Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
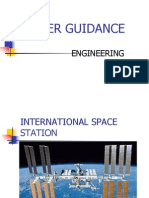
n the field of biomedical engineering, specifically with biomechanics, transport phenomena, biomechatronics, bionanotechnology, and modelling of biological systems. W16 engine of the Bugatti Veyron. Mechanical engineers design engines, power plants, other machines... ...structures, and vehicles of all sizes. History Education Job duties Subdisciplines Modern tools Areas of research Related fields See also References Further reading External links Last edited 4 days ago by Smenjas Wikipedia Content is available under CC BY-SA 3.0 unless otherwise noted. Terms of UsePrivacyDesktop
Încărcat de
APLCTNDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
n the field of biomedical engineering, specifically with biomechanics, transport phenomena, biomechatronics, bionanotechnology, and modelling of biological systems. W16 engine of the Bugatti Veyron. Mechanical engineers design engines, power plants, other machines... ...structures, and vehicles of all sizes. History Education Job duties Subdisciplines Modern tools Areas of research Related fields See also References Further reading External links Last edited 4 days ago by Smenjas Wikipedia Content is available under CC BY-SA 3.0 unless otherwise noted. Terms of UsePrivacyDesktop
Încărcat de
APLCTNDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Mechanical engineering
Language
Download PDF
Watch
Edit
Mechanical engineering is the discipline that applies engineering physics, engineering mathematics, and
materials science principles to design, analyze, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems. It is one of
the oldest and broadest of the engineering disciplines.
Mechanical engineering
Occupation
Names
Mechanical engineer
Activity sectors
applied mechanics, dynamics, thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, heat transfer, production technology, and
others
Description
Competencies
technical knowledge, management skills, design (see also glossary of mechanical engineering)
Education required
See professional requirements below
Fields of
employment
technology, science, exploration, military
The mechanical engineering field requires an understanding of core areas including mechanics, dynamics,
thermodynamics, materials science, structural analysis, and electricity. In addition to these core principles,
mechanical engineers use tools such as computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing
(CAM), and product lifecycle management to design and analyze manufacturing plants, industrial
equipment and machinery, heating and cooling systems, transport systems, aircraft, watercraft, robotics,
medical devices, weapons, and others. It is the branch of engineering that involves the design, production,
and operation of machinery.[1][2]
Mechanical engineering emerged as a field during the Industrial Revolution in Europe in the 18th century;
however, its development can be traced back several thousand years around the world. In the 19th century,
developments in physics led to the development of mechanical engineering science. The field has
continually evolved to incorporate advancements; today mechanical engineers are pursuing developments
in such areas as composites, mechatronics, and nanotechnology. It also overlaps with aerospace
engineering, metallurgical engineering, civil engineering, electrical engineering, manufacturing
engineering, chemical engineering, industrial engineering, and other engineering disciplines to varying
amounts. Mechanical engineers may also work in the field of biomedical engineering, specifically with
biomechanics, transport phenomena, biomechatronics, bionanotechnology, and modelling of biological
systems.
W16 engine of the Bugatti Veyron. Mechanical engineers design engines, power plants, other machines...
...structures, and vehicles of all sizes.
History
Education
Job duties
Subdisciplines
Modern tools
Areas of research
Related fields
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Last edited 4 days ago by Smenjas
Wikipedia
Content is available under CC BY-SA 3.0 unless otherwise noted.
