Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
BIO3153 - Lecture 1: Cell Biology - Introduction
Încărcat de
James OkenyDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
BIO3153 - Lecture 1: Cell Biology - Introduction
Încărcat de
James OkenyDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
BIO3153 -- Lecture 1
Cell Biology- Introduction
Short cut to do bullets on the keyboard – ctrl-shft-L
Professor Dr. Jonz – GNN260. Office hours are Fridays 2:30pm-4:00pm
Cyto=cell
The cytoskeleton is like a network of tracks that bring things from point A to Point B
For the midterm we will cover topics 1, 2, and 3. Then after the course will have the final involve all five
topics.
Protein sorting will be focussed specifically when the protein leaves the ribosome.
There are membrane transporters that select only water molecules and wont even select a proton. It is
in very specific.
LECTURE START – general aspects of cell biology
For the most part in this course we focus on EUKARYOTES, we will not really focus on the
prokaryotes.
It’s a large field that has had to be divided
Structure is studied so we can understand function. We will talk about conformation changes and
structure and this is done to talk about function.
Directed cell proliferation is what developmental biology.
There will be substantial conversation about neuroscience and related topics due to profs interest
In the start of the course we will cover evolution. We find that proteins have highly conversed
sequences, for explain we will find proteins in human then compare in a yeast, then notice the
sequences of amino acids are quite similar.
Theres another eay to classify organisms – by the cellular classifaction ( look at next point)
Point of this is to in cellular fashion instead of interms of aninmals. This is to say in
earlier bio classes we classified animals, but we can be even simpler and classify the types of
cells ( archeabacteria, eubacteria, and eukaryotes)
Also what where the notable properties of water ( interactions) that made life possible ?
H-bond interactions important for transient interactions between other water molecules for which
the biochemical reactions could take place .
Eukaryote cells are usually the smallest is 5 microns
Recently discovered that prokaryotes do have a type of cytoskeleton
Eukaryotes cytoskeletons are more dynamic than prokaryote cytoskeleton
The eukaryotes have internal membranes complarwhile prokaryotes don’t
Compartments are surrounded by internal membreanes
Unique about eukaryotes cells is that they have intercellular communication. And they have a high
high degree of compartmentalizations
Cells are truly made of a lot water about 70%.
Water is where all biochemical reactions occurs. And it is the selection for cells to use
ATP is used in many reactions to get them going
The reason why life evolved is because water and membranes came to be and compartmentalize.
This happened by the coagulations or bringing together of the lipids
Water is constantly interaction with water usine transient interaction such as wan der waals ( h-
bonding too)
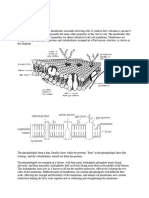
All lipids / membrane are amphiphatic molecules, one side likes water and the other likes oil (non-
charged, non -polar liqueids)
Phosopholipis bilayers formed because they can form bilayers, in the form of spheres. Within the
membrane we have a oily environment(non-polar) then on the very inside of micelles is aqueous
and on the very outside is aqueous
A micelle is
How do things get across the cell membrane bilayer ? sugars cross, maybe they are transported or
spontaneously.
It turns out with membrance proteins they have sections that are exposed to the aqueous
environment is soluble there, while the part of the same protein that is in the non-polar bilayer
region is stabilized to so it can remain, that part of the protein maybe fat-soluble. This allows the
protein to serve a purpose of transporting things from inside out or vice versa
You can think of the cytosol as a compartment itself, in that it helps to tells us how proteins get
transported from the cytosol to the nucleus.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- BIO3153 - Lecture 1: Cell Biology - IntroductionDocument2 paginiBIO3153 - Lecture 1: Cell Biology - IntroductionJames OkenyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xüsusi Histologiya Dərslik 2015-1Document14 paginiXüsusi Histologiya Dərslik 2015-1aydinmemmedov9009Încă nu există evaluări
- DLS 213 Selected Topics in BiologyDocument15 paginiDLS 213 Selected Topics in BiologyNiña Angeline PazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elementary Anatomy and Micro Techniques Chapter #2Document38 paginiElementary Anatomy and Micro Techniques Chapter #2Mirza WaleedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument15 paginiGen Bio ReviewerAwaawa D orianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Biology 1Document22 paginiGeneral Biology 1joveljanerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure and Functions of PhospholipidsDocument15 paginiStructure and Functions of Phospholipidsalina blueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Membrane Structure-And FunctionDocument5 paginiCell Membrane Structure-And FunctionEmmanuel MwaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- AS Biology - Module 1 Chapter 1: Structure and Function of The Cell Introduction To The CellDocument11 paginiAS Biology - Module 1 Chapter 1: Structure and Function of The Cell Introduction To The CellJosebeth CairoÎncă nu există evaluări
- O Level Biology Notes MapurangaDocument95 paginiO Level Biology Notes Mapurangapeterchiyanja100% (2)
- Fluid Mosaic Model NotesDocument4 paginiFluid Mosaic Model NotesanzalnaamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- b4ln Eukcell p1 EditedDocument4 paginib4ln Eukcell p1 EditedMonica BaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Biology 1Document5 paginiGeneral Biology 1M GetutuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 Study Guide AK - Cell Structure and FunctionDocument6 paginiUnit 3 Study Guide AK - Cell Structure and Functionweijun wuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellular StructureDocument6 paginiCellular StructureVela STEM Naron, Claire KylaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Form 5Document373 paginiBiology Form 5shonotano71Încă nu există evaluări
