Decline
New Product Development Process PRICE
1. Idea Generation
2. Screening – S&W Pricing Objectives
3. Idea Evaluation – concept testing 1. Profit-oriented
4. Development – prototypes; market test - profit as an objective; target return
5. Commercialization – putting into the market 2. Sales-oriented
- objectives seek to boost volume or market
PLACE share
3. Status quo oriented
Distribution channel - chain of intermediaries - don’t-rock-the-boat objectives
through which a good or service passes until it - copies the price levels of its competitors or
reaches the final buyer or the end consumer maintains the current price levels of similar
products or services in the market
Direct – maintains control; lower costs; no
intermediaries; direct contact w consumers Pricing Policies
Indirect – through intermediaries Administered prices – prices set by firms
Regrouping Activities One-price policy – same price to all customers
Assortment Flexible-price policy – same product & quantities to
Sorting – separating products into grades & qualities diff customers at diff prices
by diff target markets
Assorting – putting together variety of products to Dynamic pricing – products at a price changing
give target market what it wants depending on the level of demand, customer or
Quantity season
Accumulating – collecting products from many Price-cutting – cut prices to dominate market
small producers
Bulk-breaking – dividing larger quantities into smaller PP Over the Product Life Cycle
quantities as it approach the final market Skimming Price- sets a relatively high initial price
then lowers the price over time
Types of Channel Penetration Pricing – sets a low initial price to attract
1. Traditional new customers
2. Vertical Marketing Introductory Price Dealing - set low prices in order to
enter a new market for your company and raises
Market Exposure Strategies prices after introductory is over
1. Intensive - when a business ignores market
segmentation and decides to supply their DISCOUNTS
product to every market available - are deductions from the list price
2. Selective - through intermediaries who will
give their product special attention Quantity Discounts – encourage customers to buy in
3. Exclusive – selling in only one intermediary in large quantities
a particular location a. Cumulative - encourages repeat buying;
adds potential discount to every purchase
Entering International Markets b. Non-cumulative- a one-time discount
1. Exporting
2. Licensing Seasonal Discounts - are offered on seasonal goods
3. Management Contracting during a certain season
4. Joint Venture
5. Direct Investment Cash Discounts - encourages customers to pay bills
earlier (ex 2% if paid within 5 days)
Logistics – physical distribution
Physical Distribution Concept – transporting, storing Trade Discount (functional) - discount given by the
& product-handling activities of a firm and a whole seller as a deduction in the list price
channel system should be coordinated
Total Cost Approach – evaluating each possible PD Sale Price – temporary discount; encourages
system and identifying all costs for each alternative immediate buying
ALLOWANCES
- these are reduction in the price due to a problem Price Setting
with the product or service Cost-Oriented Approach
- takes into account the company's profit
Common Types of Allowances objectives and that covers its costs of production
Advertising All. - price reductions given to firms to 1. Markups - amount added to the cost price
get the word out about the product of goods to cover overhead and profit
2. Average-cost pricing - setting prices close to
Stocking All. – or slotting allowances; given to average cost ; maximize sales while
intermediaries such as retailers to get shelf space for maintaining normal profit; dangerous; no
their products allowances
a. Average-variable – depends on output
Push Money – spiffs; given to retailers to ensure that b. Average-fixed – fixed cost
they display the product significantly and ensuring c. Average-total – sum of all production
that products will be sold costs
Trade-in allowances - the amount a seller reduces Types of Total Costs
to a certain thing in return for a new product 1. Total Fixed Cost
bought 2. Total Variable Cost
3. Total Cost – sum of the two
Rebates or Cash back - unlike discount, these are
given to a customer after the payment of the full 3. Breakeven Analysis – cost and income to
amount determine profit
4. Marginal Analysis – examination of the
GEOGRAPHICAL PRICING associated costs and potential benefits;
- practice of modifying a basic list price based on profit maximization
the location of the buyer
Demand-Oriented Approach
Geographic Pricing Policies - uses the customer demand to set up the price in
Freight on board - the shipping fee is paid by the the market
purchaser 1. Value-in-use Pricing – based on the
Zone pricing - prices increase as distance increases product’s value to customers
(LBC) 2. Auctions – bidding for the selling item
Uniform delivery pricing - the same price is 3. Sequential price Reductions – starts at a
charged to all relatively high price then step by step
Freight-absorption pricing - seller absorbs all or a reductions
