Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Filogenia de Briofitos Sensulato
Încărcat de
YuyitoS2714Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Filogenia de Briofitos Sensulato
Încărcat de
YuyitoS2714Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
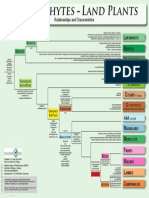
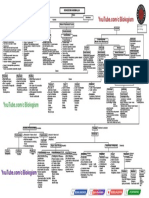
Bryophyte Phylogeny Nonvascular Land Plants (Liverworts, Mosses, Hornworts) – Systematics and Characteristics
Treubiales
Anacrogynous. Lvs in three rows (2 lateral, succubous, 1 dorsal lobule). Oil bodies scattered. Mucilage on ventral surface
Central strand parenchymatous, with glomerophycotean fungus
Di- or monoicous. Single S per gynoecium. Gemmae in axils of dorsal lobules Treubiaceae
Subterranean axis. Lvs mostly isophyllous. Rhizoids –
shoot calyptra + Central strand +, cells thin-walled, perforated
Haplomitriales
Di- or monoicous. Gametangia lateral, bracts –. Seta +, massive
Blepharoplast: lamellar strip and spline < 90 microtubules, aperture on left side. Several S/gynoecium
Haplomitriaceae
M
CAP 4-valved; walls unistratose. Elaterophore basal. Elaters filamentous. Asex repro –
Thalli winged ("leafy"), 2 ventral scale rows. Air chambers –, gametangiophores –
a Ventral "auricles" with Nostoc. Dioicous. AN dorsal, solitary. AR dorsal, behind apex
Blepharoplast: marchantialean. CAP 4(-6)-valved
r Elaters 2-helical. Elaterophore basal, rudimentary
Gemmae receptacles flasked-shaped (unique in liverworts) Blasiales Blasiaceae
c Air chambers +, chlorophyllose filaments –
h Rhizoids smooth
Neohodgsoniales
Ventral scales +, appendages –
a Liverworts
Archegoniophores branched
Gemmae Neohodgsoniaceae
n Thalli rosettes or stems; axes: winged or lobes leaf-like
t Air chambers –, mucilage cells –, pores –
Sphaerocarpales
AR and S in pear-shaped involucres (dorsal on thallus)
i Rhizoids +, smooth
Seta +, very short. CAP cleistocarpous. Elaters – Riellaceae Sphaerocarpaceae
o Thallus differentiated; air pores +
p Air chambers +, chlorophyllose filaments +, storage parenchyma +
Aytoniaceae Cleveaceae Conocephalaceae Cyathodiaceae
Marchantiales
Ventral scales +. Rhizoids +, pegged or smooth
h Di- or monoicous. Antheridiophores +, archegoniophores +. AR ventral, involucre usu. +
Pseudoperianths usu. –. Seta +, short. Elaters usu. 2-3-helical. Gemmae Dumortieraceae Exormothecaceae Lunulariaceae
y Thallus differentiated. Air pores +/– Marchantiaceae Monosoleniaceae Targioniaceae
t
Air chambers +, chlorophyllose filaments –. Ventral scales +. Rhizoids +
Di- or monoicous. AN, AR dorsal, involucre +/–. S embedded or sessile
a CAP cleistocarpous. Elaters –, spores large (40-200 µm)
Asex repro occ tubers Ricciales Ricciaceae Oxymitraceae
Pelliaceae: Thallus. Branching pseudodichotomous. Di- or monoicus
AN individual in covered chambers (dorsal). AR in distinct groups (dorsal). Involucre +, short-tubular or flaplike
CAP with 4 valves. Elaterophores basal. Asex. reprod. very rare
Pelliales
Thallose or foliose
Rhizoids +. Oil bodies +
Perforated water-conducting cells
Noterocladaceae: Thalli leafy. Lvs succubous. Branching lateroventral. AN in ostiolate chambers. AR clustered, involucre +
CAP spheroidal. Seta +, <10 cm. Spores large (<100 µm), "multicellular", germination endosporic +/–. Elaterophores basal Noterocladaceae Pelliaceae
Mycothallus with endophytic Glomeromycota Thallose, leaflike lobes succubous, obliquely inserted
Gametangia protective structures + Rhizoids purplish (rarely pale brown)
Gametangial ontogeny without apical cells AN and AR in simple acropetal sequence
Blepharoplast: plastid and associated posterior
