Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Engineering Thermodynamics
Încărcat de
tua0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
3K vizualizări7 paginiTitlu original
ENGINEERING-THERMODYNAMICS
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
3K vizualizări7 paginiEngineering Thermodynamics
Încărcat de
tuaDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 7
ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
1. What is the weight of a 66-kgm man at standard condition? 66 kgf
2. The weight of an object is 50 lb. what is its mass at standard condition? 50 lbm
2
3. Five masses in a region where the acceleration due to gravity is 30.5 ft/s are as
4461.07 gm
follow: m1 is 500 g of mass; m2 weighs 800 gf; m3 weighs 15 poundal; m4 weighs
9.83 lbm
3 lbf; m5 is 0.10 slug of mass. What is the total mass expressed (a) in grams, (b)
0.306 slugs
in pounds, and (c) in slugs.
4. Note that the gravity acceleration at equatorial sea level is g=32.088 fps 2 per
1000 ft ascent. Find the height in miles above the point for which (a) the gravity 528000 ft or 100 miles
acceleration becomes 30.504 fps2, (b) the weight of a given man is decreased by 30.484 fps2
5%, (c) what is the weight of a 180 lbm man atop the 29,131 ft Mt. Everest in 179.03 lbf
Tibet, relative to this point.
5. Two liquids of different densities (ρ1=1500 kg/m3, ρ2=500 kg/m3) are poured
45 kg
together into a 100 L tank, filling it. If the resulting density of the mixture is 800
35 kg
kg/m3, find the respective quantities of liquids used. Also, find the weight of the
78.93 kgf
mixture; local g=9.675 mps2.
6. A vertical column of water will be supported to what height by standard
33.9 ft
atmospheric pressure.
7. The pressure of a boiler is 9.5 kg/cm2. The barometric pressure of the
10.54 kg/cm2
atmosphere is 768 mm Hg. Find the absolute pressure in the boiler.
8. A pressure gage registers 40 psig in a region where the barometer us 14.5 psia. 54.5 psia
Find the absolute pressure in psia, and in kPa. 375.78 kPa
9. Given the barometric pressure of 14.7 psia (29.92 in. Hg abs), make these
94.7 psia, 5.44 atm
conversions:
9.92 in. Hg abs, 4.87 [si
a. 80 psig to psia and to atmosphere
4.7 psi vacuum, 32407 Pa
b. 20 in. Hg vacuum to in. Hg abs and to psia
44.92 in. Hg. 381 torrs, 50780
c. 10 psia to psi vacuum and to Pa
Pa(gage)
d. 15 in. Hg gage to psia, to torrs, and to Pa
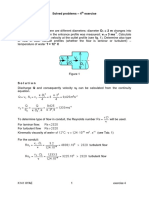
10. Two gaseous streams enter a combining tube and leave as a single mixture.
These data apply at the entrance section:
For one gas, A1=75 in2, v=500 fps, ν=10 ft3/lb
400 fps
For the other gas, A2=50 in2, m2=16.67 lb/s, ρ2=0.12 lb/ft3
42.71 lb/s
At exit, v=350 fps, v3=7ft3/lb.
0.8542 ft2
Find:
a. the speed v2(fps) at section 2, and
b. the flow and area at the exit section.
11. A 10-ft diameter by 15-ft height vertical tank is receiving water (ρ=62.1 lb/cu.ft) at
the rate of 300 gpm and is discharging through a 6-in ID line with a constant
3.91 ft
speed of 5 fps. At a given instant, the tank is half-full. Find the water level and
the mass change in the tank 15 min. later.
340.2 gm
12. What is the mass in grams and the weight in dynes and in gram-force of 12 oz of
328,300 dynes
salt? Local g is 9.65 m/s2. 1lbm=16 oz.
334.8 gf
13. A mass of 0.10 slug in space is subjected to an external vertical force of 4lb. If
the local gravity acceleration is g=30.5 fps2 and if friction effects are neglected, 9.5 fps2
determine the acceleration of the mass if the external vertical force is acting (a) 70.5 fps2
upward and (b) downward
14. The mass of a given airplane at sea level (g=32.1 fps2) is 10 tons. Find its mass
20,000 lbm
in lb, slugs, and kg and its (gravitational) weight in lb when it is travelling at a
621.62 slugs
50000 ft elevation. The acceleration of gravity g decreases 3.33x10 -6 fps2 for
19850 lbf
each foot of elevation.
15. A lunar excursion module (LEM) weights 1500 kgf on earth where g=9.75 mps 2.
261.5 kgf
What will be its weight on the surface of the moon where gm=1.70 mps 2. On the
1538.5 kgf
surface of the moon, what will be the force in kgf and in Newton required to
15087 N
accelerate the module at 10 mps2?