part of the cost of shipping as a promotional tactic 4. Reference Prices – prices customers expect
to pay (competition)
Value Pricing – setting a fair price level based on 5. Leader Pricing – setting very low prices to sell
the value consumers perceive a service or good to large quantities and also buy other products
have 6. Bait Pricing – set low prices to attract
customers and try to sell expensive brands
Legality of Pricing Policies once the customer is in store; false advertise
Unfair Trade Practice Acts – places a lower limit on 7. Demand-backward Pricing – estimates the
prices price from a consumer perspective and
Dumping – pricing a product in a foreign market adjusts accordingly
below the cost of producing it 8. Psychological – special appeal to customers
Phony List Prices – prices shown to customer to Odd-even – ends in certain numbers
suggest discounts 9. Price Lining - separating goods into cost
Price Fixing - the maintaining of prices at a certain categories in order to create various quality
level by agreement between competing sellers levels in the minds of consumers
Price Discrimination – selling same products to diff 10. Prestige – setting a high price to suggest
buyers at diff prices high quality
Full-line Pricing – setting prices for a whole line of Product-bundle – one price for a set of products
products Bid Pricing – offering a specific price for each
Complementary product – set prices on several possible job
products as a group Negotiated Price – based on bargaining
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- CASE STUDY Can One Size Fit It AllDocument4 paginiCASE STUDY Can One Size Fit It AllAngelica B. PatagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accounting NotesDocument8 paginiAccounting NoteskaikoÎncă nu există evaluări
- GE-LIT 101 Syllabus Midyear Term 2022-23 (PT)Document10 paginiGE-LIT 101 Syllabus Midyear Term 2022-23 (PT)Zoe FormosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bond Investment - FVOCI: Subject Intermediate Accounting Teacher Dessa Dianna MadridDocument23 paginiBond Investment - FVOCI: Subject Intermediate Accounting Teacher Dessa Dianna MadridJohn Warren MestiolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Please Pay This AmountDocument1 paginăPlease Pay This AmountGio DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spark Notes - Julius Caesar - Themes, Motifs & SymbolsDocument3 paginiSpark Notes - Julius Caesar - Themes, Motifs & SymbolsLeonis MyrtilÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 Intertrod Maritime Vs NLRCDocument3 pagini02 Intertrod Maritime Vs NLRCDavid Antonio A. EscuetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 5 Production TheoryDocument27 paginiModule 5 Production TheoryCharice Anne VillamarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coblaw Chap1 3Document25 paginiCoblaw Chap1 3Charlene Tia100% (1)
- Corporation Part IIDocument56 paginiCorporation Part IILyn Roldan-Nepomuceno100% (1)
- Sample Divorce Petition DraftDocument41 paginiSample Divorce Petition DraftAyantika Mondal100% (1)
- Interest Rates and Bond ValuationDocument75 paginiInterest Rates and Bond ValuationOday Ru100% (1)
- Contact CivilDocument33 paginiContact CivilKartik RajputÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10 Corporations - Retained Earnings Exercises T3AY2021Document6 paginiChapter 10 Corporations - Retained Earnings Exercises T3AY2021Carl Vincent BarituaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IEEE Guide For Solar Power Plant Grounding For Personal ProtectionDocument24 paginiIEEE Guide For Solar Power Plant Grounding For Personal Protectioncjabes100% (3)
- Request For Repair of Ict EquipmentDocument1 paginăRequest For Repair of Ict EquipmentAdrian AtillagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLSU FDNMark Principles of Marketing Midterm 1st Term AY 20-21Document2 paginiDLSU FDNMark Principles of Marketing Midterm 1st Term AY 20-21Andrew ContapayÎncă nu există evaluări
- AAA FDNMARK 01 - Introduction To Marketing ManagementDocument49 paginiAAA FDNMARK 01 - Introduction To Marketing ManagementMarco Vicente SanvictoresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cost Volume Profit RelationshipDocument15 paginiCost Volume Profit RelationshipzaimfaizahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 - Inventories: Revised EditionDocument7 paginiChapter 5 - Inventories: Revised EditionMelyssa Dawn Gullon0% (1)
- Corporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and DividendsDocument43 paginiCorporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and Dividendsanon_355962815Încă nu există evaluări
- Accounting For Purchases and Sale of MerchandiseDocument4 paginiAccounting For Purchases and Sale of MerchandiseRaissa MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- FDNACCT Reflection Paper PDFDocument4 paginiFDNACCT Reflection Paper PDFCrystal Castor LabragueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classifications of PartnershipDocument3 paginiClassifications of PartnershipFely MaataÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 CFAS Course Assessment A To DDocument4 pagini2 CFAS Course Assessment A To DKing SigueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 3: Worksheet 3: Remedial Lesson 3: Adjusting EntriesDocument2 paginiLesson 3: Worksheet 3: Remedial Lesson 3: Adjusting EntriesAleana joy PabelicÎncă nu există evaluări