mitochondrion positioned at cell terminus
S protected by caudocalyx; CAP wall 2-6 stratose. Spores sculptured
Asex repro fleshy stems (stolons), subterranean tubers, endogenous gemmae Fossombroniales Fossombroniaceae Petalophyllaceae
Zygote division transversal: epi- and hypobasal cells Pelliidae Thallose or leafy, prostrate, erect or dendroid
Seta + Central strand +, cells thick-walled, with pores
CAP without columella AN/AR clustered dorsally on thallus
Elaters (unicellular). Stomata –
ca. 5000 spp
Lunularic acid
S protected by inner involucre or shoot calyptra
Seta +, massive. CAP 2-14 valved, wall bistratose Pallaviciniales Pallavicinaceae
Apical cell with 2 cutting faces (unique in leafy liverworts)
Lvs bilobed, smaller leaf lobe usu. a complex water sac; trigones very large
Evidence of zoophagy. Amphigastria –
Gametangiophores on short lateral-axillary branches, gynoecia partly sterile. Perianth elongate
CAP spherical to short-ovoid. Germination endosporic. Usu. epiphytic Pleuroziales Pleuroziaceae
thalloid Thalli linear, winged; branching dichotomous; midrib distinct (Metzgeriaceae) or thalli irregularly or
lvs from 3 prim. initials pinnately branched (Aneuraceae). Central strand –. Unicellular hairs +/–. Oil bodies +/– or very small
Metzgeriales
Di- or autoicous. Gametangia on short branches arising from midrib or reduced lateral branches
Metzgeriidae
Shoot calyptra +. Pseudoperianth –. Seta +. CAP 4-valved, elaterophore apical
Elaters 1- or ehelical. Asex repro – or gemmae/adventive thalli/caducous branches Aneuraceae Metzgeriaceae
Cauloid 1-3-pinnate. Rhizoids scarce
Lvs incubous, transversely inserted, bilobed (and further subdivided); margins ciliate
Oil bodies 15-40/leaf cell. Amphigastria +, bilobed, ciliate
Dioicous. Gametangiophores apically on shoot. Perianth bottle-shaped, perigynium –
CAP wall 4-7-stratose. Germination exo-/endosporic Ptilidiales Ptilidiaceae
Branches lateral, exogenous
Lvs incubous, unequally 2-/3-lobed, often conduplicate bilobed, lobules often inflated water sacs;
amphigastria +/–. S enclosed by a perianth and CY or shoot calyptra or stem perigynium
Jubulaceae Frullaniaceae Lejeuneaceae Lepidolaenaceae
leafy
lvs from 2 prim. initials
Germination endosporic
Gemmae + (rare). Fungal endosymbionts – Porellales Porellaceae Radulaceae
Branches exo- or endogenous, ventral or lateral. Lvs succubous, incubous, or transverse,
Jungermanniidae undivided or variously lobed, sometimes conduplicate bilobed, but then usu. with the smaller
Acrobolbaceae Balantiopsaceae Calypogeiaceae
Jungermanniales
lobe(s), or lobules, dorsal (inflated water sacs rare); amphigastria +/–
S enclosed by a perianth or stem perigynium. Spore germination usu. exosporic
Gemmae +/–. Fungal endosymbionts + Cephaloziaceae Cephaloziellaceae Geocalycaceae
Gymnomitriaceae Jungermanniaceae Lepidoziaceae
Cladocarpous. Main stems with capitulum: central parenchyma, internal cylinder, cortex
Branches fascicled, rarely –; retort cells +/–. Lvs with hyalocysts and chlorocysts Lophoziaceae Scapaniaceae Trichocoleaceae
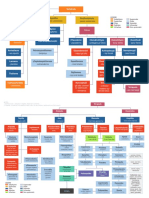
Sphagnales
Dioicous, occ. autoicous. AN single, subglobose, long-stalked in lvs axils
AR terminal on short branches in capitulum. Spore sac dome-shaped
Spores in tetrads, trilete mark +. CY +. Bogs and mires (peat mosses) Sphagnaceae Flatbergiaceae Ambuchananiaceae
Protonema –. Rhizoids –. Acrocarpous. Complex shoot system of rhizomatous axes, erect leafy shoots
Perforated water-conducting cells
Dioicous. AN 1-2 in lvs axils of (3-)4-lobed lvs. AR solitary and scattered (1-4/shoot). S (only in T. ceratophylla, rarely encountered)
