Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Precipitate Labor, Uterine Inversion, Uterine Rupture
Încărcat de
Abbeygale Galan100%(2)100% au considerat acest document util (2 voturi)
407 vizualizări3 paginiTitlu original
PRECIPITATE-LABOR
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
100%(2)100% au considerat acest document util (2 voturi)
407 vizualizări3 paginiPrecipitate Labor, Uterine Inversion, Uterine Rupture
Încărcat de
Abbeygale GalanDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
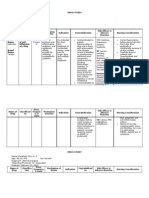
PRECIPITATE LABOR Continuously monitor uterine
contractions and FHR patterns
Refers to labor that lasts 3 hours or
less Encourage the woman to relax as
possible
More common in multiparous
patients and in women who have Explain all procedures and
received oxytocin induction or treatments being initiated.
amniotomy.
Instruct the woman with a history of
The mother is at risk for hemorrhage precipitate labor that it may occur
secondary to premature separation with future pregnancies; advise to
of the placenta and for lacerations plan for such an occurrence in
due to the force and rapidity of the advance.
birth.
UTERINE INVERSION
Causes:
The inverted fundus may lie within
Lack of maternal tissue resistance to the uterine cavity of the vagina or, in
the passage of the fetus. total inversion, protrude from the
vagina.
** The fetus is at risk for subdural
hematoma, possibly from the rapid Causes :
release of pressure on the fetal head.
May occur after the birth of the
Assessment Findings : neonate, especially if traction is
applied to the uterine fundus when
Strong uterine contractions with the uterus is not contracted.
signs of premature placental
separation. May also occur when the placenta is
inserted at the fundus, during birth
Treatment : the passage of the fetus pulls the
A tocolytic may be administered to fundus down.
reduce the strength and frequency Assessment Findings :
of the contractions.
A large sudden gush of blood from
Plans for immediate delivery are the vagina.
necessary.(CS)
Non-palpable fundus in the
Nursing Interventions: abdomen
Provide emotional and physical Signs and symptoms of shock if the
support to the woman and family. loss of blood continues unchecked
for more than few minutes
Hypotension Assist with the measures to relax
the uterus
Pallor
Provide emotional support and
dizziness and diaphoresis explaination what's happening and
Possible exsanguination if bleeding procedures being done
continues unchecked Be prepared to perform CPR if the
Treatment : woman's heart fails from the sudden
blood loss.
IV fluids and blood component
therapy to replace fluid volume and Anticipate administering antibiotic as
blood loss ordered
General anesthesia, or tocolytic may UTERINE RUPTURE
be administered to relax the uterus Occurs when the uterus undergoes
Due to uterine exposure, antibiotic is more strain than it's capable of
indicated postpartally sustaining and then ruptures.
As a last resort, the patient may Rupture can be complete, going
require an emergency hysterectomy. through endometrium, myometrium,
and peritoneum, or incomplete,
Nursing Interventions : leaving the peritoneum intact.
Initiate IV therapy as ordered – if the Causes :
woman has an IV line in place,
increased the flow rate to achieve Usually occurs from a previous
optimal flow of fluid to restore fluid cesarean birth, such as when a
volume. vertical scar from a previous incision
is present.
Administer oxygen by mask as
ordered Can also occur from hysterectomy
repair.
Keep in mind that administering an
oxytoxic only compounds the Other causes include :
inversion prolonged labor, faulty
Never attempt to remove the presentation, multiple gestation,
placenta if it's still attached because use of oxytocin, traumatic
this will create more bleeding. maneuvers using forceps or
traction.
Monitor VS at least every 15
minutes. Assessment Findings :
Indentation appearing across the Anticipate the use of IV oxytocin to
abdomen over the uterus contract the uterus and minimize
(pathologic retraction ring) bleeding.
Strong uterine contractions without Prepare the woman for a possible
any cervical dilation. laparotomy as an emergency
measure – explanation is necessary.
Indications of complete uterine
rupture If applicable, offer emotional support
for the loss of this child or loss of
sudden, severe pain during a future children (if hysterectomy or
strong labor contraction tubal ligation is performed).
report of a tearing sensation Allow them to express their
emotions without feeling threatened.
cessation of uterine contractions
hemorrhage
Treatment :
Focuses on the following measures :
Fluid replacement
IV oxytocin to contract the uterus
and minimize bleeding
A cesarean birth will be done to
ensure safety of neonate
Manual removal of the placenta
under general anesthesia may be
necessary.
