Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Cheat Sheet For Cancer
Încărcat de
Effie Cloe Marie BitengDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Cheat Sheet For Cancer
Încărcat de
Effie Cloe Marie BitengDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
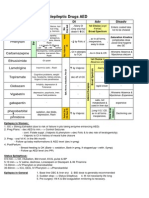
Types of Cancer Risk Factors Screenings/ Diagnostics Treatments
Age Breast self-examination (BSE) Surgery (partial or total
1. Breast Cancer Gender Mammogram mastectomy)
- Ductus Chemotherapy
Family and/or personal history MRI/ NMRI, chest x-ray, ultrasound
carcinoma in
Radiation therapy Thermography Radiation therapy
situ
- Lobular Weight (over weight) Tissue sampling (biopsy) Hormonal therapy
carcinoma in Diet high in fat Blood chemistry Biological/ immunotherapy
situ Lack of exercise Hormonal receptor assay
Alcohol consumption
Smoking
Exposure to estrogen
Use of oral contraceptives
Stress and anxiety
Age Complete blood count Stem cell transplant
2. Cancer of the Genetic Blood protein testing Immunotherapy
Blood:
Smoking Peripheral blood firm Chemotherapy
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma Chemical exposures (eg. Tumor marker test
- Myeloma Benzene) Circulating tumor cell test
Previous use of chemotherapy Bone marrow biopsy
drugs Lymph node biopsy
Radiation exposure CT-scan, MRI, PET scan
Certain blood disorders (eg. X-ray, ultrasound
Polycythemia vera)
Age Comprehensive health history taking Amputation
3. Bone Cancer: Family history, heredity and physical assessment Chemotherapy
- Osteosarcoma X-ray, CT scan, MRI, Bone scan
Previous fragility fracture Radiation therapy
- Chondrasarcoma
Diseases such as Rheumathoid Biopsy (core, surgical and bone Stem cell transplant
- Ewing Sarcoma
arthritis, Paget Disease marrow aspiration) Targeted cell therapy
Bone marrow transplant Cell and tissue studies
Use of metal orthopaedic
device
Radiation exposure
Decrease Ca and Vit. D intake
Chronic infection with HBV or Blood testing (AFP) Surgery
4. Liver Cancer HCV Ultrasound - Surgery to remove
(hepatocellular Cirrhosis tumor
CT scan
sarcoma) - Liver transplant
Certain inherited liver MRI
disease Radiation therapy
Biopsy (Liver tissue)
Diabetes Freezing cancer cells
Non-alcoholic fatty liver (cryoablation)
disease Injecting alcohol into
Exposure to aflotoxins the tumor
Excessive alcohol consumption Injecting chemotherapy
drugs into the liver
Targeted drug therapy
Immunotherapy
Supportive (palliative)
care
Chemotherapy
HPV infection HPV test Chemotherapy
5. Female Immune system deficiency Pap test Radiation therapy
reproductive
Herpes (genital) Visual inspection with acetic acid Targeted therapy
cancers:
- Uterine Cancer Smoking Tumor markers Immunotherapy
- Cervical Age Surgery
cancer Socioeconomic factor - Lymphadenectomy
- Ovarian Cancer Oral contraceptives - TAH BSO
- Hysterectomy
Exposure to
diethylstilbestrol (DES)
Age and gender (older male Cryotherapy Chemotherapy
6. Male reproductive 60-80 years old Fluoroal Radiation therapy
cancers: Undescended testes Imuguimoid Immunotherapy
- Penile Cancer
- Testicular Poor hygiene Inguinal lymphadenectomy Targeted cell therapy
cancer HPV Penectomy Surgery
- Prostate - Penectomy
Tobacco use
cancer
Over or underuse Inguinal lymphadenectomy
Uncircumcised
Older age Blood tests Interventional therapy
7. Colon cancer Race (African-american) Colonoscopy Gene targeted therapy
- Colorectal
Personal history of CT scan Green chemotherapy
cancer
colorectal cancer or polyps Sigmoidoscopy TCM and western medicine
Inflammatory intestinal Fecal Immunochemical test Radiotherapy
conditions High sensitivity fecal occult Chemotherapy
Family history blood test Surgical
Low-fiber, high-fat diet DNA stool test
Sedentary lifestyle
Genetics Neurologic examination Chemotherapy
8. Brain cancer: Male MRI, CT scan, PET scan Radiation therapy
- Glioma
History of cancer Immunotherapy
- Non-glioma
Head injury Targeted cell therapy
Exposure to cardiogenic agents Surgery
- Craniotomy
Smoking X-ray, CT scan Surgery
9. Lung cancer Exposure to secondhand and Sputum cytology - Wedge resection
thirdhand smoke Tissue sampling (biopsy) - Segmental resection
Exposure to radon gas - Lobectomy
- Pneumonectomy
