Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Antiviral Drugs Table
Încărcat de
Jennifer Heredia0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
35 vizualizări16 paginiantiviral drugs summarized
Titlu original
ANTIVIRAL DRUGS TABLE
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentantiviral drugs summarized
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
35 vizualizări16 paginiAntiviral Drugs Table
Încărcat de
Jennifer Herediaantiviral drugs summarized
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 16
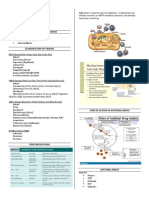
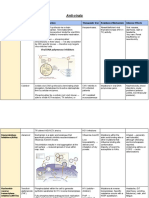
ANTI-HERPES AGENTS
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
Not affected by food
Widely distributed in CSF, Well-tolerated Alteration in viral
Acyclovir to acyclovir breast milk, amniotic fluid, Oral > topical thymidine kinase or
triphosphate (require viral placenta Oral: nausea, diarrhea, DNA polymerase
ACYCLOVIR
HSV-I > HSV II > VZV and EBV
kinases) competitively IV more effective for rash, headache Crystalluria due to IV infusion: Cross-resistance to
inhibits herpes virus DNA primary HSV infection Topical: mucosal irritation, give adequate hydration valacyclovir,
CMV not affected
polymerase to incorporate (CNS HSV) burning sensation famciclovir,
dGTP into viral DNA Oral: genital herpes, Renal insufficiency ganciclovir
varicella, post-organ CNS side effects
transplant
VALACYCLOVIR Zoster associated pain
(L-valyl ester prodrug of acyclovir) (herpetic neuralgia): High dose lead to:
Genital herpes Converted to acyclovir via Oral: 54-70% valacyclovir > acyclovir Thrombotic
Varicella zoster first pass metabolism CSF: 50% of plasma Nausea, vomiting, rash thrombocytopenic purpura
Prevent CMV after transplant Confusion, hallucination, Hemolytic uremic syndrome
Prevent VZV reactivation seizures at high doses
Similar to acyclovir
FAMCICLOVIR/PENCICLOVIR Headache, diarrhea,
(penciclovir triphosphate)
(acyclic guanosine analog) Oral penciclovir: low nausea, burning sensation
Famciclovir – oral drug Cross-resistance to
HSV-1, HSV-2, VZV, HBV for bioavailability Testicular toxicity with no
metabolized to acyclovir and
both Oral famciclovir: higher changes in sperm
penciclovir famciclovir
Add EBV for famciclovir bioavailability morphology or motility
Penciclovir – no chain
Genital herpes, herpes labialis Mammary adenocarcinoma
termination
Inhibition of fusion between
DOCOSANOL
host cell plasma membrane
(long chain saturated 22 carbon
and HSV envelope
aliphatic alcohol)
prevent viral entry and
Orolabial herpes (topical)
replication
TRIFLURIDINE Irreversible inhibition of
(fluorinated pyrimidine nucleoside) thymidylate synthase
HSV-1, HSV-2, CMV Trifluridine triphosphate Hypersensitivity reactions
Adenoviruses as competitive inhibitor
Eye irritation
of thymidine triphosphate
Primary keratoconjunctivitis
for incorporation into
Recurrent epithelial keratitis DNA
ANTI-CYTOMEGALOVIRUS AGENTS
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
Myelosuppression
GANCICLOVIR (neutropenia)
(acyclic guanosine analog) CNS side effects Probenecid and
Mutation in UL97
Infusion-related phlebitis trimethoprim increase
CMV infection (retinitis, organ Same as acyclovir Poor oral absorption and UL54 in DNA
ganciclovir and didanosine
transplant, colitis, esophagitis, Competitively inhibit viral Bioavailability: IV > oral Azotemia, anemia, rash polymerase
levels
pneumonitis) DNA polymerase Clearance linearly related Liver function abnormalities Cross-resistance
Cyclosporine and
HSV, VZV, EBV, HHV-6, HHV-8 Cause chain termination with creatinine clearance Diarrhea with cidofovir and
