Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Blaise Pascal Lab
Încărcat de
sadaf jamadarDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Blaise Pascal Lab
Încărcat de
sadaf jamadarDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Survey on Blaise Pascal Lab
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
Networking is such a broad and complex field, no single event represents its point of
origin. We can think of the 1960's as a curly period, however because that's when the
digital computer began to significantly affect the lives of ordinary individuals and the
operations of businesses and governments.
Networks in the 60’s were the beginning era of the computer networks. Networks in the
70's was early development of computer networks and the Ethernet technology and the
networks in the 80's was Computer networks for everyone and Standardization of
Ethernet.
1.1 What Is Network?
A Network is an interconnection of autonomous computers, as shown in Fig 1.1. Two
computers are said to be inter connected if they are capable of exchanging the
information. No computers on the network can start, stop or control another.
Fig 1.1 Client Server Network
Department Of ISE, KLEIT, Hubballi Page |4
Survey on Blaise Pascal Lab
1.2 Network Goals
1. Resource Sharing: The aim is to make all the programs, data and peripherals available
to any one on the network irrespective of the physical location of the resources and the
user.
2. Reliability: A file can have copies on two or three different machines, so if one of
them is unavailable, the other copies could be used.
3. Cost Factor: Personal computers have better price/performance ratio than
microcomputers.
Department Of ISE, KLEIT, Hubballi Page |5
Survey on Blaise Pascal Lab
CHAPTER 2
LABORATORYSURVEY AND LITERATURE SURVEY
In this chapter we discuss literature and laboratory survey with respect to computer
networks.
2.1. Laboratory Survey
The information obtained after surveying BLAISE PASCAL LAB as follows:
Table 2.1 Blaise Pascal Specification
1. NUMBER OF SYSTEMS 30
2. SYSTEM SPECIFICATIONS
(HP PRO3090)
PROCESSOR INTEL R DUAL CORE I3@2.7GHZ.
MEMORY 8GB RAM.
HARD DRIVE 500GB 720RPM
CHIP SET INTEL
MONITOR HP
TOPOLOGY STAR TOPOLOGY
3. OTHER ACCESSORIES
PROJECTOR DETACHABLE PROJECTOR
UPS EMERSONNETWORKPOWER(6KVA)
PRINTER HP
4.SOFTWARES
SYSTEM WINDOWS-10 64 BIT
APPLICATION DOS BOX,XAMP,ECLIPSE,UBUNTU
Department Of ISE, KLEIT, Hubballi Page |6
Survey on Blaise Pascal Lab
5. NETWORKING
LAN
WITHIGBPS/UNMANAGED
SWITCH-24 PORT-2 NO
6. INTERNET
BROAD BAND LINE WITH 1 CONTENTION RATIO
100MBPS
7.CABELS CAT 6 HP SWITCHED
8.ISP BSNL
Fig.2.1. Computers in lab
1. There are 30 computers in the laboratory.
2. Figure 2.1 shows the systematic set up of the computers in the lab.
3. Star topology is adopted for connecting all individual nodes to central connection
point like hub or switch.
4. The carpet area of the lab is 100 square meters.
Department Of ISE, KLEIT, Hubballi Page |7
Survey on Blaise Pascal Lab
5. The type of network that is followed for connection is LAN (Local Area
Network) with 1 Gbps / Unmanaged switch -24 Port -2 no.
6. The network of computers in lab is further connected to CS Server room(ISP)
which is further connected to EC Server room.
7. The power cable which is black in colour is connected to the monitor and the
LAN CABLE which is white in colour is connected to AMP JUNCTION BOX.
This configuration is same for all the 30 computers.
8. Fig 2.2 shows cable configuration in Blaise Pascal lab and Fig 2.3 shows the main
switch used in the lab.
Fig 2.2 The Cable Configuration
Fig 2.3: Switch used in the laboratory
Department Of ISE, KLEIT, Hubballi Page |8
Survey on Blaise Pascal Lab
2.2 LITERATURE SURVEY
2.2.1 SERVER
A server is a computer that provides data to other computers. It may serve data to systems
on a local area network (LAN) or wild arcs network (WAN) over the internet. Many types
of server exists, including web server mail server and file server. Each type runs software
specific to the purpose of the server. Fig 2.4 shows the campus network of our college.
Fig 2.4 Network infrastructure in our college
2.3 INTERCOM SERVER
Ultimate availability and security.