Stomata on S –. Seta persistent. CAP twisted, dehisce along single slit. CY +
Asex repro by deciduous lvs or shoots Takakiales Takakiaceae
Central strand –. Lvs cells (rounded-)quadrate. Costa +/– homogeneous or –
Autoicous, rarely syn- or dioicous. AN without specialized cap. Seta –
Mosses CAP elevated by a pseudopodium; valves 4-10, attached at apex
Spore sac dome-shaped. Germination endosporic. CY small, usu. bistratose
Predom. cool-temp and trop-mont Saxicolous Andreaeaeales Andreaeaceae
Central strand –. Lvs cells (rounded-)quadrate. Costa +
Dioicous. Perichaetia developing after fertilization. AN without specialized cap
Seta short, massive. CAP valves irregular (often 4-5 main and 1-2 shorter ones), also separate
Andreaeobryales Andreaeobryaceae
B
at apex Spore sac dome-shaped. Germination endosporic. CY covering entire CAP
acro-
r carpous Central strand +/–. Lvs cells parenchymatous. Costa +, homogeneous
Autoicous. CAP erect, symmetric, cylindric, stomata +/–. Annulus –
y Operculum +. PS of 4 teeth.CY small, mitrate, glabrous. Gemmae + (Tetraphis)
Predom. north-temp. On various substrates in moist sites Tetraphidales Tetraphidaceae
o Protonema short-lived or persistent. Subterranean root-like "rhizome". Central strand of hydroids and leptoids
p Costa complex (Polytrichum-type), often broad, with adaxial lamellae
Polytrichales
Dioicous, rarely autoicous. Perigonia often conspicuous (splash cups). Seta +. CAP erect to horizontal,
h rounded or 2-4-angled; stomata +. PS of 16, 32 or 64 teeth, CAP with epiphragm. Spores small (up to 60x106/CAP)
CY mitrate or cucullate, hairy to glabrous often covering CAP. Largest terrestrial mosses Oedipodiaceae Polytrichaceae
y Protonema persistent. G reduced; ♂ of one leaf surrounding single AN
t PS
(nemato-
Lvs ecostate. Dioicous. Seta +. CAP usu. asymmetric, flattened on upper side
Annulus +. Operculum +. PS of Buxbaumia-type;
a Buxbaumiales
dontous)
hydroids exostome + (short teeth in 1-4 rings; endostome + (membranaceous); parastome +
CY small, mitrate or cucullate Buxbaumiaceae
Protonema short-lived, funnel-shaped. Central strand –
Lvs 2(-3)-stratose. Costa +. Dioicous. Perichaetial lvs ciliate above, costa long-excurrent
Seta + very short. CAP asymmetric, stomata phaneropore. Annulus +. Operculum +
Protonema thallose. Leafy
Lvs cells parenchymatous
PS of Buxbaumia-type (exostome – or rudimentary, endostome +, parastome –)
CY small, mitrate Diphysciales Diphysciaceae
Rhizoids multicellular Protonema short-lived. Leafy stems short from subterranean axes; central strand –
Mykorrhiza – Cladocarpous. Lvs cells usu. collenchymatous. Costa + (in Gigaspermum –)
Gigaspermales
Gametangial ontogeny with apical cells Par- or synoicous. Seta + (very short)
Blepharoplast: plastid and associated
posterior mitochondrion positioned F
CAP gymnostomous or cleistocarpous. Stomata with 2 guard cells
Spores large. CY small, mitrate, fugacious. Gemmae +
Gigaspermaceae
along inner nuclear surface; u
n Protonema short-lived. Central strand +. Lvs a cells rectangular to hexagonal. Costa +
occurrence of stray microtubules Aut- or paroicous, rarely syn- or polyoicous. Seta +. CAP symmetric or asymmetric,
a
Seta + operculate or rarely cleistocarpous; stomata phaneropore or cryptopore,
Funariales
r
CAP with PS and columella
Elaters –
protonema
filamentous in
ii
d
slit-like, each with a single guard cell. Annulus+/–. Operculum +. PS of Funaria-type or –
CY large, cucullate or mitrate, typically lobed Disceliaceae Encalyptaceae Funariaceae
Stomata on S chloro- and a
ca. 13,000 spp.
