Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Normal Modes - Rigid Element Analysis With RBE2 and CONM2
Încărcat de
karthekeyanmenonTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Normal Modes - Rigid Element Analysis With RBE2 and CONM2
Încărcat de
karthekeyanmenonDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
WORKSHOP 17
Normal Modes - Rigid Element
Analysis with RBE2 and CONM2
Y
Y
ZZ
Z X
Objectives:
■ Create a geometric representation of a tube.
■ Use the geometry model to define an analysis model
comprised of plate elements.
■ Idealize a rigid end using RBE2 elements.
■ Define a concentrated mass, to represent the weight of the
rigid enclosure (CONM2).
■ Run an MSC.Nastran normal modes analysis.
■ Visualize analysis results.
MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook 17-1
17-2 MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 17 Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2
Model Description:
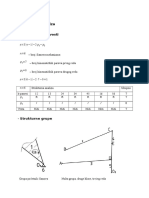
Figure 17.1 is a finite element model of a hollow tube. The end of the
tube is rigidly connected to a large structure.
Instead of adding to the model size by modeling the entire structure, use
a RBE2 and CONM2 to account for the rest of the structure attached to
the cylinder. Table 17.1 contains information for the finite element
model: the cylinder dimensions, material properties, and cylinder
thickness.
Figure 17.1 - Finite Element Model of a Hollow Tube
19
25 13
20
26 31
14 7
21
27 32
15 43 8
1
22 123456(CID=1)
28 33 44 49 123456(CID=1)
16 9 2 61 123456(CID=1)
55
23
29 34 45 50 123456(CID=1)
17 10 62 123456(CID=1)
3 56
24
30 35 46 51
18 11 63 123456(CID=1)
4 123456(CID=1)
57
36 52
47 12 64 123456(CID=1)
5 123456(CID=1)
999 58 123456(CID=1)
48 53 65
6
59
54 66
60
Table 17.1 - Model Properties
Radius: 15 in
Thickness: 0.125 in
Length: 90 in
Elastic Modulus: 10E+06 lb/in2
Density: 0.101 lbs/in3
Poisson Ratio: 0.3
MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook 17-3
Suggested Exercise Steps:
■ Generate a finite element representation of the cylinder structure
(i.e., The nodes (GRID) and element connectivities (CQUAD4)
should be defined manually).
■ Define material (MAT1) and element (PSHELL) properties.
■ Create grid point 999 at the center of the rigid end. This point is
to serve as the load application point, as well as the connection
point for the rigid element.
■ Idealize the rigid end with rigid elements (RBE2).
■ Apply the fixed boundary constraints (SPC1).
■ Apply a concentrated mass at the center of the top enclosure,
Grid 999 (CONM2).
■ Prepare the model for normal modes analysis (SOL 103).
■ Generate an input file and submit it to the MSC.Nastran solver
for normal modes analysis.
■ Review the results.
17-4 MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 17 Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2
Exercise Procedure:
1. Create a new database called workshop17.db.
File/New...
New Database Name: workshop17
OK
In the New Model Preference form set the following:
Tolerance: ◆ Default
Analysis code: MSC.Nastran
OK
NOTE: Whenever possible, toggle off the ❑ Auto Execute option by left clicking
the check box.
2. Create a cylindrical coordinate frame.
◆ Geometry
Action: Create
Object: Coord
Method: 3 Point
Type: Cylindrical
Apply
3. Define a curve.
Action: Create
Object: Curve
Method: XYZ
Vector Coordinates List: <0, 0, 90>
Origin Coordinates List: [15, 0, 0]
Apply
MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook 17-5
Change the view to an isometric view by using the Iso 1 View icon on the
toolbar.
Iso 1 View
4. Construct a surface to model the cylinder by revolving the curve.
Action: Create
Object: Surface
Method: Revolve
Axis: Coord 0.3
Total Angle: 180
Curve List: Curve 1
Apply
4a. Repeat this step a second time to complete the cylinder. This time select the curve
opposite Curve 1 which is Surface 1.2. (see Figure 17.3)
Action: Create
Object: Surface
Method: Revolve
Axis: Coord 0.3
Total Angle: 180
Curve List: Surface 1.2
Apply
17-6 MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 17 Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2
Figure 17.3
Surface 1.2
Surface 1.3
Curve 1
Y
Z X Surface 2.3
5. Create a mesh using the surfaces. Use Mesh Seeds to define the mesh density.
◆ Finite Elements
Action: Create
Object: Mesh Seed
Type: Uniform
◆ Number of Elements
Number: 5
Curve List: Curve 1, Surface 1.3, 2.3
(See Fig. 22.3)
Apply
5a. After defining the mesh seeds, mesh the surface.
