Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
PROBABILITY
Încărcat de
Pratyush PatilDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
PROBABILITY
Încărcat de
Pratyush PatilDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
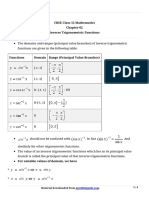
CBSE
Class 12 Mathematics
Chapter-13
Probability
Sample Space: The set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment. It is denoted
by the symbol S.
Sample points: Elements of the sample space.
Event: A subset of the sample space.
Impossible Event: The empty set.
Sure Event: The whole sample space.
Complementary event or "not event": The set "S" or S - A.
The event A or B: The set A B.
The event A and B: The set A B.
The event A but not B: A - B.
Mutually exclusive events: A and B are mutually exclusive if A B = .
Exhaustive and Mutually exclusive events: Events E1, E2,........, En are mutually
exclusive and exhaustive if E1 E2 ....... En = S and Ei Ej = for all .
Exiomatic approach to probability: To assign probabilities to various events, some
axioms or rules have been described.
Let S be the sample space of a random experiment. The probability P is a real values function
whose domain is the power set of S and range is the interval [0, 1] satisfying the following
axioms:
(a) For any event E, P(E) 0
(b) P(S) = 1
(c) If E and F are mutually exclusive event, then P(E F) = P(E) + P(F)
If E1, E2, E3............ are n mutually exclusive events, then
Probability of an event in terms of the probabilities of the same points
(outcomes): Let S be the sample space containing n exhaustive outcomes
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 1 / 4
i.e., S =
Now from the axiomatic definition of the probability:
(a) 0 P(Wi) 1, for each .
(b) P(W1) + P(W2) + .......+ P(W3) = P(S) = 1
(c) For any event A, P(A) =
Equally likely outcomes: All outcomes with equal probability.
Classical definition of the probability of an event: For a finite sample space with
equally likely outcome, probability of an event A.
P(A) =
where = Number of elements in the set A. and = Number of elements in set S.
If A is any event, then P(not A) = 1 - P(A)
The conditional probability of an event E, given the occurrence of the event F is given
by
Theorem of total probability:
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 2 / 4
be a partition of a sample space and suppose that each of
has non zero probability. Let A be any event associated with S, then
Bayes' theorem: If are events which constitute a partition of sample
space S, i.e. are pairwise disjoint and
be any event with non-zero probability, then,
Random variable: A random variable is a real valued function whose domain is the
sample space of a random experiment.
Probability distribution: The probability distribution of a random variable X is the
system of numbers
Where,
Mean of a probability distribution: Let X be a random variable whose possible
values occur with probabilities respectively.
The mean of X, denoted by is the number . The mean of a random variable
X is also called the expectation of X, denoted by E (X).
Variance: Let X be a random variable whose possible values occur
with probabilities respectively. Let be the
mean of X. The variance of X, denoted by Var (X) or is defined as
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 3 / 4
or equivalently . The non-
negative number, is called the standard
deviation of the random variable X.
Bernoulli Trials: Trials of a random experiment are called Bernoulli trials, if they
satisfy the following conditions:
(i) There should be a finite number of trials.
(ii) The trials should be independent.
(iii) Each trial has exactly two outcomes: success or failure.
(iv) The probability of success remains the same in each trial.
