Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
CHP 3.11 Common and Statute Law
Încărcat de
Aaron0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
9 vizualizări1 paginăTitlu original
Chp 3.11 Common and Statute Law
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
9 vizualizări1 paginăCHP 3.11 Common and Statute Law
Încărcat de
AaronDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
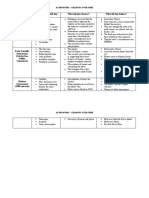
Chp 3.
11 - Common and Statute Law
Statue Law
Laws that are written by the Parliament
History:
o Based on the Magna Carta made in 1215 in England
o Promising to give all lords and some commoners a say in law making
o Made the House of Commoners and the House of Lords which the House of
Representatives and the Senate are based on
Statute law is law made by elected representatives of federal, state and local governments,
who debate the details of proposed legislation in order to come up with the best possible
laws for the people of Australia
Is a very long process as the law must go through readings in both the upper and lower
houses of Parliament.
Laws are made by the Federal Parliament that effected the whole country and then states
make laws that effect only their state
When laws made by the state contradict those of the Federal parliament then the laws of
Federal parliament overall the states.
Statute law always succeeds over Common law
Australia is made up of both Common and Statute Law
Common Law
Are laws that are developed by judges through the problems that they hear in court. It is
based on the decisions of the judges
History:
o Inherited from the English (Westminster) legal system
o Started in England in 1154 with King Henry II where people could only prove their
innocence by trial by ordeal or combat.
o King Henry II decided that everyone should have the right for royal justice and the
Kings court travelled around England where the judgements were recorded.
o Then judges recorded these decisions and based their future decisions off them
These types of laws rely on precedent, where judges make their decisions based on
previous decisions on similar crimes.
Where no precedent has been made before then the judge must set the precedent and it is
then submitted into the “Law Reports” which holds all precedents made in court
Precedent also occurs when a judge interprets a law. As laws use the complicated
language however certain words or phrases are first interpreted they then after that must
be followed in the same way.
Lower courts must follow the precedent of supreme courts however higher courts do not
have to follow the precedent of lower courts
Precedent is often used in criminal cases when sentencing and repayments in civil cases
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Lesson 1Document8 paginiLesson 1AaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagrams For AssessmnetDocument5 paginiDiagrams For AssessmnetAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marett & Barwick - Endangered SongsDocument8 paginiMarett & Barwick - Endangered SongsAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stationary Points - Points of InflectionDocument4 paginiStationary Points - Points of InflectionAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Sexual HealthDocument1 paginăUnderstanding Sexual HealthAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pittosporum/privet Forest Both Eucalyptus ForestDocument2 paginiPittosporum/privet Forest Both Eucalyptus ForestAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Darwin QuestionsDocument1 paginăDarwin QuestionsAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shakespearean Comedies GuideDocument2 paginiShakespearean Comedies GuideAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hard Trig QuestionsDocument1 paginăHard Trig QuestionsAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pittosporum Forest Eucalyptus Forest: PilularisDocument1 paginăPittosporum Forest Eucalyptus Forest: PilularisAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moving From HomeDocument1 paginăMoving From HomeAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Table of Science Fiction Literature and Time PeriodsDocument4 paginiTable of Science Fiction Literature and Time PeriodsAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Snowy Mountain SchemeDocument2 paginiSnowy Mountain SchemeAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Superannuation WorksheetDocument2 paginiSuperannuation WorksheetAaron100% (1)