Terms of UsePrivacyDesktop
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Mechanical Engineering Is The Discipline That AppliesDocument1 paginăMechanical Engineering Is The Discipline That AppliesRyan Compala LictagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineering Is The Discipline That AppliesDocument1 paginăMechanical Engineering Is The Discipline That Appliesrakha adiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineering Is An Engineering Branch That Combines Engineering Physics and Mathematics Principles With Materials Science To DesignDocument1 paginăMechanical Engineering Is An Engineering Branch That Combines Engineering Physics and Mathematics Principles With Materials Science To DesignkhumisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dhimas SalinanDocument1 paginăDhimas SalinanAnggun PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineering Is The Discipline That Applies The Principles ofDocument1 paginăMechanical Engineering Is The Discipline That Applies The Principles ofJeric Paul FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 BCME NotesDocument23 paginiUnit 1 BCME NotesMANOJKUMAR MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineering Is A Discipline ofDocument1 paginăMechanical Engineering Is A Discipline ofLGCPÎncă nu există evaluări
- IME - Module 1 - NotesDocument26 paginiIME - Module 1 - NotesSudheer KiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical EngineeringDocument5 paginiMechanical EngineeringZeina Zeina Mohamed EmarahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineering Is A Discipline ofDocument1 paginăMechanical Engineering Is A Discipline ofImbran SheriffÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Role of Mech Engrs in Nation BuildingDocument41 paginiThe Role of Mech Engrs in Nation BuildingEnibuetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning Task 3Document2 paginiLearning Task 3ansor yunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 paginiMechanical EngineeringdopinderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 2Document9 paginiAssignment 2AwAis KiYaNiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineering The King of EngineeringDocument2 paginiMechanical Engineering The King of EngineeringEditor IJTSRDÎncă nu există evaluări
- EngineeringDocument249 paginiEngineeringSivabalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Branches of EngineeringDocument5 paginiBranches of Engineeringrondick88% (8)
- INTRODUCTION TO ME Chapter 2Document11 paginiINTRODUCTION TO ME Chapter 2Muhd ArifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Industry ProfileDocument4 paginiMechanical Industry Profiledevang parulekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical EngineeringDocument20 paginiMechanical Engineeringashaikhimran7Încă nu există evaluări
- Carrer CounsellingDocument28 paginiCarrer CounsellingIntikhab AlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME Laws MODULE 1Document10 paginiME Laws MODULE 1Niaz KilamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Outline of EngineeringDocument9 paginiOutline of Engineeringriz2010Încă nu există evaluări
- Article About Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 paginiArticle About Mechanical EngineeringdopinderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1Document23 paginiLecture 1adsiztayfaÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 paginiHistory of Mechanical Engineeringkate trishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EngineeringDocument7 paginiEngineeringTaha Al-husnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering, презентацияDocument10 paginiEngineering, презентацияРуслана ТокареваÎncă nu există evaluări
- BmeDocument3 paginiBmechantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Career Guidance EnggDocument26 paginiCareer Guidance Enggsourav6108Încă nu există evaluări
- The Gains of Studying Mechanical EngineeringDocument10 paginiThe Gains of Studying Mechanical Engineeringyikaha7594Încă nu există evaluări
- Artikel MekanikalDocument8 paginiArtikel Mekanikalmaw ardyÎncă nu există evaluări
