Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Electric Power Distribution: Objectives
Încărcat de
Priyanth AcharyaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Electric Power Distribution: Objectives
Încărcat de
Priyanth AcharyaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
The firm was established in 1991 in Chikkamagalur with the specific understanding to meet the
demands of the growing market in the field of Electrical Power Distribution and control systems.
We are one of the leading ISO 9001-2008 Engineering organizations in Chikkamagalur. And
PWD registered CLASS ‘A’ electrical contractor. The members of the Company’s senior
management team have an average experience of approximately 10 years in diverse areas of the
energy market including development, engineering, construction, finance, operations, asset
management, and energy trading and Contracting.
OBJECTIVES: Our objective is to achieve customer satisfaction and continual improvement of
customer services. Establishing long term mutually rewarding relationship and Provide excellent
quality services to meets the requirement of our customers.
AIM: Our aim is to provide high quality of Services to all our clients and make continual
improvement to our services and people. Maintain customer satisfaction is prime factor in our
Success.
OUR CREDENTIALS: Precisely covering electrical fields, as an act of local success by
providing most of the major industries, Firms and projects located all around the country, we have
been involved Over the years, project planning and turnkey electrical installations. This enables
our customers to turn over a concept to us and walk away from the project with the confidence that
it will be completed in a timely and cost efficient manner. We are proficient in the execution of
either pre-designed or design & build projects. Our field of experience covers all types of
Electrical installation/Security services in projects. This can only be achieved with good
communication and understanding, and the correct use of contract management tools: Reporting,
Progress evaluation, and an imaginative flexible approach to solving problems. Now we are
providing one step solution to all turnkey projects covering the electrical field including designing
and setting up of interiors. We also deal in Advance Lightning Arrestors Building Intelligence
system and Specialized Earthing Solutions. Power equations have a superior track record of
successful projects in the energy industry and a highly experienced management team.
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 1
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
CHAPTER 2
BACKGROUND
2.2 Need of electricity:
Electricity is one of the greatest technological innovations of mankind. It has now become a
part of our daily life and one cannot think of a world without electricity. Electricity is now an
important part of homes and industries.Almost whole the devices at homes, businesses and
industries are running because of electricity. The primary use of electricity depends on the
place where it is used and the nature of the facility.
For example, importance of electricity in our daily life:
At home: Electricity is important to run your appliances at home efficiently. Ex: Lighting,
Fan, TV, etc.
In travelling: As electricity is an important part of our daily lives so is the travelling. Today a
vast number of travelling medium like the electric train, aeroplanes, electrical cars, etc.
In medical facility: The medical sector is considering the place where you find continues
flow of electricity 24*7*365. Ex: X-Ray machines, ECG, etc.
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 2
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
CHAPTER 3
DISTRIBUTION
Electric power distribution is the final stage in the delivery of electric power; it carries
electricity from the transmission system to individual consumers. Distribution substations
connect to the transmission system and lower the transmission voltage to
medium voltage ranging between 2 kV and 35 kV with the use of transformers.
Primary distribution lines carry this medium voltage power to distribution
transformers located near the customer's premises. Distribution transformers again lower the
voltage to the utilization voltage used by lighting, industrial equipment or household
appliances. Often several customers are supplied from one transformer
through secondary distribution lines. Commercial and residential customers are connected to
the secondary distribution lines through service drops. Customers demanding a much larger
amount of power may be connected directly to the primary distribution level or the sub
transmission level.
3.1 Power Distribution System
A distribution substation is located near or inside city/town/village/industrial area. It
receives power from a transmission network. The high voltage from the transmission line is
then stepped down by a step-down transformer to the primary distribution level voltage.
Primary distribution voltage is usually 11 kV, but can range between 2.4 kV to 33 kV
depending upon region or consumer.
A typical power distribution system consists of -
Distribution substation
Feeders
Distribution Transformers
Distributor conductors
Service mains conductors
Along with these, a distribution system also consists of switches, protection
equipment, measurement equipment etc.
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 3
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
CHAPTER 4
ELECTRIC POLES
4.1 Concrete poles
Several power poles made of concrete The most widespread use of concrete poles is
in marine environments and coastal zones where excellent corrosion resistance is required to
reduce the impact of sea water, salt fog, and corrosive soil conditions (e.g., marsh). Their
heavy weight also helps the concrete poles resist the high winds possible in coastal areas. The
various designs for concrete poles include tapered structures and round poles made of solid
concrete; pre-stressed concrete (spun-cast or statically cast); and a hybrid of concrete and steel
.The drilling of installed concrete poles is not feasible. Users may wish to have the attachment
hardware cast into the concrete during the pole manufacture. As a result of these operational
difficulties, banded hardware has become the more popular means to attach cable plant to
concrete poles. Design criteria and requirements for concrete poles can be derived from
various industry documents including, but not limited to, ASCE-111, ACI-318, ASTM C935,
and ASTM C1089.
4.2 Steel poles
Steel poles can provide advantages for high-voltage lines, where taller poles are required for
enhanced clearances and longer span requirements. Tubular steel poles are typically made
from 11-gauge galvanized steel, with thicker 10- or 7-gauge materials used for some taller
poles because of their higher strength and rigidity. For tall tower-type structures, 5-gauge
materials are used. Although steel poles can be drilled on-site with an annular drill bit or
standard twist drill, it is not a recommended practice. As with concrete poles, bolt holes could
be built into the steel pole during manufacture for use as general attachment points or places
for steps to be bolted into the pole .Welding of attachment hardware or attachment ledges to
steel poles may be a feasible alternate approach to help provide reliable attachment points.
However, operational and practical hazards of welding in the field may make this process
undesirable or uneconomical. Steel poles should meet industry specifications such as:
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 4
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
TIA/EIA-222-G, Structural Standard for Antenna Supporting Structures and
Antennas (current); TIA/EIA-222; Structural Standards for Steel; and TIA/EIA-RS-222, or an
equivalent requirement set to help ensure a robust and good quality pole is being used.
