Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Experiment No: 8 A) Familiarization With Construction and Working of A Transformer B) Verification of Turns Ratio of Transformer
Încărcat de
Saad AliKhanTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Experiment No: 8 A) Familiarization With Construction and Working of A Transformer B) Verification of Turns Ratio of Transformer
Încărcat de
Saad AliKhanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
EE-201 Lab Manual, ME Department, Wah Engineering College
EXPERIMENT No: 8
a) Familiarization with construction and working of a Transformer
b) Verification of Turns Ratio of Transformer
Objective:
o To determine the turn ratio of a Transformer.
o To verify that a transformer transfers electrical power without change in frequency.
Apparatus:
Single phase transformer trainer
Voltmeter
Ammeter
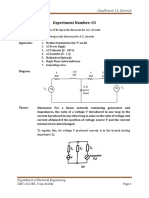
Schematic Diagram:
Theory:
A transformer is a static device that changes ac electric power at one voltage level to ac electric
power at another voltage level through the action of electromagnetic induction.
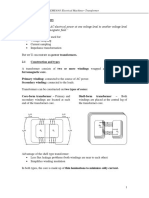
The basis of a transformer is mutual induction between two circuits linked by a common
magnetic flux. One of the transformer winding connected to ac supply mains, is called Primary
winding and the other from which energy is drawn out is called secondary winding. The two
inductive coils are electrically separated but magnetically linked through a path of low
reluctance.
In brief, a transformer is a device that
Transfers electrical power from one circuit to another
EE-201 Lab Manual, ME Department, Wah Engineering College
The two electrical circuits are in mutual inductive influence of each other.
Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction
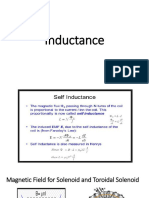
Whenever a magnetic flux linked with a conductor changes, an e.m.f. is always induced in it.
Whenever a conductor cuts magnetic flux, an e.m.f. in induced in that conductor.
The magnitude of induced voltage is equal to the rate of change of flux linkages
TASK-I: To determine the turn ratio of a Transformer
We can calculate the turn ratio by two ways.
By voltage
By Current
By voltage ratio we can calculate the ratio of the turns.
By Current ratio we can calculate the ratio
of the turns.
Turn Ratio from voltages
Voltage across primary coil Voltage across secondary coil Turn Ratio
Vp (V) Vs (V) N= Ns/Np
EE-201 Lab Manual, ME Department, Wah Engineering College
The turn ratio calculated from voltages and current in the primary and secondary coils is almost
same as shown below, however the little difference is due to precise instruments.
TASK-II: There is no change in frequency in transformer action
Frequency means number of cycle’s do the wave completes in only one second. The frequency
of output voltage is same as that of input supply. The change in transformer is only in
magnitudes of voltages and currents. Frequency is inverse of Time Period and the time period
can be measured by the CRO. In PAKISTAN the frequency is 50 Hz so the time period is
0.02sec.
Procedure:
To verify our objective we connect the Primary side
of our transformer to the channel 1 of CRO and the
individually calculate the time periods of both
signals it gives 0.02 sec for both signals which
shows that the frequency is 50 Hz for both input and
output of transformer.
Conclusion:
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsDe la EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5)
- Transformer: Mahindra École Centrale EE101: Basic Electrical Engineering (Fall 2015) Experiment 10Document6 paginiTransformer: Mahindra École Centrale EE101: Basic Electrical Engineering (Fall 2015) Experiment 10nirmalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - TransformersDocument25 paginiChapter 2 - TransformersYousab CreatorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expt No 1Document5 paginiExpt No 1sanjuÎncă nu există evaluări
- DCMTDocument37 paginiDCMTGloria HolcombÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multistage Transistor AmplifierDocument23 paginiMultistage Transistor AmplifierHemant SaraswatÎncă nu există evaluări
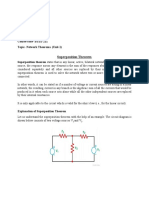
- Superposition Theorem (BTEE-211) (U-1, P-1)Document10 paginiSuperposition Theorem (BTEE-211) (U-1, P-1)Bernard BraingixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excitation Phenomena in Transformers Excitation Phenomena With Out HysteresisDocument2 paginiExcitation Phenomena in Transformers Excitation Phenomena With Out Hysteresism_mustaqeem100% (1)
- Verification of Reciprocity Theorem AIMDocument4 paginiVerification of Reciprocity Theorem AIMJenifer StalinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semiconductors Short Notes in The Form ofDocument58 paginiSemiconductors Short Notes in The Form ofadi_risingsun0% (1)
