Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Sulfiding Contingency Guideline For DHDS
Încărcat de
bikas_sahaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Sulfiding Contingency Guideline For DHDS
Încărcat de
bikas_sahaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Sulfiding Contingency Guideline
Loss of Recycle Gas Compressor
In case of Recycle Gas Compressor Tripping, Charge pump and Combined Feed Heater
will automatically trip by ESD112 and ESD136
a) Below 245°C – Temperature is low enough that metal reduction is not possible.
Await reinstatement of Recycle Gas Flow if duration of non-availability of the
Compressor is less than 4 hours. If duration is longer than 4 hours, reduce Reactor
Bed Peak temperature below 205°C.
b) Above 245°C – Temperature is high enough to cause metal reduction. Start routing
Make up Hydrogen in the Compressor discharge to bring down the temperature. If
Hydrogen routing can not be done, depressurize to bring down Bed Peak
temperature to less than 245°C. Upon completion of low rate de-pressuring, re-
pressurize the unit with make up Hydrogen to increase the Reactor pressure. For
non-availability of the Compressor for longer duration, it is recommended to cool the
Unit further to below 150°C.
Loss of Hydrogen Make up
Hydrogen is consumed during activation by the liquid Feed. With the loss of make up
Hydrogen gas flow, Hydrogen level can deplete and can affect sulfiding of the catalyst.
If the make up Hydrogen flow can be re-instated in less than 4 hours, reduce Reactor
temperature to below 205°C and stop the Sulfiding agent injection. Monitor Hydrogen in
the Recycle Gas stream.
If the make up Hydrogen flow can be re-instated only in more than 4 hours, reduce
Reactor temperature to below 205°C, stop the Sulfiding agent injection and stop Charge
Pump. Monitor Hydrogen in the Recycle Gas stream.
Loss of Charge Pump
If the Charge pump trips, DMDS injection also stops. This is critical during the sulfiding
stages as sulfur is still being absorbed by the catalyst and H2S level in the recycle gas
can drop to a level where metal reduction is possible.
a) Below 245°C – Loss of Feed pump is not critical as long as Reactor temperatures
are less than 245°C. If pump non-availability is longer than 4 hours, reduce Reactor
temperature below 205°C.
b) Above 245°C – Reduce Reactor temperature below 245°C using Recycle Gas
circulation and await for the Pump to be fixed. If duration of the pump non-availability
is more than 4 hours, reduce Reactor temperature below 205°C.
Exotherm during Sulfiding
Sulfiding reactions are exothermic and particularly at the start of the sulfiding, sharp
increase of catalyst bed temperature might be observed. In the event that a temperature
excursion occurs during Sulfiding, fuel to the Combined Feed Heater should be cut and
DMDS injection to be stopped.
Decline in H2S level of the Recycle Gas
This contingency is specially aimed at the Second stage Sulfiding where maintaining
H2S level above 1000 ppm is critical to prevent metal reduction.
Reactor outlet H2S concentration should be maintained min 3000 ppm always.
If H2S level falls below 1000 ppm, keep Reactor temperature constant until H2S
concentration greater than 3000 ppm is re-established. Increase DMDS injection rate. If
after 2 hours H2S level does not come back to more than 3000 ppm, then reduce
Reactor temperature at the rate of 20°C per hour monitoring H2S content in Recycle
Gas. Once 245°C Reactor temperature has been achieved, stop Reactor Temperature
reduction.
Loss of DMDS Pump
This contingency is specially aimed at the First and Second stage Sulfiding where
maintaining H2S level above 1000 ppm is critical to prevent metal reduction.
a) Below 245°C – If DMDS can be reintroduced in less than 4 hours, hold Reactor
temperature below 245°C. If the DMDS injection can not be restarted within 4 hours,
reduce Reactor temperature below 205°C.