amphotericin B reduce
Reduce risk for Kaposi sarcoma Insomnia foscarnet
clearance
in AIDS Peripheral neuropathy
Pregnancy category C
VALGANCICLOVIR
(L-valyl ester prodrug of
ganciclovir)
Metabolized to ganciclovir Overdose can result to renal
CMV retinitis Myelosuppression
60% oral bioavailability toxicity
Prophylaxis in high risk solid
organ
Prevent CMV in transplant
FOSCARNET Inhibits viral nucleic acid Not require activation by Nephrotoxicity
/trisodium phosphonoformate synthesis by interacting phosphorylation Electrolyte imbalance CMV UL54 gene
(inorganic pyrophosphate analog) directly with DNA Not undergo significant Infusion-related nausea Point mutation in
All herpesvirus and HIV polymerase or reverse intracellular metabolism Elevate liver transaminases Prevent toxicity by using DNA polymerase
HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6 transcriptase Only in IV Anemia, leukopenia infusion pump to control rate of gene
and 8, HIV 1 and 2 Reversibly binds with Dose adjustment in renal Ca and PO4 imbalances infusion Mutations in HIV-1
End-organ CMV disease (retinitis, pyrophosphate binding failure Low K and Mg reverse
colitis, esophagitis) site Large volumes required CNS toxic transcriptase gene
Acyclovir resistant HSV and VZV since poorly soluble Genital ulcerations
Given via IV Dose-dependent Administer with high dose
CIDOFOVIR Competitive inhibitor of
2 metabolites: cidofovir proximal tubule probenecid to block active Cross-resistant with
(cytidine nucleoside analog) deoxycytidine triphosphate
diphosphate and cidofovir nephrotoxicity tubular secretion and ganciclovir
CMV retinitis, HSV-1 and 2, VZV, (dCTP) into viral DNA
phosphocholine Eyes: uveitis, ocular decrease nephrotoxicity Mutation in viral
EBV, HHV-6 and 8 polymerase and becomes
hypotony Avoid administering with DNA polymerase
Poxvirus, polyomavirus, HPV alternative substrate
Neutropenia nephrotoxic drugs
ANTI-INFLUENZA DRUGS – NEURAMINIDASE INHBITORS
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
Interfere with the release of
NEURAMINIDASE INHIBITORS Low level of
progeny influenza virus
Influenza A and B resistance
from infected host cells
H7N9 avian virus
Nausea Used in
Activated by hepatic Probenecid reduces renal
Vomiting uncomplicated acute
esterases clearance
OSELTAMIVIR Headache influenza in patients
80% bioavailable Dose adjustment in renal
Diarrhea >1
Not impaired by food failure
Neuropsychiatric events Prophylaxis of
influenza in >13
Cough
Inhaled Not recommended if with
Bronchospasm
ZANAMIVIR Renally eliminated with no underlying respiratory disease
Transient nasal and throat (asthma or COPD)
dose adjustment
discomfort
ANTI-INFLUENZA DRUGS – ADAMANTANES
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
High level of
ADAMANTANES Inhibitory to 3 antigenic
resistance
Uniquely configured tricyclic subtypes of influenza A
Treatment of influenza A2 High rates of
amines (H1N1, H2N2, H3N2)
Parkinsonism resistant strains of
Influenza A
H1N1 and H3N2
Dose adjustment in:
Mediated by single
Inhibit early step in viral Well-absorbed CNS side effects: anxiety, Patients >65 years
nucleotide changes
replication viral uncoating Excreted unchanged in insomnia, impaired thinking, Creatinine clearance <50
AMANTADINE involving
by acting on M2 protein urine confusion, lightheadedness, mL/min transmembrane
hallucinations Contraindicated in untreated portion of molecule
angle closure glaucoma
Oral well-absorbed
Dosage adjustment in elderly
RIMANTADINE Extensive metabolism:
and renal and hepatic
4x to 10x more active in vitro hydroxylation, conjugation, impairments