Exposure to asbestos and
other carcinogens Radiation therapy
Family history of lung cancer Chemotherapy
Radiosurgery
Targeted drug therapy
Immunotherapy
Palliative care
References:
Breastcancer.Org (2019). “Breast Cancer Risk Factors”. Retrieved from: www.breastcancer.org/symptoms/understand_bc/risk/factors
Breast Cancer Institute (2019). “Breast Cancer Screening”. Retrieved from: www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/breast-screening-pdq
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2018). “How breast cancer is treated”. Retrieved from: www.cdc.gov/cancer/breast/basic-
info/treatment.html
Indus Health plus (2018). “Blood Cancer: Causes and Risk Factors”. Retrieved from: www.indushealthplus.com/blood-cancer-causes-risk-
factors.html
Mayoclinic (2017). “Cancer blood tests: Lab tests used in cancer diagnosis”. Retrieved from: www.mayoclinic.org/disease-conditions/cancer-
diagnosis/art-20046459
Mayoclinic (2018). “Liver Cancer”. Retrieved from: www.mayoclinic.org/disease-condition/liver-cancer/diagnosis.html
Cancer.net (2018). “Cervical Cancer: Screening and Prevention”. Retrieved from: www.cancer.net/cancer-types/cervical-cancer/screening.html
Colon Cancer Coalition (2019). “Colon Cancer”. Retrieved from: https://coloncancercoalition.org/get-educated/get-screened/colon-cancer/
Mayoclinic (2019). “Lung Cancer”. Retrieved from:mayoclinic.org/disease-condition/lung-cancer/
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- AntimicrobialsDocument1 paginăAntimicrobialsRomaine Barrett100% (1)
- Uti Treatment PlanDocument3 paginiUti Treatment PlanbeatriceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotic Classification: Generic Name Brand Names Common UsesDocument5 paginiAntibiotic Classification: Generic Name Brand Names Common Usesade_lubu100% (1)
- Penicinillase - Sensible: Inhibit Clasification AntibioticsDocument1 paginăPenicinillase - Sensible: Inhibit Clasification AntibioticsАндрій ДанильцівÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug ChartDocument8 paginiDrug Chartstudentalwaysstudy100% (1)
- Cancer Drugs Drugs Indication Adverse Effects Interaction and ContraindicationDocument5 paginiCancer Drugs Drugs Indication Adverse Effects Interaction and ContraindicationOndari gisemba OSINDEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Care for Anorexia Nervosa: The MARSIPAN Guidelines in PracticeDe la EverandCritical Care for Anorexia Nervosa: The MARSIPAN Guidelines in PracticeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abx FinalDocument3 paginiAbx Finalyanks1120Încă nu există evaluări
- Pharm C Exam 10 Drug ListDocument2 paginiPharm C Exam 10 Drug ListVokdadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCOL Maps PDFDocument11 paginiPCOL Maps PDFZinc YuloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotic GuideDocument6 paginiAntibiotic GuideAnnTran100% (1)
- Acromegaly, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandAcromegaly, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology Dr. Scott PDFDocument90 paginiPharmacology Dr. Scott PDFSingey LhendupÎncă nu există evaluări
- AntibioticsDocument2 paginiAntibioticsPGI Custodio, Ed KristianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE AdvDocument1 paginăAntiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE Advrayooona88Încă nu există evaluări
- 3 Treatment of HypertensionDocument7 pagini3 Treatment of HypertensiontiaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimal Life: Essentials of AsthmaDe la EverandOptimal Life: Essentials of AsthmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartDocument6 paginiMicrobiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartM Patel100% (1)
- Antibiotic ClassificationDocument29 paginiAntibiotic ClassificationDr Sumant Sharma100% (1)
