Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Formation Evaluation
Încărcat de
NA NA0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
11 vizualizări1 paginăFE
Titlu original
Formation Evaluation(60)
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentFE
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
11 vizualizări1 paginăFormation Evaluation
Încărcat de
NA NAFE
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
Log Measurements and Tools
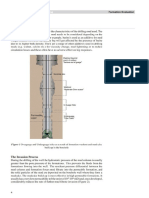
Normally the mudcake has much higher resistance than the formation such that the
cexcesspressure created inthe latteris negligible. Oncethe mudeake permeability drops
very low (normally below 1 mD). this condition no longer holds and the formation
next to the borehole may become supercharged. The similar phenomenon occurs in
low permeability formations where filtrate invasion (in pressure communication with
mad column) continues for a long period and which is why supercharging occurs,
Boreal (3H,
Po 'Mudeake (MC)
Flushed zone FZ)
‘Transition zone (12)
Figure 2 Invasion of the drilling fuid into the formation
‘Very close 10 the borehole most of the originé! formation water and some of the
hydrocarbons may be flushed away by the filtrate (Figure 2a). This zone is referred
toas the flushed zone. It contains, if the flushing is complete, only mud filtrate; if
the formation was originally hydrocarbon beariag, only residual hydrocarbons. Oil-
based mud invasion gives additional challenges, not least for its tendency to gravity
segregation in the formation.
Further out from the borehole, the displacement of the formation fluids by the mud
filtrate is less and less complete, resulting in a transition from mus filtrate saturation
tooriginal formation water saturation. This zene is referred to as the transition or
invaded zone. The extent or depth of the flushed and transition zones depends on
‘many parameters such as:
Instute of Petoleum Engneerng, Heriot-Watt University 5
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Formation EvaluationDocument1 paginăFormation EvaluationNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation EvaluationDocument1 paginăFormation EvaluationNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation EvaluationDocument1 paginăFormation EvaluationNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation EvaluationDocument1 paginăFormation EvaluationNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation EvaluationDocument1 paginăFormation EvaluationNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation EvaluationDocument1 paginăFormation EvaluationNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation EvaluationDocument1 paginăFormation EvaluationNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation EvaluationDocument1 paginăFormation EvaluationNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation EvaluationDocument1 paginăFormation EvaluationNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation EvaluationDocument1 paginăFormation EvaluationNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation EvaluationDocument1 paginăFormation EvaluationNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Toxicity of Drilling Fluids Used in Mexican Offshore Facilities Tested With Postlarvae White ShrimpDocument4 paginiAcute Toxicity of Drilling Fluids Used in Mexican Offshore Facilities Tested With Postlarvae White ShrimpNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation EvaluationDocument1 paginăFormation EvaluationNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation EvaluationDocument1 paginăFormation EvaluationNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Thixotropic Barrier Fluid Used To Prevent The Commingling of Fluids While Tripping On Managed Pressure Drilling WellsDocument6 paginiA Thixotropic Barrier Fluid Used To Prevent The Commingling of Fluids While Tripping On Managed Pressure Drilling WellsNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advances in Inhibitive Water-Based Drilling Fluids - Can They Replace Oil-Based MudsDocument8 paginiAdvances in Inhibitive Water-Based Drilling Fluids - Can They Replace Oil-Based MudsNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Slip-Crushing Considerations For Deepwater DrillingDocument14 paginiAdvanced Slip-Crushing Considerations For Deepwater DrillingNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accurate Bottomhole Pressure For Fracture Gradient Prediction and Drilling Fluid Pressure Program - Part IDocument9 paginiAccurate Bottomhole Pressure For Fracture Gradient Prediction and Drilling Fluid Pressure Program - Part INA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- IADC/SPE 74488 Advanced Slip Crushing Considerations For Deepwater DrillingDocument15 paginiIADC/SPE 74488 Advanced Slip Crushing Considerations For Deepwater DrillingJaaTa Da shaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accurate Prediction of Gas Hydrate Suppression Capability of Water-Based Drilling Fluids in Deepwater DrillingDocument8 paginiAccurate Prediction of Gas Hydrate Suppression Capability of Water-Based Drilling Fluids in Deepwater DrillingNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abandonment of Seabed Deposition of Drill Cuttings During Offshore DrillingDocument4 paginiAbandonment of Seabed Deposition of Drill Cuttings During Offshore DrillingNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Systematic Approach in Deepwater Flow Assurance Fluid CharacterizationDocument12 paginiA Systematic Approach in Deepwater Flow Assurance Fluid CharacterizationNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Successful Short Radius Re-Entry With Aerated Mud in VenezuelaDocument15 paginiA Successful Short Radius Re-Entry With Aerated Mud in VenezuelaNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advances in Chromatographic Analysis of Hydrocarbon Gases in Drilling Fluids - The Application of Semi-Permeable Membrane Technology To High Speed TCD Gas ChromatographyDocument9 paginiAdvances in Chromatographic Analysis of Hydrocarbon Gases in Drilling Fluids - The Application of Semi-Permeable Membrane Technology To High Speed TCD Gas ChromatographyNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Dynamic Imaging Particle Analysis System For Real-Time Analysis of Drilling MudsDocument7 paginiA Dynamic Imaging Particle Analysis System For Real-Time Analysis of Drilling MudsNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- A CT Scan Study of The Leakoff of Oil-Based Drilling FluidsDocument25 paginiA CT Scan Study of The Leakoff of Oil-Based Drilling FluidsNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Cost-Effective Rig MoveDocument4 paginiA Cost-Effective Rig MoveNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Critical Analysis of Shear Failure Pressure and Chemical Osmosis During Fluid - Shale InteractionsDocument11 paginiA Critical Analysis of Shear Failure Pressure and Chemical Osmosis During Fluid - Shale InteractionsNA NAÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)