- MecanicalDocument3 paginiMecanicalNajeeb MashwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research: Dette DetteDocument8 paginiMinistry of Higher Education and Scientific Research: Dette Dettemaian sajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Study GuideDocument6 paginiEngineering Study GuideAngel Anne EspinosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineering Is A Discipline Of: There Are Two Ways We Can Produce Electricity From The SunDocument2 paginiMechanical Engineering Is A Discipline Of: There Are Two Ways We Can Produce Electricity From The SunfahnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yas ManDocument6 paginiYas ManJohn WickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature StudyDocument10 paginiLiterature StudyVikrant ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toyta Project File 1Document36 paginiToyta Project File 1MR. GOLDYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineering No ParaphrasingDocument3 paginiMechanical Engineering No ParaphrasingLiliane AlameddineÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Engineering BranchesDocument7 paginiList of Engineering Branchesmep.Încă nu există evaluări
- Engineering and Measuring Systems PDFDocument26 paginiEngineering and Measuring Systems PDFSergioVegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical EngineeringDocument15 paginiMechanical EngineeringKuo MabucchiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Republique Algerienne Democratique Et PopulaireDocument11 paginiRepublique Algerienne Democratique Et Populaireasmaa brkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineering Is An Engineering BranchDocument4 paginiMechanical Engineering Is An Engineering BranchSteven Claude DigamonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 Me ProfessionDocument38 paginiLesson 1 Me Professiontest 2Încă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineers Role in SocietyDocument2 paginiMechanical Engineers Role in SocietyVishaldattÎncă nu există evaluări
- EngineeringDocument1 paginăEngineeringAidil JohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Axiom Rs 5Document1 paginăAxiom Rs 5api-696780392Încă nu există evaluări
- WEEK 7 Introduction To Mechanical EngineeringDocument42 paginiWEEK 7 Introduction To Mechanical EngineeringRahim AssaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nars Characterization of Mechanical Design and Production EngineeringDocument8 paginiNars Characterization of Mechanical Design and Production EngineeringDr_M_SolimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingles 3Document1 paginăIngles 3Alvaro RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch. 1Document3 paginiCh. 1Sandy ShohdyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trends in Mechatronic Engineering and Education: Nnovation Industrial ProgressDocument13 paginiTrends in Mechatronic Engineering and Education: Nnovation Industrial Progressanmol6237Încă nu există evaluări
- The Main Branches of Engineering Выучите словаDocument3 paginiThe Main Branches of Engineering Выучите словаВладимир ЧирковÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why I Should Chose Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 paginiWhy I Should Chose Mechanical EngineeringR S PappuÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Engineering? (Definition and Types)Document14 paginiWhat Is Engineering? (Definition and Types)mshukridÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering - A Way Ahead: Main Branches of EngineeringDocument4 paginiEngineering - A Way Ahead: Main Branches of EngineeringJustin K KurianÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Different Types of Engineering JobsDocument3 pagini6 Different Types of Engineering JobsJames TengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Awards and Honors Questions and Answers PDFDocument11 paginiAwards and Honors Questions and Answers PDFAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- RRB NTPC Post-Wise Job Profile and Description 2022Document1 paginăRRB NTPC Post-Wise Job Profile and Description 2022APLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1 2SC5200 & 2SA1943 Pow AmplifierDocument2 pagini2.1 2SC5200 & 2SA1943 Pow AmplifierAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Padole Driving School - 093259 22170 - AmravatiDocument1 paginăPadole Driving School - 093259 22170 - AmravatiAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arihant SBIPHASE1 Practice Set 1Document10 paginiArihant SBIPHASE1 Practice Set 1Praveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moil Limited: MOIL Bhavan, 1-A, Katol Road, NAGPUR-440 013 Website: WWW - Moil.nic - In, Fax: 0712-2592073, E-MailDocument16 paginiMoil Limited: MOIL Bhavan, 1-A, Katol Road, NAGPUR-440 013 Website: WWW - Moil.nic - In, Fax: 0712-2592073, E-MailAnsuman SatapathyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Set: Clerical Cadre (Pre.) ExamDocument9 paginiPractice Set: Clerical Cadre (Pre.) ExamAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ac Motor Controller For Modern Appliances Using Ls7311: FeaturesDocument3 paginiAc Motor Controller For Modern Appliances Using Ls7311: FeaturesAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- SC 5200 2.1 TDA7265 AmplifierDocument2 paginiSC 