16. The mass of a fluid system is 0.311 slug, its density is 30 lb/ft3 and g is 31.90 0.0333 ft3/lb
fps2. Find (a) the specific volume, (b) the specific weight, and (c) the total 29.75 lb/ft3
volume. 0.3335 ft3
17. A cylindrical drum (2ft diameter, 3 ft height) is filled with a fluid whose density is 9.43 ft3
377.2 lb
40 lb/ft3. Determine (a) the total volume of fluid, (b) its total mass in pounds and 11.72 slugs
slugs, (c) its specific volume, and (d) its specific weight where g=31.90 fps 2. 0.025 ft3/lb
39.66 lb/ft3
18. A weatherman carried aneroid barometer from the ground floor to his office atop
he Sears Tower in Chicago. On the ground level, the barometer read 28.607 in.
1455 ft
Hg absolute. Assume that the average atmospheric air density was 0.075 lb/ft3
and estimate the height of the building.
19. A vacuum gauge mounted on a condenser reads 0.66 m Hg. What is the
absolute pressure in the condenser in kPa when the atmospheric pressure is 13.28 kPa
101.3 kPa?
20. Convert the following readings of pressure to kPa absolute, assuming that the
barometer reads 760 mm Hg: 221.24 kPa;
a. 90 cm Hg gage 48 kPa
b. 40 cm Hg vacuum 790.83 kPa
c. 100 psig 74.213 kPa
d. 8 in Hg vacuum, and 358.591 kPa
e. 76 in. Hg gage
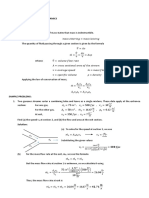
21. A fluid moves in a steady flow manner between two sections in a flow line. At
sections 1: A1=10ft2, u1=100 fpm, v1=4ft3/lb. at section 2: A2=2ft2, ρ2=0.20 lb/ft3.
15000 lb/hr
Calculate:
10.42 fps
a. The mass flow rate
b. The speed at section 2
22. If a pump discharges 75 gpm of water whose specific weight is 61.5 lb/ft3
(g=31.95 fps2), find:
621.2 lb/min
a. The mass flow rate in lb/min
93.97 min
b. The total time required to fill a vertical cylinder tank 10 ft in diameter and 12
ft high.
23. During a steady flow process, the pressure of the working substance drops from
200 to 20 psia, the speed increases from 200 to 1000 fps, the internal energy of
13.24 BTU/lb
the open system decreases 25 Btu/lb, and the specific volume increases from 1
3.12 Hp
to 8 ft3/lb. no heat is transferred. Determine the work per lb. is it done on or by
the substance? Determine the work in Hp for 10 lb per min.
24. Steam is supplied to a fully loaded 100 Hp turbine at 200 psia with u1=1163.3
BTU/lb, v1=2.65 ft3/lb and v1=400 fps. Exhaust is at 1 psia with u2=925 BTU/lb,
v2=294 ft3/lb and v2=1100 fps. The heat loss from the steam in the turbine is 10 251 BTU/lb
BTU/lb. neglect potential energy change and determine: 1014 lb/hr
a. The work per lb steam
b. The steam flow rate in lb/hr
25. An air compressor (an open system) receives 272 kg per min of air at 99.29 kPa
and a specific volume of 0.026 m3/kg. the air flows steady through the
compressor and is discharged at 689.5 kPa and 0.0051 m3/kg. The initial
-2954 kJ/min
internal energy of the air is 1594 J/kg; at discharge, the internal energy is 6241
J/kg. the cooling water circulated around the cylinder carries away 4383 J/kg of
air. The change in kinetic energy is 986 J/kg increase. Compute the work.
26. A centrifugal pump operating under steady flow conditions delivers 2270 kg/min
of water from an initial pressure of 82470 Pa to a final pressure of 275,800 Pa.
-458.1 kJ/min
The diameter of the inlet pipe to the pump is 15.24 cm and the diameter of the
discharge pipe is 10.16 cm. What is the work?
27. A turbine operates under steady flow conditions receiving steam at the following
state: pressure 1200 kPa, temperature 1880C, enthalpy 2785 kJ/kg, speed 33.3
m/s and elevation 3m. The steam leaves the turbine at the following state;
112.52 kW
pressure 20 kPa, enthalpy 2512 kJ/kg, speed 100 m/s and elevation 0m. Heat is
lost to the surroundings at the rate of 0.29 kJ/s. If the rate of steam flow through
the turbine is 0.42 kg/s, what is the power output of the turbine in kW?
28. Assuming that there are no heat effects and no frictional effects, find the kinetic
energy and speed of a 3220-lb body after it falls 778 ft from rest. Start with the 224 fps
steady flow equation, deleting energy terms which are irrelevant.