◆ Finite Elements
Action: Create
Object: Mesh
Type: Surface
Node Coordinate Frames...
MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook 17-7
Analysis Coordinate Frame: Coord 1
Refer. Coordinate Frame: Coord 1
OK
Surface List: Surface 1, 2
Apply
5b. Equivalence the model to connect the mesh.
Action: Equivalence
Object: All
Method: Tolerance Cube
Apply
6. Define material properties for the plate.
◆ Materials
Action: Create
Object: Isotropic
Method: Manual Input
Material Name: mat_1
Input Properties...
Elastic Modulus: 10.0E6
Poisson Ratio: 0.3
Density: 0.101
OK
Apply
7. Define element properties.
◆ Properties
Action: Create
Dimension: 2D
17-8 MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 17 Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2
Type: Shell
Property Set Name: wall
Input Properties...
Material Name: m:mat_1
Thickness: 0.125
OK
Select Members: Surface 1, 2
Add
Apply
Define loads and boundary conditions to the model.
8. Constrain the right edge in all six degrees of freedom. To make the
entity selection easier change the view to a Right View by selecting
the Right Side View icon.
Right Side View
Figure 17.4
Nodes 6:36:6 48:66:6 999 Nodes 1:31:6, 43:61:6
◆ Loads/BCs
MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook 17-9
Action: Create
Object: Displacement
Type: Nodal
New Set Name: fixed
Input Data...
Translations <T1 T2 T3> <0, 0, 0>
Rotations <R1 R2 R3> <0, 0, 0>
Analysis Coordinate Frame: Coord 1
OK
Select Application Region...
Geometry Filter: ◆ FEM
Curve List: Node 1:31:6, 43:61:6
(See Fig. 22.4)
Add
OK
Apply
9. Define a node for the concentrated mass.
◆ Finite Elements
Action: Create
Object: Node
Method: Edit
Node ID List: 999
Analysis Coordinate Frame: Coord 1
Refer. Coordinate Frame: Coord 1
❑ Associate with Geometry
Node Location List: [0, 0, 90]
Apply
17-10 MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 17 Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2
10. Create the rigid element.
◆ Finite Elements
Action: Create
Object: MPC
Type: RBE2
Define Terms...
◆ Create Dependent
Node List: Node 6:36:6, 48:66:6
Type the nodes into the list directly or select the nodes from the
viewport by changing back to an isometric view and selecting the
nodes on the left edge of the model.
Select DOFs by holding the Shift key down while clicking with the
left mouse button.
DOFs: UX
UY
UZ
Apply
◆ Create Independent
Node List: Node 999
Apply
Cancel
Apply
Change the view to an isometric view by using the Iso 1 View icon
on the toolbar.
Iso 1 View
MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook 17-11
Figure 17.5
123456(CID=1)
123456(CID=1)
123456(CID=1)
T
123456(CID=1)
123456(CID=1)
1
Z R
123456(CID=1)
123456(CID=1)
123456(CID=1)
123456(CID=1)
123456(CID=1)
X
Z
11. Define a point element on Node 999 for the concentrated mass.
◆ Finite Elements
Action: Create
Object: Element
Method: Edit
Shape: Point
Topology: Point
Node 1: Node 999
Apply
12. Define a concentrated mass.
◆ Properties
Action: Create
Dimension: 0D
Type: Mass
Property Set Name: concentrated_mass
Options(s): Lumped
17-12 MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 17 Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2
Input Properties...
Mass: 500
OK
Select Members: Element 51
hint: Use the Point Element filter on the Entity Selection menu.
Point Element
Add
Apply
13. Generate an input file for analysis.
◆ Analysis
Action: Analyze
Object: Entire Model
Method: Analysis Deck
Jobname: workshop17
Solution Type...
Solution Type: ◆ NORMAL MODES
Solution Parameters...