- Chapter - 2 DC & AC BridgesDocument18 paginiChapter - 2 DC & AC Bridgesvnyshreyas100% (2)
- PCEG 403 Lab No. 1 Title: Simulation of Single Phase Half Wave Converter DC DriveDocument5 paginiPCEG 403 Lab No. 1 Title: Simulation of Single Phase Half Wave Converter DC DriveJanup PokharelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 Review of Magnetic Terms and QuantitiesDocument16 paginiLesson 1 Review of Magnetic Terms and QuantitiesRouel LeonenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pitch Factor N Distribution FactorDocument5 paginiPitch Factor N Distribution FactorKim KeatÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC-Choppers Class A B C D EDocument18 paginiDC-Choppers Class A B C D EAnonymous iTJLpNVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report On HVDCDocument18 paginiReport On HVDCBARUN SINGHÎncă nu există evaluări
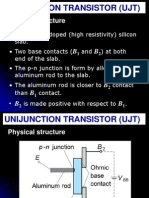
- Ujt Relaxation OscillatorsDocument47 paginiUjt Relaxation OscillatorsGeorge CamachoÎncă nu există evaluări
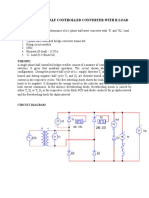
- Single Phase Half Controlled Converter With R LoadDocument3 paginiSingle Phase Half Controlled Converter With R LoadB ANIL KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple BJT Networks: Jay-R M. Ballon, MaieDocument23 paginiMultiple BJT Networks: Jay-R M. Ballon, MaieJay R Ballon100% (2)
- UNIT-1 DC Machines: ConstructionDocument54 paginiUNIT-1 DC Machines: ConstructionT.ThilagamaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- EDC Question BankDocument6 paginiEDC Question BankSudershan DolliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 Power ElectronicsDocument212 pagini02 Power Electronicsmarkschurer223453Încă nu există evaluări
- Synchronous Generators - 2 Marks Questions and AnswersDocument3 paginiSynchronous Generators - 2 Marks Questions and AnswersJoseph Harindranath67% (3)
- Electrical Machines I Lab Twisted QuestionsDocument4 paginiElectrical Machines I Lab Twisted QuestionsPranav MenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit I (Magnetic Field and Circuits - Electromagnetic Force and Torque)Document43 paginiUnit I (Magnetic Field and Circuits - Electromagnetic Force and Torque)UpasnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phasor Representation of ACDocument21 paginiPhasor Representation of ACKavitha NaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrodynamometer Type InstrumentDocument9 paginiElectrodynamometer Type Instrumentanon_463330020Încă nu există evaluări
- Three-Phase Transformers ExperimentDocument11 paginiThree-Phase Transformers ExperimentAbdulrahman Aldeek0% (1)
- InductanceDocument6 paginiInductancechristian maranan100% (1)
- Zener Diode and Diode ApplicationDocument62 paginiZener Diode and Diode Applicationnibar dyllanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capacitor Start/Run Induction Motor: ExperimentDocument9 paginiCapacitor Start/Run Induction Motor: ExperimentMarcos Roberto ReinertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Avalanche BreakdownDocument15 paginiAvalanche BreakdownsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction Motors Part ADocument88 paginiInduction Motors Part AArpit PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ac MachinesDocument102 paginiAc Machinesdipti100% (1)
- DC Machines Lab Manual PDFDocument54 paginiDC Machines Lab Manual PDFMuralichintakailuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Questions For Electrical Machines and DrivesDocument14 paginiReview Questions For Electrical Machines and DrivesClifford MkongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oscilloscope & Function Generator Operation: Department of Electrical Engineering Network Analysis LabDocument3 paginiOscilloscope & Function Generator Operation: Department of Electrical Engineering Network Analysis LabUsairum MirzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- I DT DT DT DT: Class Notes On Electrical Measurements & InstrumentationDocument71 paginiI DT DT DT DT: Class Notes On Electrical Measurements & InstrumentationTia Nur AmaliahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chopper Notes1Document7 paginiChopper Notes1Ruthra DeviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Report: Submitted ToDocument7 paginiLab Report: Submitted ToMd. Al Amin 201-15-34790% (1)
- Expt - 3 - Verification of Reciprocity Theorem For Ac CircuitsDocument3 paginiExpt - 3 - Verification of Reciprocity Theorem For Ac CircuitsChaitanya Vivek DeshpandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase Induction Motor Cross-Field TheoryDocument15 paginiSingle Phase Induction Motor Cross-Field TheoryShoaib Khan100% (1)