b) Above 245°C – If DMDS can be reintroduced in less than 4 hours, reduce Reactor
temperature below 245°C and monitor H2S in Recycle Gas. If H2S content in the
Recycle Gas is less than 1000 ppm, reduce Reactor temperature to 205°C. If
duration of the pump non-availability is more than 4 hours, start Feed only sulfiding
with once through line up of the Unit.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Catalyst Activation - Emergency Guidelines - PTTGC (Updated 14 Jun 13) PDFDocument6 paginiCatalyst Activation - Emergency Guidelines - PTTGC (Updated 14 Jun 13) PDFNattapong PongbootÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ammonia ProductionDocument44 paginiAmmonia ProductionBalamurali BalamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recommended Procedure For Alkali Boil OutDocument18 paginiRecommended Procedure For Alkali Boil OutsprotkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydro Treating CompleteDocument19 paginiHydro Treating CompleteFaiq Ahmad Khan100% (3)
- W3V20 - Refining Processes2 - HandoutDocument9 paginiW3V20 - Refining Processes2 - HandoutgbengaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HD Ro FinishingDocument6 paginiHD Ro FinishingMuhammad sherazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalyst RegenerationDocument57 paginiCatalyst RegenerationSyed Abdul RehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
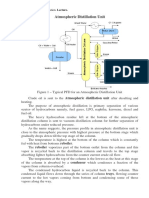
- Atmospheric Distillation UnitDocument3 paginiAtmospheric Distillation UnitGilles DakouriÎncă nu există evaluări
- DA (Pressurized) - Specification Data Sheet (3400)Document9 paginiDA (Pressurized) - Specification Data Sheet (3400)Manojkumar ThilagamÎncă nu există evaluări
- C CC CC: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCDocument27 paginiC CC CC: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCMuhammadTanzeeLUsmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 HydrotreatingDocument31 pagini8 HydrotreatingAmroKasht100% (2)
- SulphurRecovery PDFDocument22 paginiSulphurRecovery PDFfatamorgganaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Sodium Salts On Demercaptanization ProcessDocument4 paginiEffect of Sodium Salts On Demercaptanization ProcessInternational Journal of Science and Engineering InvestigationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important RegenerationDocument8 paginiImportant RegenerationrawadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On IoclDocument39 paginiPresentation On IoclRashmi AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler Cooling MethodDocument7 paginiBoiler Cooling Methodjp mishra100% (1)
- Vacuum Distillation (Ok)Document112 paginiVacuum Distillation (Ok)Ahmed Mohamed Khalil100% (1)
- Haldia Institute of Technology: Name: Bipasha Barai Class Roll No: 17/CHE/054 University Roll No: 10300617054Document9 paginiHaldia Institute of Technology: Name: Bipasha Barai Class Roll No: 17/CHE/054 University Roll No: 10300617054Roshan Kumar LohaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSH AaaaaaaaaaaaDocument7 paginiPSH AaaaaaaaaaaaEdris SalamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sru UnitDocument6 paginiSru Unitparthdpatel131822Încă nu există evaluări
- S-Zorb (Conophillips) : Prepared By: Sadia Urooj Submitted To: Sir Zeeshan ZakiDocument4 paginiS-Zorb (Conophillips) : Prepared By: Sadia Urooj Submitted To: Sir Zeeshan ZakiSadia UroojÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre-Sulfiding On-Line Sulfiding ProceduresDocument8 paginiPre-Sulfiding On-Line Sulfiding ProceduresIrma Brennan0% (1)
- MiscibleDocument32 paginiMiscibleMohanad Hussien100% (1)
- Performance of HT & LT Catalyst: Amit Kumar Jha MT (Chemical) # 0247/7161Document25 paginiPerformance of HT & LT Catalyst: Amit Kumar Jha MT (Chemical) # 0247/7161sb1984_hithaldiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler CommissioningDocument29 paginiBoiler Commissioningbratishkaity100% (8)
- Sulfinol ProcessDocument50 paginiSulfinol Processsada sivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enhanced Oil RecoveryDocument43 paginiEnhanced Oil RecoveryDigvijay DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal EDocument43 paginiThermal EMohanad HussienÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRP Unit - 5Document13 paginiPRP Unit - 5Abdul GhafoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- CDUDocument17 paginiCDUmitpgandhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nitric Acid Process AbstractDocument2 paginiNitric Acid Process AbstractEduardo MagallonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal EorDocument42 paginiThermal EorPetroleum PetroleumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam Jet Refrigeration and Vapour Absorption SystemDocument21 paginiSteam Jet Refrigeration and Vapour Absorption SystemmohitÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Use of Hydrogen in Refineries About This ChapterDocument7 paginiThe Use of Hydrogen in Refineries About This ChapterFernanda GuerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section-IV Shutdown Rev4Document12 paginiSection-IV Shutdown Rev4Balasubramanian CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visbreaking, Thermal Cracking, and Coking: Mercaptan ExtractionDocument4 paginiVisbreaking, Thermal Cracking, and Coking: Mercaptan ExtractionChetan CherryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressurized Deaerator SpecificationsDocument9 paginiPressurized Deaerator SpecificationsarjmandquestÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 Sulphur Recovery UnitDocument32 paginiUnit 5 Sulphur Recovery Unitkhalimn100% (1)