caulonema
e Central strand +. Lvs in 8 rows, base sheathing
Lvs cells in sheath linear, in limb quadrate to hexagonal, mamillose. Costa +
Di- or autoicous. Seta +. CAP inclined to pendulous, stomata phaneropore
Annulus +. Operculum +. PS +, exostome of 16 large teeth;
endostome of 64 filaments from basal membrane. CY cucullate, often persistent Timmiales Timmiaceae
Protonema short-lived or rarely persistent
Acrocarpous, occ. cladocarpous. Central strand +/–
Lvs cells quadrate, rectangular, or more rarely elongate Bruchiaceae Calymperaceae Catoscopiaceae
Alar cells often differentiated
Costa + (Dicranum-type, leucobryoid, or reduced). PS +/– Dicranales Dicranaceae Ditrichaceae Fissidentaceae
Protonema short-lived or rarely persistent. Acrocarpous, occ. cladocarpous Leucobryaceae Rhabdoweisiaceae
Central strand usu. +. Lvs cells often papillose, glass hairs often +
Alar cells rarely differentiated
PS
haplo-
Costa + or reduced, Pottia-type. PS usu. + (pottioid) or –
Often xerophytes of "harsh environments" Pottiales Pottiaceae Ephemeraceae
lepideous
Protonema short-lived. Acrocarpous, occ. cladocarpous
Central strand usu. +
Lvs cells often incrassate, sinuous, glass hairs common. Alar cells +/–
Grimmiales
D
i
c
Costa + (Dicranum-type). PS usu. + (seligerioid)
Usu. saxicolous Grimmiaceae Seligeriaceae
r
Protonema globular or filamentous
a
Acro-, rarely cladocarpous. Central strand –
stomata n
Hedwigiales
Pseudoparaphyllia +. Costa usu. –. CAP immersed or exserted
ii
acro-
d
Annulus –. PS usu. –. Spore germination exo- or endosporic
CY cucullate, smooth, glabrous
Hedwigiaceae Helicophyllaceae Rhacocarpaceae
a
carpous e
Stems tomentose, central strand +. Lvs often sheathed, limb narrow
occ. Lvs cells mamillose or papillose. Costa +. Di-, syn-, par-, or autoicous
Bartramiales
clado- Perigonia occ. splash cups. Seta +. CAP globose ("apple mosses")
PS of Bryum-type +/–; Annulus –. Operculum +
carpous
CY usu. minute, cucullate. Asex. repro: deciduous branchlet and bulbils Bartramiaceae
Acrocarpous. Central strand +
Lvs cells usu. rhombic. Costa +. Di- or autoicous
Splachnales
CAP neck often differentiated into broad and colored hypophysis
PS
diplo-
PS usu. +
Often coprophytes, spores fly-dispersed Meesiaceae Splachnaceae
lepideous-
alternate
Acrocarpous. Pseudoparaphyllia usu. –
Lvs cells rhombic-hexagonal. Costa +
B
r
Seta +. CAP often pyriform, pendulous ("pear mosses")
PS +/– (Bryum-type) Bryales Bryaceae Mniaceae Plagiomniaceae
y
i Acro- or cladocarpous. Central strand –. Upper lvs cells rounded, occ. elongate, thick-walled, usu.
d papillose Costa +. Gonio- or cladautoicous, dioicous, or phyllodioicous Seta +
Orthotrichales
a CAP immersed or exserted, smooth or 8- (rarely 16-)ribbed, stomata phaneropore or cryptopore
e PS + (Orthotrichum-type) or reduced. Annulus – or rudimentary. Operculum +. CY +, often hairy
Gemmae +/–. Saxicolous, corticulous
Orthotrichaceae
Acrocarpous (not Hymenodon). Central strand +. Costa +
Aut-, par-, or dioicous, rarely heteroicous. Seta +
Orthodontiales
CAP erect to horizontal, often furrowed, stomata phaneropore
Liverworts
Annulus –. Operculum +. PS reduced, cilia –. Spores ± papillose
CY cucullate. Axillary propagules or rhizoidal gemmae Orthodontiaceae
Mosses Acro- or pleurocarpous. Central strand +
Lvs cells rounded-hexagonal. Costa +. Di-, aut-, or synoicous
Calomniaceae Cyrtopodaceae Mitteniaceae
Rhizogoniales
Perichaetia basally in tomentum. Seta +, short or long
Hornworts CAP widest at orifice. PS +/–. CY cucullate
Lycophytes
Predom. trop. mostly on forest floor Rhizogoniaceae Spiridentaceae
Pl tomentose. Acrocarpous (Aulacomnium) or pleurocarpous
Ferns pleurocarpids Central strand +. Lvs cells rounded-hexagonal, smooth or papillose
Aulacomniales
(incl. horsetails) Costa +. Di- or autoicous. Perichaetia lateral. Seta +
Theodor C. H. Cole, Dipl. Biol. Palmferns
CAP often striate to sulcate. Annulus +. Operculum +. CY cucullate
Gemmae-bearing pseudopodia (Aulacomnium). Predom. temp. Aulacomniaceae
Institute of Pharmacy and Ginkgo
Ephedra
Pl often stipitate ("dendroids")
Molecular Biotechnology Welwitschia
Central strand +/–. Pseudoparaphyllia +, foliose
Braithwaiteaceae Hypnodendraceae
Hypnodendrales
Seed Gymnosperms Gnetum
Heidelberg University Plants Conifers
Costa +/–. Seta +. Operculum +. PS +/–
Predom. trop.