The normally electrical pole which we use is PCC and RCC pole. The full form of PCC pole
is plain cement concrete and the full form of RCC pole is reinforced cement concrete. The
plain cement concrete pole is made with cement and concrete, the PCC pole has low
mechanical strength. The reinforced cement concrete is made with cement concrete and some
rods to increase the strength of the pole, the RCC pole has high mechanical strength.
The weight of 8 meter RCC pole is more between 420 to 450 kg, the pole has three holes at
the top to fix cross arm of diameter 18 mm as shown in the above figure. The depth of
planting or digging for an 8-meter pole is 1.5m. The top width of the electric pole is 145 mm
and the bottom width is 290 mm . The weight of the 9 meter RCC pole is somewhat more
600 kg. The top width of the pole is 185mm and the bottom weight of the pole is 355 mm.
Picture of 8 meter and 9 Meter poles are given below
Fig 4.1
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 5
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
Fig 4.2
4.3 DOUBLE POLE TRANSFORMER STRUCTURE
The double pole dtr structure is constructed using two poles, some horizontal cross arms, clamps,
nuts, and bolts. The function of the DP structure is to step-down the incoming voltage i.e., of 11
KV to 440 volts (three phases) or 230 volts (single-phase).
The materials used in the DP structure are :
4.3.1 Lightning Arrestors
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 6
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
Fig 4.1
11 KV class lightning arrestors are used and lightning arrestors are fixed at the top of the DP
structure as you can see in the above image. The function of the lightning arrestor is to protect
the transformer from lightning tenders. When the lightning occurs and falls on structure the
lightning arrestor transfers lightning stocks to the ground and thus protect the transformer. A
total of three lightning arrestors is provided.
4.3.2 Fuse
Fig 4.2
It is called horn gap fuse for the protection of the transformer from overload and short circuit
current.When overhead occurs on the ht line (11KV line), the fuse will isolate the circuit and
thus protect the transformer.
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 7
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
4.3.3 GOS
Fig 4.3
The most commonly used switch in small to medium substations is a gang-operated, air-break
disconnect switch. "Gang-operated" because the three separate switches for each phase are
operated as a group from a single control; "air-break" because the switch operates in air rather
than in another medium, such as oil.
The purpose of this switch is to disconnect the substation from the incoming line, not to
disconnect the transformer from the load. It is like a large safety switch with no load breaking
capability. It can only break, or "interrupt" the relatively small "magnetizing current" of the
substation transformer. (This is the small amount of current needed to set up the magnetic
field in the transformer core.) A substation must first be disconnected from its secondary or
load side before the primary or high voltage side can be disconnected using the disconnect
switch.
4.3.4 Distribution Transformer
A distribution transformer or service transformer is a transformer that provides the
final voltage transformation in the electric power distribution system, stepping down the
voltage used in the distribution lines to the level used by the customer. The invention of a
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 8
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
practical efficient transformer made AC power distribution feasible; a system using
distribution transformers was demonstrated as early as 1882.
The main purpose of the transformer is to step down the voltage from 11 KV to 440 volts
( three phases) or 230 volts (single-phase)
Fig 4.4
4.3.5 CROSS ARM
Cross Arm is a cross-piece fitted to the pole top end portion by means of brackets, known as
pole brackets, for supporting insulators. Cross arms are of various types such as MS channel,
angle iron or wooden. These may be straight, U-shaped, Ushaped or zigzag shaped. Wooden
cross arms are commonly employed on 11 KV and 33 KV lines. These are made of sal wood,
seasoned Sheridan wood or creosoted firewood.Wooden cross arms are preferred owing to
their insulating property which provides safety to line staff and minimizes flash-over due to
the bridge.
The usual lengths and x-sections of wooden cross arms in use are 1.5m×125mm×125mm for
11 KV lines and 2.1m×125mm×125mm for 11 KV lines and 2.1m×125m×125mm for 33 KV
lines. Wooden cross arms need replacement owing to decay after 5-7 years depending upon
weather conditions .Steel cross arms are stronger and are generally used on steel poles. For lv
distribution, the angle iron or channel iron cross arms shall be of a size not less than
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 9
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
50mm×50mm×6.4mm and 76mm×38mm.The length of the cross arms shall be suitable for the
spacing of the conductors .Cross arms shall be suitable and strong enough to withstand the
resultant forces caused by insulators, their pins, and deadweight of insulator attachments, etc.
To avoid bridge on HT lines, V-shaped cross arms are used with pin insulators while straight
cross arms are used with disc insulators. The cross arm is fixed to the pole in such a manner
that the load of the conductors is taken by the cross arm and not the clamp or bolt that fixes
the cross arm to the pole.
Fig 4.5
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 10
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
CHAPTER 5
GUARDING
A guarding is provided for the safety of life, installation, and communication circuits.
The guarding for 11 KV lines is provided at road crossings, canal crossings, railway crossing,
crossing over lt lines or communication lines. Regarding guarding of line crossings or
approaching each other IER 87 provides all-important guidelines, IER(Indian Electricity
Rule) 88 provides that every guard wire shall be connected with the earth at each point at
which electrical continuity is broken. Every guard wire should have sufficient current-
carrying the capacity to ensure the circuit rendering dead, without risk of fusing of the guard
wire or wires till the contact of any line wire has been removed There are various other rules
relating to guarding where lines cross trolley wires as mentioned in sub rule (5) of IER 88.
Various guarding arrangements are shown below.
