Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Dec Cardiac Output NCP
Încărcat de
Joehoney Barrera0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
1K vizualizări2 paginiThe patient presented with decreased cardiac output due to altered glucose levels as evidenced by edema, hyperglycemia, hypercholesterolemia, fatigue, activity intolerance, anemia, lung issues, and decreased urine output. The nursing interventions were to closely monitor fluid intake and output, limit fluids and sodium as ordered, examine lab results, and position the patient appropriately. The short term goals were for the patient to understand actions and precautions for their cardiac condition and the long term goal was compliance with testing and treatment.
Descriere originală:
Nursing care plan
Titlu original
dec cardiac output ncp
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThe patient presented with decreased cardiac output due to altered glucose levels as evidenced by edema, hyperglycemia, hypercholesterolemia, fatigue, activity intolerance, anemia, lung issues, and decreased urine output. The nursing interventions were to closely monitor fluid intake and output, limit fluids and sodium as ordered, examine lab results, and position the patient appropriately. The short term goals were for the patient to understand actions and precautions for their cardiac condition and the long term goal was compliance with testing and treatment.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
1K vizualizări2 paginiDec Cardiac Output NCP
Încărcat de
Joehoney BarreraThe patient presented with decreased cardiac output due to altered glucose levels as evidenced by edema, hyperglycemia, hypercholesterolemia, fatigue, activity intolerance, anemia, lung issues, and decreased urine output. The nursing interventions were to closely monitor fluid intake and output, limit fluids and sodium as ordered, examine lab results, and position the patient appropriately. The short term goals were for the patient to understand actions and precautions for their cardiac condition and the long term goal was compliance with testing and treatment.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
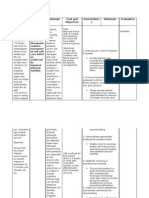
Identified Problem: Decreased Cardiac Output
Nursing Diagnosis: Decreased cardiac output related to altered glucose level
CUES OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Objective cues: Short term Record intake and Reduced Short term:
Bipedal edema Objective: output. If patient is cardiac After 4-8
Hyperglycemia After 4-8 acutely ill, measure output results hours of
(FBS: 21.11 mmol/L) hours of hourly urine output in reduced nursing
Hypercholesterolemia nursing and note decreases perfusion of intervention
( Cholesterol: 8.84 intervention in output. the kidneys, patient was
the patient with a able to
mmol/L)
will verbalize verbalize
Fatigue actions and
resulting
understanding
Activity intolerance precautions to
decrease in
on actions
Anemia (decreased take for urine output. and
RBC : 2.37/L cardiac limit fluids and precautions to
Sub segmental disease. sodium as ordered. Fluid take for
atelectasis restriction cardiac
Chest pain .Long term Closely monitor decreases disease. Goal
Left ventricular objective: fluid intake extracellular met
cardiomegaly After 3 including IV lines. fluid volume
Decrease urine days of Maintain fluid and reduces
output nursing restriction if demands of Long term:
intervention ordered. the heart. After 3
the patient days of
will be Examine laboratory Patient may nursing
Subjective cues: compliant on data, especially be receiving intervention
testing blood arterial blood gases patient wasn’t
cardiac
“ Naa juy usahay naa glucose level. and electrolytes, able to test for
glycosides
maglisud kog ginhawa og including potassium FBG level and
and the Hgt for some
magsakit ako dughan” as
potential for financial
verbalized by SO
toxicity is reason. Goal
Monitor laboratory greater with unmet
tests such as
hypokalemia;
complete blood
hypokalemia
count, sodium
is common in
level, and serum
creatinine. heart patients
because of
diuretic use.
Position patient in Monitor
semi-Fowler’s to laboratory
high-Fowler’s. tests such as
complete
blood count,
sodium level,
and serum
creatinine. A
low serum
sodium level
often is
observed with
advanced
heart failure
and can be a
poor
prognostic
sign. Serum
creatinine
levels will
elevate in
patients with
severe heart
failure
because of
decreased
perfusion to
the kidneys.