The communication solution integrates smoothly with existing IT infrastructures.
Physical separation of IT and communication server.
Compact all in one package including Fumrsu hardware and VIRTUOSIS
intercom server software.
Provides full range of VIRTUOSIS functions flexible licensing scheme for
VIRTUOSIS intercom server software.
Optimize for rack installation.
Copy protection without key subscriber or dongle based on 'PM 1.2.
Extremely low operating cost thanks to high energy efficiency.
Department Of ISE, KLEIT, Hubballi Page |9
Survey on Blaise Pascal Lab
2.4 CISCO ROUTERS
Cisco routers switches and modems arc one of the most well-known devices of its kind.
The Cisco 2100 modem's 121-45 port is connected to WAN port of your router. The
Cisco 2100 modem's default IP is 10.2.0.1. No this will not be used in your router settings
but just as reference.
Fig. 2.5 Cisco router
Router IP Address
Usually the default IP of your router is one of these: 192.168.0.1,192.168.1.1 or
192.1682.1 or similar to that of the modem.
How To Access Router's Web Interface?
You can access router's configuration by typing-in your router's IP address bar of a web
browser. Login using appropriate user name and password.
Configuring Your Router
The only thing you need to configure is the LAN settings of your router. Change it to
10.2.1.1 so that it will not get conflict with the CISCO 2100cabel modem. Also change
the subnet mask to 255.255.255.0.
Department Of ISE, KLEIT, Hubballi P a g e | 10
Survey on Blaise Pascal Lab
2.5 BATON SWITCHING
8 PORT 10/100M UNMANAGED SWITCH
Compiles with IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.3u standards.
8 10/100mbps auto-negotiation RJ45 ports, supporting auto MDI/MDIX
Green technology.
Easy plug and play.
It does not supply power when there is no power in link.
11 auto-adjust the power over cable according to its length supports IEEE 802.3x
flow, control for full duplex mode and acknowledge pressure for half duplex
mode.
1.6Gbps switching capacity.
Non-blocking switching architecture that forwards and filters packets at full speed
for maximum throughput.
Supports MAC address auto-learning and auto-aging.
Store and forward switching method.
2.6 NETWORK DEVICES
1. MODEM : MODEM allows you to combine the power of your computer with the
global reach of the telephone system. A modem changes the digital data from your
computer into data, a format that can be carried by telephone lines.
Fig 2.6 Modem
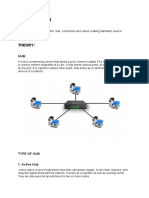
2. HUB : HUB is a hardware device used to connect several computers together. A hub
thatcontains multiple independent but connected modules of network and inter
networkedequipment.
Department Of ISE, KLEIT, Hubballi P a g e | 11
Survey on Blaise Pascal Lab
3. SWITCH : A switch is a device that is used to segment networks into different sub-
networks called subnets or LAN segments. A switch is responsible for filtering i.e.
transforming data in a specific way and for forwarding packets between the LAN
segments.
Fig 2.7 Hub and Switch
How A Switch Functions?
The switch establishes a temporary connections between the source and the destination
and the terminates the connection once the conversation is done.
4. ROUTER : A device that works like a bridge but can handle different protocols is
known as router. If the destination is unknown to a router it sends the traffic to another
router which knows the destination.
Fig 2.8 Router
Department Of ISE, KLEIT, Hubballi P a g e | 12
Survey on Blaise Pascal Lab
2.7 NETWORK TOPOLOGY
A network topology is the arrangement of a network, including its nodes and connecting
lines. There are two ways of defining network geometry: the physical topology and the
logical (or signal) topology.
The different types of Network Topology are: Bus topology, Star topology, Ring
Topology, Mesh Topology and Tree Topology.
In the bus network topology fig 2.9, every workstation is connected to a main
cable called the bus. Therefore, in effect, each workstation is directly connected to every
other workstation in the network.
Fig 2.9 Bus Topology
In the star network topology fig 2.10, there is a central computer or server to
which all the workstations are directly connected. Every workstation is indirectly
connected to every other through the central computer.
Fig 2.10 Star Topology
In the ring network topology fig 2.11, the workstations are connected in a closed
loop configuration. Adjacent pairs of workstations are directly connected. Other pairs of
Department Of ISE, KLEIT, Hubballi P a g e | 13
Survey on Blaise Pascal Lab
workstations are indirectly connected, the data passing through one or more intermediate
nodes.
