Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Coret 2
Încărcat de
Bayu Muhammad AjiTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Coret 2
Încărcat de
Bayu Muhammad AjiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
C athodic protection is a proven corrosion control method for protection of underground and undersea metallic
structures, such as oil and gas pipelines, cables, utility lines and structural foundations. Cathodic protection is now
widely applied in the protection of oil drilling platforms, dockyards, jetties, ships, submarines, condenser tubes in
heat exchangers, bridges and decks, civil and military aircraft and ground transportation systems.
The designing of cathodic protection systems is rather complex, however, it is based on simple electrochemical
principles described earlier in Chapter 2. Corrosion current flows between the local action anodes and cathodes due
to the existence of a potential difference between the two (Fig. 5.1). As shown in Fig. 5.2, electrons released in an
anodic reaction are consumed in the cathodic reaction. If we supply additional electrons to a metallic structure, more
electrons would be available for a cathodic reaction which would cause the rate of cathodic reaction to increase and
that of anodic reaction to decrease, which would eventually minimize or eliminate corrosion. This is basically the
objective of cathodic protection. The additional electrons are supplied by direct electric current. On application of
direct current, the potential of the cathode shifts to the potential of the anodic area. If sufficient direct current is
applied, the potential difference between the anode and cathode is eliminated and corrosion would eventually cease
to occur.
Perancangan sistem perlindungan katodik agak rumit, namun, ini didasarkan pada prinsip-prinsip elektrokimia
sederhana yang dijelaskan sebelumnya pada Bab 2. Aliran arus korosi antara anoda aksi lokal dan katoda karena
adanya perbedaan potensial antara keduanya (Gbr. 5.1) ). Seperti ditunjukkan pada Gambar 5.2, elektron yang
dilepaskan dalam reaksi anodik dikonsumsi dalam reaksi katodik. Jika kita memasok elektron tambahan ke struktur
logam, lebih banyak elektron akan tersedia untuk reaksi katodik yang akan menyebabkan laju reaksi katodik
meningkat dan reaksi anodik menurun, yang pada akhirnya akan meminimalkan atau menghilangkan korosi. Ini
pada dasarnya adalah tujuan perlindungan katodik. Elektron tambahan dipasok oleh arus listrik langsung. Pada
penerapan arus searah, potensi katoda bergeser ke potensi daerah anodik. Jika arus searah yang cukup diterapkan,
perbedaan potensial antara anoda dan katoda dihilangkan dan korosi pada akhirnya akan berhenti terjadi.
This type of cell is formed when an external current is introduced into the system. It may consist of all the basic
components of galvanic cells and concentration cells plus an external source of electrical energy. Notice that anode
has a (+) polarity and cathode has (—) polarity in an electrolytic cell, where external current is applied. This is the
type of cell set up for electrically protecting the structures by cathodic protection. The polarity of an electrolytic cell
is opposite to that in a galvanic (corrosion) cell (Fig. 2.7).