Creatinine
may also
elevate
because of
ACE
inhibitors.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- NCP For CTTDocument2 paginiNCP For CTTKay D. BeredoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument2 paginiNCPDidith AbanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan For RabiesDocument1 paginăNursing Care Plan For RabiesAngel VillamorÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument2 paginiNCPNikai PabayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan2 CVADocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan2 CVAhermesdave1Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP 1Document1 paginăNCP 1hsiriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For Dizziness and HeadacheDocument4 paginiNCP For Dizziness and Headachekarthi karthi100% (1)
- NCP - Excessive Fluid VolumeDocument4 paginiNCP - Excessive Fluid VolumeryanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Template ObDocument7 paginiNCP Template ObMae CeaesarÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 paginiNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP HemoDocument2 paginiNCP HemoJigs HechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJennirose JingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan NyaDocument3 paginiAssessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan Nyaangel_pearl413100% (2)
- Assessment Dianosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 paginiAssessment Dianosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationkyaw100% (1)
- Tarasoff CaseDocument2 paginiTarasoff Casealyssa marie salcedo100% (1)
- NCP RiskDocument3 paginiNCP RiskMaricar Azolae MascualÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impaired Liver FunctionDocument1 paginăImpaired Liver FunctionShop Dzubiri Here75% (4)
- NCP1 Knowledge DeficitDocument2 paginiNCP1 Knowledge DeficitNOslipperyslope100% (1)
- Risk For SuffocationDocument2 paginiRisk For SuffocationKimberly Subade Mandilag100% (2)
- Date / Time Focus Data Action Response: Lack of Knowledge On Diabetes Management or Blood Glucose ManagementDocument1 paginăDate / Time Focus Data Action Response: Lack of Knowledge On Diabetes Management or Blood Glucose ManagementDanica Kate GalleonÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument4 paginiNCPAnn AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study. GeamhDocument5 paginiDrug Study. GeamhMacky RobentaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IMPAIRED PHYSICAL MOBILITY RT Neuromuscular Involvement (Right Sided Paresthesia Aeb Inability To Purposefully Move Body Parts.Document2 paginiIMPAIRED PHYSICAL MOBILITY RT Neuromuscular Involvement (Right Sided Paresthesia Aeb Inability To Purposefully Move Body Parts.Senyorita KHaye67% (3)
- NCP Pain HypertensionDocument3 paginiNCP Pain HypertensionEzron Kendrick Duran50% (2)
- Drug Study NorepinephrineDocument2 paginiDrug Study NorepinephrinePearl JuntillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP AfDocument3 paginiNCP AfAngelica Mercado SirotÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - Altered ComfortDocument2 paginiNCP - Altered ComfortJhudiel Gabriel Go0% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocument1 paginăNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- AlanervDocument3 paginiAlanervCen Janber CabrillosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertension NCPDocument1 paginăHypertension NCPj4royce100% (1)
- NCP FolliculitisDocument3 paginiNCP Folliculitismichpadua50% (2)
- IsoketDocument2 paginiIsoketJaessa Feliciano100% (1)
- Uti NCPDocument1 paginăUti NCPAngelique Vinoya100% (2)
- NCP LocDocument2 paginiNCP LocMel RodolfoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDocument5 paginiNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- Course Task CU 7Document7 paginiCourse Task CU 7Kyla PamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1Document8 paginiRisk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1kint manlangitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument6 paginiAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationChristine Denise Venus ValentinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument3 paginiImpaired Urinary EliminationAgcopra MtchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan (Post Op Exlap)Document2 paginiNursing Care Plan (Post Op Exlap)Kay D. BeredoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP FoodDocument1 paginăNCP FoodAdrian ArdamilÎncă nu există evaluări
- TB, Ineffectivbe Breathing PatternsDocument1 paginăTB, Ineffectivbe Breathing PatternsnikkilyceeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument1 paginăNCPhaniehaehae100% (1)
- Cad NCPDocument1 paginăCad NCPKrizzia Mae F. MayoresÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Cva Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 paginăNCP Cva Ineffective Tissue Perfusionexcel21121Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP HypertensionDocument1 paginăNCP HypertensionCharisse VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For SVTDocument6 paginiNCP For SVTRen VillenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Thinking ExerciseDocument1 paginăCritical Thinking ExerciseMaye ArugayÎncă nu există evaluări
- HRZE (Kid's Kit), Toradol, CiprobayDocument4 paginiHRZE (Kid's Kit), Toradol, CiprobayiloveanneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Pain Related To Tissue Trauma and InjuryDocument4 paginiAcute Pain Related To Tissue Trauma and Injuryprickybiik50% (2)
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 paginiRisk For Decreased Cardiac Output NCPMae Denn LabordoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Risk For Decreased CO 1 PDFDocument2 paginiNCP Risk For Decreased CO 1 PDFdubsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPDocument5 paginiAcute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPMyrvic Ortiz La OrdenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tams NCP and DrugDocument5 paginiTams NCP and DrugNicholas Xavier VenturaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OUTPUTDocument3 paginiOUTPUTRoshin Mae E. TejeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Management of Client With Hypokalemia ACTUAL 1Document4 paginiNursing Care Management of Client With Hypokalemia ACTUAL 1Angel Nieto PengsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Analysis: Pre-OperativeDocument12 paginiCase Analysis: Pre-OperativeMaria ThereseÎncă nu există evaluări
