Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Mechanical Part: Sliding Contact Bearings ( Đ Trư T)
Încărcat de
kara_250 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
12 vizualizări6 paginidedd
Titlu original
Mechanical Part
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
XLSX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentdedd
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca XLSX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
12 vizualizări6 paginiMechanical Part: Sliding Contact Bearings ( Đ Trư T)
Încărcat de
kara_25dedd
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca XLSX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 6
MECHANICAL PART
No Definition Function Classification Remark
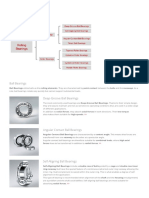
- Sliding contact bearings (ổ đỡ trượt) :
Rotating shaft has a sliding contact with the
bearing, the friction is relatively high, require more
lubrication.
+ Journal bearings: When the load on a bearing
is perpendicular (normal) to the shaft axis, term
‘journal’, refers to part of shaft contact with
bearing
+ Thrust bearings: Support shafts subjected to
axial loads. Classified into: pivot or foot-step
bearings and collar bearings.
'- Rolling contact bearings (Ổ lăn) : rolling
friction is present. As rolling friction is very much
less than sliding friction, also antifriction
bearings.Consists of four parts: inner race, outer
race, balls or rollers and a cage or retainer.The
Supports for shafts, providing inner race is fitted tight into the stationary housing.
stability, and free and smooth The mounting of a shaft with a ball bearing. The
rotation. arrangement also illustrates the method used to
1 Bearing Ex: Supporting requirement of prevent the axial movement of the bearing.
machine tool spindles, engine + Radial bearings: Resist normal (radial) loads
crankshafts, transmission or line acting on the shafts. These bearings are sub-
shafts in workshops, etc. divided on the basis of the shape of the rolling
elements used, viz., ball bearings (ổ bi cầu), roller
bearings (ổ đũa) and taper roller bearings (ổ bi
côn).
+ Thrust bearings: Support shafts subjected to
axial loads. In general,balls as rolling elements
are used in these bearings and rollers only in
special cases.
- Rigid shaft couplings: Connecting shafts
having collinear axes. Classified into muff or
sleeve couplings and flanged couplings.
- Flexible couplings: Perfect alignment of two
shafts is impossible to achieve and difficult to
maintain, because of inevitable bearing wear and
other reasons. To overcome the trouble, flexible
couplings are employed. These permit relative
rotation or variation in the alignment of shaft axes
within certain limits.
- Disengaging couplings: Power transmission
from one shaft to another is intermittent. With this,
Join/ connect two shafts in such a the shafts can be engaged or disengaged as and
way that when both the shafts rotate, when required, even during rotation. A dis-
they act as one unit and transmit engaging coupling in general consists of one part
power from one shaft to the other. firmly fixed to the driving shaft and another one
Shafts to be connected or coupled mounted with provision for sliding over the driven
may have collinear axes, intersecting shaft. The part that is mounted on the driven shaft,
2 Shalf Coupling axes or parallel axes at a small can be made to slide at will to engage or
distance. Based on the requirements, disengage from the rotating driving shaft. The
the shaft couplings are classified as: following are the examples of dis-engaging
(i) rigid couplings, (ii) flexible couplings.
couplings, (iii) loose or dis-engaging - Non-aligned couplings: Transmit power
couplings and (iv) non-aligned between two shafts which are not coaxial. The
couplings. following are the examples of non-aligned
couplings:
Materials used to control or stop
leakage of fluids (liquids and/or
gases) or of solid dry products
through mechanical clearances when
PACKINGS,
3 the contained material is under
GASKETS, AND SEALS
pressure or vacuum. The mechanical
clearances to be sealed may be
between either fixed or moving
components.