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 11
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
Fig 5.1
CHAPTER 6
INSULATORS
6.1 Pin Insulator
A pin insulator is a device that isolates a wire from a physical support such as a pin (a wooden
or metal dowel of about 3 cm diameter with screw threads) on a telegraph or utility pole. It is
a formed, single layer shape that is made out of a non-conducting material, usually porcelain
Fig 6.1
or glass. It is thought to be the earliest developed overhead insulator and is still popularly used
in power networks up to 33 KV. Single or multiple pin insulators can be used on one physical
support, however, the number of insulators used depends upon the application's voltage.
6.2 Polymeric Pin Insulator
It is an electrical device consisting of insulation section made of polymer materials and metal
fittings.
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 12
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
The insulation unit is made of fibreglass. The protective ribbed mold is made of silicon
organic rubber. Flanges are made of anti-rust alloy thus providing safe long-term operation
under various climatic conditions.
Insulation section – an element bearing mechanical and electric loads and consisting of
insulation core unit covered with protective mould.
Insulation core unit – a rod made of composite dielectric substance – fibreglass, as a rule
(tar reinforced with fibreglass) or consisting of separate elements assembled at the unit in a
particular order.
Fig 6.2
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 13
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
6.3 Strain insulator
A strain insulator is an electrical insulator that is designed to work In
mechanical tension (strain), to withstand the pull of a suspended electrical wire or cable. They
are used in overhead electrical wiring, to support radio antennas and overhead power lines. A
strain insulator may be inserted between two lengths of wire to isolate them electrically from
each other while maintaining a mechanical connection, or where a wire attaches to a pole or
tower, to transmit the pull of the wire to the support while insulating it electrically.
Fig 6.3
6.4 Shackle type Insulator
Shackle type Insulators However, unlike strain insulators, shackle insulators are designed to
support lower voltages. These insulators are single, round porcelain parts that are mounted
horizontally or vertically. In early days, the shackle insulators were used as strain insulators.
But now a days, they are frequently used for low voltage distribution lines. Such insulators
can be used either in a horizontal position or in a vertical position. They can be directly fixed
to the pole with a bolt or to the cross arm
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 14
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
Fig 6.4
6.5 Disk insulator
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 15
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
Fig 6.5
In suspension insulator numbers of insulators are connected in series to form a string and the
line conductor is carried by the bottom most insulator. Each insulator of a suspension string is
called disc insulator because of their disc like shape.
6.6 ASCR CONDUCTORS
6.6.1 Weasel ASCR conductor
Weasel ASCR conductor is a type of aluminium conductor steel reinforced. It is uses as bare
overhead transmission conductor and as primary and secondary distribution conductor and
messenger support.
Fig 6.6
6.6.2 Rabbit ASCR Conductor
A “RABBIT” conductor is a ACSR cable with nominal aluminium cross-sectional area of 50
mm². It has 6 aluminium strands of 3.35 mm diameter and 1 steel strand of 3.35 mm diameter.
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 16
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
Fig 6.7
6.6.3 Coyote ACSR conductor
ACSR coyote conductor is a popular type of aluminium conductor steel reinforced wire.
This wire is produced according to the BS215 standard. Like other acsr wire, coyote
conductor also consists of stranded aluminium and steel wire. The aluminium wire diameter is
26/2.54mm, and the stranding steel diameter is 7/1.91mm
Fig 6.8
6.6.4 Lynx ACSR conductor
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 17
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
ACSR lynx conductor is one of the kind of aluminium conductor steel reinforced. It is
the ACSR-BS215 standards. ACSR lynx conductor strands 30 aluminium and 7 steels, and
their diameter is the same, and they are all 2.79 mm. After the cabling, the overall diameter is
19.53 mm.
Fig 6.9
6.6.5 Guy wire
Guy wire is a tensioned wire used to stabilise a free standing structure like a ship masts or an
electric wire support pole. It is also called stay wire or guide wire. One end of this wire is
attached to the structure and the other end to the solid ground.
Fig 6.10
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 18
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
6.6.6 GI wire
Full-form of GI wire is Galvanized Iron wire, which is mostly used for fencing of all
purposes. Galvanization (the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron, to
prevent rusting) has two types, one is electroplated galvanization and second is hot dip
galvanization.
Fig 6.11
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 19
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
6.6.7 Spiral Earth electrodes
Spiral Earth electrodes are specifically designed and installed to improve a systems earthing.