❒ Automatic Constraints
(Deselect Automatic Constraints.)
Mass Calculation: Coupled
Wt. -Mass Conversion = .00259
OK
OK
Apply
MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook 17-13
An MSC.Nastran input file called workshop17.bdf will be
generated. This process of translating the model into an input file is
called the Forward Translation. The Forward Translation is
complete when the Heartbeat turns green.
17-14 MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 17 Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2
Generating an Input File for MSC.Nastran Users:
MSC.Nastran users can generate an input file using the data from
Table 22.1. The result should be similar to the output below.
14. MSC.Nastran input file: workshop17.dat
ID SEMINAR,workshop 17
SOL 103
TIME 600
CEND
SEALL = ALL
SUPER = ALL
TITLE = Normal Modes w/ RBE2
ECHO = NONE
MAXLINES = 999999999
SUBCASE 1
METHOD = 1
SPC = 2
BEGIN BULK
PARAM AUTOSPC NO
PARAM COUPMASS 1
PARAM WTMASS .00259
PARAM,NOCOMPS,-1
EIGRL 1 10 0
PSHELL 1 1 .125 1 1
CQUAD4 1 1 1 2 8 7
= *1 = *1 *1 *1 *1
=3
CQUAD4 6 1 7 8 14 13
= *1 = *1 *1 *1 *1
=3
CQUAD4 11 1 13 14 20 19
= *1 = *1 *1 *1 *1
=3
CQUAD4 16 1 19 20 26 25
= *1 = *1 *1 *1 *1
=3
CQUAD4 21 1 25 26 32 31
= *1 = *1 *1 *1 *1
=3
CQUAD4 26 1 31 32 44 43
= *1 = *1 *1 *1 *1
=3
CQUAD4 31 1 43 44 50 49
= *1 = *1 *1 *1 *1
=3
CQUAD4 36 1 49 50 56 55
= *1 = *1 *1 *1 *1
=3
CQUAD4 41 1 55 56 62 61
= *1 = *1 *1 *1 *1
=3
CQUAD4 46 1 61 62 2 1
= *1 = *1 *1 *1 *1
MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook 17-15
=3
CONM2 51 999 500.
MAT1 1 1.+7 .3 .101
RBE2 52 999 123 6 12 18 24 30 + A
+ A 36 48 54 60 66
GRID 1 1 15. 0. 0. 1
= *1 = = = *18 =
=4
GRID 7 1 15. 36. 0. 1
= *1 = = = *18 =
=4
GRID 13 1 15. 72. 0. 1
= *1 = = = *18 =
=4
GRID 19 1 15. 108. 0. 1
= *1 = = = *18 =
=4
GRID 25 1 15. 144. 0. 1
= *1 = = = *18 =
=4
GRID 31 1 15. 180. 0. 1
= *1 = = = *18 =
=4
GRID 43 1 15. 216. 0. 1
= *1 = = = *18 =
=4
GRID 49 1 15. 252. 0. 1
= *1 = = = *18 =
=4
GRID 55 1 15. 288. 0. 1
= *1 = = = *18 =
=4
GRID 61 1 15. 324. 0. 1
= *1 = = = *18 =
=4
GRID 999 1 0. 0. 90. 1
SPCADD 2 1
SPC1 1 123456 1 7 13 19 25 31 + B
+ B 43 49 55 61
CORD2C 1 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. + C
+ C 1. 0. 0.
ENDDATA
17-16 MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 17 Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2
Submitting the Input File for Analysis:
15. Submit the input file to MSC.Nastran for analysis.
15a. To submit the MSC.Patran .bdf file for analysis, find an
available UNIX shell window. At the command prompt
enter: nastran workshop17.bdf scr=yes. Monitor the
run using the UNIX ps command.
15b. To submit the MSC.Nastran .dat file for analysis, find an
available UNIX shell window. At the command prompt
enter: nastran workshop17.dat scr=yes. Monitor the
run using the UNIX ps command.
16. When the run is completed, edit the workshop17.f06 file and
search for the word FATAL. If no matches exist, search for the
word WARNING. Determine whether existing WARNING
messages indicate modeling errors.
17. While still editing workshop17.f06, search for the word:
E I G E N (spaces are necessary)
What are the first five modes?