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- NSK CAT E1102m A20-23 PDFDocument2 paginiNSK CAT E1102m A20-23 PDFChetan PrajapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arrangements and Their Bearing TypesDocument4 paginiArrangements and Their Bearing TypesCesar VasquesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of BearingsDocument7 paginiTypes of BearingsSameed YounusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling Element Bearings: Defintions and Useful InformationDocument6 paginiRolling Element Bearings: Defintions and Useful InformationRobert Michael CorpusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learn About Antifriction Bearings and SealsDocument68 paginiLearn About Antifriction Bearings and Sealsarda akkayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mccu 228 Manual T12Document20 paginiMccu 228 Manual T12Perú Lima Navidad MayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crossed Roller DesignGuideDocument17 paginiCrossed Roller DesignGuidenaruto256Încă nu există evaluări
- Bearing ArrangementDocument5 paginiBearing ArrangementSubbarayan SaravanakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maintain and Repair Mechanical Drives and Transmission AssembliesDocument141 paginiMaintain and Repair Mechanical Drives and Transmission AssembliesMelku Abebe100% (1)
- Mod 6 Book 5 Springs Bearings Control Systems GearsDocument40 paginiMod 6 Book 5 Springs Bearings Control Systems Gearsranjit prasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling Contact BEARINGS - Part1: ME 308 Machine Elements IiDocument58 paginiRolling Contact BEARINGS - Part1: ME 308 Machine Elements Iixxx100% (1)
- Plan Linear BearingDocument20 paginiPlan Linear BearingJanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch3rolconbear1 200312773Document56 paginiCh3rolconbear1 200312773Mix TubeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design, Materials &processes Identifying BearingDocument23 paginiDesign, Materials &processes Identifying BearingKirk SwabyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal Bearings 1Document20 paginiJournal Bearings 1gokul rajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling Bearings GuideDocument12 paginiRolling Bearings GuideBhawani Singh RajawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Shaft Couplings ExplainedDocument5 paginiTypes of Shaft Couplings ExplainedsathiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bearing Basics and Types of Bearings: Satyendra Ispat Digest 1 CommentDocument6 paginiBearing Basics and Types of Bearings: Satyendra Ispat Digest 1 CommentFallo SusiloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report On BearingDocument21 paginiReport On BearingashwinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shafts: Types of ShaftDocument4 paginiShafts: Types of Shaftvamshi jaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling Bearing Types: Bearings Are Designed To DecreaseDocument4 paginiRolling Bearing Types: Bearings Are Designed To DecreaseNaeem 56Încă nu există evaluări
- Rolling-Contact Bearings: Overview and Expectations For This WeekDocument23 paginiRolling-Contact Bearings: Overview and Expectations For This WeekGaurav AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coupling - WikipediaDocument40 paginiCoupling - WikipediaManojkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH01 BearingsDocument27 paginiCH01 BearingsYahya Faiez WaqqadÎncă nu există evaluări
- HCH BearingDocument2 paginiHCH BearingSh.nasirpurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ball Bearings GuideDocument10 paginiBall Bearings GuideAsst.Prof MECHÎncă nu există evaluări
- FKL - Steel-MillDocument20 paginiFKL - Steel-MillThái PhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODULE 5 - Rolling Element BearingDocument6 paginiMODULE 5 - Rolling Element BearingBoris PalaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Information: Product Finder Home PageDocument6 paginiTechnical Information: Product Finder Home PageawemetalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bearing TypesDocument2 paginiBearing TypesMustafa AlyousefÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 Rolling Contact BearingDocument18 pagini13 Rolling Contact BearingRaushan KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lva1 App6891Document54 paginiLva1 App6891rahul singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- BWK de enDocument16 