For Binomial distribution
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 4 / 4
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Acr-Rpms TrainingDocument4 paginiAcr-Rpms TrainingHardy MisagalÎncă nu există evaluări
- BBA Lecture NotesDocument36 paginiBBA Lecture NotesSaqib HanifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aashto T90Document4 paginiAashto T90Katherine Quintero Ortíz100% (1)
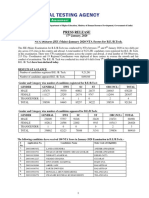
- Press Relese Result (English) 1579313942Document3 paginiPress Relese Result (English) 1579313942Pratyush PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 Maths Key Notes CH 11 Three Dimensional GeometryDocument4 pagini12 Maths Key Notes CH 11 Three Dimensional GeometryYUGESH SINGARAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 Maths Key Notes CH 10 Vector AlgebraDocument2 pagini12 Maths Key Notes CH 10 Vector AlgebraRahuz CraftzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inverse Trigo PDFDocument4 paginiInverse Trigo PDFPratyush PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- DETERMINANTDocument3 paginiDETERMINANTPratyush PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determinant and OtherDocument9 paginiDeterminant and Otherpema karmoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2008 - An Optical, EPR and Electrical Conductivity Study of Blue Barium TitanateDocument8 pagini2008 - An Optical, EPR and Electrical Conductivity Study of Blue Barium TitanateBeh NaatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Education Prelims TopicsDocument36 paginiHealth Education Prelims TopicsAmiel Francisco ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter4-Working With Dask Bags For Unstructured DataDocument33 paginiChapter4-Working With Dask Bags For Unstructured DataKomi David ABOTSITSEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 Part 2 Integrity of CreationDocument23 paginiModule 3 Part 2 Integrity of CreationNimfa GumiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Banerjee, 2020Document15 paginiBanerjee, 2020dwi ayuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legaledge Test Series: Mock Common Law Admission Test 2024 Mock Clat - 03Document40 paginiLegaledge Test Series: Mock Common Law Admission Test 2024 Mock Clat - 03Ashutosh MalviyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSCE Worksheet Mod 3 Lessons12 - FAMILY-NAME-3Document7 paginiBSCE Worksheet Mod 3 Lessons12 - FAMILY-NAME-3RINCONADA ReynalynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Averaged Switch Modeling,: AC Equivalent Circuit ModelingDocument12 paginiAveraged Switch Modeling,: AC Equivalent Circuit ModelingJulián RincónÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department: Uils: Environmental Law & Wildlife Protection Amanat Kahlon Assistant Professor Chandigarh UniversityDocument7 paginiDepartment: Uils: Environmental Law & Wildlife Protection Amanat Kahlon Assistant Professor Chandigarh UniversityHarneet KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Film Art Study Guide Key TermsDocument8 paginiFilm Art Study Guide Key TermsnormanchamorroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elastomers Presentation BrochureDocument20 paginiElastomers Presentation BrochureFrench CorvetteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dwnload Full Introduction To Environmental Geology 5th Edition Keller Test Bank PDFDocument35 paginiDwnload Full Introduction To Environmental Geology 5th Edition Keller Test Bank PDFgilmadelaurentis100% (12)
- Writer's Block and Procrastination in CIPD Level 5 AssignmentsDocument1 paginăWriter's Block and Procrastination in CIPD Level 5 AssignmentsCIPD Assignment HelpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics - Unit 6 - Part 1Document7 paginiPhysics - Unit 6 - Part 1Mahdi ElfeituriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ce121 Lec5 BuoyancyDocument18 paginiCe121 Lec5 BuoyancyPetForest Ni JohannÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tic Tac Toe CodeDocument4 paginiTic Tac Toe CodeluisrogaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plac908 Dap Record 5 2023Document3 paginiPlac908 Dap Record 5 2023api-706977810Încă nu există evaluări
- PYL100: EM Waves and Quantum Mechanics Vector Analysis Problem Set 1Document4 paginiPYL100: EM Waves and Quantum Mechanics Vector Analysis Problem Set 1Franklin GarysonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light Previous Years Shobhit NirwanDocument12 paginiLight Previous Years Shobhit NirwanPramod ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Story Telling Templetes 2023Document1 pagină2 Story Telling Templetes 2023serkovanastya12Încă nu există evaluări
- Driving Collaboration Efqm ModelDocument41 paginiDriving Collaboration Efqm ModelViviane EspositoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refined Technologies, Inc.: Material Safety Data SheetDocument3 paginiRefined Technologies, Inc.: Material Safety Data SheetisleepinadrawerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aqa 8300 RS Nov23Document12 paginiAqa 8300 RS Nov23leomaunganidze8Încă nu există evaluări
- Whole Brain Learning System Outcome-Based Education: Oral Communication Grade 11Document20 paginiWhole Brain Learning System Outcome-Based Education: Oral Communication Grade 11HeiyoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Predicting The Related Parameters of Vortex Bladeless Wind Tur-Bine by Using Deep Learning MethodDocument18 paginiPredicting The Related Parameters of Vortex Bladeless Wind Tur-Bine by Using Deep Learning MethodJosafatÎncă nu există evaluări
- US Declaration of Interdependence 1976Document10 paginiUS Declaration of Interdependence 1976FranSwizzle SimsÎncă nu există evaluări