- Science Chapter 5Document17 paginiScience Chapter 5Jose DomingoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Class 9Document19 paginiBiology Class 9Vikranth PonnalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIT5 07SCF13 Lec1 PDFDocument15 paginiMIT5 07SCF13 Lec1 PDFMarta GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1. What Is Biochemistry? Life at The Molecular LevelDocument15 paginiLecture 1. What Is Biochemistry? Life at The Molecular LevelFatima fernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre-Lims ReviewerDocument4 paginiPre-Lims ReviewerANGEL RIZAREÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell MebraneDocument10 paginiCell MebraneChandra SihombingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 - Cell Structure & FunctionDocument13 paginiUnit 2 - Cell Structure & FunctionJ15Încă nu există evaluări
- Module 7, Anatomy and Physiogy (ABEGAIL C. RELUNIA)Document4 paginiModule 7, Anatomy and Physiogy (ABEGAIL C. RELUNIA)Abegail ReluniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Activity in The Cell: After You Have Finished Reading This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToDocument21 paginiChemical Activity in The Cell: After You Have Finished Reading This Chapter, You Should Be Able TojohnnwakanmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Cell MembraneDocument9 paginiThe Cell MembraneShuchi HossainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochem Notes Week 1Document6 paginiBiochem Notes Week 1Leah Mariz RocaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells Study Guide 2020 KEYDocument4 paginiCells Study Guide 2020 KEYLaarni GeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- L7 - Epitheila Function StructureDocument7 paginiL7 - Epitheila Function StructureLogan SalisburyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gen. Bio. Week 5 - Lesson 9Document7 paginiGen. Bio. Week 5 - Lesson 9EZRA THERESE DE JESUSÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Biology Unit 2 Student NotesDocument21 paginiAP Biology Unit 2 Student NotesjanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Keystone Exam ReviewDocument58 paginiBiology Keystone Exam ReviewLian LzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Essays January 4Document7 paginiTest Essays January 4Stephanie JenkinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 4: Cell Membrane and Its PermeabilityDocument12 paginiLesson 4: Cell Membrane and Its PermeabilityremshopÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes CHP - The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument4 paginiNotes CHP - The Fundamental Unit of LifeShreyasi PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Biology First Stage Lec 2 Cell Structure: by Dr. Shatha M.AliDocument19 paginiMedical Biology First Stage Lec 2 Cell Structure: by Dr. Shatha M.AlimohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- WEEK3 ModuleLec (BIO101)Document10 paginiWEEK3 ModuleLec (BIO101)Maricris GatdulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure and Function of CellDocument11 paginiStructure and Function of CellWoobin RealÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Membranes: by Hajar SaihiDocument10 paginiBiological Membranes: by Hajar SaihiMariam El KhatibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Cell Structure and Importance of Cell Organelles I Post Harvest PhysiologyDocument10 paginiPlant Cell Structure and Importance of Cell Organelles I Post Harvest Physiologychristom karungariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sciencia Du Gaia - Introduccion Du Sciencia BioDocument56 paginiSciencia Du Gaia - Introduccion Du Sciencia BioRETLAWÎncă nu există evaluări
- Studyguide AnswerkeyDocument23 paginiStudyguide Answerkeyapi-237676607Încă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Sheet BIO 101 - MSFPDocument11 paginiTutorial Sheet BIO 101 - MSFPhopekingbwalya23Încă nu există evaluări
- ANPH-M1-CU2. The Cell & Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction (Mitosis and Meiosis)Document26 paginiANPH-M1-CU2. The Cell & Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction (Mitosis and Meiosis)ajdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 CellsDocument19 paginiChapter 3 CellsEuniece AnicocheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes - The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument6 paginiNotes - The Fundamental Unit of LifeffxfuddiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument30 paginiEarth and Life ScienceChristian VitalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Cell MembraneDocument1 paginăThe Cell MembranemonikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter6 PDFDocument21 paginiChapter6 PDFsgw67Încă nu există evaluări
- Module 6 (GenBio)Document2 paginiModule 6 (GenBio)Christian Angel GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 5 EALSDocument9 paginiModule 5 EALSKleffer YnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOENERGETICSDocument8 paginiBIOENERGETICSSarah CalventasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Structure and Function: Tenets of Cell TheoryDocument9 paginiCell Structure and Function: Tenets of Cell Theoryjey011Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Membrane Grade 12Document8 paginiCell Membrane Grade 12Olayinka SalmonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of Cell Components and Its Functions NoteskartsDocument18 paginiStructure of Cell Components and Its Functions NoteskartsNiranjit SanasamÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Biology Modules 1 3Document36 paginiGeneral Biology Modules 1 3Glen MillarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 11 Biology Module 1 2023 NotesDocument55 paginiYear 11 Biology Module 1 2023 NotesLÎncă nu există evaluări
- QuestionaryDocument3 paginiQuestionaryDANIELA NICOLE PAZMI�O CADENAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Biology 1St Edition Mason Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument31 paginiUnderstanding Biology 1St Edition Mason Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFerik.looney743100% (11)
- BM3251 Important QuestionsDocument2 paginiBM3251 Important QuestionsAmen MuhammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2022 LS Grade 11 June Exam Paper 1Document12 pagini2022 LS Grade 11 June Exam Paper 1bothaj2006Încă nu există evaluări