- Lecture Objectives: Working Principle of Alternator OR Synchronous Generator StatorDocument5 paginiLecture Objectives: Working Principle of Alternator OR Synchronous Generator StatorZ_JahangeerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec2 Transformers IIDocument17 paginiLec2 Transformers IIMohammed Dyhia AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Characteristics of ThyristorDocument4 paginiDynamic Characteristics of ThyristordamiesiksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zenerdiodes 150209070235 Conversion Gate02Document29 paginiZenerdiodes 150209070235 Conversion Gate02Pushkin RathoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interpretation of Data and Result and Conclusion. Exp.6 - Resonance FrequencyDocument1 paginăInterpretation of Data and Result and Conclusion. Exp.6 - Resonance FrequencydummyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase TransformerDocument15 paginiSingle Phase TransformerAgnivesh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 6: B J T B: Ipolar Unction Ransistor IasingDocument7 paginiLab 6: B J T B: Ipolar Unction Ransistor IasingAhmed Ch100% (1)
- Experiment 4Document5 paginiExperiment 4verboseÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW 3 SolDocument3 paginiHW 3 SolJonathan Bathistoel100% (1)
- Transformer Design Module 2 NewDocument17 paginiTransformer Design Module 2 NewRajath SuryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase Induction MotorDocument5 paginiSingle Phase Induction MotorSridhar SridharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Double Revolving Field TheoryDocument2 paginiDouble Revolving Field TheoryNaresh Gollapalli100% (1)
- Full-Wave Bridge RectifierDocument26 paginiFull-Wave Bridge RectifierSmallhorse1984Încă nu există evaluări
- Energy Conversion Lab 1Document3 paginiEnergy Conversion Lab 1Mohammad HossainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Transformers PDFDocument25 paginiChapter 2 - Transformers PDFAmmar Safwt0% (1)
- Transformers PDFDocument23 paginiTransformers PDFVageesha Shantha Veerabhadra SwamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Big O Exercises and SolutionsDocument14 paginiBig O Exercises and SolutionsAlhaji BatureyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ObjectiveDocument28 paginiObjectiveSaad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ObjectiveDocument18 paginiObjectiveSaad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CEA - M&I (Lab)Document13 paginiCEA - M&I (Lab)Saad khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Canonical Forms For Boolean LogicDocument10 paginiCanonical Forms For Boolean LogicKevin Steven AsistinÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNDERTAKINGDocument1 paginăUNDERTAKINGSaad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gravitational ForceDocument13 paginiGravitational ForceSaad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Journal of Engine Research: Irregular Combustion in Supercharged Spark Ignition Engines PhenomenaDocument15 paginiInternational Journal of Engine Research: Irregular Combustion in Supercharged Spark Ignition Engines PhenomenaSaad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 2, A-1Document22 paginiQuiz 2, A-1Saad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Wah Wah Engineering College: Assignment # 5Document2 paginiUniversity of Wah Wah Engineering College: Assignment # 5Saad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation 1Document19 paginiPresentation 1Saad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1effective Communication SkillsDocument17 pagini1effective Communication SkillsyakarimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automotive Suspension SystemsDocument20 paginiAutomotive Suspension SystemsAkhil0% (1)
- Gear Drive Mechanism For Continuous Variable Valve Timing of IC EnginesDocument6 paginiGear Drive Mechanism For Continuous Variable Valve Timing of IC EnginesSaad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATLAB - T# 3 - 5 - CE (PR.)Document12 paginiMATLAB - T# 3 - 5 - CE (PR.)Saad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment MEDocument3 paginiAssignment MESaad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Report AUTOMATIC JACKDocument27 paginiProject Report AUTOMATIC JACKRohan Arora62% (13)
- 1 10 PDFDocument9 pagini1 10 PDFIan TobyÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of PLCs Over MicroDocument3 paginiWhat Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of PLCs Over MicroNipuna Thushara Wijesekara100% (7)
- TWDocument1 paginăTWSaad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Runge Kutta MethodDocument29 paginiRunge Kutta MethodSaad AliKhan100% (1)
- Working PrincipleDocument9 paginiWorking PrincipleSaad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 2, ADocument22 paginiQuiz 2, ASaad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch-1 IntroductionDocument20 paginiCh-1 Introductionnouman khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Workshop: Topic: Go Down WiringDocument9 paginiElectrical Workshop: Topic: Go Down WiringSaad khan100% (1)