A laparotomy may be necessary as
an emergency measure to control
bleeding and repair the rupture;
hysterectomy or tubal ligation may
be performed.
Nursing Interventions :
Administer emergency fluid
replacement therapy as ordered.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Case Presentation On CholedocholithiasisDocument11 paginiA Case Presentation On CholedocholithiasisPaul Vincent EspereÎncă nu există evaluări
- UTERINE PROLAPSE - Case ReportDocument3 paginiUTERINE PROLAPSE - Case ReportIOSRjournalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forcep Delivery..Document3 paginiForcep Delivery..Kristelle Joy Capili SicatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal Problems With PowerDocument2 paginiMaternal Problems With PowerAlex CvgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ectopic Pregnancy GuideDocument27 paginiEctopic Pregnancy GuideuunuunuunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q&A 3ednDocument15 paginiQ&A 3ednrohitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amniotic Fluid Embolism (AFE)Document26 paginiAmniotic Fluid Embolism (AFE)sanjivdas100% (1)
- Nursing care for anticipatory grieving after pregnancy lossDocument1 paginăNursing care for anticipatory grieving after pregnancy lossYsabelle GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- #3 Cesarean SectionDocument20 pagini#3 Cesarean SectionDunice Lloyd Mata100% (1)
- Spontaneous AbortionDocument8 paginiSpontaneous Abortionsaber_fate_11Încă nu există evaluări
- Vacuum Extraction (Ventouse)Document3 paginiVacuum Extraction (Ventouse)dusty kawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Incompetent CervixDocument29 paginiIncompetent CervixCyrelle Jen TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cephalopelvic DisproportionDocument2 paginiCephalopelvic DisproportionWirahadi SanjayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DystociaDocument31 paginiDystociamarsan120% (1)
- Cephalopelvic DisproportionDocument3 paginiCephalopelvic DisproportionAira MiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study Generic Name (Brand Name) Indication Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Adverse Reaction Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilityDocument3 paginiDrug Study Generic Name (Brand Name) Indication Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Adverse Reaction Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilityKimm Charmaine RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care of Induction and Augmentation of LaborDocument17 paginiNursing Care of Induction and Augmentation of LaborZyrene RiveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Client Care Study on CholedocholithiasisDocument29 paginiClient Care Study on CholedocholithiasisNehdu AkahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument2 paginiNifedipine Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cephalopelvic Disproportion FinalDocument7 paginiCephalopelvic Disproportion FinalJesie Mel Bacena100% (1)
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument3 paginiAbruptio Placentachichilovesyou100% (1)
- Retraction RingDocument5 paginiRetraction RingAna100% (2)
- LevofloxacinDocument3 paginiLevofloxacinapi-3797941100% (2)
- Management of Breech PresentationDocument27 paginiManagement of Breech Presentationapi-370504683% (6)
- Cord Presentation ProlapseDocument10 paginiCord Presentation ProlapseJHONESSA LAYOSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complications of The Third Stage of LabourDocument6 paginiComplications of The Third Stage of LabourSong QianÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Retained Placenta?Document4 paginiWhat Is A Retained Placenta?Baharudin Yusuf Ramadhani0% (1)
- Mechanism of LaborDocument12 paginiMechanism of LaborSaidatul Safarah Md HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of Fetal DeathDocument9 paginiEvaluation of Fetal DeathVinisia TakaraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiology of LaborDocument16 paginiPhysiology of LaborRodrerick De lafuentesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case StudyDocument19 paginiCase Studywella goÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoulder Dystocia NCPDocument6 paginiShoulder Dystocia NCPNicole Genevie MallariÎncă nu există evaluări
- COMPLICATIONS OF LABOR AND DELIVERYDocument19 paginiCOMPLICATIONS OF LABOR AND DELIVERYkrizele ann santosÎncă nu există evaluări
- SDL4Document2 paginiSDL4Juviely PremacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoulder DystociaDocument22 paginiShoulder Dystociaamulan_aÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCLXDocument5 paginiNCLXkhadeejakhurshidÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Case Study About Cervical PolypsDocument8 paginiA Case Study About Cervical PolypsJisel-Apple BulanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal and Child Nursing - Intrapartum PeriodDocument91 paginiMaternal and Child Nursing - Intrapartum Periodchuppepay20% (5)
- CASE STUDY Acute Pain Related To Laceration 1Document29 paginiCASE STUDY Acute Pain Related To Laceration 1Maria Jessica Dumdum100% (1)
- Prolonged LabourDocument47 paginiProlonged LabourBharat ThapaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Now, Try Some Big Leap.: Keep GoingDocument10 paginiNow, Try Some Big Leap.: Keep GoingCameron De GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument25 paginiPregnancy Induced HypertensionPauPauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care of Postpartum ComplicationsDocument13 paginiNursing Care of Postpartum ComplicationsLyca Mae AurelioÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPD, Dystocia, Fetal Distress OutputDocument8 paginiCPD, Dystocia, Fetal Distress OutputJohn Dave AbranÎncă nu există evaluări