5200 2.1 TDA7265 AmplifierAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders LimitedDocument13 paginiMazagon Dock Shipbuilders LimitedMohammed HarunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arihant SBIPHASE1 Practice Set 1Document10 paginiArihant SBIPHASE1 Practice Set 1Praveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sbi Po Exam: Prelims (English) Previous PaperDocument12 paginiSbi Po Exam: Prelims (English) Previous PaperAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adda247 - No. 1 APP For Banking & SSC PreparationDocument6 paginiAdda247 - No. 1 APP For Banking & SSC PreparationAnirudhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ibps RRB Clerk Prelims 2020 Model Paper PDF Set 1Document25 paginiIbps RRB Clerk Prelims 2020 Model Paper PDF Set 1APLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- SBI Clerk Prelims 2020 English LanguageDocument4 paginiSBI Clerk Prelims 2020 English LanguagePATIL POORNA CHANDRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1 Home 2030 PDFDocument5 pagini2.1 Home 2030 PDFSidiq Nur HidayatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1 Home 2030 PDFDocument5 pagini2.1 Home 2030 PDFSidiq Nur HidayatÎncă nu există evaluări
- n the field of biomedical engineering, specifically with biomechanics, transport phenomena, biomechatronics, bionanotechnology, and modelling of biological systems. W16 engine of the Bugatti Veyron. Mechanical engineers design engines, power plants, other machines... ...structures, and vehicles of all sizes. History Education Job duties Subdisciplines Modern tools Areas of research Related fields See also References Further reading External links Last edited 4 days ago by Smenjas Wikipedia Content is available under CC BY-SA 3.0 unless otherwise noted. Terms of UsePrivacyDesktopDocument2 paginin the field of biomedical engineering, specifically with biomechanics, transport phenomena, biomechatronics, bionanotechnology, and modelling of biological systems. W16 engine of the Bugatti Veyron. Mechanical engineers design engines, power plants, other machines... ...structures, and vehicles of all sizes. History Education Job duties Subdisciplines Modern tools Areas of research Related fields See also References Further reading External links Last edited 4 days ago by Smenjas Wikipedia Content is available under CC BY-SA 3.0 unless otherwise noted. Terms of UsePrivacyDesktopAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- MechanicalDocument2 paginiMechanicalAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- HomeDocument4 paginiHomeAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- SC 5200 1943Document2 paginiSC 5200 1943APLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- n the field of biomedical engineering, specifically with biomechanics, transport phenomena, biomechatronics, bionanotechnology, and modelling of biological systems. W16 engine of the Bugatti Veyron. Mechanical engineers design engines, power plants, other machines... ...structures, and vehicles of all sizes. History Education Job duties Subdisciplines Modern tools Areas of research Related fields See also References Further reading External links Last edited 4 days ago by Smenjas Wikipedia Content is available under CC BY-SA 3.0 unless otherwise noted. Terms of UsePrivacyDesktopDocument2 paginin the field of biomedical engineering, specifically with biomechanics, transport phenomena, biomechatronics, bionanotechnology, and modelling of biological systems. W16 engine of the Bugatti Veyron. Mechanical engineers design engines, power plants, other machines... ...structures, and vehicles of all sizes. History Education Job duties Subdisciplines Modern tools Areas of research Related fields See also References Further reading External links Last edited 4 days ago by Smenjas Wikipedia Content is available under CC BY-SA 3.0 unless otherwise noted. Terms of UsePrivacyDesktopAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1 TDA7265 AmplifierDocument1 pagină2.1 TDA7265 AmplifierAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schematic Mono-4558b Sheet-1 20180420211056 PDFDocument1 paginăSchematic Mono-4558b Sheet-1 20180420211056 PDFAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethics in Clinical ResearchDocument3 paginiEthics in Clinical ResearchAPLCTN100% (1)
- Competitive Exams: Capacitors: ExamraceDocument1 paginăCompetitive Exams: Capacitors: ExamraceAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Competitive Exams: Capacitors: ExamraceDocument1 paginăCompetitive Exams: Capacitors: ExamraceAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wiring Diagram Immersion Heaters1Document1 paginăWiring Diagram Immersion Heaters1APLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- TDA2030 Subwoofer PCB BoardDocument1 paginăTDA2030 Subwoofer PCB BoardAPLCTNÎncă nu există evaluări