Mode 1 = _________ Hz
Mode 2 = _________ Hz
Mode 3 = _________ Hz
Mode 4 = _________ Hz
Mode 5 = _________ Hz
MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook 17-17
Comparison of Results:
18. Compare the results obtained in the .f06 file with the
results on the following page:
17-18 MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 17
R E A L E I G E N V A L U E S
MODE EXTRACTION EIGENVALUE RADIANS CYCLES GENERALIZED GENERALIZED
NO. ORDER MASS STIFFNESS
1 1 3.128183E+04 1.768667E+02 2.814921E+01 1.000000E+00 3.128183E+04
2 2 3.128183E+04 1.768667E+02 2.814921E+01 1.000000E+00 3.128183E+04
3 3 9.379013E+05 9.684531E+02 1.541341E+02 1.000000E+00 9.379013E+05
Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2
4 4 1.225376E+06 1.106967E+03 1.761793E+02 1.000000E+00 1.225376E+06
5 5 1.225376E+06 1.106967E+03 1.761793E+02 1.000000E+00 1.225376E+06
6 6 1.273205E+06 1.128364E+03 1.795847E+02 1.000000E+00 1.273205E+06
7 7 1.273205E+06 1.128364E+03 1.795847E+02 1.000000E+00 1.273205E+06
8 8 1.749829E+06 1.322811E+03 2.105319E+02 1.000000E+00 1.749829E+06
9 9 2.463450E+06 1.569538E+03 2.497998E+02 1.000000E+00 2.463450E+06
10 10 2.463450E+06 1.569538E+03 2.497998E+02 1.000000E+00 2.463450E+06
R E A L E I G E N V A L U E S
MODE EXTRACTION EIGENVALUE RADIANS CYCLES GENERALIZED GENERALIZED
NO. ORDER MASS STIFFNESS
MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook
1 1 3.128183E+04 1.768667E+02 2.814921E+01 1.000000E+00 3.128183E+04
2 2 3.128183E+04 1.768667E+02 2.814921E+01 1.000000E+00 3.128183E+04
3 3 9.379013E+05 9.684531E+02 1.541341E+02 1.000000E+00 9.379013E+05
4 4 1.225376E+06 1.106967E+03 1.761793E+02 1.000000E+00 1.225376E+06
5 5 1.225376E+06 1.106967E+03 1.761793E+02 1.000000E+00 1.225376E+06
6 6 1.273205E+06 1.128364E+03 1.795847E+02 1.000000E+00 1.273205E+06
7 7 1.273205E+06 1.128364E+03 1.795847E+02 1.000000E+00 1.273205E+06
8 8 1.749829E+06 1.322811E+03 2.105319E+02 1.000000E+00 1.749829E+06
9 9 2.463450E+06 1.569538E+03 2.497998E+02 1.000000E+00 2.463450E+06
10 10 2.463450E+06 1.569538E+03 2.497998E+02 1.000000E+00 2.463450E+06
17-19
19. MSC.Nastran Users have finished this exercise.
MSC.Patran Users should proceed to the next step.
20. Proceed with the Reverse Translation process, that is attaching the
workshop.xdb results file into MSC.Patran. To do this, return to the
Analysis form and proceed as follows:
◆ Analysis
Action: Attach XDB
Object: Result Entities
Method Local
Select Results File...
Select Results File: workshop17.xdb
OK
Apply
21. When the translation is complete bring up the Results form.
◆ Results
Action: Create
Object: Deformation
Select Result Case(s): Default, Mode 8:Freq.=210.53
Select Deformation Result: Eigenvectors, Translational
Show As: Resultant
Quit MSC.Patran after completing this exercise.