paginiBWK de enlolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bearings: Mcdes 2 ME - 505Document20 paginiBearings: Mcdes 2 ME - 505AngeloTomalonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes On Ball Bearings: Bearing NomenclatureDocument9 paginiNotes On Ball Bearings: Bearing NomenclatureSalman KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Bearing Definitions: Motion Design GuideDocument16 paginiLinear Bearing Definitions: Motion Design GuideDracoRodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- TDocument33 paginiTTheodoros AtheridisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shafts: Moments and Twisting Moments and Sometimes To Axial LoadsDocument11 paginiShafts: Moments and Twisting Moments and Sometimes To Axial Loadsabddul128Încă nu există evaluări
- University of Gaziantep Bearing PresentationDocument17 paginiUniversity of Gaziantep Bearing PresentationHazim Hazim100% (1)
- Thrust BearingsDocument7 paginiThrust BearingsMilan KanriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preloading bearings for optimal performanceDocument4 paginiPreloading bearings for optimal performanceOmaroMohsenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling Element Bearings: Fitting of Balls in A Ball BearingDocument17 paginiRolling Element Bearings: Fitting of Balls in A Ball BearingSiva KulanjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 360 Degree Flexible Drilling Machine PaperDocument5 pagini360 Degree Flexible Drilling Machine Papersumit bijweÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rigid Flexible Coupling AnalysisDocument6 paginiRigid Flexible Coupling AnalysisFood burstÎncă nu există evaluări
- Puli Dan RantaiDocument15 paginiPuli Dan RantaiWahyu SaputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bearing Basics: Purpose, Design Features of Common ElementsDocument3 paginiBearing Basics: Purpose, Design Features of Common ElementsJoseGarciaRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beng in Mechanical Engineering - Engineering Design 2A: Fig 6 Fig 7Document18 paginiBeng in Mechanical Engineering - Engineering Design 2A: Fig 6 Fig 7PAVAN KALYANÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument6 paginiUntitledabdul rehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carb en Pulp & PaperDocument4 paginiCarb en Pulp & PaperGUSTAVO HOLGUIN RAMIREZÎncă nu există evaluări
- BearingDocument423 paginiBearingaubd100% (2)
- Workshop Couplings: Name: Carlos Farfan Group: 1IM702Document5 paginiWorkshop Couplings: Name: Carlos Farfan Group: 1IM702Antonio CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bearing design considerationsDocument21 paginiBearing design considerationsOmar AbdelAzizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bearing Types, Specs & ApplicationsDocument41 paginiBearing Types, Specs & ApplicationsTejesh ShamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compression Members Part - I PDFDocument8 paginiCompression Members Part - I PDFsanjana jainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Joints and Couplings GuideDocument13 paginiMechanical Joints and Couplings GuideRajandra VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bearing Types and ApplicationsDocument26 paginiBearing Types and ApplicationsKrishna MurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bearings - Rolling Contact BearingsDocument34 paginiBearings - Rolling Contact BearingsRohit GhulanavarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Couplings and ClutchesDocument14 paginiCouplings and ClutchesBhotka BhutkiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsDe la EverandBearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Shafting, Pulleys, Belting and Rope TransmissionDe la EverandShafting, Pulleys, Belting and Rope TransmissionÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.5.8 Who Should Decide How To Carry Out A Repair?: 1.5 Quality OF MaintenanceDocument1 pagină1.5.8 Who Should Decide How To Carry Out A Repair?: 1.5 Quality OF Maintenancekara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- Preparation For Maintenance: FIGURE 1-13Document1 paginăPreparation For Maintenance: FIGURE 1-13kara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 10.1016@0009 25096780187 8Document11 pagini10.1016@0009 25096780187 8kara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- Crowe 1975Document6 paginiCrowe 1975kara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.5 