Im Neuenheimer Feld 364
ANA grade Pterobryellaceae Racopilaceae
D-69120 Heidelberg, Germany Central strand –. Paraphyllia +/–. Lvs plicate
Magnoliids cells ± incrassate. Costa +, double or –
Ptychomniales
Dioicous or phyllodioicous. Seta +. CAP stomata +/–. Annulus +/–
Angiosperms Monocots Spore germination occ. precocious. CY usu. cucullate
Gemmae +. Trop. to south-temp. Usu. epiphytic
Garovagliaceae Ptychomniaceae
Fabids core pleurocarpids Central strand +/–. Paraphyllia (–)
only pleurocarpous Pseudoparaphyllia rare
Daltoniaceae Hookeriaceae Hypopterygiaceae Leucomiaceae
Hookeriales
lvs cells prosenchymatous
Malvids costa homogeneous or – Lvs cells often large, lax
Rosids PS Bryum-type Costa +, single/double, rarely –
Prof. Dr. Hartmut H. Hilger Lamiids homocostate
Operculum +. CY usu. mitrate Pilotrichaceae Saulomataceae Schimperobryaceae
Institute of Biology pleurocarps
Campanulids Central strand +/–
Botany – Morphology and Systematics Asterids Pseudoparaphyllia usu. + Amblystegiaceae Anomodontaceae Brachytheciaceae Calliergonaceae
Freie Universität Berlin
Altensteinstr. 6
Alar cells often +. CY cucullate
> 4200 spp (ca. 1/3 of all mosses) Hypnales Campyliaceae Cryphaeaceae Hypnaceae Hylocomiaceae Hypopterygiaceae
D-14195 Berlin, Germany Lembophyllaceae Leskeaceae Meteoriaceae Miyabeaceae
Neckeraceae Plagiotheciaceae Pterobryaceae Pylaisiadelphaceae
Angiosperm A Sematophyllaceae Thuidiaceae Trachylomaceae
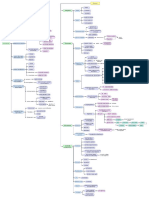
Phylogeny n Nostoc in longitudinal canals. Pyrenoid –
Poster t
Spores yellow, smooth, monolete mark +
Pseudoelaters long, usu. unicellular Leiosporocerotales Leiosporocerotaceae (Leiosporoceros)
h
Hornworts o AN jacket of 4 cell tiers
Tracheophyte c
Spores dark-brown/blackish, trilete mark +, spinose
Pseudoelaters helical thickenings partly present Anthocerotales Anthocerotaceae (Anthoceros, Sphaerosporoceros) Foliocerotaceae (Folioceros)
Phylogeny
Poster Thallus orbicular or strap-like, often rosettes e AN 2-8 per chamber
Nostoc in schizogenous slime cavities
r S with/without stomata
(mostly ventral via mucilage clefts)
Chloroplast usu. 1/cell with pyrenoid
Oil droplets + o
Spores yellow-blackish, trilete mark +, equatorial girdle +
Pseudoelaters sometimes – Notothyladales Notothyladaceae (Notothylas, Phaeoceros, Paraphymatoceros, Hattorioceros, Mesoceros)
Bryophyte
Water-conducting cells –
AN 1–many, of endogenous origin t AN 1-3 per chamber
AR single, embedded on dorsal thallus surface
o AN jacket Thalli narrow, lingulate. Pyrenoid –
Phylogeny
Poster
Blepharoplast: spline of 12 microtubules (inaperturate),
lamellar strip rhomboidal,
basal bodies 2 of equal size, side by side p
cells
irregularly
Dioicous. Spores yellow, later darkening
Pseudoelaters without helical thickenings Phymatocerotales Phymatocerotaceae (Phymatoceros)
arranged
Zygote division longitudinal, three-tiered embryo
Seta –. S mostly horn-like, h AN one per chamber
growing from base by indeterminate meristematic activity,
y S without stomata
• hypothetical tree based on molecular phylogenetic data (Feb. 2013)
• branch lengths deliberate, not expressing actual time scale position of
many characters on tree unclear; some minor orders/families omitted
columella well or poorly defined. Stomata on S
Pseudoelaters (mostly multicellular)
Spore production continuous t
Spores transparent or yellow
Pseudoelaters with helical thickenings Dendrocerotales Dendrocerotaceae (Dendroceros, Megaceros, Nothoceros, Phaeomegaceros)
• if a character is marked as being a potential synapomorphy at a particular node,
a
© The Authors (CC-BY)
Lignans +, flavonoids –
this does not mean that all members of that clade possess that character ca. 200 spp
• Phylogenetic References: Judd W et al. (2007); Simpson M (2010); Soltis DE et al. (2005);
Cox et al. (2010); Knoop (2010); Villarreal et al. (2010); Shaw et al. (2011)
• Characters from: Frey et al. (2009) and Goffinet/Shaw (2009); Ligrone et al. (2012)
• Abbreviations: G gametophyte, S sporophyte, AR archegonia, AN antheridia,
CAP capsule, CY calyptra, PS peristome
• Special thanks to Harald Kürschner (Berlin), Dietmar Quandt (Bonn),
Bernard Goffinet (Storrs, CT), Juan Carlos Villarreal (Munich)
Vascular Plants see Tracheophyte and Angiosperm Phylogeny Posters