- Cancer DrugsDocument5 paginiCancer DrugsLinh HoangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotics Chart 1Document7 paginiAntibiotics Chart 1Vee MendÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Guide and Charts: AlbuminDocument16 paginiRenal Guide and Charts: AlbuminYaima JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inu's Super Step 1 Summary - GuideDocument9 paginiInu's Super Step 1 Summary - GuidedeductionisthekeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prefix, Suffix of DrugsDocument6 paginiPrefix, Suffix of DrugsBriel Jake CabusasÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Aid Pharmacology AntimicrobialsDocument23 paginiFirst Aid Pharmacology AntimicrobialsLaura Lopez RocaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunopharmacology: GlucocorticoidsDocument9 paginiImmunopharmacology: GlucocorticoidsCas BuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology Medical Suffixes Cheat SheetDocument1 paginăPharmacology Medical Suffixes Cheat SheetPattyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedia Stickers PDFDocument8 paginiPedia Stickers PDFAshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, InteractionsDocument6 paginiHmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, Interactionswaste78Încă nu există evaluări
- Pharm TableDocument35 paginiPharm TableHannah BaldwinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Document48 paginiNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharma MnemonicsDocument10 paginiPharma MnemonicsMuhammad Ali Aziz100% (4)
- Pharmacology Drug ChartDocument50 paginiPharmacology Drug ChartEssentialForLivingÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnxietyDocument5 paginiAnxietyJohn HolmesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antimicrobial Drugs TableDocument19 paginiAntimicrobial Drugs TableLaylee ClareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gout DrugsDocument1 paginăGout DrugsMichael BrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generic Name Brand Names Common Uses Possible Side Effects Mechanism of ActionDocument13 paginiGeneric Name Brand Names Common Uses Possible Side Effects Mechanism of Actionangel3424Încă nu există evaluări
- UWorld - Psych Review Charts (From Questions)Document47 paginiUWorld - Psych Review Charts (From Questions)uowhywxuuiragjadchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharma CollectionDocument40 paginiPharma CollectionMuhd Nico DariyantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prefix Suffix MnemonicsDocument5 paginiPrefix Suffix MnemonicsPj MontecilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- AntibioticsDocument6 paginiAntibioticsManzoor AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beta Lactam AntibioticsDocument1 paginăBeta Lactam AntibioticsCourtney TownsendÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Physiology and Pharmacology: The EssentialsDe la EverandClinical Physiology and Pharmacology: The EssentialsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Complete Drug GuideDocument225 paginiComplete Drug GuideJessica 'Baker' IsaacsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thyroid DiseaseDocument1 paginăThyroid DiseaseZiyadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psycho PharmaDocument8 paginiPsycho PharmaMark JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug TerminologyDocument5 paginiDrug Terminologyimdaking123Încă nu există evaluări
- AntiemeticsDocument25 paginiAntiemeticsPridho GaziansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDe la EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Simple Guide to Hyperaldosteronism, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDe la EverandA Simple Guide to Hyperaldosteronism, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview of by Mechanism 2Document16 paginiOverview of by Mechanism 2daven100% (1)
- Classification of Drugs PDFDocument15 paginiClassification of Drugs PDFmuhammad ihtisham ul hassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Different Body Receptors PDFDocument1 paginăDifferent Body Receptors PDFSantosh patelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultimate Pharm GuideDocument41 paginiUltimate Pharm GuideeanguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mu 002Document10 paginiMu 002chandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Medium Thyroid Healing TestimonialsDocument15 paginiMedical Medium Thyroid Healing TestimonialsGeri SulanjakuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ovarian CancerDocument1 paginăOvarian CancerMicheleFontanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CMS 