This system most used in earthing of overhead distribution lines
Fig 6.12
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 20
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
CHAPTER 7
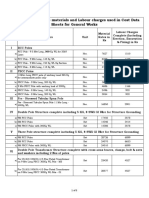
COST DATA
Rates for various Line materials and Labour charges used in Cost Data
Sheets for General Works
Labour Charges
Material
Complete (Including
SL No Particulars Unit Rates in
Erection, Excavation
Rs
& Fixing) in Rs
I RCC Poles
RCC Pole - 9.5 Mtr Long, 300 Kg WL for
a) 33kV Nos. 7627 1510
Lines
b) RCC Pole - 9 Mtr Long, 145 Kg WL Nos. 6258 1166
c) RCC Pole - 9 Mtr Long, 150 Kg WL Sq Nos. 7165 1166
Section
d) RCC Pole - 8 Mtr Long, 115 Kg WL Nos. 4706 932
II PSCC Poles
11Mtrs Long PSCC pole of working Load 365
a) Nos. 7874 1707
Kg for intermediate poles only
b) PSCC Pole - 9 Mtr Long, 200 Kg WL Nos. 3689 1166
c) 9 Mtr PSCC Pole with working load of 300Kg Nos. 4686 1166
d) PSCC Pole - 8 Mtr Long, 140 Kg WL Nos. 2496 932
e) PSCC Pole - 8 Mtr Long, 200 Kg WL Nos. 3054 932
III Pre - Stressed Tubular Spun Pole
Pre - Stressed Tubular Spun Pole 11 Mtr Long
a) - Nos. 16850 2901
500Kg WL
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 21
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
IV Double Pole Structure complete including 5 KG, 8 SWG GI Wire for Structure Grounding
a) 9M RCC Poles Set 17450 3578
b) 8M RCC Poles Set 14346 3414
c) 9M PSCC Poles with 300Kg WL Set 14306 3578
V Three Pole structure complete including 5 KG, 8 SWG GI Wire for Structure Grounding
a) 9M RCC Poles Set 28726 6899
b) 8M RCC Poles Set 24070 6653
c) 9M PSCC Poles with 300Kg WL Set 24010 6899
Double Pole Transformer Structure complete with cross arms braces, clamps, bolt & nuts and
VI
washers including 2 Nos of poles
For 25/63/100kVA 4/5 Star Rated
a) Transformer on 9 Mtr Long PSCC 300Kg WL Set 23420 4527
Pole - MS
For 25/63/100kVA 4/5 Star Rated
b) Transformer on 9 Mtr Long PSCC 300Kg WL Set 28577 4527
Pole - GI
For 25/63/100kVA 4/5 Star Rated
c) Transformers using 9 mtr RCC Pole 145Kg Set 26439 4527
WL - MS
For 25/63/100kVA 4/5 Star Rated
d) Transformers using 9 mtr RCC Pole 145Kg Set 31550 4527
WL - GI
For 100/300kVA 4/5 Star Rated Transformer
e) on Set 27314 4662
PSCC 9Mtr Long 300Kg WL - MS
Labour Charges
Material
Complete (Including
SL No Particulars Unit Rates in
Erection, Excavation
Rs
& Fixing) in Rs
f) For 100/300kVA 4/5 Star Rated Transformer Set 33912 4662
on
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 22
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
PSCC 9Mtr Long 300Kg WL - GI
For 100/300kVA 4/5 Star Rated Transformers
g) Set 30213 4662
using 9 mtr RCC Pole 145Kg WL - MS
For 100/300kVA 4/5 Star Rated Transformers
h) Set 36721 4662
using 9 mtr RCC Pole 145Kg WL - GI
Fixing Single Pole Mounted Transformer kit on 9mtrs Square section/ RCC/PSCC Poles (Excluding
VII
erection of poles )
Single Pole Mounted Transformer kit for
25/63 kVA 4/5 Star Rated Transformer on 9
a) Set 4604 1118
mtr RCC Poles (Square Section) Without H
Frame - MS
Single Pole Mounted Transformer kit for
25/63 kVA 4/5 Star Rated Transformer on 9
b) Set 6349 1118
mtr RCC Poles (Square Section) Without H
Frame - GI
Single Pole Mounted Transformer kit for
25/63 kVA 4/5 Star Rated Transformer on 9
c) mtr RCC Set 9180 1118
Poles (Square Section) With H Frame - MS
Single Pole Mounted Transformer kit for
25/63 kVA 4/5 Star Rated Transformer on 9
d) mtr RCC Set 12633 1118
Poles (Square Section) With H Frame - GI
Single Pole Mounted Transformer Structural
materials for mounting 25kVA 4/5 Star Rated
e) Transformer using 9 mtr PSCC Pole 300Kg Set 5584 1733
WL
Without H Frame – MS
f) Single Pole Mounted Transformer Structural Set 7690 1733
materials for mounting 25kVA 4/5 Star Rated
Transformer using 9 mtr PSCC Pole 300Kg
WL
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 23
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
Without H Frame - GI
Single Pole Mounted Transformer Structural
materials for mounting 25kVA 4/5 Star Rated
g) Transformer using 9 mtr PSCC Pole 300Kg Set 9576 1733
WL
With H Frame - MS
Single Pole Mounted Transformer Structural
materials for mounting 25kVA 4/5 Star Rated
h) Transformer using 9 mtr PSCC Pole 300Kg Set 13176 1733
WL
With H Frame - GI
VIII Fixing Single Pole Mounted Transformer kit on 11 mtrs Spun Pole (Excluding erection of poles)
Labour Charges
Material
Complete (Including
SL No Particulars Unit Rates in
Erection, Excavation
Rs
& Fixing) in Rs
Single H Frame with Transformer Seating and
a) Seating angle support X arm for 11 mtr Spun Set 19691 2236
Pole for 25kVA (OH Line) - MS
Single H Frame with Transformer Seating and
b) Seating angle support X arm for 11 mtr Spun Set 27065 2236
Pole for 25kVA (OH Line) - GI
Three H Frame with Transformer Seating and
c) Seating angle support X arm for 11 mtr Spun Set 26734 2236
Pole for 250kVA (UG Cable) – MS
Three H Frame with Transformer Seating and
d) Seating angle support X arm for 11 mtr Spun Set 36728 2236
Pole for 250kVA (UG Cable) - GI
Single H Frame without Transformer Seating