glucuronidation
ANTI-HEPATITIS B AGENTS – NUCLEOSIDE ANALOGS (HBV+HIV: Tenofovir, Lamivudine, Adefovir dipivoxil)
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
Inhibits HBV DNA Lactic acidosis
Resistance with long
NUCLEOSIDE ANALOGS polymerase and suppress Hepatomegaly
term treatment
HBV replication Steatosis
Headache
Inhibits all three function of
Fatigue Higher barrier to
HBV DNA polymerase:
ENTACAVIR Dizziness resistance: entecavir
Base priming 100% bioavailable Interaction with drugs that
For HBV DNA: entecavir > Nausea > lamivudine
Reverse transcription of Glomerular filtration reduce renal function
lamivudine or adefovir Upper abdominal pain Weak anti-HIV
(-) strand
Lung adenomas and M148V variant
Synthesis of (+) strand
carcinomas in mice
Renal, excreted unchanged
Inhibit HIV reverse Headache Discontinuation: flare of
Rapidly absorbed Emergence of
transcriptase and HBV DNA Nausea hepatitis in HBV+HIV co-
LAMIVUDINE Poor CSF penetration lamivudine-resistant
polymerase with Vomiting infection
Increased bioavailability HBV isolates
deoxycytidine triphosphate Skin rash Prolonged treatment: HCC
with TMP-SMX
Fatigue
Phosphorylated by cellular Headache
Resistance with
kinases to active Oral bioavailability Cough
duration of therapy
TELBIVUDINE triphosphate to Unaffected by food Nausea
exceeding 1 year
competitively inhibit HBV Diarrhea virologic rebound
DNA polymerase Myopathy
Myalgia
ANTI-HEPATITIS B AGENTS – NUCLEOTIDE ANALOGS
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
Headache 29% after more than
ADEFOVIR DIPIVOXIL Phosphorylated by cellular Glomerular filtration Reversible increase in serum
Diarrhea 5 years use
(diester prodrug kinases to active 59% bioavailable creatinine after 4-5 years of
Asthenia No cross-resistance
acyclic phosphonated adenine diphosphate metabolite and Hydrolyzed to parent treatment
nucleotide analog) Abdominal pain between adefovir
competitively inhibits HBV compound by intestinal and Pivalic acid causes
Dose-dependent and lamivudine or
Chronic HBV infections DNA polymerase blood esterases decreased carnitine levels
nephrotoxicity entecavir
TENOFOVIR DISOPROXIL Inhibits replication of Renal Nausea No resistance
Used in pregnancy HBV by inhibiting HBV Abdominal pain
polymerase Diarrhea
Tenofovir > adefovir Dizziness Dose adjustment with renal
Fatigue impairment
ANTI-HEPATITIS B AGENTS – INTERFERON
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
INTERFERONS
Alpha & beta
- All cells
- Anti-viral and anti-proliferative Decompensated cirrhosis
- Stimulate cytokine activity Immune pathway Flu-like symptoms Increase theophylline and
modulation Transient hepatic enzyme methadone levels
- Upregulate class 1 MHC
MHC complex antigen elevations Increase risk of hepatic Absence or lack of
Alpha – hepatitis, tumors
expression Neurologic toxicities (mood failure with didanosine resistance
Beta – multiple sclerosis
Enhanced phagocytic disorders, depression, Increase risk of BM
Gamma
activity somnolence, confusion, suppression with zidovudine
- T-lymphocytes and NK cells seizures)
- Less antiviral activity
- More potent
immunoregulatory effects
Increased theophylline and
Route of elimination:
methadone levels
undergoes rapid proteolytic
Flu-like symptoms With didanosine: hepatic
Inhibits HBV replication degradation during tubular
absorption Transient hepatic failure
INTERFERON-ALPHA Induces Apobec3G
Liver metabolism
elevations With zidovudine:
protein expression
Neurotoxicity exacerbate cytopenia
Biliary excretion
Abortifacient in primates
SQ or IM
(not used in pregnancy)
PEGYLATED INTERFERON Definite treatment duration and