- And Vaginal Bleeding (In Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy)Document9 paginiAnd Vaginal Bleeding (In Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy)Clareen JuanicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cord ProlapseDocument3 paginiCord ProlapseEka Cyril67% (3)
- Uterine ProlapseDocument11 paginiUterine ProlapseMelDred Cajes BolandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument2 paginiDrug StudySORENI SORENIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnesium SulfateDocument2 paginiMagnesium SulfateGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- Manage uterine contractions and bleeding with MetherginDocument2 paginiManage uterine contractions and bleeding with MetherginOtan Cuison100% (1)
- Drug Study ObDocument6 paginiDrug Study Obednaria100% (1)
- Cesarean SectionDocument16 paginiCesarean SectionRaghad Al-Shabani67% (3)
- Pregnacy Induced Hypertension PhysiologyDocument1 paginăPregnacy Induced Hypertension PhysiologyCyrus De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ob MaternityDocument46 paginiOb MaternityJohanna Erazo Padilla100% (1)
- Idiophatic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in PregnancyDocument27 paginiIdiophatic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in PregnancyAdietya Bima PrakasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument4 paginiAbruptio PlacentaChelzie LasernaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ncma219 Week 4Document9 paginiNcma219 Week 4Aruxi YoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- M102 Remedial ModuleDocument14 paginiM102 Remedial ModuleMA. JYRELL BONITOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uterine Inversion Uterine Rupture Amniotic Fluid Embolism MaglangitDocument6 paginiUterine Inversion Uterine Rupture Amniotic Fluid Embolism Maglangitmaglangitjoannamarie1920Încă nu există evaluări
- Joshi Abhishek F.Y.P.B.B.SC - Nursing Govt College of Nursing JamnagarDocument49 paginiJoshi Abhishek F.Y.P.B.B.SC - Nursing Govt College of Nursing JamnagarPoonam RanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Terbutaline SulfateDocument1 paginăTerbutaline SulfateIvanne Hisoler100% (2)
- Journal #1 The Role of Nurses in Community Awareness and Preventive HealthDocument3 paginiJournal #1 The Role of Nurses in Community Awareness and Preventive HealthAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal InjuryDocument2 paginiMaternal InjuryAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk For InfectionDocument1 paginăRisk For InfectionAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gender and Society Week 1 - HWDocument2 paginiGender and Society Week 1 - HWAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk For InfectionDocument1 paginăRisk For InfectionAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Certificate for online class webinar participationDocument1 paginăCertificate for online class webinar participationAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theoretical FrameworkDocument2 paginiTheoretical FrameworkAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ra1425 Rizal FamilyDocument7 paginiRa1425 Rizal FamilyRoselle JoyceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ra1425 Rizal FamilyDocument7 paginiRa1425 Rizal FamilyRoselle JoyceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific BasisDocument2 paginiScientific BasisAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific BasisDocument2 paginiScientific BasisAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedia Final NCPDocument10 paginiPedia Final NCPAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GALANDocument2 paginiGALANAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GALANDocument2 paginiGALANAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP CP2Document4 paginiNCP CP2Abbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCN PartialDocument9 paginiMCN PartialAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GALANDocument2 paginiGALANAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Management of a Client with Eclampsia: A Case StudyDocument72 paginiNursing Care Management of a Client with Eclampsia: A Case StudyMauren Daza100% (4)
- NCP CP2Document4 paginiNCP CP2Abbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedia Final NCPDocument10 paginiPedia Final NCPAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCN PartialDocument9 paginiMCN PartialAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NewncpformDocument4 paginiNewncpformAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- HEJE. Family Health Assessment Form.Document9 paginiHEJE. Family Health Assessment Form.Abbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GALANDocument2 paginiGALANAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP CP2Document4 paginiNCP CP2Abbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCN PartialDocument9 paginiMCN PartialAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCN PartialDocument9 paginiMCN PartialAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCN PartialDocument9 paginiMCN PartialAbbeygale GalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- FP TCLDocument2 paginiFP TCLlaliejhessÎncă nu există evaluări