17-20 MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook
17-21 MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook
Mode 1 = 28.149 Hz
Mode 2 = 28.149Hz
Mode 3 = 154.13 Hz
Mode 4 = 176.18 Hz
Mode 5 = 176.18 Hz
Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2 WORKSHOP 17
17-22 MSC.Nastran 120 Exercise Workbook
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Linear Static - Rigid Element Analysis With RBE2 and CONM2Document16 paginiLinear Static - Rigid Element Analysis With RBE2 and CONM2karthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clustering L7Document7 paginiClustering L7u- m-Încă nu există evaluări
- Cirrus: Illustrated Parts Catalog Models Sr22 and Sr22TDocument2 paginiCirrus: Illustrated Parts Catalog Models Sr22 and Sr22Thector joel lizarragaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 2 - MinitabDocument7 paginiExercise 2 - MinitabLawrence BelloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math Basic TrainingDocument50 paginiMath Basic TrainingGinoDayo16Încă nu există evaluări
- KmeansDocument6 paginiKmeansRaghavendra SwamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 1 024Document3 paginiProblem 1 024imadusÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Evaluation of The GCI For Unstructured GridsDocument33 paginiAn Evaluation of The GCI For Unstructured GridsSachin RoutÎncă nu există evaluări
- C-Mos Serial I/O: DD DDDocument2 paginiC-Mos Serial I/O: DD DDelieÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Categorical FDDocument3 paginiFor Categorical FDVerolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strukturna Analiza: - Stepen PokretljivostiDocument13 paginiStrukturna Analiza: - Stepen PokretljivostiArmin KovačevićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insert Wanted Parameter Settings and Press Enter Ssdesdl - 92 Qdesdl 30 Lcompdl 6 Qcompdl 70Document12 paginiInsert Wanted Parameter Settings and Press Enter Ssdesdl - 92 Qdesdl 30 Lcompdl 6 Qcompdl 70Anonymous DUua3A5Încă nu există evaluări
- Sinclair Enterprise Physics Engineering ElectronicsDocument160 paginiSinclair Enterprise Physics Engineering ElectronicsOsegasin Grupo AlertaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CDX 802Document19 paginiCDX 802Mario LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- C-Mos FDC (Floppy Disk Controller)Document3 paginiC-Mos FDC (Floppy Disk Controller)Bos QuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Which Is The Missing Section?: 62 Test and Assess Your Brain QuotientDocument10 paginiWhich Is The Missing Section?: 62 Test and Assess Your Brain QuotientRd manÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: A Right Choice For The Real AspirantDocument15 paginiSri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: A Right Choice For The Real AspirantZaid khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: A Right Choice For The Real AspirantDocument15 paginiSri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: A Right Choice For The Real AspirantZaid khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SystemC Based JPEGDocument17 paginiSystemC Based JPEG08-Phạm Gia HuyÎncă nu există evaluări
- StatsDocument17 paginiStatsAryan BudhirajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- T2 ถูกแล้วDocument3 paginiT2 ถูกแล้วAtragalusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 12 Maths Project HelpfulDocument23 paginiClass 12 Maths Project HelpfulParam Waje100% (1)
- Stat 4Document5 paginiStat 4francis pacaigueÎncă nu există evaluări
- RealizabilityDocument2 paginiRealizabilityanjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Relation Between Quark Confinement and Chiral Sym-Metry Breaking in Odd-Number Lattice QCDDocument8 paginiAnalytical Relation Between Quark Confinement and Chiral Sym-Metry Breaking in Odd-Number Lattice QCDcrocoaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deluxe Tunnels & Trolls Cheat SheetDocument2 paginiDeluxe Tunnels & Trolls Cheat Sheettruffle1bootsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module-2 System of Linear Equations and Eigen Value Problems Important Numerical Methods in Module-IDocument24 paginiModule-2 System of Linear Equations and Eigen Value Problems Important Numerical Methods in Module-IJawa freakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module-2 System of Linear Equations and Eigen Value Problems Important Numerical Methods in Module-IDocument24 paginiModule-2 System of Linear Equations and Eigen Value Problems Important Numerical Methods in Module-Ivenkat sathwik kethepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parvez 4 PDFDocument24 paginiParvez 4 PDFJawa freakÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW 2Document2 paginiHW 2kalaputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Note #10 Correlation and RegressionDocument7 paginiNote #10 Correlation and Regressiontwanda bryanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SketcherDocument83 paginiSketcherNicholas StrangeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sae MethodologyDocument35 paginiSae MethodologyessentialstatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Models: Group 4 (BSA - 1A)Document36 paginiNetwork Models: Group 4 (BSA - 1A)Raicen Gonzales MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hce Performance Model: SolabsDocument20 paginiHce Performance Model: SolabsYeshwanth KohliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wu Icip08Document4 paginiWu Icip08Navneet ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CNN Architectures 01Document66 paginiCNN Architectures 01Abdul hadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Truss ExampleDocument8 paginiTruss Exampledixn__Încă nu există evaluări