Fig 2.11 Ring Topology
The mesh network topology fig 2.12, employs either of two schemes called full
mesh and partial mesh. In the full mesh topology, each workstation is connected directly
to each of the others. In the partial mesh topology, some workstations are connected to all
the others and some are connected only to those other nodes with which they exchange
the most data.
Fig 2.12 Mesh Topology
Department Of ISE, KLEIT, Hubballi P a g e | 14
Survey on Blaise Pascal Lab
The tree network topology fig 2.13, uses two or more star networks connected
together. The central computers of the star networks are connected to a main bus. Thus, a
tree network is a bus network of star networks.
Fig 2.13 Tree Topology
Department Of ISE, KLEIT, Hubballi P a g e | 15
Survey on Blaise Pascal Lab
CONCLUSION
By this survey of Blaise pascal networking lab, we know the different types of network
topologies, their working and connections made from server to different computers in the
lab. It also describes the network broadband connections used in the lab. This survey has
also helped us to understand the different cables used in overall network connections.
Department Of ISE, KLEIT, Hubballi P a g e | 16
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Ccna PDFDocument20 paginiCcna PDFhimanshu kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To The Lab: Ceng/Bilm 362 Computer Networks Lab ManualDocument26 paginiIntroduction To The Lab: Ceng/Bilm 362 Computer Networks Lab ManualAvinash Cool BuddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Lab FileDocument4 paginiSample Lab FileAdarsh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Science & Engineering: KCT College of Engg and Tech. Village Fatehgarh Distt - SangrurDocument19 paginiComputer Science & Engineering: KCT College of Engg and Tech. Village Fatehgarh Distt - SangrurAmitabh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE521FL - Activity 7Document17 paginiECE521FL - Activity 7SM Mecreg0% (1)
- 2 Lab Manual 2 CNDocument5 pagini2 Lab Manual 2 CN70131127Încă nu există evaluări
- Open-Source Robotics and Process Control Cookbook: Designing and Building Robust, Dependable Real-time SystemsDe la EverandOpen-Source Robotics and Process Control Cookbook: Designing and Building Robust, Dependable Real-time SystemsEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- Install Network CablesDocument17 paginiInstall Network CablesPEAC RELATEDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yaun - PRELIM EXAMINATION IS 213-3Document10 paginiYaun - PRELIM EXAMINATION IS 213-3Michiko YaunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session 2 Network ToolsDocument14 paginiSession 2 Network ToolsMary Ann BarcelonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dcomm Lab1Document6 paginiDcomm Lab1Ismail SheikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data and Com AnswersDocument2 paginiData and Com AnswersRicky FrankÎncă nu există evaluări
- G12 Q2 Activity Sheets 1Document7 paginiG12 Q2 Activity Sheets 1Rose Anne Patrimonio0% (1)
- Basic Networking Hardware: Kamal Harmoni Kamal AriffDocument22 paginiBasic Networking Hardware: Kamal Harmoni Kamal Ariffismail333100% (2)
- Assignmen T Computer Security: Name: Alian Khan Roll No: 08 Department: CISDocument7 paginiAssignmen T Computer Security: Name: Alian Khan Roll No: 08 Department: CISjohn kevinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIS - 07 - Alian KhanDocument7 paginiCIS - 07 - Alian Khanjohn kevinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Essentials Fundamentals of NetworkingDocument11 paginiNetwork Essentials Fundamentals of Networkingneeraj kumar singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- CN Manual RemovedDocument76 paginiCN Manual Removedsanikalohar2018Încă nu există evaluări
- FINALREQ Group02..Document7 paginiFINALREQ Group02..NOEL GALLOÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCN Project 19ET7039Document6 paginiCCN Project 19ET7039Akanksha BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- CN Lab ManualDocument42 paginiCN Lab ManualRuthvika BhimavarapuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.0 NetworkDocument24 pagini2.0 NetworkChinta QaishyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CN LAB EXP 1 Tushar SharmaDocument3 paginiCN LAB EXP 1 Tushar Sharmaayush sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Working of Hub, Switch and Router.Document11 paginiWorking of Hub, Switch and Router.NISHANT RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- UMUC Case Study SolutionDocument10 paginiUMUC Case Study SolutionShivaani AggarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nos AssignmentDocument16 paginiNos AssignmentSahilÎncă nu există evaluări