- Australopiteco A HomoDocument10 paginiAustralopiteco A HomoChristian MarzanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 9 Science Reviewer Quarter 1 PDFDocument16 paginiGrade 9 Science Reviewer Quarter 1 PDFDane Gian Angelo TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legg-Calvé-Perthes DiseaseDocument59 paginiLegg-Calvé-Perthes DiseaseCatalina Elena González CarvajalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macromolecule BrochureDocument1 paginăMacromolecule BrochureMohammad IzadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- WHO - Active Applications - Covid Testing - EULDocument6 paginiWHO - Active Applications - Covid Testing - EULbharat1102Încă nu există evaluări
- Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocument6 paginiAgarose Gel ElectrophoresisAhmad A. ArabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amnion Si CorionDocument12 paginiAmnion Si CorionMaria JanticÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNH Qualicon Brochure Ribo 1A-0771 1212 WEB PDFDocument11 paginiDNH Qualicon Brochure Ribo 1A-0771 1212 WEB PDFpatricioÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZakriyaDocument6 paginiZakriyaapi-512107573Încă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine System: Theoretical HandoutDocument153 paginiEndocrine System: Theoretical HandoutAmy AmyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expansion of The Knockdown Resistance Human Head Lice (Phthiraptera: Pediculidae) From Orphanages in South Sumatera (Indonesia)Document13 paginiExpansion of The Knockdown Resistance Human Head Lice (Phthiraptera: Pediculidae) From Orphanages in South Sumatera (Indonesia)index PubÎncă nu există evaluări
- TEAS 6 Science by KellyDocument22 paginiTEAS 6 Science by KellyLily GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Compounds WorksheetDocument1 paginăOrganic Compounds Worksheettssandoval100% (4)
- Full Download Book New and Future Developments in Sustainable Agriculture Advances in Microbe Based Biostimulants PDFDocument22 paginiFull Download Book New and Future Developments in Sustainable Agriculture Advances in Microbe Based Biostimulants PDFbenjamin.contreras157100% (14)
- Mendelian InheritanceDocument37 paginiMendelian InheritanceMasni Shah NingÎncă nu există evaluări
- PROFED 1 - MODULE 3 Issues On Human DevelopmentDocument3 paginiPROFED 1 - MODULE 3 Issues On Human DevelopmentKaren Felipe100% (3)
- Basic Taxonomic Concept & Principles, Description, Nomenclature, Identification & ClassificationDocument28 paginiBasic Taxonomic Concept & Principles, Description, Nomenclature, Identification & ClassificationKaela Sophia AndalisÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMYLOIDOSISDocument16 paginiAMYLOIDOSISSourav NathÎncă nu există evaluări
- VITMEE M.TechMCA Syllabus 2023Document18 paginiVITMEE M.TechMCA Syllabus 2023Siva Teja RajaneniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amino AcidsDocument6 paginiAmino AcidsserkanitoguapitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NegOr Q4 GenBio2 SLKWeek4 v2Document20 paginiNegOr Q4 GenBio2 SLKWeek4 v2Maribel Ruedas RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- All India Test Series (Neet) : RMCT-01ADocument14 paginiAll India Test Series (Neet) : RMCT-01AManmeet SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Role of IgADocument3 paginiThe Role of IgAullifannuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis - Data-Driven Cell Engineering of Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells Through Machine LearningDocument102 paginiThesis - Data-Driven Cell Engineering of Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells Through Machine LearningMaxwell PryceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Procreative HealthDocument13 paginiProcreative HealthGizzi Asbelle EspirituÎncă nu există evaluări
- WBI01 01 Rms 20190124Document28 paginiWBI01 01 Rms 20190124Adrian Safa khouryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polyplus Transfection® Life Science Research and Non-Viral In-Vivo Transfection ReagentsDocument6 paginiPolyplus Transfection® Life Science Research and Non-Viral In-Vivo Transfection ReagentsDiego GarridoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 s2.0 S1568988322000166 MainDocument12 pagini1 s2.0 S1568988322000166 MainAlexandru IorgescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceDe la EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (517)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDe la EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDe la EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDe la EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (393)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)De la EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (411)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessDe la EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessÎncă nu există evaluări
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesDe la EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (397)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDe la EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (69)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDe la EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (137)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessDe la Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (33)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceDe la EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (18)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeDe la EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationDe la EverandWater: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (37)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedDe la EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (11)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionDe la EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (812)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseDe la EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (52)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveDe la EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (66)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemDe la EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (115)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomDe la EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (216)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperDe la EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (15)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainDe la EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (110)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorDe la EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorÎncă nu există evaluări