- HypertensionDocument2 paginiHypertensionRodel Yacas0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermDocument11 paginiNursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermYumeko JabamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free Affidavit of Identity TemplateDocument2 paginiFree Affidavit of Identity TemplateJoehoney BarreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2022 Affidavit of One and The Same PersonDocument1 pagină2022 Affidavit of One and The Same PersonJoehoney BarreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPR StepsDocument6 paginiCPR StepsJoehoney BarreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cues Objective S Interventions Rationale Evaluatio NDocument2 paginiCues Objective S Interventions Rationale Evaluatio NJoehoney BarreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Coronavirus? What Is A Novel Coronavirus?Document7 paginiWhat Is A Coronavirus? What Is A Novel Coronavirus?Joehoney BarreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Icu Journal. FinalDocument6 paginiIcu Journal. FinalJoehoney BarreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case ManagementDocument2 paginiCase ManagementJoehoney BarreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- La Wa Wla NDocument4 paginiLa Wa Wla NJoehoney BarreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- T2R Survival Guide - 2019Document22 paginiT2R Survival Guide - 2019chioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Improving Occupational Safety Health and Risk ManagementDocument68 paginiImproving Occupational Safety Health and Risk ManagementReichstein CaduaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HKS777Document21 paginiHKS777Nelson OrcinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cerebro Vaskuler Disease Pada Kasus FashduDocument60 paginiCerebro Vaskuler Disease Pada Kasus Fashduotha polmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deformity QuestionnaireDocument2 paginiDeformity Questionnairevikash kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Takaful Smart Plus BrochureDocument27 paginiTakaful Smart Plus BrochureSubang Jaya Youth ClubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Metodu EN1276 PDFDocument13 paginiTest Metodu EN1276 PDFhcsoyleyiciÎncă nu există evaluări
- STOCK OPNAME Agustus 2017Document10 paginiSTOCK OPNAME Agustus 2017farid akbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common SynonymsDocument15 paginiCommon SynonymsHong Dang100% (1)
- ArticleDocument11 paginiArticleTry WirantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Role of Aging and Movement Disorders: EditorsDocument461 paginiThe Role of Aging and Movement Disorders: EditorsAntonio tapiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCM Who Academy Guide FinalDocument88 paginiMCM Who Academy Guide FinalHilal Mohamed NorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scalp Acup & Cerebral PalsyDocument4 paginiScalp Acup & Cerebral PalsyAngelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drying Kinetics of Green Banana FlourDocument11 paginiDrying Kinetics of Green Banana FlourUsha BbattaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transcript Foundational Herbcraft Part 1Document32 paginiTranscript Foundational Herbcraft Part 1Stacey DianeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enzyme POGILDocument6 paginiEnzyme POGILnewhaventeacherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benign Essential Blepharospasm Information Page - National Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeDocument2 paginiBenign Essential Blepharospasm Information Page - National Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeJP OmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 139588I030320231722239655591 EAPP SharonDocument12 pagini139588I030320231722239655591 EAPP SharonRacell VelascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Webinar Famiy Doctors 1 - 10 - 2020Document62 paginiWebinar Famiy Doctors 1 - 10 - 2020NoaEfratBen-BaruchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre Analitica X 3 Libros Variabilidad BiologicaDocument20 paginiPre Analitica X 3 Libros Variabilidad BiologicaUlises Saldias RoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penyakit Berjangkit Di Kalangan Penagih Heroin Yang Menerima Rawatan Pesakit Luar Di MuarDocument8 paginiPenyakit Berjangkit Di Kalangan Penagih Heroin Yang Menerima Rawatan Pesakit Luar Di MuarPenjejak BadaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 528-Article Text-2283-1-10-20220418Document9 pagini528-Article Text-2283-1-10-20220418Apotik ApotekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deformities: Karl V. Bustamante Johara Micah RegidorDocument28 paginiDeformities: Karl V. Bustamante Johara Micah Regidorcharlo_camachoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heart Failure COncept MapDocument2 paginiHeart Failure COncept MapJrBong SemaneroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Useof International Caries Detectionand Assessment Systemina National Health ServiceDocument9 paginiUseof International Caries Detectionand Assessment Systemina National Health Serviceأمال داودÎncă nu există evaluări
- Root Dilaceration: A Case Report and Literature ReviewDocument11 paginiRoot Dilaceration: A Case Report and Literature ReviewAstrid HutabaratÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Study DesignDocument60 pagini3 Study DesignNour KoraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Best HealthDocument84 paginiBest HealthAlfred LagbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines For Preventive Activities in General PracticeDocument382 paginiGuidelines For Preventive Activities in General PracticeDr. Serin KuriakoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mtendere Community Youth TeamDocument2 paginiMtendere Community Youth TeamReal KezeeÎncă nu există evaluări