- NetworkingDocument25 paginiNetworkingPrajwal DahalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adhoc Mobile Wireless Network Enhancement Based On Cisco DevicesDocument7 paginiAdhoc Mobile Wireless Network Enhancement Based On Cisco DeviceslakhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 5Document9 paginiLesson 5Kean Rafael MarianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Network UNIT-1Document22 paginiComputer Network UNIT-1bhumsi7890Încă nu există evaluări
- CN Lab Manual - 230327 - 200335Document26 paginiCN Lab Manual - 230327 - 200335Rishubh GandhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Communication and Computer Networking Lab ManualDocument66 paginiDigital Communication and Computer Networking Lab ManualJoey TribianniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 Network Hardware EssentialsDocument38 pagini02 Network Hardware EssentialsCheryl Marie AlimbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ijatcse 38862019Document5 paginiIjatcse 38862019ClementÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 07Document44 paginiCH 07Varun SrinivasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Exam Fall2010Document5 paginiFinal Exam Fall2010DJSynÎncă nu există evaluări
- DCCN Project FNL 5Document8 paginiDCCN Project FNL 5Pratik SahuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab MannualDocument30 paginiLab MannualRahul SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- ITC LAB 3 - NetworkingDocument10 paginiITC LAB 3 - NetworkingpathwayÎncă nu există evaluări
- CNE Tutorial 02 - LAN Configuration With DHCPDocument7 paginiCNE Tutorial 02 - LAN Configuration With DHCPXuân Dương VươngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Software Defined Networking, A Comparison With The Legacy NetworkDocument9 paginiSoftware Defined Networking, A Comparison With The Legacy NetworkTalha ÜnalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Planning and Cabling NetworksDocument35 pagini10 Planning and Cabling NetworksErangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cnprac 1Document28 paginiCnprac 1dhimmar464Încă nu există evaluări
- Intranet Design-SampleDocument8 paginiIntranet Design-Sampleamritsapkota77335500Încă nu există evaluări
- Hub Bridge Switch Router Assignment - Computer NetworkDocument12 paginiHub Bridge Switch Router Assignment - Computer Networkyabaidullah100% (1)
- CNS Practical 3Document9 paginiCNS Practical 3How to download AnythingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Exercise 01 LABDocument7 paginiLab Exercise 01 LABFareen BaigÎncă nu există evaluări
- 61FIT2CNE Tutorial 02 - LAN ConfigurationDocument7 pagini61FIT2CNE Tutorial 02 - LAN ConfigurationThùy DươngÎncă nu există evaluări
- V2i10 0038Document11 paginiV2i10 0038PratyushÎncă nu există evaluări
- CN FileDocument32 paginiCN Filehkaushik467Încă nu există evaluări
- RPL Thesis ch2Document13 paginiRPL Thesis ch2Alex AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 1Document15 paginiLab 1George RybkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 12 - COMPUTER NETWORKS - NotesDocument24 paginiClass 12 - COMPUTER NETWORKS - NotesAyushi KapoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Master'S Thesis: Simulator-Controlled Real-World Experiments in Multihop Wireless Mesh NetworksDocument62 paginiMaster'S Thesis: Simulator-Controlled Real-World Experiments in Multihop Wireless Mesh Networksramkumarit88Încă nu există evaluări
- Network Advanced - NewDocument88 paginiNetwork Advanced - Newai ikhsan2Încă nu există evaluări
- DCN Manual 2019Document73 paginiDCN Manual 2019Suhani SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Networking Finalreport Without Table of ContentDocument46 paginiNetworking Finalreport Without Table of Contentarbeen.tmzÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCSE2052 - Lab Manual - StudentVerDocument63 paginiBCSE2052 - Lab Manual - StudentVerAniket SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter No - 1: 1.1 Introduction To The ProjectDocument63 paginiChapter No - 1: 1.1 Introduction To The ProjectAkwinderKaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNADocument825 paginiCCNAGirma100% (2)
- HD 4129 Data SheetDocument2 paginiHD 4129 Data SheetIngenieria GeomexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge Primary English 4 Activity Book TOAZ - Info 2Document1 paginăCambridge Primary English 4 Activity Book TOAZ - Info 2Wafaa M. AbdAlkhaliqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 - Internet of Things - WWW - Rgpvnotes.in PDFDocument9 paginiUnit 2 - Internet of Things - WWW - Rgpvnotes.in PDFAmarjeet Singh RajputÎncă nu există evaluări