- ASTRONOMY Work Sheet 1Document2 paginiASTRONOMY Work Sheet 1AaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdhpe Assignment Stop, Think Survive Mitchell OldDocument5 paginiPdhpe Assignment Stop, Think Survive Mitchell OldAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- How the Legal System Works in 38 CharactersDocument2 paginiHow the Legal System Works in 38 CharactersAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti-War Poetry Collection Analyzes Poems on Vietnam and WWIDocument1 paginăAnti-War Poetry Collection Analyzes Poems on Vietnam and WWIAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Issue of Fairness in Using The LawDocument1 paginăIssue of Fairness in Using The LawAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHP 3.11 Common and Statute LawDocument1 paginăCHP 3.11 Common and Statute LawAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oztag RulesDocument3 paginiOztag RulesAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applying Selling TechniquesDocument2 paginiApplying Selling TechniquesAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHP 3.5 Questions: District Court Supreme Court Location Civil Claim Amounts Types of Criminal CasesDocument1 paginăCHP 3.5 Questions: District Court Supreme Court Location Civil Claim Amounts Types of Criminal CasesAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moving From HomeDocument1 paginăMoving From HomeAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding UnemploymentDocument2 paginiUnderstanding UnemploymentAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Superannuation WorksheetDocument2 paginiSuperannuation WorksheetAaron100% (1)
- Legal Issues in the Australian WorkplaceDocument1 paginăLegal Issues in the Australian WorkplaceAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Royal Diamonds Pty LTD V ButtleDocument1 paginăRoyal Diamonds Pty LTD V ButtleAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 3 MethodDocument2 paginiYear 3 MethodAaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Free Ontario Security Practice TestDocument2 paginiFree Ontario Security Practice TestQuiz Ontario69% (16)
- Basic Human Rights Concept - Apr 29Document24 paginiBasic Human Rights Concept - Apr 29Pyke LaygoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meaning of FreedomDocument2 paginiMeaning of FreedomMelody B. MiguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Concept of Justice According To PlatDocument34 paginiThe Concept of Justice According To Platsadia abbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indigenous Peoples of The Philippines PowerpointDocument43 paginiIndigenous Peoples of The Philippines PowerpointFender Boyang100% (16)
- Civil Code SuccessionDocument3 paginiCivil Code SuccessionAmitaf NapsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil LawDocument29 paginiCivil LawAndrew M. AcederaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Role of Juvenile Justice System in IndiaDocument11 paginiRole of Juvenile Justice System in IndiaANADI SONIÎncă nu există evaluări
- The PSME CREED and CORE VALUESDocument22 paginiThe PSME CREED and CORE VALUESChristian LabsanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Submission of No Case To Answer in Civil ProceedingDocument10 paginiSubmission of No Case To Answer in Civil Proceedingshiladix80% (5)
- Justice Chandrachud Dissenting OpinionDocument43 paginiJustice Chandrachud Dissenting OpinionThe Wire100% (2)
- Preamble: An Intro to India's ConstitutionDocument4 paginiPreamble: An Intro to India's ConstitutionArya KumariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intentional Torts Battery Intent Vosburg v. Putney - Boy Kicks Another Boy in The Leg During Classroom TimeDocument26 paginiIntentional Torts Battery Intent Vosburg v. Putney - Boy Kicks Another Boy in The Leg During Classroom TimemattÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus LLB Semester 3Document10 paginiSyllabus LLB Semester 3Shyamsundar PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Social Contract - Jean Jacques RousseauDocument5 paginiThe Social Contract - Jean Jacques RousseauGál Katalin100% (2)
- People vs. Judge PalmaDocument2 paginiPeople vs. Judge PalmaGendale Am-is100% (1)
- Bigamy CasesDocument58 paginiBigamy Casessweet_guevÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Treatise On Arrest Complaint PDFDocument16 paginiA Treatise On Arrest Complaint PDFNat Williams100% (2)
- LEST WE FORGET-The Faces of Impunity in KenyaDocument129 paginiLEST WE FORGET-The Faces of Impunity in KenyaMuya MwenzilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legal Studies Notes For Assessment 1Document8 paginiLegal Studies Notes For Assessment 1api-259875621Încă nu există evaluări
- Pacem in TerrisDocument4 paginiPacem in TerrisAira LagunzadÎncă nu există evaluări
- UN Charter (Full Text) : We The Peoples of The United Nations DeterminedDocument20 paginiUN Charter (Full Text) : We The Peoples of The United Nations DeterminedRengie GaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Republic of UgandaDocument34 paginiThe Republic of UgandapokechoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus Structure TortsDocument4 paginiSyllabus Structure TortsSinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summaries SuccessionDocument51 paginiSummaries SuccessiongizzarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sociology Final Draft - PrakharDocument9 paginiSociology Final Draft - Prakharchetan vermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- R V Kiranjit Ahluwalia PDFDocument11 paginiR V Kiranjit Ahluwalia PDFAyan GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customs and Adoption Dispute in PunjabDocument181 paginiCustoms and Adoption Dispute in PunjabSaddy MehmoodbuttÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legal Brief - MetahumansDocument3 paginiLegal Brief - MetahumansEver Alcazar50% (2)
- Garcia vs. Macaraig, Jr. (39 SCRA 106)Document16 paginiGarcia vs. Macaraig, Jr. (39 SCRA 106)Gretel MañalacÎncă nu există evaluări