- COBLAWDocument7 paginiCOBLAWyasmeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managerial QuizDocument5 paginiManagerial QuizThuy Ngan NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Globe Reflection aCyFaR1 AWItDocument9 paginiGlobe Reflection aCyFaR1 AWIt123r12f1Încă nu există evaluări
- FinanceDocument1 paginăFinancekiler2424Încă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet For Cost and Management Accounting I (Acct 211)Document9 paginiWorksheet For Cost and Management Accounting I (Acct 211)ዝምታ ተሻለÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demand ForecastingDocument16 paginiDemand ForecastingharithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Original Chapter 4 Consumer Choice and DemandDocument12 paginiOriginal Chapter 4 Consumer Choice and DemandJohn Darrelle de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mindmap Chapter 5 Cost-Volumn Profit AnalysisDocument1 paginăMindmap Chapter 5 Cost-Volumn Profit AnalysisSimon Erick0% (1)
- FinmanDocument3 paginiFinmanKaren LaccayÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACEFIAR Quiz No. 1Document3 paginiACEFIAR Quiz No. 1Marriel Fate CullanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essay 1 - Non-Financial InformationDocument3 paginiEssay 1 - Non-Financial InformationSeiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- I - P - Financial Markets Through TImeDocument35 paginiI - P - Financial Markets Through TImeWeiyee ValenzuelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 - Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive MarketsDocument6 pagini8 - Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive MarketsMikkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pure CompetitionDocument7 paginiPure CompetitionEricka TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercises - Sept. 29Document3 paginiExercises - Sept. 29Keitheia QuidlatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Underlying AssumptionsDocument7 paginiChapter 4 Underlying AssumptionsMicsjadeCastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instruction: Write Your Name and Answer in A Journal/paper. Submit A MAXIMUM OF 6 PICTURES OnlyDocument1 paginăInstruction: Write Your Name and Answer in A Journal/paper. Submit A MAXIMUM OF 6 PICTURES Onlyhokage astroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Pricing Techniques: Ninth Edition Ninth EditionDocument28 paginiAdvanced Pricing Techniques: Ninth Edition Ninth EditionMosiur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 1100 - Chapter 9-12Document42 paginiMath 1100 - Chapter 9-12tangwanlu91770% (1)
- CH2 - Financial Reporting MechanicsDocument32 paginiCH2 - Financial Reporting MechanicsStudent Sokha ChanchesdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of CostDocument4 paginiClassification of CostSha Heradura AngadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blaw Prelims ReviewerDocument17 paginiBlaw Prelims ReviewerVanessa dela Torre0% (1)
- ACCCOB1 - Reviewer FormationDocument4 paginiACCCOB1 - Reviewer Formationbea's backupÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Accounting 4th Edition Chapter 2Document67 paginiFinancial Accounting 4th Edition Chapter 2Joey TrompÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 3b Adjusting The AccountsDocument3 paginiLesson 3b Adjusting The AccountsBenedict CladoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity Number 5 Elasticity of Demand & SupplyDocument5 paginiActivity Number 5 Elasticity of Demand & SupplyLovely Madrid0% (1)
- Selling For Relationships First, Inc Case StudyDocument3 paginiSelling For Relationships First, Inc Case StudyKATAKURI CharlotteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acquirer Obtains Control of One or More Businesses.: ConceptDocument6 paginiAcquirer Obtains Control of One or More Businesses.: ConceptJohn Lexter MacalberÎncă nu există evaluări
- WIKI - The Statement of Cost of Goods SoldDocument5 paginiWIKI - The Statement of Cost of Goods SoldHanna GeguillanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Acc ReviewerDocument7 paginiBasic Acc ReviewerReign PangilinanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.1 Debt and Equity FinancingDocument13 pagini4.1 Debt and Equity FinancingAliza UrtalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Introduction To Managerial FinanceDocument25 paginiChapter 3 Introduction To Managerial FinanceEunice NunezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 7Document38 paginiQuiz 7nikhil gangwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manulife PhilippinesDocument4 paginiManulife PhilippinesvhinereyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Circular Flow of Economics ActivitiesDocument7 paginiThe Circular Flow of Economics ActivitiesLuna AdrianneÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 Sqe Reviewer - Fundamentals of Accounting Parts 1 and 2 PDFDocument23 pagini2019 Sqe Reviewer - Fundamentals of Accounting Parts 1 and 2 PDFJohn Marfhel PrestadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memorandums and Letters: Apply Correct Memo and Letter FormatsDocument17 paginiMemorandums and Letters: Apply Correct Memo and Letter FormatsAqib Sheikh100% (1)