29. A reciprocating compressor draws in 500 cubic feet per minute of air whose 56.25 Hp
density is 0.079 lb/ft3 and discharges it with a density of 0.304 lb/ft3. At the
suction, p1=15 psia; at discharge, p2=80 psia. The increase in the specific
internal energy is 33.8 BTU/lb and the heat transferred from the air by cooling is
13 BTU/lb. Determine the work on the air in BTU/min and in Hp. Neglect change
in kinetic energy.
30. Steam enters a turbine with an enthalpy of 1292 BTU/lb and leaves with an
enthalpy of 1098 BTU/lb. The transferred heat is 13 BTU/lb. What is the work in 512.3 Hp
BTU/min and in Hp for a flow of 2 lb/s?
31. A thermodynamic steady flow system receives 4.56 kg per min of a fluid where
p1=137.90 kPa, v1=0.0388 m3/kg, v1=122 m/s, u1=17.16 kJ/kg. The fluid leaves
the system at a boundary where p2=551.6 kPa, v2=0.193 m3/kg, v2=183 m/s -486 kJ/min
and u2=52.80 kJ/kg. During passage through the system the fluid receives 3000
J/s of heat. Determine the work.
32. Air flows steadily at the rate of 0.5 kg/s through an air compressor, entering at 7
m/s speed, 100 kPa pressure nd, 0.95 m3/kg specific volume, and leaving at 5
m/s, 700 kPa, and 0.19 m3/kg. The internal energy of the air is 90 kJ/kg greater -122 kW
than that of the air entering. Cooling water in the compressor jackets absorbs
heat from the air at the rate of 58 kW. Compute the work in kW.
33. In a steady flow apparatus, 135 kJ of work is done by each kg of fluid. The
specific volume of the fluid, pressure, and speed at the inlet are 0.37 m3/kg, 600
kPa, and 16 m/s. The inlet is 32 m above the floor, and the discharge pipe is at
floor level. The discharge conditions are 0.62 m3/kg, 100 kPa, and 270 m/s. The -20.01 kJ/kg
total heat loss between the inlet and the discharge is 9 kJ/kg of fluid. In flowing
through this apparatus, does the specific internal energy increase or decrease,
and by how much?
34. Steam enters a turbine stage with an enthalpy of 3628 kJ/kg at 70 m/s and
leaves the same stage with an enthalpy of 2846 kJ/kg and a velocity of 124 m/s. 776.8 kJ/kg
Calculate the work done by the system.
35. A drum 6 inches in diameter and 40 inches long contained acetylene at 250
psia and 900F. After some of the acetylene was used, the pressure was 200 psia
and the temperature was 850F, 19.26%
a. What proportion of the acetylene was used? 2.105 ft3
b. What volume would the used acetylene occupy at 14.7 psia and 80 0F? R for
acetylene is 59.35 ft-lb/lb-0R
36. The volume of a 6x12 ft tank is 339.3 cubic feet. It contains air at 200 psig and
850F. How many 1 cubic feet drums can be filled to 50 psig and 80 0F if it is
1009
assumed that the air temperature in the tank remains at 85 0F? The drums have
been sitting around in the atmosphere which is at 14.7 psia and 80 0F.
37. It is planned to lift and move logs from almost inaccessible forest areas by
means of balloons. Helium at atmospheric pressure (101.325 kPa) and
temperature 21.10C is to be used in the balloons. What minimum balloon 33.3m
diameter (assume spherical shape) will be required for a gross lifting force of 20
metric tons?
38. Two vessels A and B of different sizes are connected by a pipe with a valve.
Vessel A contains 142 L of air at 2767.92 kPa, 93.33 0C. Vessel B, of unknown
volume, contains air at 68.95 kPa, 4.440C. The valve is opened and, when the 110.4 L
properties have been determined, it is found that pm=1378.96 kPa, tm=43.330C.
What is the volume of vessel B?
39. For a certain ideal gas R=25.8 ft-lb/lb-0R and k=1.09 cp=312.47 ft-lb/lb-0R;0.4016
a. What are the values of cp and cv? BTU/lb-0R
b. What mass of this gas would occupy a volume of 15 ft3 at 75 psia and 80 0F? cv=0.3685 BTU/lb-0R
c. If 30 BTU are transferred to this gas at constant volume in (b), what are the m=11.63 lb
resulting temperature and pressure? p2=76 psia
40. For a certain gas R=320 J/kg-K and cv=0.84 kJ/kg-K.
1.16 kJ/kg-K
a. Find cp and k
k-1.381
b. If 5 kg of this gas undergo a reversible non-flow constant pressure process
ΔU=1425.5 kJ
from V1=1.133 m3 and p1=690 kPa to a state where t2=5550C, find ΔU and
ΔH=1968.5 kJ
ΔH.
41. An automobile tire is inflated to 32 psig pressure at 50 0F. After being driven the
temperature rise to 750F. Determine the final gage pressure assuming the 34.29 psig
volume remains constant.