- Recommended Procedure For Alkali Boil OutDocument3 paginiRecommended Procedure For Alkali Boil OutretrogradesÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Presentation On Lithium Bromide Absorption Refrigeration SystemDocument15 paginiA Presentation On Lithium Bromide Absorption Refrigeration SystemAmir AbbaszadehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boilers OperationDocument50 paginiBoilers Operationtsrinivasan5083100% (1)
- HVAC and Refrigeration System: What Is A Ton of Refrigeration?Document36 paginiHVAC and Refrigeration System: What Is A Ton of Refrigeration?seaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 102 & 103 Hydrotreater ReportDocument31 pagini102 & 103 Hydrotreater ReportMuhammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydro ProcessingDocument24 paginiHydro Processingjeygar12Încă nu există evaluări
- Module 4 (KTU)Document118 paginiModule 4 (KTU)Aravind G100% (1)
- Thermal CrackingDocument24 paginiThermal Crackingmihir kumar100% (1)
- Module 5 (KTU)Document95 paginiModule 5 (KTU)Aravind GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acid CleaningDocument32 paginiAcid Cleaningsekhar_ntpcÎncă nu există evaluări
- CrackingDocument32 paginiCrackingMuhammad HAmAd QureshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- RDO ProcedureDocument2 paginiRDO Procedureprof.ankurtrivediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crude Oil DistillationDocument109 paginiCrude Oil Distillationshreshth chawlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 Steam StrippersDocument10 pagini13 Steam StrippersMohsin EhsanÎncă nu există evaluări
- COMBINED CYCLE POWER GENERATION Characterics of Ideal Working FluidDocument15 paginiCOMBINED CYCLE POWER GENERATION Characterics of Ideal Working Fluidlp mishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPT Unit 3 InorganicDocument86 paginiCPT Unit 3 InorganicMicrosoft GamingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitDe la EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesDe la EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesEvaluare: 2.5 din 5 stele2.5/5 (3)
- Thumb Rules - Xls For Chemical EngineerDocument46 paginiThumb Rules - Xls For Chemical EngineerAnuj KaliyerÎncă nu există evaluări
- JERP Brief ProcessDocument14 paginiJERP Brief Processbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GlossaryDocument5 paginiGlossarybikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 PDFDocument7 pagini01 PDFbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NaphthaDocument2 paginiNaphthabikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standerds Fro Cathodic ProtectionDocument32 paginiStanderds Fro Cathodic Protectionbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity: Dec-07 Jan-08 FRB 08 Mar-08Document4 paginiActivity: Dec-07 Jan-08 FRB 08 Mar-08bikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Progress W.R.T. Rev-2 Manhour Estimation: Reliance Petroleum Ltd. - Jamnagar Export Refinery ProjectDocument2 paginiCurrent Progress W.R.T. Rev-2 Manhour Estimation: Reliance Petroleum Ltd. - Jamnagar Export Refinery Projectbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ALKYLATION START Up StepsDocument2 paginiALKYLATION START Up Stepsbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Start Up of Alkylation Reactor R101Document4 paginiStart Up of Alkylation Reactor R101bikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- R201 V201 Leak Test Inertisation On 10.03.2008 (With Pump)Document47 paginiR201 V201 Leak Test Inertisation On 10.03.2008 (With Pump)bikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Advt Questn - APO - DIP. ELECT - ALLDocument6 paginiInternal Advt Questn - APO - DIP. ELECT - ALLbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corrosion Under InsulationDocument1 paginăCorrosion Under Insulationbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- R101 To R801 Start Up PlanDocument21 paginiR101 To R801 Start Up Planbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer Key For Operator To Panel Officer - Question Data BankDocument3 paginiAnswer Key For Operator To Panel Officer - Question Data Bankbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HTLN and H2SO4 Requirement For Flushing Two TrainDocument1 paginăHTLN and H2SO4 Requirement For Flushing Two Trainbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Milind - SystemsDocument61 paginiMilind - Systemsbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Test Paper - Baroda 02.04.06Document7 paginiChemical Test Paper - Baroda 02.04.06bikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interview - Questionaire - SoftwareEngineerDocument5 paginiInterview - Questionaire - SoftwareEngineerbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OPTR PO Overall Rev 1Document20 paginiOPTR PO Overall Rev 1bikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anser Key De-Engg-2005Document8 paginiAnser Key De-Engg-2005bikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Advt Questn - APO - DIP. MECH - B SC - ALLDocument9 paginiInternal Advt Questn - APO - DIP. MECH - B SC - ALLbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Advt Questn - APO - DIP. ELECT - Filtered - 50 - CPPDocument7 paginiInternal Advt Questn - APO - DIP. ELECT - Filtered - 50 - CPPbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Helium Survey-Leak IdentificationDocument1 paginăHelium Survey-Leak Identificationbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer Key For Operator To Panel Officer - Question Data BankDocument3 paginiAnswer Key For Operator To Panel Officer - Question Data Bankbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Please (X) Mark in The Answer Sheet For Marking The Correct AnswerDocument6 paginiPlease (X) Mark in The Answer Sheet For Marking The Correct Answerbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical - 1 - De-Engg - 2004Document7 paginiChemical - 1 - De-Engg - 2004bikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Paper Inst TOCDocument8 paginiQuestion Paper Inst TOCbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q (Lab) - Revised - 50 - Filerted - QDocument6 paginiQ (Lab) - Revised - 50 - Filerted - Qbikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model Questions: (All Questions Are For 1 Mark Each)Document23 paginiModel Questions: (All Questions Are For 1 Mark Each)bikas_sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AAC BlocksDocument24 paginiAAC BlocksgururajÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Effect of Using An Ethanol Blended Fuel On Emissions in An SI EngineDocument6 paginiThe Effect of Using An Ethanol Blended Fuel On Emissions in An SI EngineVinay GowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingersoll Rand RR150rv5C DocumentationDocument23 paginiIngersoll Rand RR150rv5C DocumentationSergei KurpishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Megger - The Complete Guide To Electrical Insulation TestingDocument24 paginiMegger - The Complete Guide To Electrical Insulation TestingMan Minh SangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Automobiles: EmmisionDocument76 paginiBasics of Automobiles: EmmisionRavindra Joshi100% (1)
- GT Load Effect On HRSGDocument3 paginiGT Load Effect On HRSGsatishchemeng100% (1)
- Development of Sodium Leak Detectors For PFBRDocument13 paginiDevelopment of Sodium Leak Detectors For PFBRWilliam MunnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example For Corporate Presentation Veolia PresentationDocument41 paginiExample For Corporate Presentation Veolia PresentationswordprakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 Numerical ProblemsDocument3 paginiAssignment 1 Numerical ProblemsNetra PujarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 - Living ThingsDocument3 paginiUnit 1 - Living ThingsLoles Lopez FresnedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vc-90200.01.03-En Ecoline DJDocument6 paginiVc-90200.01.03-En Ecoline DJGary IrawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 Reservoir EngineeringDocument4 paginiAssignment 1 Reservoir EngineeringMarlisa SalamatÎncă nu există evaluări
- PIA B2 - Module 2 (PHYSICS) SubModule 2.5 (Wave Motion and Sound) FinalDocument17 paginiPIA B2 - Module 2 (PHYSICS) SubModule 2.5 (Wave Motion and Sound) Finalsamarrana1234679Încă nu există evaluări
- The Greening of Wal Mart's Supply ChainDocument8 paginiThe Greening of Wal Mart's Supply ChainmuputismÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Maagement Term PaperDocument3 paginiProject Maagement Term PaperMarwa Kazi Mohammed100% (1)
- Pulley Systems Printed Handout - HeilmanDocument46 paginiPulley Systems Printed Handout - HeilmanGerman ToledoÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO 361 Exam 1 (Fall 2015) With AnswersDocument11 paginiBIO 361 Exam 1 (Fall 2015) With AnswersRuchi Patel100% (1)
- Coal Fired Power Plant PDFDocument1 paginăCoal Fired Power Plant PDFboyzes100% (2)
- Manual de ServicioDocument196 paginiManual de ServicioJuan P. Ibanez CorreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIP Thickener DesignDocument3 paginiMIP Thickener DesignHatem SalahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indoor Icerink Dehum SizingDocument4 paginiIndoor Icerink Dehum SizingmohdnazirÎncă nu există evaluări
- QuotationDocument7 paginiQuotationSikder MizanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rotary ActuatorsDocument34 paginiRotary Actuatorsmr3478Încă nu există evaluări
- MGG155N2: Gaseous Generator Parts ManualDocument94 paginiMGG155N2: Gaseous Generator Parts ManualYAKOVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clark Forklift C20-32CL (Lot No - 9855)Document279 paginiClark Forklift C20-32CL (Lot No - 9855)Григорий Усачёв100% (7)
- Catálogo VPADocument2 paginiCatálogo VPARafael LimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEM Power-Systems BrochureDocument16 paginiNEM Power-Systems Brochurehung100% (1)
- Equivalencing The Collector System of A Large Wind Power PlantDocument16 paginiEquivalencing The Collector System of A Large Wind Power PlantAaron VergaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- DGA SamplingDocument2 paginiDGA SamplingSreeram PanigrahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- VLSI Design Unit-2 Mosfet TransistorDocument5 paginiVLSI Design Unit-2 Mosfet Transistorselvi0412Încă nu există evaluări