- MRKTG Reviewer g12Document18 paginiMRKTG Reviewer g12Katherine JanohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Did Korean Monetary Policy Help Soften The Impact of The Global Financial Crisis of 2008-09?Document47 paginiDid Korean Monetary Policy Help Soften The Impact of The Global Financial Crisis of 2008-09?Trish BernabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECOCAL2 Seatwork #2Document1 paginăECOCAL2 Seatwork #2Trish BernabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wika PDFDocument1 paginăWika PDFTrish BernabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing UniqloDocument4 paginiMarketing UniqloTrish BernabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing StrategyDocument1 paginăMarketing StrategyTrish BernabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing StrategyDocument1 paginăMarketing StrategyTrish BernabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Impact of Tertiary Education To The Employment Rate in The PhilippinesDocument4 paginiThe Impact of Tertiary Education To The Employment Rate in The PhilippinesTrish BernabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Choosing The Right Wife in IslamDocument4 paginiChoosing The Right Wife in IslamAhmad TamimiÎncă nu există evaluări
- From The Office of The Principal O23Document2 paginiFrom The Office of The Principal O23FatehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accounting & Control: Cost ManagementDocument40 paginiAccounting & Control: Cost ManagementBusiness MatterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Accounting-2Document8 paginiFinancial Accounting-2Deepa KulalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deed of Sale of Motor VehicleDocument1 paginăDeed of Sale of Motor VehicleJonah ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllab of Dip in Life Ins UnderwritingDocument17 paginiSyllab of Dip in Life Ins Underwritinganon_303912439100% (1)
- Atp 2023 2024 AdvertDocument2 paginiAtp 2023 2024 AdvertDavid Lemayian SalatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- MPEP Chapter 1200 AppealsDocument72 paginiMPEP Chapter 1200 AppealsSam HanÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Do You Umpire in NetballDocument3 paginiHow Do You Umpire in NetballNita NorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fria Law: Sole Proprietorship Duly Registered With The Department of Trade and Industry (DTIDocument10 paginiFria Law: Sole Proprietorship Duly Registered With The Department of Trade and Industry (DTIReigh Harvy CantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The DBCCDocument3 paginiThe DBCCAgentSkySkyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monzo Warns Job Candidates Not To Use ChatGPT During Application Process - HR Software - HR Grapevine - NewsDocument1 paginăMonzo Warns Job Candidates Not To Use ChatGPT During Application Process - HR Software - HR Grapevine - NewsMaxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parkway Building Conditional Use Permit Approved - Can Challenge To March 1st 2021Document15 paginiParkway Building Conditional Use Permit Approved - Can Challenge To March 1st 2021Zennie AbrahamÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Opinion Article (CounterfeitingDocument1 paginăAn Opinion Article (CounterfeitingYousra HasniÎncă nu există evaluări
- NSTP Chapter 2Document5 paginiNSTP Chapter 2NicoleVideñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Working Tariff: Sindh Sales Tax On ServicesDocument22 paginiWorking Tariff: Sindh Sales Tax On ServicesshahzaibÎncă nu există evaluări
- S1720, S2700, S5700, and S6720 V200R011C10 Configuration Guide - Interface ManagementDocument121 paginiS1720, S2700, S5700, and S6720 V200R011C10 Configuration Guide - Interface ManagementkfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethics Lectures The Space Shuttle Challenger Tragedy - An: MAE 175aDocument6 paginiEthics Lectures The Space Shuttle Challenger Tragedy - An: MAE 175aAhmedAmer1Încă nu există evaluări
- Certified List of Candidates For Congressional and Local Positions For The May 13, 2013 2013 National, Local and Armm ElectionsDocument2 paginiCertified List of Candidates For Congressional and Local Positions For The May 13, 2013 2013 National, Local and Armm ElectionsSunStar Philippine NewsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ifrs 9: Financial InstrumentsDocument18 paginiIfrs 9: Financial InstrumentsPhebieon MukwenhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accountant Resume 14Document3 paginiAccountant Resume 14kelvin mkweshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer Key Ch-8-Women, Caste and ReformsDocument4 paginiAnswer Key Ch-8-Women, Caste and ReformsBtdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: SOCIOLOGY 9699/41Document4 paginiCambridge International AS & A Level: SOCIOLOGY 9699/41maharanaanauyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mysore Gazetteer 02 (Hayavadana Rao Edit) PDFDocument814 paginiMysore Gazetteer 02 (Hayavadana Rao Edit) PDFArunÎncă nu există evaluări