42. If 100 ft3 of atmospheric air at zero Fahrenheit temperature are compressed to a
volume of 1 ft3 at a temperature of 2000F, what will be the pressure of the air in 2109 psig
psi?
43. A 10 ft3 tank contains gas at a pressure of 500 psia, temperature of 85 0F and a
weight of 25 pounds. A part of the gas was discharged and the temperature and 15.43 lb
pressure changed to 700F and 300 psia, respectively. Heat was supplied and the 10 ft3
temperature was back to 850F. Find the final weight, volume and pressure of the 308.5 psia
gas.
44. Four hundred cubic centimeters of a gas at 740 mm Hg absolute and 18 0C
undergoes a process until the pressure becomes 760 mm Hg absolute and the 365 cc
temperature 00C. What is the final volume of the gas?
45. A motorist equips his automobile tires with a relief-type valve so that a pressure
inside the tire never will exceed 240 kPa (gage). He starts a trip with a pressure
of 200 kPa (gage) and a temperature of 230C in the tires. During the long drive,
0.0064 kg
the temperature of the air in the tires reaches 83 0C. Each tire contains 0.11 kg of
182.48 kPa
air. Determine
a. The mass of air escaping each tire,
b. The pressure of the tire when the temperature returns to 23 0C.
46. A 6-m3 tank contains helium at 400K and is evacuated from atmospheric
pressure to a pressure of 740 mm Hg vacuum. Determine
0.01925 kg
a. Mass of helium remaining in the tank
0.7123 kg
b. Mass of helium pumped out
1.886 kPa
c. The temperature of the remaining helium falls to 10 0C.
What is the pressure in kPa?
47. An automobile tire contains 3730 cubic inches of air at 32 psig and 80 0F
a. What mass of air is in the tire?
0.5041 lb
b. In operation, the air temperature increases to 145 0F. If the tire is inflexible,
17.53%
what is the resulting percentage increase in gage pressure?
0.0542 lb
c. What mass of the 1450F air must be bled off to reduce the pressure back to
its original value?
48. A spherical balloon is 40 ft in diameter and surrounded by air at 60 0F and 29.92
in Hg abs.
a. If the balloon is filled with hydrogen at a temperature of 70 0F and 2381 lb
atmospheric pressure, what total load can it lift? 2209 lb
b. If it contains helium instead of hydrogen, other conditions remaining the
same, what load can it lift?
49. A reservoir contains 2.83 m3 of carbon monoxide at 6895 kPa and 23.6 0C. An
evacuated tank is filled from the reservoir to a pressure of 3497 kPa and a
temperature of 12.40C, while the pressure in the reservoir decreases to 6205 0.451 m3
kPa and the temperature to 18.30C. What is the volume of the tank? R for Co is
296.92 J/kg-K
50. A gas initially at 15 psia and 2 ft3 undergoes a process to 90 psia and 0.60 ft3,
during which the enthalpy increases by 15.5 BTU; cv=2.44 BTU/lb-0R.
11.06 BTU
Determine:
3.42 BTU/lb-0R
a. ΔU
762.4 ft-lb/lb-0R
b. cp
c. R
51. For a certain gas, R=0.277 kJ/kg-K and k=1.384.
a. What are the value of cp and cv? 0.7214 and 0.004 kJ/kg-K
b. What mass of this gas would occupy a volume of 0.425 m 3 at 517.11 kPa 2.647 kg
and 26.70C 43.270C
c. If 31.65 kJ are transferred to this gas at constant volume in (b), what are the 545.75 kPa
resulting temperature and pressure?
52. Ten cubic feet of air at 300 psia and 4000F is cooled to 1400F at constant
volume. What are 209 psia
a. Final temperature 0
b. The work -420 BTU
c. The change in internal energy -420 BTU
d. The transferred heat -588 BTU
e. The change of enthalpy -0.581 BTU/0R
f. The change of entropy
53. There are 1.36 kg of gas, for which R=377 J/kg-K and k=1.25, that undergo a 999K
non-flow constant volume process from p1=551.6 kPa and t1=600C to p2=1655 -1260.5 kJ
kPa. During the process the gas is internally stirred and there are also added 2.253 kJ/K
105.5 kJ of heat. Determine
a. T2
b. The work input
c. The change in entropy
54. A group of 50 persons attended a secret meeting in a room which is 12 meters
wide by 10 meters long and a ceiling of 3 meters. The room is completely sealed
off and insulated. Each person gives off 150 kcal per hour of heat and occupies 33.10C
a volume of 0.2 cubic meter. The room has an initial pressure of 101.3 kPa and
temperature of 160C. Calculate the room temperature after 10 minutes.
55. A 1 Hp stirring motor is applied to a tank containing 22.7 kg of water. The stirring
action is applied for 1 hour and the tank loses 850 kJ/hr of heat. Calculate the
19.3C0
rise in temperature of the tank after 1 hour, assuming that the process occurs at
constant volume and that cv for water is 4.187 kJ/kg- 0C.