Quality OF Maintenance: FIGURE 1-12Document1 pagină1.5 Quality OF Maintenance: FIGURE 1-12kara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.5.4 Failure To Understand How Things Work or How They Are ConstructedDocument1 pagină1.5.4 Failure To Understand How Things Work or How They Are Constructedkara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- Preparation For Maintenance: FIGURE 1-18Document1 paginăPreparation For Maintenance: FIGURE 1-18kara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.6 A Personal NoteDocument1 pagină1.6 A Personal Notekara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.6 A Personal Note: ReferencesDocument1 pagină1.6 A Personal Note: Referenceskara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- Over Large Pools of Water. Spillages Some Distance Away Might Be IgnitedDocument1 paginăOver Large Pools of Water. Spillages Some Distance Away Might Be Ignitedkara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.5.5 Treating The Symptoms Instead of The Disease: 1. Preparation For MaintenanceDocument1 pagină1.5.5 Treating The Symptoms Instead of The Disease: 1. Preparation For Maintenancekara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.5.2 Use of Excessive Force: 1. Preparation For MaintenanceDocument1 pagină1.5.2 Use of Excessive Force: 1. Preparation For Maintenancekara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.5.6 Flameproof Electrical Equipment: 1.5 Quality OF MaintenanceDocument1 pagină1.5.6 Flameproof Electrical Equipment: 1.5 Quality OF Maintenancekara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.5 Quality OF Maintenance: FIGURE 1-16Document1 pagină1.5 Quality OF Maintenance: FIGURE 1-16kara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- Do. This May Not Be The Same As The Job He Was Expected To Do. TheDocument1 paginăDo. This May Not Be The Same As The Job He Was Expected To Do. Thekara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.4.6 Excavations: 1. Preparation For MaintenanceDocument1 pagină1.4.6 Excavations: 1. Preparation For Maintenancekara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.5 Quality OF Maintenance: FIGURE 1-12Document1 pagină1.5 Quality OF Maintenance: FIGURE 1-12kara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- FIGURE 1-14: 1.5 Quality OF MaintenanceDocument1 paginăFIGURE 1-14: 1.5 Quality OF Maintenancekara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- Over Large Pools of Water. Spillages Some Distance Away Might Be IgnitedDocument1 paginăOver Large Pools of Water. Spillages Some Distance Away Might Be Ignitedkara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- Do. This May Not Be The Same As The Job He Was Expected To Do. TheDocument1 paginăDo. This May Not Be The Same As The Job He Was Expected To Do. Thekara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- Preparation For Maintenance: FIGURE 1-13Document1 paginăPreparation For Maintenance: FIGURE 1-13kara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.4.7 A Permit To Work Dangerously?: 1.5 Quality of MaintenanceDocument1 pagină1.4.7 A Permit To Work Dangerously?: 1.5 Quality of Maintenancekara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.5.2 Use of Excessive Force: 1. Preparation For MaintenanceDocument1 pagină1.5.2 Use of Excessive Force: 1. Preparation For Maintenancekara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.4.3 Jobs Near Plant Boundaries: 1. Preparation For MaintenanceDocument1 pagină1.4.3 Jobs Near Plant Boundaries: 1. Preparation For Maintenancekara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.4.3 Jobs Near Plant Boundaries: 1. Preparation For MaintenanceDocument1 pagină1.4.3 Jobs Near Plant Boundaries: 1. Preparation For Maintenancekara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.4.2 Protective Clothing Not WornDocument1 pagină1.4.2 Protective Clothing Not Wornkara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.3.6 Trapped Pressure: 1. Preparation For MaintenanceDocument1 pagină1.3.6 Trapped Pressure: 1. Preparation For Maintenancekara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.3.7 Equipment Sent Outside The Plant: 1.3 Removal of HazardsDocument1 pagină1.3.7 Equipment Sent Outside The Plant: 1.3 Removal of Hazardskara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.4 Procedures Not Followed: 1.4.1 Equipment Used After A Permit Has Been IssuedDocument1 pagină1.4 Procedures Not Followed: 1.4.1 Equipment Used After A Permit Has Been Issuedkara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- Preparation For MaintenanceDocument1 paginăPreparation For Maintenancekara_25Încă nu există evaluări