- ITN ERP Connector For Pentaho Data Integration v4Document6 paginiITN ERP Connector For Pentaho Data Integration v4Daniel PaniaguaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embedded Systems Assignment 3Document6 paginiEmbedded Systems Assignment 3ramrevolt55Încă nu există evaluări
- Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA) User Manual How To Add Dewa Marafeq Smart Services in Cad ApplicationsDocument65 paginiDubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA) User Manual How To Add Dewa Marafeq Smart Services in Cad ApplicationsON ROADING CONTRACTING LLCÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2511 Q Winter 2014 Wednesday John Kucharczuk Rev Course OutlineDocument8 pagini2511 Q Winter 2014 Wednesday John Kucharczuk Rev Course OutlineJack DenialsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oyo Business-AnalystDocument2 paginiOyo Business-AnalystHarshÎncă nu există evaluări
- PAVIRO Factory Default System: Application NoteDocument5 paginiPAVIRO Factory Default System: Application NoteMajid MehmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- USE Only: Aruba Networks, A Hewlett Packard Enterprise CompanyDocument35 paginiUSE Only: Aruba Networks, A Hewlett Packard Enterprise CompanyLaith ZuraiqiÎncă nu există evaluări
- WsCube Tech Online MERN Stack CourseDocument24 paginiWsCube Tech Online MERN Stack CourseSnehaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Information DIGSI5 V06.20Document48 paginiProduct Information DIGSI5 V06.20feromagnetizamÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Simple MakefileDocument14 paginiA Simple Makefilekantha_hnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low Power Vlsi Design: Architecture Optimizations/SynthesisDocument13 paginiLow Power Vlsi Design: Architecture Optimizations/SynthesisSanthoshReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Release Notes - BUSY 18: DisclaimerDocument8 paginiRelease Notes - BUSY 18: Disclaimerjatin guptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab GUI Tutorial - Basic Data Processing Tool: Quan QuachDocument43 paginiMatlab GUI Tutorial - Basic Data Processing Tool: Quan QuachAgung WicaksonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Evolution of Cybersecurity - Secure Mail Gateway QuizDocument2 paginiThe Evolution of Cybersecurity - Secure Mail Gateway Quizchhun25% (4)
- Cat 2 Question Bank With All Part PDFDocument32 paginiCat 2 Question Bank With All Part PDFJJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test & Data Management Software: The Integrated Testing SolutionDocument12 paginiTest & Data Management Software: The Integrated Testing SolutionAristides AnselmoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obstacle Avoidance Robot Using Ultrasonic Sensors - FPGAVHDLDocument18 paginiObstacle Avoidance Robot Using Ultrasonic Sensors - FPGAVHDLDipak Bhogulkar100% (1)
- LPC1779 User ManualDocument849 paginiLPC1779 User ManualMartinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compiler Construction Principles and Practice K C LoudenDocument19 paginiCompiler Construction Principles and Practice K C LoudenSrijan ApurvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite NetworkDocument29 paginiSatellite NetworkChaitanya VanarseÎncă nu există evaluări
- CanBus UpdateMainControllerand DisplayDocument51 paginiCanBus UpdateMainControllerand DisplayBoran CarmonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-3 ER ModelDocument12 paginiChapter-3 ER ModelHala GharibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution Manager 7.1 SP5 Outside Discovery TroubleshootingDocument28 paginiSolution Manager 7.1 SP5 Outside Discovery TroubleshootingPaul Crauwels100% (1)
- Data Warehousing and Business IntelligenceDocument390 paginiData Warehousing and Business IntelligenceSamirkÎncă nu există evaluări
- OpenScape 4000 CSTA and Phone Services - Installation GuideDocument122 paginiOpenScape 4000 CSTA and Phone Services - Installation GuideWilliam TshimangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Introduction To Microcontroller and BioelectronicsDocument15 paginiCourse Introduction To Microcontroller and BioelectronicssampotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Log Review Checklist For Security Incidents PDFDocument1 paginăCritical Log Review Checklist For Security Incidents PDFviny2010Încă nu există evaluări