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Bayu Muhammad Aji - Curriculum VitaeDocument2 paginiBayu Muhammad Aji - Curriculum VitaeBayu Muhammad AjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Bayu Muhammad Aji - Curriculum Vitae and Portofolio - CompressedDocument5 paginiBayu Muhammad Aji - Curriculum Vitae and Portofolio - CompressedBayu Muhammad AjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Tugas PPPM3 - Bayu Muhammad Aji 02511950010008Document3 paginiTugas PPPM3 - Bayu Muhammad Aji 02511950010008Bayu Muhammad AjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Tugas 1 TermodinamikaDocument15 paginiTugas 1 TermodinamikaBayu Muhammad AjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- 785 Truck Electrical System: 8GB418-UPDocument2 pagini785 Truck Electrical System: 8GB418-UPEdwin Ruiz VargasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- gp2 Speed IncreaserDocument2 paginigp2 Speed Increasermayur22785Încă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Advances in FerroelectricsDocument542 paginiAdvances in FerroelectricsPhelippe Mendonça de PaivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Solow Model Extension-Human CapitalDocument16 paginiSolow Model Extension-Human CapitalQusay Falah Al-dalaienÎncă nu există evaluări
- LVS x00 DatasheetDocument3 paginiLVS x00 DatasheetEmanuel CondeÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Summa Roll Cutters: S One - S Class 2 Series World Renowned Vinyl and Contour CuttersDocument32 paginiSumma Roll Cutters: S One - S Class 2 Series World Renowned Vinyl and Contour CuttersPU PUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- SMPS Teune Mee PDFDocument71 paginiSMPS Teune Mee PDFbacuoc.nguyen356Încă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- CV Bilal Ur Rehman RF EngineerDocument4 paginiCV Bilal Ur Rehman RF Engineermudassar2k4Încă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Ritual To Use The Seals of SolomonDocument4 paginiRitual To Use The Seals of Solomonrarmandjr8474100% (11)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Piping Presentation - PpsDocument61 paginiPiping Presentation - PpsVijayabaraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
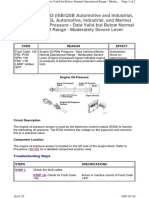
- Code Reason Effect: Step 1. Step 1ADocument2 paginiCode Reason Effect: Step 1. Step 1AAhmedmahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Clavius' ElementaDocument818 paginiClavius' Elementapenttila86Încă nu există evaluări
- MyLabX8 160000166 V02 LowRes PDFDocument8 paginiMyLabX8 160000166 V02 LowRes PDFhery_targerÎncă nu există evaluări
- JEE Mains (2024) AprilDocument129 paginiJEE Mains (2024) Aprilsophos408Încă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Mechatronics Eng 07 08 EtDocument86 paginiMechatronics Eng 07 08 EtVenu Madhav ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Nowledge ObjectivesDocument2 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Nowledge ObjectivesErwin B. NavarroÎncă nu există evaluări
- NRC RG 1.99 Rev. 2 PDFDocument10 paginiNRC RG 1.99 Rev. 2 PDFlalitÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Thesis - AN Fertiliser Properties Applic and Safety FinlandDocument256 paginiThesis - AN Fertiliser Properties Applic and Safety FinlandGonzalo O'ortiz Araneda's IIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mulligan Vs ART PDFDocument4 paginiMulligan Vs ART PDFwernsickleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proceedings of Spie: Design and Simulation Analysis of A Magnetic Shielding Box For Ring Laser GyroscopeDocument9 paginiProceedings of Spie: Design and Simulation Analysis of A Magnetic Shielding Box For Ring Laser GyroscopeTanzil ZaidiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NTPC Nabinagar BiharDocument3 paginiNTPC Nabinagar BiharTECH FoReVerÎncă nu există evaluări
- GeaDocument17 paginiGeaEasy WriteÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Sainsbury 2010 PDFDocument13 paginiSainsbury 2010 PDFronaldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mass Balance Equations For Deformable Porous MediaDocument9 paginiMass Balance Equations For Deformable Porous MediaJonathan TeixeiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- A1 - Full Papers PS1 10834 2022Document18 paginiA1 - Full Papers PS1 10834 2022DmitryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Cooled Chiller (SHUBAILY GRAND MALL)Document40 paginiWater Cooled Chiller (SHUBAILY GRAND MALL)kdpmansiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Logic of Faith Vol. 1Document39 paginiThe Logic of Faith Vol. 1Domenic Marbaniang100% (2)
- Chapter 8 RevaDocument20 paginiChapter 8 RevaanildhakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACI 305 Hot Weather Concrete PDFDocument9 paginiACI 305 Hot Weather Concrete PDFCristhian MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 84 Cómo Crear Una User Exit para Activos Fijos ANLUDocument8 pagini84 Cómo Crear Una User Exit para Activos Fijos ANLUPedro Francisco GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)