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Bryophyte Phylogeny Poster (BPP) - Systematics and Characteristics of Nonvascular Land Plants (Mosses, Liverworts and Hornworts) v7 (2019)Document1 paginăBryophyte Phylogeny Poster (BPP) - Systematics and Characteristics of Nonvascular Land Plants (Mosses, Liverworts and Hornworts) v7 (2019)Videsh RamsahaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.kingdom Plantae NIE Class 11Document10 pagini3.kingdom Plantae NIE Class 11Sasuke UchihaÎncă nu există evaluări
- P3-Cole Al 2018 - Pôster TraqueófitasDocument1 paginăP3-Cole Al 2018 - Pôster TraqueófitasDayane ValencioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embryophytes Land Plants - Relationships and Characteristics (2019)Document1 paginăEmbryophytes Land Plants - Relationships and Characteristics (2019)Videsh RamsahaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 PlatyhelminthesDocument1 pagină2 Platyhelminthescameronjuli.patubo.sciÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1bacteriology CompleteDocument22 pagini1bacteriology CompleteLem obadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parasitology Notes Topic: CestodesDocument4 paginiParasitology Notes Topic: Cestodesehehe agikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tracheophyte Phylogeny Poster (TPP) - Vascular Plants: Systematics and Characteristics, 2016Document2 paginiTracheophyte Phylogeny Poster (TPP) - Vascular Plants: Systematics and Characteristics, 2016Dayvson CostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Mind MapsDocument2 paginiAnatomy of Flowering Plants - Mind MapsanmolthegreatwarriorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kingdom Animalia Deep FlowchartDocument2 paginiKingdom Animalia Deep Flowchartmeerab uroojÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apg Iii (2009) PDFDocument1 paginăApg Iii (2009) PDFAnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animalia File 2023-1Document12 paginiAnimalia File 2023-1Syed Zee Waqar GillaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Kingdom - 01Document9 paginiPlant Kingdom - 01ihunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deuterostomia Protostomia Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa: Lophophore AcelomateDocument3 paginiDeuterostomia Protostomia Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa: Lophophore AcelomateGiulia CostantiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deuterostomia Protostomia Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa: Lophophore AcelomateDocument3 paginiDeuterostomia Protostomia Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa: Lophophore AcelomateGiulia CostantiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Key Points KINGDOM ANIMALIA EngeeconDocument2 paginiKey Points KINGDOM ANIMALIA EngeeconUsama Iqbal33% (3)
- Kingdom AnimiliaDocument1 paginăKingdom AnimiliaNoman ZakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant ClassificationDocument3 paginiPlant ClassificationAshutosh MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plantphylogeny PDFDocument1 paginăPlantphylogeny PDFElFaboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Kingdom ChartDocument1 paginăPlant Kingdom ChartTanya SiyagÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 Lec - Intro - Platyhelminths + Liver FlukesDocument6 pagini02 Lec - Intro - Platyhelminths + Liver FlukesAsyeon GhaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 3 PPT Characteristics and Classification FA MADocument47 paginiWeek 3 PPT Characteristics and Classification FA MAMoza AlaliliÎncă nu există evaluări
- APG IV Poster PDFDocument1 paginăAPG IV Poster PDFintan100% (1)
- Climatic: SomesDocument8 paginiClimatic: SomesDaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bryophytes: Semester - I Paper: Bot-111 Unit - IvDocument13 paginiBryophytes: Semester - I Paper: Bot-111 Unit - IvAshu ShewaleÎncă nu există evaluări
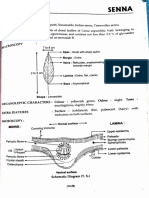