- Lab No 9Document3 paginiLab No 9Saad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CEA - M&I (Lab)Document13 paginiCEA - M&I (Lab)Saad khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creep: Materials Science Stresses Yield StrengthDocument3 paginiCreep: Materials Science Stresses Yield StrengthSaad khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yasir Mudakir Khan: Familiarization With The Oscilloscope and Proteus SoftwareDocument4 paginiYasir Mudakir Khan: Familiarization With The Oscilloscope and Proteus SoftwareSaad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of Materials-II Lab: Presented byDocument27 paginiMechanics of Materials-II Lab: Presented bySaad AliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECA Course FileDocument154 paginiECA Course FilebinduscribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Se P5 Series Add On Power Optimizer Datasheet NaDocument2 paginiSe P5 Series Add On Power Optimizer Datasheet NaMohammad ZakoutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psoc BookDocument534 paginiPsoc Bookoss6000100% (1)
- PIC Microcontroller Projects HandsonDocument192 paginiPIC Microcontroller Projects HandsonDung Huynh Xuan100% (1)
- Alexander CH 08 Final R1Document18 paginiAlexander CH 08 Final R1utpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arduino Guide Book V1.0Document209 paginiArduino Guide Book V1.0Harry Kurt Kahn CanalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kirchoff Law in C++ ProgramDocument23 paginiKirchoff Law in C++ ProgramIsmail Ibrahim67% (6)
- System Verilog Basic Introduction && Assertions: Presenter - Suman HalderDocument18 paginiSystem Verilog Basic Introduction && Assertions: Presenter - Suman HalderSuman HalderÎncă nu există evaluări
- AirFiber AF-11FX DSDocument10 paginiAirFiber AF-11FX DSLuis PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antena Omni Indoor Comba IXD-360V03NNDocument1 paginăAntena Omni Indoor Comba IXD-360V03NNOscar LinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- OMNIALOG en 03 Omnialog DataloggerDocument6 paginiOMNIALOG en 03 Omnialog DataloggerTudor StanciuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 1Document12 paginiLab 1roopa_kothapalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE-103: Electrical Engineering: Chap:9 Sinusoids and PhasorsDocument33 paginiEE-103: Electrical Engineering: Chap:9 Sinusoids and PhasorsZarak KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDP-11/70 Processor Handbook (1977-1978)Document284 paginiPDP-11/70 Processor Handbook (1977-1978)TheAnonymousLugia100% (1)
- Short Questions: (CHAPTER 18) ElectronicsDocument9 paginiShort Questions: (CHAPTER 18) ElectronicsEhtesham Ali KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice: Figure 1: An Analog MultiplierDocument2 paginiPractice: Figure 1: An Analog MultiplierHùng NghiêmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Whitepaper SMT enDocument12 paginiWhitepaper SMT enYounes Ben TaherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verilog Lab 201101 PDFDocument28 paginiVerilog Lab 201101 PDFNuthan kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- VM-702B ShinkawaDocument78 paginiVM-702B ShinkawaRakesh DashÎncă nu există evaluări
- TransformerDocument28 paginiTransformerEngr Umar AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- System Description: Brief Description OF Static Excitation EquipmentDocument8 paginiSystem Description: Brief Description OF Static Excitation EquipmentKuenley TiNy OndeÎncă nu există evaluări
- HT SF470 CatalogDocument3 paginiHT SF470 CatalogSrinivasan Sampath KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAN BasicDocument44 paginiSAN BasicAnonymous kHqLhBB2CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Novel Address Decoders and Sense Amplifier For Sram Based MemoryDocument54 paginiDesign of Novel Address Decoders and Sense Amplifier For Sram Based MemoryVikas JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- VIC Computing February 1982 Vol 1 Issue 3Document32 paginiVIC Computing February 1982 Vol 1 Issue 3viccomputing100% (2)
- Samsung LN46D550K1FXZA Fast Track GuideDocument4 paginiSamsung LN46D550K1FXZA Fast Track GuideRonytec SuporteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Black and WhitheDocument16 paginiBlack and Whithealeksandarla3561Încă nu există evaluări
- Ultrasonic Pulse Generator Using The Transducer As A FrequencyDocument48 paginiUltrasonic Pulse Generator Using The Transducer As A FrequencyBrenda BenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ae - Lab 6Document6 paginiAe - Lab 6Usman KhalilÎncă nu există evaluări
- P4V533-MX: User GuideDocument60 paginiP4V533-MX: User GuideVincwlsonÎncă nu există evaluări