and Seating angle support X arm for 11 mtr
e) Set 10171 2236
Spun Pole for 63/100/250/500kVA (OH Line)
- MS
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 24
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
Single H Frame without Transformer Seating
and Seating angle support X arm for 11 mtr
f) Set 13992 2236
Spun Pole for 63/100/250/500kVA (OH Line)
- GI
Three H Frame without Transformer Seating
and Seating angle support X arm for 11 mtr
g) Set 16352 2236
Spun Pole for 63/100/250/500kVA (UG
Cable) - MS
Three H Frame without Transformer Seating
and Seating angle support X arm for 11 mtr
h) Set 22463 2236
Spun Pole for 63/100/250/500kVA (UG
Cable) - GI
11 kV Horizontal cross arm with HT Single Top support, clamp,bolts, nuts and washers -
IX
MS
a) For RCC Poles Set 444 106
b) For PSCC Poles 140 KG WL Set 435 106
c) For PSCC Poles 200 KG WL Set 438 106
d) For PSCC Poles 300 KG WL Set 447 106
IX 11 kV Horizontal cross arm with HT Single Top support, clamp,bolts, nuts and washers -GI
a) For RCC Poles Set 586 106
b) For PSCC Poles 140 KG WL Set 573 106
c) For PSCC Poles 200 KG WL Set 579 106
d) For PSCC Poles 300 KG WL Set 589 106
X 11 kV Horizontal cross arm, clamp,bolts, nuts and washers for DC Lines - MS
a) For RCC Poles Set 332 89
b) For PSCC Poles 140 KG WL Set 323 89
c) For PSCC Poles 200 KG WL Set 326 89
d) For PSCC Poles 300 KG WL Set 335 89
XI 11 kV Horizontal cross arm, clamp, bolts, nuts and washers for DC Lines - GI
a) For RCC Poles Set 441 89
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 25
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
Labour Charges
Material
Complete (Including
SL No Particulars Unit Rates in
Erection, Excavation
Rs
& Fixing) in Rs
b) For PSCC Poles 140 KG WL Set 428 89
c) For PSCC Poles 200 KG WL Set 434 89
d) For PSCC Poles 300 KG WL Set 444 89
XII 4 - Pin cross arm with pole clamp, bolts, nuts and washers with braces - MS
a) For RCC Poles Set 272 106
b) For PSCC Poles 140 KG WL Set 263 106
c) For PSCC Poles 200 KG WL Set 266 106
d) For PSCC Poles 300 KG WL Set 275 106
XIII 4 - Pin cross arm with pole clamp, bolts, nuts and washers with braces - GI
a) For RCC Poles Set 360 106
b) For PSCC Poles 140 KG WL Set 347 106
c) For PSCC Poles 200 KG WL Set 353 106
d) For PSCC Poles 300 KG WL Set 363 106
XIV 2 - Pin cross arm with pole clamp, bolts, nuts and washers with braces - MS
a) For RCC Poles Set 168 106
b) For PSCC Poles 140 KG WL Set 159 106
c) For PSCC Poles 200 KG WL Set 162 106
d) For PSCC Poles 300 KG WL Set 171 106
XV 2 - Pin cross arm with pole clamp , bolts, nuts and washers with braces - GI
a) For RCC Poles Set 223 106
b) For PSCC Poles 140 KG WL Set 210 106
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 26
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
c) For PSCC Poles 200 KG WL Set 216 106
d) For PSCC Poles 300 KG WL Set 226 106
LT Cross arm for vertical configuration
XVI Set 645 316
with clamps, bolts, nuts and washers (MS)
HT Single Top support with bolt, nuts and
XVII Set 112 70
washers (MS)
LT Single Top support with bolt, nuts and
XVIII Set 95 70
washers (MS)
XIX Insulators
a) 11kV Ceramic Pin insulator with GI pin No 105
b) No.15 Strain Insulator No 35
c) No.8 Strain Insulator No 16
d) 1.1 KV Ceramic Pin Insulator With GI pin No 48
11 KV, 5KN composite/Polymeric Pin
e) Insulator No 180
(24mm Dia FP Rod) Included in stringing
f) 45 kN Disc Insulator No 301
g) 70 kN Disc Insulator (Ball & Socket type) No 431
h) 90 kN Disc Insulator (Ball & Socket type) No 493
i) 11KV, 45 KN Polymeric Insulator No 164
j) 1KV, 70 KN Polymeric insulator No 264
XX ACSR conductor as per IS : 398 (Part - 2/1996) are the latest revision
Weasel ACSR
a) (6/2.59 mm Al + 1/2.59 mm St), Std Wt : 128 Kms 21552 2104
kgs/km
Labour Charges
Material
Complete (Including
SL No Particulars Unit Rates in
Erection, Excavation
Rs
& Fixing) in Rs
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 27
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
Rabbit ACSR
b) (6/3.35 mm Al + 1/3.35 mm St), Std Wt : 214 Kms 36497 2869
kgs/km
Coyote ACSR
c) (26/2.54 mm Al + 7/1.90 mm St), Std Wt : Kms 100111 5011
521 kgs/km
Lynx ACSR
d) (30/2.79 mm Al + 7/2.79 mm St), Std Wt : Kms 148499 -
842 kgs/km
XXI Guy Wire & GI Wire
7/10 SWG Guy Wire
a) MT 65137
(7/3.251mm Dia), Std Wt : 128 kgs/km
8 SWG GI Wire
b) MT 63293
(4.064 mm Dia), Std Wt: 125kgs/km
10 SWG GI Wire
c) MT 66777
(3.251mm Dia), Std Wt : 128 kgs/km
d) GI Barbed Wire 12 SWG MT 78584
XXII Guarding
Providing guarding for HT & LT line at Road
crossings,Telephone line crossings etc up to Rs. 80 per
a) Per Span 663
span of 60 Mtrs. (Including labour for fixing mtr
of necessary cross arms)
Providing guarding between HT & LT line up
Rs. 80 per
b) to a Span of 40 Mtrs. (Including labour for Per Span 663
mtr
fixing of necessary cross arms)
Providing guarding between HT & LT line
above 40 Mtrs span. (Including labour for Rs. 80 per
c) fixing of Per Span 1165
mtr
necessary cross arms)
XXIII Guy Set
a) Guy set with No.15 strain insulator & Set 830 390
Concreting materials as per Drwg No.