- LeopoldsDocument2 paginiLeopoldsMhianne SarmientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scholomance 8 MindfuckDocument21 paginiScholomance 8 MindfuckFabiano SaccolÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMAH Patient Information Leaflet v3Document5 paginiEMAH Patient Information Leaflet v3SonaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Talis Sharma +2k Birth ControlDocument29 paginiTalis Sharma +2k Birth ControlTalis SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ctg نهائيDocument37 paginictg نهائيdr.nahlla hellesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Response To Guttmacher Institute Criticisms by Koch Et Al. On The Impact of Abortion Restrictions On Maternal Mortality in ChileDocument19 paginiResponse To Guttmacher Institute Criticisms by Koch Et Al. On The Impact of Abortion Restrictions On Maternal Mortality in ChilePaulita Aracena100% (1)
- Clinical Guideline: Enteral Feeding - Iron Supplementation: Neonatal Clinical Oversight GroupDocument12 paginiClinical Guideline: Enteral Feeding - Iron Supplementation: Neonatal Clinical Oversight GroupStphn WllngtnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pregnancy Course Manual-1Document49 paginiPregnancy Course Manual-1BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female Sex HormonesDocument20 paginiFemale Sex HormonesAlina ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Facility MappingDocument39 pagini2 Facility MappingJessa MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Secretary List 2022Document18 paginiSecretary List 2022Yashodhan RajwadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process of SpermatogenesisDocument3 paginiProcess of SpermatogenesisMarian FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- My Study Plan Guide For AmcDocument7 paginiMy Study Plan Guide For Amc0d&H 8Încă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care of A Family Experiencing A Sudden Pregnancy ComplicationDocument5 paginiNursing Care of A Family Experiencing A Sudden Pregnancy ComplicationCrisheila Sarah PiedadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory Disorders and PregnancyDocument23 paginiRespiratory Disorders and PregnancyAngelie RojasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demographics Abortion PhilippinesDocument3 paginiDemographics Abortion PhilippinesspringdingÎncă nu există evaluări
- PBL 2 Blood Components and Blood GroupsDocument14 paginiPBL 2 Blood Components and Blood GroupsadaumedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sexual-Health-and-HygieneDocument10 paginiSexual-Health-and-Hygiene2ndyearacc05Încă nu există evaluări
- FertilizationDocument63 paginiFertilizationDheressaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation Tool - Clinical Practice: Delivery Room-Nursery (SLUHSH)Document4 paginiEvaluation Tool - Clinical Practice: Delivery Room-Nursery (SLUHSH)Keanu PeraltaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CONTRACEPTIONDocument38 paginiCONTRACEPTIONGopala HariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy Physiology of The Male Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 paginiAnatomy Physiology of The Male Female Reproductive SystemLilian JerotichÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pasar p1 Exam CutieDocument10 paginiPasar p1 Exam CutieLeevine DelimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge and Application of Apgar ScoreDocument5 paginiKnowledge and Application of Apgar Scorefebiola sihiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ Weighing ScaleDocument2 paginiMCQ Weighing ScaleSara RezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midwifery Pharmacology-38Document1 paginăMidwifery Pharmacology-38georgeloto12Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 39 Endorcrine and Reproductive SystemDocument20 paginiChapter 39 Endorcrine and Reproductive SystemgjaenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Report Alpha DogDocument130 paginiSample Report Alpha DogUsman DastgirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Confidentiality in The WorkplaceDocument3 paginiConfidentiality in The WorkplaceAlex ChernovÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDe la EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (13)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDe la EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDe la EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDe la EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDe la EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (402)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDe la EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDe la EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (78)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementDe la EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (40)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDe la EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (169)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDe la EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesDe la EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (34)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDe la EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (327)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsDe la EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingDe la EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeDe la EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (253)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingDe la EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (41)
- Seeing What Others Don't: The Remarkable Ways We Gain InsightsDe la EverandSeeing What Others Don't: The Remarkable Ways We Gain InsightsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (288)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingDe la EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (33)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossDe la EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDe la EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (8)