2013 Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS) Claims/Registry Measure Specifications ManualDocument637 paginiCMS 2013 Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS) Claims/Registry Measure Specifications ManualHLMeditÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept Map Leukemia PDFDocument7 paginiConcept Map Leukemia PDFMichael AmandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord TumorsDocument7 paginiSpinal Cord TumorsVALERIA TEJEDA SANCHEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brain Cancer Concept MapDocument3 paginiBrain Cancer Concept MapIced Coffee100% (4)
- Syllabus For BPKMCH NEPALDocument7 paginiSyllabus For BPKMCH NEPALDeep SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCRT Cervix2Document27 paginiCCRT Cervix2Marfu'ah Nik EezamuddeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- TNMC CreditDocument7 paginiTNMC CreditSathyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CANCER - LEUKEMIA - Edgar Cayce (PDFDrive)Document115 paginiCANCER - LEUKEMIA - Edgar Cayce (PDFDrive)Solve WalterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uterine SarcomaDocument44 paginiUterine SarcomajojolilimomoÎncă nu există evaluări
- India As "The Oral Cancer Capital of The World": The Rising Burden of Oral Malignancies Across The NationDocument9 paginiIndia As "The Oral Cancer Capital of The World": The Rising Burden of Oral Malignancies Across The NationHindol DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Life Without ComputersDocument14 paginiLife Without Computersapi-488738864Încă nu există evaluări
- Camp Lejeune Water Contamination LawyersDocument7 paginiCamp Lejeune Water Contamination LawyersCamp Lejeune Water ActÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEDSURG - Cellular AberrationDocument10 paginiMEDSURG - Cellular AberrationLeslie CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14 Meron Mehari Kifle 2016 Knowledge and Practice of Breast Self Examination Among Female College Students in EritreaDocument6 pagini14 Meron Mehari Kifle 2016 Knowledge and Practice of Breast Self Examination Among Female College Students in EritreaArick Frendi AndriyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Natural Dyes - Alternative For Synthetic DyesDocument7 paginiNatural Dyes - Alternative For Synthetic DyesviswaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr.I.Selvaraj, I.R.M.S: B.SC., M.B.B.S., (M.D, Community Medicine) ., D.P.H.,D.I.H.,PGCH&FW (NIHFW, New Delhi)Document61 paginiDr.I.Selvaraj, I.R.M.S: B.SC., M.B.B.S., (M.D, Community Medicine) ., D.P.H.,D.I.H.,PGCH&FW (NIHFW, New Delhi)Mushtaq MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- 800 +MCQs-ONLY SUCCESS MRCS-A (UPDATED)Document378 pagini800 +MCQs-ONLY SUCCESS MRCS-A (UPDATED)DrTawfik Shabaka100% (1)
- 8 - Cancer - ManagementDocument90 pagini8 - Cancer - ManagementMaviel Maratas SarsabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DMCH PresentationDocument40 paginiDMCH PresentationshuaibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ito Et - Al.pubDocument6 paginiIto Et - Al.pubKamado NezukoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functional Foods and Their Role in Cancer Prevention and Health PromotionDocument30 paginiFunctional Foods and Their Role in Cancer Prevention and Health PromotionSílfide XanatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Investigatory Project: Study On CancerDocument24 paginiBiology Investigatory Project: Study On CancerAthiya Zainab100% (1)
- Determining The Expected Competencies For OncologyDocument5 paginiDetermining The Expected Competencies For OncologyNaghib BogereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health and Wellness Women HealthDocument24 paginiHealth and Wellness Women HealthShimmering MoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPC JanuariDocument25 paginiCPC JanuariMika KresnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lewis CH 42 GIDocument13 paginiLewis CH 42 GIwismommyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tema e Diplomes Kanceri GastrikDocument35 paginiTema e Diplomes Kanceri GastrikDorisa BahjaÎncă nu există evaluări