56. A closed constant-volume system receives 10.5 kJ of paddle work. The system
contains oxygen at 344 kPa, 278 K, and occupies 0.06 m3. Find the heat (gain or 12.49 kJ
loss) if the final temperature is 400K.
57. During an isothermal process at 880F, the pressure on 8lb of air drops from 80
421.2 BTU
psia to 5 psig. For an internally reversible process, determine
421.2 BTU
a. the work of a non-flow process
421.2 BTU
b. the work of a steady flow process
0
c. Q
0
d. ΔU and ΔH
0.7686 BTU/0R
e. ΔS
58. During a reversible process there are abstracted 317 kJ/s from 1.134 kg/s of a
0.301 m3/s
certain gas while the temperature remains constant at 26.7 0C. for this gas,
0.0498 m3/s
cp=2.232 and cv=1.713 kJ/kg-K. The initial pressure is 586 kPa. For both non-
3542 kPa
flow and steady flow process, determine
-317 kJ/s
a. V1, V2, p2
-1.058 kJ/K-s
b. Work
0
c. ΔS and ΔH
59. Air flows steadily through an engine at constant temperature, 400K. Find the
work per kilogram if the exit pressure is one-third the inlet pressure and the inlet
126.1 kJ
pressure is 207 kPa. Assume that the kinetic and potential energy variation is
negligible.
603.4 ft3
60. From a state defined by 300 psia, 100 ft3 and 2400F, helium undergoes and
-248.70F
isentropic process to 0.3 psig. Find
-5822 BTU
a. V2 and t2
-9698 BTU
b. ΔU and ΔH
5822 BTU
c. Ws
9698 BTU
d. Wn
0
e. Q and ΔS
0
61. An adiabatic expansion of air occurs through a nozzle from 828 kPa and 71 0C to 0.1193 m3/kg
138 kPa. The initial kinetic energy is negligible. For an isentropic expansion, -670C
compute the specific volume, temperature and speed at the exit section. 527.1 m/s
62. During a polytropic process, 10 lb of an ideal gas, whose R=40 ft-lb/lb- 0R and
cp=0.25 BTU/lb-0R, changes state from 20 psia and 400F to 120 psia and 3400F. n=1.356
Determine: ΔU=595.8 BTU
a. n ΔH=750 BTU
b. ΔU and ΔH ΔS=0.2543 BTU/0R
c. ΔS Q=162.3 BTU
d. Q Wn=-433.3 BTU
e. Non-flow work Ws=-587.6 BTU
f. Steady flow-work
P2=1184.9 kPa
63. Compress 4 kg/s of CO2 gas polytropically (pV1.2=C) from p1=103.4 kPa, W=-631.13 kJ/s
t1=600C to t2=2270C. Assuming ideal gas action, find p2, W, Q, ΔS as nonflow. Q=-193.8 kJ/s
ΔS=-0.4694 kJ/K-s
64. A perfect gas has a value of R=58.8 ft-lb/lb- 0R and k=1.26. if 20 BTU are added T2=563.8 0R
to 5 lb of this gas at constant volume when the initial temperature is 90 0F, find: ΔH=25.27 BTU
a. T2 ΔS=0.036 BTU/0R
b. ΔH ΔU=20.06
c. ΔS Wn=
d. ΔU
e. Work for non-flow process.
65. A reversible, non-flow, constant volume process decreases the internal energy
by 316.5 kJ for 2.268 kg of gas for which R=430 J/kg-K and k=1.35. For the
process, determine 0
a. The work -316.5 kJ
b. Q -0.7572 kJ/K
c. ΔS
The initial temperature is 204.4 0C.
66. A 10 ft3 vessel of hydrogen at a pressure of 305 psia is vigorously stirred by
paddles until the pressure becomes 400 psia. Determine
434 BTU
a. ΔU
-434 BTU
b. W
No heat is transferred, cv=2.434 BTU/lb-0R
67. Three pounds of a perfect gas with R=38 ft-lb/lb-0R and k=1.667 have 300 BTU
of heat added during a reversible non-flow constant pressure change of state.