- SC200 RevDocument2 paginiSC200 RevAshraf MuhtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surface Roughness by Different Processing MethodsDocument1 paginăSurface Roughness by Different Processing Methodsapi-3848892100% (1)
- Voided Biaxial Slabs - State of Art: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental ScienceDocument10 paginiVoided Biaxial Slabs - State of Art: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental ScienceShinde vishalÎncă nu există evaluări
- DriPak - Prod - Mark - SHT - AFP 1 120F NewDocument2 paginiDriPak - Prod - Mark - SHT - AFP 1 120F NewsandroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 Longest Bridges in The WorldDocument15 pagini7 Longest Bridges in The WorldWai Lana ButlerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3G Training Module-07 Nov-15Document50 pagini3G Training Module-07 Nov-15technobrat_guy100% (1)
- CVV CableDocument7 paginiCVV CableNopÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ref Qty Part # Part Description UsageDocument2 paginiRef Qty Part # Part Description UsageJusaNadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planning The Millennium City: The Politics of Place-Making in Gurgaon, IndiaDocument16 paginiPlanning The Millennium City: The Politics of Place-Making in Gurgaon, IndiaParul SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Honda Fit (Jazz) Front Door Panel Removal & Speaker Replacement Guide With Picture Illustrated InstrDocument1 paginăHonda Fit (Jazz) Front Door Panel Removal & Speaker Replacement Guide With Picture Illustrated InstrcamtomleeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atlas Metals HandbookDocument45 paginiAtlas Metals HandbookJim GrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- BrochureDocument4 paginiBrochureChristina MaierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Five Masterworks by Louis Sauer - 9103559 PDFDocument64 paginiFive Masterworks by Louis Sauer - 9103559 PDFAntonello Martinez GianfredaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aker Kvaerner Powergas Pvt. Ltd. Process Department: Checklist CL-PC-0012Document4 paginiAker Kvaerner Powergas Pvt. Ltd. Process Department: Checklist CL-PC-001212mchc07Încă nu există evaluări
- Multipass Ring Oscillator Based Dual Loop PLL For High Frequency SynthesizersDocument7 paginiMultipass Ring Oscillator Based Dual Loop PLL For High Frequency SynthesizersInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vtu HR Project On Employee Job Satisfaction.Document70 paginiVtu HR Project On Employee Job Satisfaction.Naveen Babu DÎncă nu există evaluări
- 70.3 Tanque de Almacenamiento de Productos QuimicosDocument5 pagini70.3 Tanque de Almacenamiento de Productos QuimicosDiana V. RosalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class Flanges Bolt Torque Loads PDFDocument2 paginiClass Flanges Bolt Torque Loads PDFHomer SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAT D9T Status ReportDocument28 paginiCAT D9T Status ReportRoberto BlazquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sikadur®-42 PC: Product Data SheetDocument4 paginiSikadur®-42 PC: Product Data SheetMohammed AwfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ansi-Asa s12.60 Part 1Document46 paginiAnsi-Asa s12.60 Part 1Inriyani DulminÎncă nu există evaluări
- C Library Math.h Functions - GeeksforGeeksDocument11 paginiC Library Math.h Functions - GeeksforGeeksSoumadip Banerjee100% (1)
- E-RAB Abnormal Release Causes: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDDocument14 paginiE-RAB Abnormal Release Causes: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDMShabbar Syed0% (1)
- Airport Practice Note 9 - Wildlife Hazard Management at AirportsDocument96 paginiAirport Practice Note 9 - Wildlife Hazard Management at AirportsexpairtiseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bearing SPM Condition Analyser BVT 111Document2 paginiBearing SPM Condition Analyser BVT 111industrialindiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Utmost TFT Training Part1Document96 paginiUtmost TFT Training Part1gideontargrave7Încă nu există evaluări
- User Acceptance and System Test Checklist Proven Practice v1Document5 paginiUser Acceptance and System Test Checklist Proven Practice v1skeezixxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bill of Materials Computation SheetDocument45 paginiBill of Materials Computation SheetNicole RodilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light, Shadow & ReflectionDocument3 paginiLight, Shadow & ReflectionirfannmsÎncă nu există evaluări