- SennahDocument4 paginiSennahAmaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesDocument4 paginiBot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesXearis SangalangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Kingdom M PDFDocument10 paginiPlant Kingdom M PDFAbu SubhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant KingdomDocument10 paginiPlant KingdomInfinite SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Krell Kranston 2004 Which Side Is BasalDocument3 paginiKrell Kranston 2004 Which Side Is BasalKatherine Gomez RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 25MonocotOrigin PDFDocument62 pagini25MonocotOrigin PDFPragyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 5 Epidermis and Secretory StructuresDocument30 paginiLab 5 Epidermis and Secretory StructuresSunflowerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kingdom Animilia - BiologismDocument1 paginăKingdom Animilia - BiologismMuhammad SibtainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 11 Systematics and Phylogeny, VirusesDocument21 paginiLecture 11 Systematics and Phylogeny, Virusesnikitamzamo7Încă nu există evaluări
- TPP eDocument1 paginăTPP eOliva R. SeguraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 14 Taxonomy and BiodiversityDocument26 paginiChapter 14 Taxonomy and BiodiversityNur Aisya Ardyla binti Rudy RukiminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agnatha Gnathostomata: - Jawless Vertebrates - Jawed VertebratesDocument2 paginiAgnatha Gnathostomata: - Jawless Vertebrates - Jawed VertebratesCharles Jeff DoriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal KingdomDocument16 paginiAnimal Kingdomsaifali986254Încă nu există evaluări
- AP Biology Classification Project 2010Document4 paginiAP Biology Classification Project 2010Tang SeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4Document9 paginiUnit 4Laddu KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Families AnimaliaDocument1 paginăFamilies Animaliaimranminhas2006Încă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants Mind MapDocument2 paginiAnatomy of Flowering Plants Mind MapAstha Agrawal100% (8)
- Platyhelminthes (Flatworms, Tapeworms) : Diversity of Life - AnimalsDocument21 paginiPlatyhelminthes (Flatworms, Tapeworms) : Diversity of Life - AnimalskingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Helminths 12Document34 paginiHelminths 12malakaiad212Încă nu există evaluări
- GenBioL Mod 9 Flower PDFDocument2 paginiGenBioL Mod 9 Flower PDFKimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Blueprints PresentationDocument29 paginiAnimal Blueprints Presentationmia perezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Vertebrates 8.4.2019Document33 pagini3 Vertebrates 8.4.2019hakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mahogany FamiliesDocument1 paginăMahogany FamiliesRicardo TerrabuzziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistic TMDocument10 paginiStatistic TMINDUMATHI RAMESHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angiosperms Lab ActivityDocument11 paginiAngiosperms Lab ActivityHaris Khan100% (1)
- NEMATODES: Hookworms General Info: Hookworm (In General) Strongyloides StercoralisDocument6 paginiNEMATODES: Hookworms General Info: Hookworm (In General) Strongyloides StercoralisMary ChristelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 12: Bryophytes: Mosses and Liverworts (And Hornworts)Document28 paginiLab 12: Bryophytes: Mosses and Liverworts (And Hornworts)marcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cockroaches Morphology and Structures NotesDocument4 paginiCockroaches Morphology and Structures NotesKrisha Mae VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood and Tissue Flagellates para LecDocument8 paginiBlood and Tissue Flagellates para LecLian MallareÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 28 - AlgaeDocument3 paginiCH 28 - AlgaeElle QuizonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 65770183ff2a2700189cb21f - ## - Anatomy of Flowering P - 231221 - 215303Document2 pagini65770183ff2a2700189cb21f - ## - Anatomy of Flowering P - 231221 - 215303shivrajcma007Încă nu există evaluări
- The GymnospermsDocument6 paginiThe GymnospermsraianandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemastix Presumptive Test For BloodDocument2 paginiHemastix Presumptive Test For BloodPFSA CSIÎncă nu există evaluări