The initial temperature is 1000F. Determine the 9190F
a. Final temperature 120 BTU
b. ΔH 180 BTU
c. W 0.3301 BTU/0R
d. ΔU
e. ΔS
68. While the pressure remains constant at 689.5 kPa the volume of a system of air
changes from 0.567 m3 to 0.283 m3. What are
a. Final temperature
b. ΔH
c. W
d. ΔU
e. ΔS
69. Four pounds of air gain 0.491 BTU/0R of entropy during a non-flow isothermal
process. If p1=120 psia and V2=42.5 ft3, find:
a. V1 and T1
b. W
c. Q
d. ΔU
70. If 10 kg/min of air are compressed isothermally from p1=96 kPa and V1=7.65
m3/min to p2=620 kPa, find the work, the change of entropy and the heat for:
A. Non-flow process
B. Steady flow process with v1=15 m/s and v2=60 m/s
71. One pound of an ideal gas undergoes an isentropic process from 95.3 psig and
a volume of 0.6 ft3 to a final volume of 3.6 ft3. If cp=0.124 and cv=0.093 BTU/lb-
0R, what are:
a. T2
b. P2
c. ΔH
d. W
72. A certain ideal gas whose R=278.6 J/kg-K and cp=1.015 kJ/kg-K expands
isentropically from 1517 kPa, 2880C to 965 kPa. For 454 g/s of this gas
determine,
a. Wn
b. V2
c. ΔU
d. ΔH
73. A polytropic process of air from 150 psia, 3000F, and 1 ft3 occurs to p2=20 psia
in accordance with pv1.3=C. Determine
a. T2 and V2
b. ΔU, ΔH and ΔS
c. Non-flow work
d. Steady flow work
74. The work required to compress a gas reversibly according to pV1.30=C is 67790
J, if there is no flow. Determine ΔU and Q if the gas is
a. Air
b. Methane. For methane, k=1.321, R=518.45 J/kg-K, cv=1.6187, cp=2.1377
kJ/kg-K
75. The working substance for a Carnot cycle is 8 lb of air. The volume at the
beginning of isothermal expansion is 9 cubic feet and the pressure is 300 psia.
The ratio of expansion during the addition of heat is 2 and the temperature of the
cold body is 900F. Find:
a. QA
b. QR
c. V3
d. P3
e. V4
f. P4
g. Pm
h. The ratio of expansion during the isentropic process
i. Overall compression ratio.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 8 ThingsDocument184 pagini8 ThingsLester Garcia33% (3)
- ProblemSetNo.1 Thermodynamics PDFDocument11 paginiProblemSetNo.1 Thermodynamics PDFDeliadina B. QuintoÎncă nu există evaluări
- H. Sta. Maria - Thermodynamics (Selected and Modified Problems)Document20 paginiH. Sta. Maria - Thermodynamics (Selected and Modified Problems)HectorCabzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics - Ideal GasDocument11 paginiThermodynamics - Ideal GasMae Belle AngayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mod. 2 Basic ElectricalDocument18 paginiMod. 2 Basic Electricalderping lemonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set No. 1: Ee 420: Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument16 paginiProblem Set No. 1: Ee 420: Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringWingel Lullaby100% (1)
- Problem SetDocument1 paginăProblem SetJohn Lester Ocampo30% (10)
- THERMO - Midterm ExamDocument2 paginiTHERMO - Midterm ExamKarl Christian FajardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Enthalpy - Entropy Diagram For Steam (MOLLIER CHART) : Problems On Processes of VaporsDocument5 paginiThe Enthalpy - Entropy Diagram For Steam (MOLLIER CHART) : Problems On Processes of VaporsEnriv Yasilad50% (4)
- Fluid MechanicsDocument6 paginiFluid MechanicsLorde Wagayen100% (1)
- Ther 1 - 111114Document33 paginiTher 1 - 111114So Nny0% (1)
- Laboratory Activity No 1rev3Document6 paginiLaboratory Activity No 1rev3Queen TvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2.4 Enthalpy and 2ND Corollary of 1ST LawDocument6 paginiModule 2.4 Enthalpy and 2ND Corollary of 1ST LawsubyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edited Thermo Problems 1Document5 paginiEdited Thermo Problems 1Darlene Bacatan AmancioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Day 2 Power Plan1Document1 paginăDay 2 Power Plan1Dennis AleaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCI 403 BSIE Batangas State University Physics 1 Electrostatics and Electricity Problem SetDocument2 paginiSCI 403 BSIE Batangas State University Physics 1 Electrostatics and Electricity Problem SetHANNAH JAZZLYN LACIDAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set 2 - Fluid MachineryDocument1 paginăProblem Set 2 - Fluid MachineryRonard Pa–aÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Problems Thermodynamics Plate 1Document2 paginiSample Problems Thermodynamics Plate 1Mahusay Neil DominicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part 1 Properties of FluidsDocument6 paginiPart 1 Properties of FluidsJoren Huerno0% (1)
- Energy Concepts For Students FileDocument19 paginiEnergy Concepts For Students Filech0k3 iii100% (1)
- MEEN 20052 - Week 2 - Salamat, Andre Agassi D.Document4 paginiMEEN 20052 - Week 2 - Salamat, Andre Agassi D.andreagassiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Isobaric ProcessDocument24 paginiIsobaric ProcessWhindy Bagawisan CasugaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Solution Manual - Compress PDFDocument7 paginiChapter 3 Solution Manual - Compress PDFreyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Ideal Gas Processes - Lecture 1Document7 paginiChapter 4 Ideal Gas Processes - Lecture 1Juan KakakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Reheat Cycle With Two Stage of Reheating Is Executed With Steam Expanding Initially From 90 Bar and 530c The Two Reheater Pressure Are 10 BarDocument1 paginăA Reheat Cycle With Two Stage of Reheating Is Executed With Steam Expanding Initially From 90 Bar and 530c The Two Reheater Pressure Are 10 BarJerico Andrada50% (4)