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 28
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
BESCOM/GM/CP/7/Dt; 24.10.07
Guy set with 2 Nos. 15 strain insulator &
b) Concreting materials as per Drwg No. Set 865 412
BESCOM/GM/CP/7/Dt; 24.10.07
Guy set with No. 8 strain insulator &
c) Concreting materials as per Drwg No. Set 811 390
BESCOM/GM/CP/7/Dt; 24.10.07
Guy concreting with Boulders, Mud & Sand
Material +
d) as per Drawing No BESCOM/GM/CP/7 Dt : Each 174
Labour
24.10.2007 (with out Cement )
XXIV EG Stirrup with GI Lacing Set/2Nos. 191 109
XXV Spiral Earth Electrode Set 165 61
Anti Climbing Device (12 Mtrs GI
XXVI Nos. 76 28
Barbed wire)
Labour Charges
Material
Complete (Including
SL No Particulars Unit Rates in
Erection, Excavation
Rs
& Fixing) in Rs
XXVII Caution/Danger Board Nos. 146 53
XXVIII Distribution Transformers - 3 Phase, 11kV/433V - Stacked Core with Oil
A. OPEN BUSHING TYPE
a) 25kVA, Aluminium Wdg, Star 1 (4 Star) Nos. 64900 750
b) 25kVA, Aluminium Wdg, Star 2 (5 Star) Nos. 74365 750
c) 63kVA, Aluminium Wdg, Star 1 (4 Star) Nos. 120360 750
d) 63kVA, Aluminium Wdg, Star 2 (5 Star) Nos. 128304 750
e) 100kVA, Aluminium Wdg, Star 1 (4 Star) Nos. 148680 1001
f) 100kVA, Aluminium Wdg, Star 2 (5 Star) Nos. 155931 1001
g) 250kVA, Aluminium Wdg, Star 1 (4 Star) Nos. 336300 1502
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 29
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
h) 250kVA, Aluminium Wdg, Star 2 (5 Star) Nos. 386745 1502
i) 500kVA, Aluminium Wdg, Star 1 (4 Star) Nos. 566400 2001
j) 500kVA, Aluminium Wdg, Star 2 (5 Star) Nos. 651360 2001
XXIX LT Distribution Boxes for Transformers -
LT Distribution Box for 100 kVA DTC with
a) Nos. 17545 501
MCCB's (Sheet Metal)
LT Distribution Box for 250 kVA DTC with
b) Nos. 17644 501
MCCB's (Sheet Metal)
LT Distribution Box for 250 kVA DTC with
c) Nos. 17644 501
MCCB's (SMC)
XXX 11 kV, GOS
a) 200 Amps, Single Break Set 7799 700
b) 400 Amps, Double Break Set 17545 777
XXXI 11 kV Solid Core HG Fuse Unit Set (3 Nos) 882 155
XXXII 11kV Class DOLO Cutouts Set (3 Nos) 4848 155
XXXIII Lightning Arresters
9kV, 5kA Metal Oxide Ceramic Type with
a) Set (3 Nos) 786 78
ground disconnector
9 kV, 5kA Polymeric Type with Ground
b) Set (3 Nos) 1335 78
disconnector
XXXIV Transformer grounding
GI Grounding pipe, B - Class, 42mm dia,
2.5mtrs long, 3.2mm thick with bolts nuts, GI
a) Strips and washers complete Per Electrode 1501 631
Minimum Weight of GI Pipe: 7.3 Kgs
b) Rod Type Set 1832 -
XXXV Concreting with Material & Labour
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 30
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
A Base concreting CC 1:4:8
a) Pole base 11/9.5/9/8 Mtrs Pole supports 500x650x150 237
mm
b) Pole base 9 Mtrs square pole 650x650x150 308
mm
c) Pole base 11 Mtrs spun pole 1000x1000x150 730
mm
B Pole concreting CC 1:2:4 (without coping)
a) 9.5 Mtrs Supports (Pole Concreting) 650x500x1850 2988
mm
b) 9 Mtrs Supports (Pole Concreting) 650x500x1700 2746
mm
c) 9 Mtrs Square Supports (Pole Concreting) 650X650x1700 3440
mm
d) 11 Mtrs Tubular Supports (Pole Concreting) 1000x1000x2500 12177
e) 11 Mtrs PSCC 650x500x2000 2912
mm
Labour Charges
Complete
Material
(Including
SL No Particulars Unit Rates in
Erection,
Rs
Excavation
& Fixing) in Rs
f) 7.5/8 Mtr Supports 400x400x1500 mm 1051
As per Drawing No.
Guy concreting with Boulders, Mud &
g) BESCOM/GM/CP/7 174
Sand
/dt: 24.10.07
C Providing Coping for Poles with CC 1:2:4 (As per actuals)
150mm around poles for a height of 300
a) mm for each 471
RCC, PSCC Poles
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 31
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
390 mm all around the pole for an height
b) each 1930
of 300 mm for Spun Poles
D Guy concreting in Marshy area:
Providing cement concrete 1:2:4 for
Anchor Rod in
a) each 881
Marshy/Black Cotton Soil 600x600x450
mm
XXXVI 11 kV, 3 Core XLPE UG Cable (Round armoured)
a) 95 Sqmm, (54 GI Wires - 2.5mm Dia) km 782621 39377
b) 120 Sqmm, (57 GI Wires - 2.5mm Dia) km 999586 39377
c) 150 Sqmm, (59 GI Wires - 2.5mm Dia) km 1149524 39377
d) 185 Sqmm, (51 GI Wires - 3.15mm Dia) km 1201800 41565
e) 240 Sqmm, (55 GI Wires - 3.15mm Dia) km 1471370 41565
f) 300 Sqmm, (58 GI Wires - 3.15mm Dia) km 1692076 43751
g) 400 Sqmm, (51 GI Wires - 4mm Dia) km 2245566 43751
Providing Electronic Trivector Meters with associated CT's Metering Box etc., on LT side of
XXXVII
Distribution Transformer Center (including cost of Energy Meter)
a) for 15/25 kVA DTC with CT ratio 50/5A Set 7812 1260
b) for 50/63 kVA DTC with CT ratio 100/5A Set 7392 1260
c) for 100 kVA DTC with CT ratio 150/5A Set 7089 1260
d) for 250 kVA DTC with CT ratio 400/5 A Set 7251 1260
e) for 500 kVA DTC with CT ratio 800/5A Set 7383 1260
CHAPTER 8
CONCLUSION
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 32
ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
In recent years, alongside with the fast increasing electric power necessity, the construction of power
network is becoming more vital. Stability of AC distribution systems and efficiency there will be
huge demand for power compensation. Hence the company and MESCOM sub division koppa,
provide me a good knowledge of electrical power distribution system and the cost data of various
material used in the power distribution system.