- Trek Bikes Manual 7500Document107 paginiTrek Bikes Manual 7500Narcis DobosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar Report On Hyperloop OneDocument21 paginiSeminar Report On Hyperloop Onechitran duttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brosur SK75-11Document8 paginiBrosur SK75-11utamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- F-15 Park Jet Plans (Assembly Drawing) Rev CDocument2 paginiF-15 Park Jet Plans (Assembly Drawing) Rev CMAIG ElectricosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inventory Variance TRXDocument48 paginiInventory Variance TRXRony OsoriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tech Test Series-09 (Automobile Engineering & Maintenance)Document20 paginiTech Test Series-09 (Automobile Engineering & Maintenance)HaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sum 01 PDFDocument28 paginiSum 01 PDFJuan Jarvey Audor RiosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spare Parts Catalog: 16 S 2230 TO Material Number: 1367.002.045 Current Date: 26.04.2017Document80 paginiSpare Parts Catalog: 16 S 2230 TO Material Number: 1367.002.045 Current Date: 26.04.2017Wang Sze Shian100% (1)
- Curtis 1232Document4 paginiCurtis 1232pyatin07Încă nu există evaluări
- Hyva Moves Your World: Hyva International B.VDocument2 paginiHyva Moves Your World: Hyva International B.VDaniel SolomonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of GMS Economic Corridors - MYA - WebDocument80 paginiAssessment of GMS Economic Corridors - MYA - Webdraftdelete101 errorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urv346 C OperDocument70 paginiUrv346 C Operfarichtape channelÎncă nu există evaluări
- AutoIDCards PDFDocument1 paginăAutoIDCards PDFPaiger RossÎncă nu există evaluări
- CM580 Yedek ParçaDocument422 paginiCM580 Yedek ParçaSales AydinkayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- JCB EPC1Document3 paginiJCB EPC1chrideerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 527Document337 paginiCase 527Николай Некрасов100% (1)
- Iveco Stralis at Ad Repair ManualDocument20 paginiIveco Stralis at Ad Repair Manualgail100% (56)
- NER2 Spare Parts ListDocument1 paginăNER2 Spare Parts Listbenji booneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulic Lifting Products Brochure-2020Document18 paginiHydraulic Lifting Products Brochure-2020igorÎncă nu există evaluări
- HIRA Cage Ladder InstallationDocument9 paginiHIRA Cage Ladder InstallationR. Ayyanuperumal AyyanuperumalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ego Solariz Parts Catalog 122019 PDFDocument52 paginiEgo Solariz Parts Catalog 122019 PDFMisterx UmieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perform Pre-Post Hydraulic Excavator ProceduresDocument111 paginiPerform Pre-Post Hydraulic Excavator Proceduresjoan dela cruz75% (4)
- PT Manggala USAHA Equipment List and Maintenance ScheduleDocument42 paginiPT Manggala USAHA Equipment List and Maintenance ScheduleMuhammad Meldi OktariandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Real Time Vehicle Tracking System Using GSM and GPDocument6 paginiReal Time Vehicle Tracking System Using GSM and GPTheIgor997Încă nu există evaluări
- CQI 9 Awareness Training Evaluation Questionnaire Before and AfterDocument6 paginiCQI 9 Awareness Training Evaluation Questionnaire Before and Afterr arumugamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chevrolet Aveo 2002 - 2011 Fuse Box DiagramDocument5 paginiChevrolet Aveo 2002 - 2011 Fuse Box DiagramChule JesusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Decision Tree For Toyota Plant CapacityDocument1 paginăCase Decision Tree For Toyota Plant CapacityRuchira BhelekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volvo Penta Saildrive 120s Workshop ManualDocument88 paginiVolvo Penta Saildrive 120s Workshop ManualJulio100% (1)
- Positive Displacement Meters for Fuels, Oils, LPG, Solvents, Acids & Other Industrial ChemicalsDocument1 paginăPositive Displacement Meters for Fuels, Oils, LPG, Solvents, Acids & Other Industrial Chemicalswarung1bensinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engine Hydraulic System: Main PumpDocument2 paginiEngine Hydraulic System: Main PumpAmankeldi uly Danabek HamzaÎncă nu există evaluări