- Chapter 7 Gas Compressors 1Document11 paginiChapter 7 Gas Compressors 1Ervenjee Basco100% (1)
- Properties of Fluids ADocument43 paginiProperties of Fluids AGlenn Frey LayugÎncă nu există evaluări
- Word Version - Thermo 2Document209 paginiWord Version - Thermo 2Kristian Paolo De Luna100% (1)
- Thermodynamics 1 Practice Problems - Chapter 2Document5 paginiThermodynamics 1 Practice Problems - Chapter 2JairoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: Lab Exp No: 2: Ee-424 Circuits 1 Laboratory Activity 3 Kirchoff'S LawDocument25 paginiName: Lab Exp No: 2: Ee-424 Circuits 1 Laboratory Activity 3 Kirchoff'S LawJohnjoseph VeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prelims ThermoDocument96 paginiPrelims ThermoJoshua BarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1Document1 pagină1Carla Berg0% (1)
- 20 The Temperature of An Ideal Gas Remains Constant While The Absolute Pressure Changes From 103Document5 pagini20 The Temperature of An Ideal Gas Remains Constant While The Absolute Pressure Changes From 103Aproski tadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved Problem 04Document8 paginiSolved Problem 04Abdullah SimpsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worktext in Electric Circuits 2Document247 paginiWorktext in Electric Circuits 2Chris Real Pabia0% (1)
- ENERCON - BrizuelaDocument13 paginiENERCON - BrizuelaEzekiel Brizuela100% (1)
- ME 1a - TOPIC 2 First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument10 paginiME 1a - TOPIC 2 First Law of Thermodynamicsjohn reyche garsuta100% (3)
- ElevatorDocument26 paginiElevatorChristine Joyce Bunyi17% (6)
- chapter 1 Fluid MechanicsDocument37 paginichapter 1 Fluid MechanicsHe YapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 3: Velocities in MachinesDocument13 paginiLesson 3: Velocities in MachinesMark MarkÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Substitution Suggested by The EquationDocument11 pagini11 Substitution Suggested by The EquationMia Manalo100% (1)
- Properties of FluidsDocument57 paginiProperties of FluidsPatricia SorianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Simple StrainDocument21 pagini2 Simple StrainFelix Violeta0% (1)
- Energy ConversionDocument24 paginiEnergy ConversionJohn Christian CoronadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common ConstantsDocument3 paginiCommon Constantskristan7Încă nu există evaluări
- Final Round and ClincherDocument8 paginiFinal Round and Clincherponcatoera0% (2)
- Module 1 Answer Key MachinesDocument4 paginiModule 1 Answer Key MachinessdanharoldÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME 2121 Module PDFDocument96 paginiME 2121 Module PDFGreen BrainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ideal Gas Equation and EntropyDocument27 paginiIdeal Gas Equation and EntropyJude Roswel GenerilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machine Design QuizDocument2 paginiMachine Design QuizMarc Graham NacuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Btu FT HR FT 2 ° F Q KA (Tmax Tmin) X Btu FT HR FT ° F FTDocument6 paginiBtu FT HR FT 2 ° F Q KA (Tmax Tmin) X Btu FT HR FT ° F FTbryant SiboaÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Study Resource Was: EE 201 Experiment (4) Section: 052Document5 paginiThis Study Resource Was: EE 201 Experiment (4) Section: 052Johnjoseph VeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 5-6Document15 paginiProblem 5-6Robert Ryan Santiago100% (2)
- Fluid Statics PDFDocument28 paginiFluid Statics PDFAnthony Leire MontealtoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Joyce M. Magdaong - Experiment 4Document7 paginiJoyce M. Magdaong - Experiment 4Joyce Manito MagdaongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermo Chapter1Document11 paginiThermo Chapter1Mon Jhio San JuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ThermoDocument2 paginiThermoKeymark SioÎncă nu există evaluări
- ThermodynamicsDocument1 paginăThermodynamicsZinzinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Problem Module 1Document3 paginiDesign Problem Module 1Ryan Philip CatapangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics 1: Gage Vac Vac AbsDocument2 paginiThermodynamics 1: Gage Vac Vac AbsItsMeRyanCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plane - Solid GeometryDocument16 paginiPlane - Solid GeometryCaro Kan LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exponents PDFDocument1.136 paginiExponents PDFCaro Kan Lopez100% (2)