WORKING EXPERIENCE
My working experience includes coordinating the site and build the electrical power
distribution in overhead facilities at MESCOM sub division koppa, also provide the
engineering supports to the employees in overhead operation. I learned installation and
erection of all overhead line parameters such as transformer, cables, pole structures,
insulators, GOS, lightning arresters etc.
EPT OF EEE, A.I.T CHIKKAMAGALURPage 33
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- BLDG Ser Elect BSCDocument12 paginiBLDG Ser Elect BSCDon MustyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Installation in Building (Politeknik)Document24 paginiElectrical Installation in Building (Politeknik)muhamad syazwan92% (12)
- Electrical WiringDocument11 paginiElectrical WiringRasydan AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 SagarDocument58 pagini3 SagarSurya TejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CJ-E - Practical HV Cable Jointing and Terminations For Engineers and TechniciansDocument10 paginiCJ-E - Practical HV Cable Jointing and Terminations For Engineers and TechniciansNii AshiiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Training Report in 220 KV Sub Station of DTLDocument59 paginiTraining Report in 220 KV Sub Station of DTLishank_bounthiyal0% (1)
- Solid State TransformerDocument5 paginiSolid State TransformerVIVA-TECH IJRIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Transformer: Profile No.: 273 NIC Code: 27102Document14 paginiCurrent Transformer: Profile No.: 273 NIC Code: 27102Rama SubrahmanyamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transmission and Distribution: Stages of Power Flow in The NetworkDocument5 paginiTransmission and Distribution: Stages of Power Flow in The NetworkTrupti NandikolmathÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Transformer ManufacturingDocument25 paginiOn Transformer ManufacturingThakur Dhananjay Singh Gaur100% (1)
- Barredo, Bsa 3a1 PDFDocument5 paginiBarredo, Bsa 3a1 PDFCrisostomo Andiong BaltazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- JidexDocument5 paginiJidexsolomon 12ableÎncă nu există evaluări
- LT Distribution in CESC LTD.Document15 paginiLT Distribution in CESC LTD.Ramen DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 220 KV GSS Heerapura ReportDocument45 pagini220 KV GSS Heerapura ReportMohit Bhavsar63% (8)
- Learning Outcome: Estimating and Costing in Electrical EngineeringDocument15 paginiLearning Outcome: Estimating and Costing in Electrical EngineeringJEFFREY BAUTISTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upcl Report - Nitesh3Document28 paginiUpcl Report - Nitesh3Vaibhav SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IE Project Report Group 3Document9 paginiIE Project Report Group 3john jkillerzsÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 1.2 Electrical Power SystemDocument4 paginiECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 1.2 Electrical Power SystemAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Construction of AC DC InverterDocument41 paginiDesign and Construction of AC DC InverterOBASAN KEHINDE O. HUSSEINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation ElectricalDocument29 paginiPresentation ElectricalSazid RajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cheryl ProjectDocument36 paginiCheryl ProjectLebron DenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anjana FileDocument32 paginiAnjana Fileks175627scribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- 220 KV GSS Heerapura ReportDocument43 pagini220 KV GSS Heerapura ReportNitin Bhardwaj100% (2)
- Bel-Electrical SubstationDocument21 paginiBel-Electrical SubstationGagan MaheyÎncă nu există evaluări
- House Wiring ReportDocument9 paginiHouse Wiring ReportCovid VirusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power FormerDocument6 paginiPower FormerVijay RichardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Construction of A 2000W Inverter: Lawal Sodiq Olamilekan 03191100Document20 paginiDesign and Construction of A 2000W Inverter: Lawal Sodiq Olamilekan 03191100Da Saint100% (1)
- VCP W en PDFDocument14 paginiVCP W en PDFharosalesvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter OneDocument28 paginiChapter OneObafemi Samuel0% (1)
- Building UtilitiesDocument50 paginiBuilding Utilitiesayeez28Încă nu există evaluări
- The Electricity Supply System - Newcastle University UKDocument10 paginiThe Electricity Supply System - Newcastle University UKkija lemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Wiring InstallationDocument11 paginiElectrical Wiring InstallationDurrahKhazalle100% (26)
- Design Report XXXDocument41 paginiDesign Report XXXashikin100% (1)
- Barau MaidammaDocument4 paginiBarau MaidammaAbdulrahaman AbdulraheemÎncă nu există evaluări
- A69 - Res1 - de Leon, Angela Mae S.Document8 paginiA69 - Res1 - de Leon, Angela Mae S.Angela MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- SLK G9-Q4wk8 Mongcopa (Refined)Document13 paginiSLK G9-Q4wk8 Mongcopa (Refined)Jeson GaiteraÎncă nu există evaluări
- HT XLPE Cables Catalogue PDFDocument32 paginiHT XLPE Cables Catalogue PDFKvj SrinivasaraoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementing Electronic Document and Record Management SystemsDocument12 paginiImplementing Electronic Document and Record Management SystemsxaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cathodic Protection of Steel in Concrete Using LXI: Application NoteDocument6 paginiCathodic Protection of Steel in Concrete Using LXI: Application NoteCPFormanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 6 Electrical Services To BuildingsDocument14 paginiTopic 6 Electrical Services To Buildingsullhan84100% (1)