Improves pharmacokinetics
(polyethylene glycol) higher rates of HBsAg and
and prolongs drug half-life Renal elimination
Superior efficacy but more HBeAg conversion but greater
(1x/week administer)
expensive adverse effects
ANTI-HEPATITIS C AGENTS – NS5A INHIBITORS
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
Plays a role in both viral
All oral
NS5A INHIBITORS replication and assembly of
Elimination: all fecal
hepatitis C
DACLATASVIR Headache
Used in combination with Fatigue Dose adjustments (reduction
sofosbuvir (HCV genotypes 1,2,3) Symptomatic bradycardia or increase) when given with
with sofosbuvir CYP3 inhibitors or inducers
Inhibitor of P-gp, OATP 1B1
and 1B3, BCRP (breast
cancer resistance protein)
ANTI-HEPATITIS C AGENTS – NS5A INHIBITORS (-ASVIR)
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
Not given with moderate
Elimination: partially and strong inducers or
Fatigue
ELBASVIR eliminated by oxidative strong inhibitors of CYP3A
Headache
Only a fixed dose combination with metabolism; primary in Contraindicated in px with
Nausea
protease inhibitor Grazoprevir for feces hepatic impairment
Elevations in serum
genotype 1, 4 Extensively bound to Interactions: OATP1B/13,
plasma aminotransferases
CYP3A, Efavirenz,
Elbasvir+Grazoprevir
No dose adjustments
Interaction: inhibitor of drug
Fatigue transporters P-gp and
LEDIPASVIR
Headache BCRP
Available as part of fixed-dose Present in feces
Asthenia Increase intestinal
combination with Sofosbuvir
Symptomatic bradycardia absorption of co-
administered substrates for
transporters
OMBITASVIR Pharmacologic booster to
Dosage precautions
Fixed dose combination with: increase plasma conc of Nausea
Contraindicated in patients
Paritaprevir + Ritonavir for HCV 4 Paritaprevir - Pruritus
Effect on CYP3A with moderate or severe
Add Dasabuvir to ^3 for HCV 1 Insomnia
hepatic impairment
No activity against HCV
VELPATASVIR First once-daily single tablet Headache and fatigue
Adjustment when given with
Fixed dose combination with regimen with pangenotypic
CYP3A and CYP2 inhibitors
sofosbuvir activity
ANTI-HEPATITIS C AGENTS – NS5B RNA POLYMERASE INHIBITORS (-BUVIR)
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
NS5B RNA POLYMERASE Involved in post-
INHIBITORS translational processing
All oral
necessary for replication of
HCV
No adjustments; not be used
Headache
Direct acting against HCV with other antivirals
Fatigue
NUCLEOSIDE/NUCLEOTIDE Prodrug converted to Potential intestinal P-gp
Renal elimination Asthenia
ANALOGS – SOFOSBUVIR active form via inducers
Symptomatic bradycardia
intracellular metabolism May decrease sofosbuvir
with amiodarone
levels
NON-NUCLEOSIDE ANALOGS – Fecal elimination Nausea
DASASBUVIR in combination with:
Pruritus
Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, Ritonavir
Insomnia
ANTI-HEPATITIS C AGENTS – NS3/4 INHIBITORS (-PREVIR)
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
Inhibitors of NS3/4A serine
protease (involved in post-
NS3/4 INHIBITORS
translational processing and
replication of HCV)
Potent, pangenotypic Not administered to px with
protease inhibitor hepatic impairment
GRAZOPREVIR
Reversibly binds to HCV Not given with:
In combination with NS5A inhibitor
N53/4A OATP1B1/3 inhibitors
Elbasvir
Fecal elimination CYP3
inducers/inhibitors
Nausea
PARITAPREVIR +Ombitasvir: HCV 4 Drug-drug interactions due to
Pruritus
+ Dasabuvir: HCV 1 CYP3A system
Insomnia
Enhanced binding affinity
and specificity to NS3/4A
SIMEPREVIR HCV 1: Simeprevir + Photosensitivity
Take meals to maximize Not recommended in px with Resistance
First available 2nd generation either: Rash (sulfa moiety)