- Problem Formation & CalculationDocument13 paginiProblem Formation & CalculationVyshnavi MankalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HP Heater 2 NewDocument69 paginiHP Heater 2 NewKuppan SrinivasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block Stock of HARCODocument76 paginiBlock Stock of HARCOPriyance NababanÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction To JPEG Compression Using Matlab: Arno Swart 28th October 2003Document5 paginiAn Introduction To JPEG Compression Using Matlab: Arno Swart 28th October 2003infiniti47Încă nu există evaluări
- Stat LabDocument4 paginiStat Labcansu parlakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solving Large Systems: 6.1 Elimination With ReorderingDocument10 paginiSolving Large Systems: 6.1 Elimination With ReorderingEfstathios SiampisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Face RecognitionDocument20 paginiFace RecognitionMubeen TajÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction To JPEG Compression Using Matlab: Arno Swart 30 October, 2003Document6 paginiAn Introduction To JPEG Compression Using Matlab: Arno Swart 30 October, 2003ankancemk0422Încă nu există evaluări
- Schematic Diagrams: 11-1 PWB-MAIN (Power)Document12 paginiSchematic Diagrams: 11-1 PWB-MAIN (Power)JasiekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade Thresholds - November 2017: Cambridge International AS & A Level History (9389)Document2 paginiGrade Thresholds - November 2017: Cambridge International AS & A Level History (9389)musa arif gillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge International As A Level History 9389Document2 paginiCambridge International As A Level History 9389musa arif gillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Systems Analysis and Control: Matthew M. PeetDocument26 paginiSystems Analysis and Control: Matthew M. PeetNour DmourÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clannad - Onaji Takami HeDocument3 paginiClannad - Onaji Takami HeikusadanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 08-01-2022 SR - super60-II Jee-Main PTM-12 Key & Sol'sDocument24 pagini08-01-2022 SR - super60-II Jee-Main PTM-12 Key & Sol'smanideepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block Stock of SerangDocument72 paginiBlock Stock of SerangPriyance NababanÎncă nu există evaluări
- LegendsDocument4 paginiLegendsKeirvin Cloi RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- K-Means Clustering: AlgorithmDocument6 paginiK-Means Clustering: AlgorithmmaiedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Programming and Partial Differential EquationsDe la EverandDynamic Programming and Partial Differential EquationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction to Programming with SpecificationsDe la EverandAn Introduction to Programming with SpecificationsEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- Building Ideas: An Architectural Guide to the University of ChicagoDe la EverandBuilding Ideas: An Architectural Guide to the University of ChicagoEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- Gray Cast Iron: The Tensile Cyclic Stress Strain CurveDocument2 paginiGray Cast Iron: The Tensile Cyclic Stress Strain CurvekarthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integration of MSC/PATRAN With Sandia National Laboratory's EXODUS II Database SystemDocument19 paginiIntegration of MSC/PATRAN With Sandia National Laboratory's EXODUS II Database SystemkarthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Divergence PDFDocument7 paginiDivergence PDFkarthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workshop 16 Stiffened Plate: WS16-1 NAS120, Workshop 16, May 2006 © 2005 MSC - Software CorporationDocument36 paginiWorkshop 16 Stiffened Plate: WS16-1 NAS120, Workshop 16, May 2006 © 2005 MSC - Software CorporationkarthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aeroservoelastic Modeling, Analysis, and Design Techniques PDFDocument12 paginiAeroservoelastic Modeling, Analysis, and Design Techniques PDFkarthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verification of A Stiffened Plate ModelDocument8 paginiVerification of A Stiffened Plate ModelkarthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prof HVLDocument51 paginiProf HVLkarthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meshing and Property Assignment: Workshop 3Document12 paginiMeshing and Property Assignment: Workshop 3karthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normal Modes Analysis of A Simply-Supported Stiffened PlateDocument6 paginiNormal Modes Analysis of A Simply-Supported Stiffened PlatekarthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Day 1: 22 July 2011 Finite Element Methods by S. Rajagopal ScientistDocument38 paginiDay 1: 22 July 2011 Finite Element Methods by S. Rajagopal ScientistkarthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mr. KameshDocument49 paginiMr. KameshkarthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAVEN PFDPU Evaluaton Rev 3Document46 paginiMAVEN PFDPU Evaluaton Rev 3karthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Center of Pressure PDFDocument2 paginiCenter of Pressure PDFkarthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Lecture Mr. Nitin S. GokhaleDocument21 pagini4 Lecture Mr. Nitin S. GokhalekarthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Applications of Aeroelastic Analysis For Aircaft Design and CertificationDocument16 paginiPractical Applications of Aeroelastic Analysis For Aircaft Design and CertificationkarthekeyanmenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerodynamic Influence Coefficients MethodsDocument106 paginiAerodynamic Influence Coefficients Methodskarthekeyanmenon100% (1)
- B.Sc. Part - I PHYSICS-Paper - I Mechanics and Properties of MatterDocument10 paginiB.Sc. Part - I PHYSICS-Paper - I Mechanics and Properties of MatterUpperwala RaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part - A Section - I: CLASS X (2020-21) Mathematics Standard (041) Sample Paper-01Document12 paginiPart - A Section - I: CLASS X (2020-21) Mathematics Standard (041) Sample Paper-01Suyash PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emags 3Document3 paginiEmags 3sygwapoooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asme y 14.5.1M-1994 (En) - 2004Document92 paginiAsme y 14.5.1M-1994 (En) - 2004Robert Marsella100% (4)
- Maths PDFDocument60 paginiMaths PDFLoh Chee WeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - MCDocument7 pagini(11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - MCsophia yeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eg Unit 4 QPDocument3 paginiEg Unit 4 QPMICHEL RAJ MechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assign 02 - CH 22-p. 01 - PHYS 102Document32 paginiAssign 02 - CH 22-p. 01 - PHYS 102Ihab RagabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 10th SA-1 MaterialDocument22 paginiClass 10th SA-1 MaterialMd MuzammilÎncă nu există evaluări
- RoundnessDocument23 paginiRoundnessKumar ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sine Bar'Document6 paginiSine Bar'Jonathan PereiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheet 4Document2 paginiSheet 4Mo 16Încă nu există evaluări
- WRC 297 Vs WRC 107Document2 paginiWRC 297 Vs WRC 107Rakesh100% (2)
- 3 Problem Solving With Flac: Section 3.1 Sections 3.2 3.9Document108 pagini3 Problem Solving With Flac: Section 3.1 Sections 3.2 3.9seif17Încă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Vessel DesignDocument21 paginiPressure Vessel DesignAbdullah AlgwhriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Projection of SolidDocument41 paginiProjection of SolidSabareesan SubramanianÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2023 MK Sample QuestionsDocument12 pagini2023 MK Sample QuestionsRubab ZahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geomagic Q12 GuideDocument30 paginiGeomagic Q12 Guidecmm5477Încă nu există evaluări
- Math IGCSE-MensurationDocument13 paginiMath IGCSE-MensurationKrish ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- (W-19) Dynamics of MachinesDocument4 pagini(W-19) Dynamics of MachinesNabeel KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal of Food Engineering: Si Zhu, Bing Li, Guibing ChenDocument10 paginiJournal of Food Engineering: Si Zhu, Bing Li, Guibing ChenYaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2006 Hs ContestDocument7 pagini2006 Hs ContestJohn TafuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CJ2 PDFDocument113 paginiCJ2 PDFZeljko Vojnic TunicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 6Document9 paginiMath 6Jhem VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Transfer: Al-Furat Al-Awsat Technical UniversityDocument23 paginiHeat Transfer: Al-Furat Al-Awsat Technical UniversityabasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Maths Set CDocument12 pagini10 Maths Set Canirudhminecraft1Încă nu există evaluări
- Buckling of Imperfect Elliptical Cylindrical Shells UnderDocument6 paginiBuckling of Imperfect Elliptical Cylindrical Shells UnderAdel MuslehÎncă nu există evaluări
- United States Patent (19) : Primary Examiner-Samuel ScottDocument7 paginiUnited States Patent (19) : Primary Examiner-Samuel ScottRockerss RockerssÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jacstone 100 - MathDocument11 paginiJacstone 100 - MathArgelyn Joy CreerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summative Test No. 1Document6 paginiSummative Test No. 1Shaine Dzyll KuizonÎncă nu există evaluări