- Power Quality in Industrial Commercial Power SystemsDocument41 paginiPower Quality in Industrial Commercial Power SystemsDomingo RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Training Presentation-400 KV GSSDocument32 paginiPractical Training Presentation-400 KV GSSRam PrakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tejada - Homework 2Document3 paginiTejada - Homework 2Denver John TejadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Services 2 Reading MaterialDocument16 paginiServices 2 Reading MaterialDhyey VaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 4Document16 paginiWeek 4Mudit AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- IecDocument24 paginiIecMuhammad SameerÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADocument72 paginiAMohit KothariÎncă nu există evaluări
- InverterDocument52 paginiInverterD'ivy M Chico100% (3)
- Project 2Document13 paginiProject 2SAYYAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Importance of Electrical EnergyDocument38 paginiImportance of Electrical EnergyrahulÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Voltage & Power System ProtectionDocument17 paginiHigh Voltage & Power System ProtectionDipok Chandra PalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics Diploma Interview Q&A: Career GuideDe la EverandPower Electronics Diploma Interview Q&A: Career GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsDe la Everand16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Empowering Networks: A Comprehensive Guide to Medium Voltage SwitchgearDe la EverandEmpowering Networks: A Comprehensive Guide to Medium Voltage SwitchgearÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsDe la EverandInsulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (5)
- Infrared PDFDocument8 paginiInfrared PDFAnonymous sv02k6GH0Încă nu există evaluări
- Dhaval VDRDocument57 paginiDhaval VDRPriyanth AcharyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MaterialDocument8 paginiMaterialPriyanth AcharyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ColdgenDocument59 paginiColdgenPriyanth AcharyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WordDocument1 paginăWordPriyanth AcharyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Description Features: Ltc4100 Smart Battery Charger ControllerDocument30 paginiDescription Features: Ltc4100 Smart Battery Charger ControllerAlexander VargasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medium Voltage CableDocument7 paginiMedium Voltage Cableakheel201Încă nu există evaluări
- Mains Interruption Counter With Indicator Circuit DiagramDocument6 paginiMains Interruption Counter With Indicator Circuit DiagramSelvy SalfitriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scilab - Ece ProgramsDocument5 paginiScilab - Ece ProgramsYash PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21 PrimepowerDocument2 pagini21 PrimepowerfernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS740 A8hDocument10 paginiCS740 A8hPaulo CardosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cicor ME Design Manual CompleteDocument24 paginiCicor ME Design Manual CompleteAybüke ÇalıkoğluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure - ASKA Mobile Light Tower - V5Document8 paginiBrochure - ASKA Mobile Light Tower - V5cool.boys4200Încă nu există evaluări
- 7SJ80Document5 pagini7SJ80Ricardo HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- FP06P Data Sheet: FP06P-S1-04-32-NU-V-77A-110A-M-30Document1 paginăFP06P Data Sheet: FP06P-S1-04-32-NU-V-77A-110A-M-30Ainayya alfatimahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part 3 - Technical SpecsDocument659 paginiPart 3 - Technical Specsateef idreesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Quiz #03 Electrical Engineering 1Document2 paginiOnline Quiz #03 Electrical Engineering 1Koo Ferdinand AdriantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Method Statement Testing and Commisioning of TransformerDocument5 paginiMethod Statement Testing and Commisioning of TransformerDante Choong Hoe Wong100% (1)
- L577-User Manual For Hardware PDFDocument30 paginiL577-User Manual For Hardware PDFLe Chi PhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Scully Groundhog™: Vehicle Static Grounding SystemDocument3 paginiThe Scully Groundhog™: Vehicle Static Grounding SystemDiego Santiago D AguiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7ST6 Pi 76Document8 pagini7ST6 Pi 76Nima MahmoudpourÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operation: Operation P846/En Op/A11 Micom P846Document28 paginiOperation: Operation P846/En Op/A11 Micom P846kessir taouilÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLCDocument56 paginiPLCFelix Lee Kah NgieÎncă nu există evaluări
- G12 Physics Pre Board - 1 QP With SolutionsDocument25 paginiG12 Physics Pre Board - 1 QP With SolutionsSreshta ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 2 - Transducer - 2Document73 paginiCHAPTER 2 - Transducer - 2RafaelTituzÎncă nu există evaluări
- I JR Et 20160533016Document6 paginiI JR Et 20160533016Beeresha R S100% (1)
- Get AttDocument3 paginiGet Attfrank azamarÎncă nu există evaluări
- References Leca+Philip Stretchable 50376-2017-Philippe-UnlockedDocument21 paginiReferences Leca+Philip Stretchable 50376-2017-Philippe-Unlockedck maitiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading Capacitor CodesDocument2 paginiReading Capacitor Codesfurious143Încă nu există evaluări
- ANSI Y32.9-1972 Simbologia Instalações PrediaisDocument42 paginiANSI Y32.9-1972 Simbologia Instalações PrediaisAlexandre PereiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual VK 10 K-SeriesDocument37 paginiManual VK 10 K-SeriesEvren PamukÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Aperture-Coupled Microstrip Antenna With Reconfigurable Radiation Pattern PDFDocument24 paginiAn Aperture-Coupled Microstrip Antenna With Reconfigurable Radiation Pattern PDFrajendrasoloniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bell 407 Troubleshooting Guide PDFDocument150 paginiBell 407 Troubleshooting Guide PDFRamónÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRONET User Manual: AC Servo DriveDocument88 paginiPRONET User Manual: AC Servo DriveJosé I. Cárcamo S.Încă nu există evaluări
- Product Data Sheet: Circuit Breaker Compact Ns800H, 70 Ka at 415 Vac, Micrologic 2.0 Trip Unit, 800 A, Fixed, 4 Poles 4DDocument3 paginiProduct Data Sheet: Circuit Breaker Compact Ns800H, 70 Ka at 415 Vac, Micrologic 2.0 Trip Unit, 800 A, Fixed, 4 Poles 4DsoyalÎncă nu există evaluări