- One Year Joint Package With AIATS For NEET 2024 - Class XII PDFDocument38 paginiOne Year Joint Package With AIATS For NEET 2024 - Class XII PDFRishabh kumar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Campbell Biology - Chapters 1 Ans 2 SummaryDocument17 paginiCampbell Biology - Chapters 1 Ans 2 SummaryYana JohansonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Westcotts Plant Disease HandbookDocument185 paginiWestcotts Plant Disease Handbooktira flechasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mareschal Et Alii, 2007, Chapter 5 Sirois Et Alii, 2008, P. 325, and Figure 1 Below, Section IIIDocument15 paginiMareschal Et Alii, 2007, Chapter 5 Sirois Et Alii, 2008, P. 325, and Figure 1 Below, Section IIIHenrique Augusto Torres SimplícioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top MNLDocument351 paginiTop MNLJas BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effecto of Harvest Date On The Nutritional Quality and Antioxidant Capacity in Hass PDFDocument5 paginiEffecto of Harvest Date On The Nutritional Quality and Antioxidant Capacity in Hass PDFEva Mayte GuadarramaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parental Attitude Research Instrument: Attitude An Approach To Use QuestionnairesDocument6 paginiParental Attitude Research Instrument: Attitude An Approach To Use QuestionnairesMaya MayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProteinsDocument2 paginiProteinsflorian layuganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 13 - Entoptic PhenomenaDocument4 paginiTopic 13 - Entoptic PhenomenashadowosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adult Development and AgingDocument44 paginiAdult Development and AgingDiana DayenÎncă nu există evaluări
- First ExercisesDocument7 paginiFirst Exercises786lailaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spot Junior Booklet - Class VI To VIII 9268 PDFDocument54 paginiSpot Junior Booklet - Class VI To VIII 9268 PDFArchanaGupta100% (1)
- GS 631 - Library and Information Services (0+1) : TopicsDocument24 paginiGS 631 - Library and Information Services (0+1) : TopicsVivek KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A 6 Years Old Girl With Intraabdomen TB, Severe Chronic Malnutrition, Post Exploration Laparotomy+Right Hemiileoctomy+ Ileocaecal AnastomosisDocument26 paginiA 6 Years Old Girl With Intraabdomen TB, Severe Chronic Malnutrition, Post Exploration Laparotomy+Right Hemiileoctomy+ Ileocaecal AnastomosisNadia ChairunnisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbe Report 2Document9 paginiMicrobe Report 2maibmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Read Up 2 - Word ListsDocument43 paginiRead Up 2 - Word ListsHANAÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Important Questions With SolutionsDocument48 paginiCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Important Questions With SolutionsRohit ChouhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 3 Eyesight Student WorksheetDocument10 paginiLesson 3 Eyesight Student WorksheetcupcakekidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curvas de Crecimiento MicrobianoDocument30 paginiCurvas de Crecimiento Microbianoluis villamarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harris Solutions OddDocument228 paginiHarris Solutions OddAndrea AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Field Trip ReportDocument28 paginiField Trip ReportTootsie100% (1)
- AMED3002 - Health Data - 2023 - DeFazioDocument68 paginiAMED3002 - Health Data - 2023 - DeFazioThomas MarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capsule Research ProposalDocument13 paginiCapsule Research ProposalTomas John T. GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument5 paginiSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsBobbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vaishnavi Sing: Zulekha Hospital LLC - (SHARJAH)Document1 paginăVaishnavi Sing: Zulekha Hospital LLC - (SHARJAH)Abc AbcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal EvolusiDocument19 paginiJurnal EvolusiAdicahyoo SentosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fascias y YogaDocument8 paginiFascias y YogaJuanCarlosCernudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent For Determination of Reducing SugarDocument7 paginiUse of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent For Determination of Reducing SugarLANAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Model Exam Set-XV (B) (2079-4-14) QuestionDocument16 paginiCommon Model Exam Set-XV (B) (2079-4-14) QuestionSameer KhanÎncă nu există evaluări