- Fliuids MechanicsDocument8 paginiFliuids MechanicsCaro Kan LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probability, Surveyng, Transpotation EngringDocument13 paginiProbability, Surveyng, Transpotation EngringCaro Kan LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differential EquationsDocument4 paginiDifferential EquationstuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering MechanicsDocument16 paginiEngineering MechanicsCaro Kan LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diesel Electric PowerplantDocument3 paginiDiesel Electric PowerplanttuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AlgebraDocument26 paginiAlgebratuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differential and Integral CalculusDocument10 paginiDifferential and Integral CalculusCaro Kan LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- PROBLEM - SET (3) - EconomyDocument3 paginiPROBLEM - SET (3) - EconomytuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TrigonometryDocument3 paginiTrigonometryCaro Kan LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Processes IntroductionDocument50 paginiIndustrial Processes IntroductiontuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Feeders and SilosDocument3 paginiFeeders and SilosAngelicaBeatrizGutierrezBalmes0% (2)
- Industrial ProcessesDocument5 paginiIndustrial ProcessestuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multi-Storage CH1Document8 paginiMulti-Storage CH1tuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Feeders and SilosDocument3 paginiFeeders and SilosAngelicaBeatrizGutierrezBalmes0% (2)
- Auto CADDocument1 paginăAuto CADtuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FDP ECE BrochureDocument3 paginiFDP ECE BrochureBalasanthosh SountharajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CMA June 2018 ExamDocument2 paginiCMA June 2018 ExamMuhammad Ziaul HaqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practices For Lesson 3: CollectionsDocument4 paginiPractices For Lesson 3: CollectionsManu K BhagavathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agent CompatibilityDocument9 paginiAgent Compatibilityajilani2014Încă nu există evaluări
- Sample FLAT FILE FOR SAPDocument6 paginiSample FLAT FILE FOR SAPMahadevan KrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daq 7steps To Success SampleDocument6 paginiDaq 7steps To Success SamplerevatharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Equipment in Hazardous LocationsDocument41 paginiElectrical Equipment in Hazardous LocationsSAYEDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adly 50 RS Parts ListDocument50 paginiAdly 50 RS Parts ListZsibrita GyörgyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab ManualDocument9 paginiLab ManualMohit SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Modeling and Design Considerations of Lithium-Ion BatteriesDocument8 paginiThermal Modeling and Design Considerations of Lithium-Ion BatteriesVarun Gupta100% (1)
- C3704 2018 PDFDocument122 paginiC3704 2018 PDFHaileyesus Kahsay100% (1)
- English Core 2005Document5 paginiEnglish Core 2005thiripura sundariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perform Cover Hole DrillingDocument12 paginiPerform Cover Hole Drillingjulianusginting00Încă nu există evaluări
- Speed Breaker Electric GenerationDocument72 paginiSpeed Breaker Electric Generationparas bhogulkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communication Technology The New Media in Society PDFDocument2 paginiCommunication Technology The New Media in Society PDFElma0% (5)
- TwistedBrush Pro Studio VideosDocument63 paginiTwistedBrush Pro Studio VideosPraveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3CP.1.3 PaperDocument4 pagini3CP.1.3 PaperAlexander ChekalinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 BoilersDocument83 pagini2 BoilersSurasan ThepsiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brakel Eura Excellent: Highly Insulated Louvred VentilatorDocument4 paginiBrakel Eura Excellent: Highly Insulated Louvred VentilatorhjduarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erection Procedures of Earthing Arrangements TNC TNS TNCS and TTDocument7 paginiErection Procedures of Earthing Arrangements TNC TNS TNCS and TTPierre Enrique Carrasco Fuentes0% (1)
- Polymer and Web ComponentsDocument26 paginiPolymer and Web ComponentsAdjetey Adjei-laryeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project SynopsisDocument2 paginiProject SynopsisEkam JotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boq IDocument7 paginiBoq IAmolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Collapsible Steering ColumnDocument2 paginiCollapsible Steering ColumnKrishna KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidance On Shipboard Towing and Mooring EquipmentDocument11 paginiGuidance On Shipboard Towing and Mooring EquipmentNuman Kooliyat IsmethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summative Exam For Ignition SystemDocument1 paginăSummative Exam For Ignition SystemJestoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supplied in A Compact and Elegant Enclosure, The A125 Adds Style To The Most Visible Component of An IPTV Deployment.Document2 paginiSupplied in A Compact and Elegant Enclosure, The A125 Adds Style To The Most Visible Component of An IPTV Deployment.Basava RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foxess 10,5K G10500 220VDocument2 paginiFoxess 10,5K G10500 220Valex reisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thps3 Manual UkDocument15 paginiThps3 Manual Uk2061551826073Încă nu există evaluări
- Plastic, Rubber & Recycling IndustryDocument7 paginiPlastic, Rubber & Recycling IndustryPassionate_to_LearnÎncă nu există evaluări