absorption hepatic impairment associated with Q80K
protease inhibitor - Peginterferon + Pruritus
Biliary excretion Interaction: CYP3A substrate mutations
Ribavirin Nausea
- Sofosbuvir w/ or w/o
Ribavirin
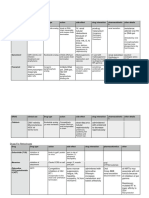
ANTIRETROVIRAL (HIV) AGENTS – NRTIS
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
Risk factors for lactic acidosis Mutations
NUCELOSIDE/NUCLEOTIDE Women
REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE Premature chain M184V
termination due to: Mitochondrial toxicity Alcoholics abacavir, didanosine,
INHIBITORS (NRTIs)
Phosphorylated to (inhibition of mitochondrial Obesity zalcitabine,
Backbone of antiretroviral therapy
triphosphates + lack of DNA polymerase gamma) Prolonged nucleoside lamivudine,
Used in combination with other
3’OH group => Lactic acidosis exposure emtricitabine
ART agents in pairs to decrease
incorporated into DNA => Hepatomegaly Stop treatment if: K65R/N
pill burden
inhibits binding of Hepatic necrosis Inc aminotransferase levels Tenofovir, abacavir,
Competitive inhibition of HIV-1 lamivudine,
incoming nucleotide Progressive hepatomegaly
reverse transcriptase emtricitabine
Metabolic acidosis
ABACAVIR Undergoes hepatic Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea Elevates transaminases and Requires 2-3
(synthetic carbocyclic guanosine glucuronidation and Headache, dyspnea creatinine kinase concomitant
analog) carboxylation Pancreatitis Screening for HLA-B*5701: mutations
Active against HIV-1 Elimination: Renal > Feces Fatal hypersensitivity abacavir-associated
FDC: Abacavir + Lamivudine syndrome (fever, abdomen
hypersensitivity reaction
A + L + Zidovudine pain, rash, respi, musculo)
ANTIRETROVIRAL (HIV) AGENTS – NRTIS
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
Buffer interferes with
DIDANOSINE absorption
(synthetic analog of Indinavir
Dose-dependent pancreatitis
deoxyadenosine) Delavirdine
Distal peripheral sensory
Active against HIV-1 and 2, Atazanavir
neuropathy
HTLV-1
Retinal changes, optic Dapsone
Decreased levels with didanosine 30-40% oral bioavailable Itraconazole
neuritis
Ciprofloxacin, Ketoconazole, Enteric coated to avoid Fluoroquinolone
Hepatotoxicity
Itraconazole inactivation by gastric acid Avoid concurrent use with
Hyperuricemia, lipoatrophy
Increases Didanosine levels Pancreatitis: Zalcitabine,
Diarrhea
Allopurinol, Tenofovir, Ganciclovir Stavudine, Ribavirine,
Decreases Didanosine levels Cardiomyopathy
Hydroxyurea
Methadone, Atazanavir, CNS toxicity
Peripheral neuropathy:
Delavirdine, Ritonavir, Tipranavir Stavudine, INH, Vincristine,
Ribavirin
EMTRICITABINE High oral bioavailability Oral prep has propylene glycol
One of the least toxic NRTIs
(cytosine analog with 2 chiral Low CSF penetration which is contraindicated in
Headache, diarrhea, nausea,
centers) Renal elimination Young children Resistance most
asthenia
Fluorinated analog of lamivudine Tenofovir + Emtricitabine: Women common: M184V/1
Hyperpigmentation of skin
Active against HIV-1 and 2,, HBV pre-exposure prophylaxis to Patients with renal and
Hepatitis flare
Recommended for pregnancy reduce HIV acquisition hepatic failure
Unaffected by food
LAMIVUDINE Neutropenia
Increase bioavailability with
(cytosine analog) Headache
TMP-SXT
Active against HIV-1 and 2, HBV Nausea Avoid lamivudine + zalcitabine:
Renal elimination
Recommended in pregnant Dizziness may inhibit intracellular
Freely crosses placenta
women GI discomfort phosphorylation of one another
Poor CSF penetration
FDC: Lamivudine + Zidovudine or Dry mouth
Abacavir Higher conc in male genital
Hepatitis flare
tract
STAVUDINE High oral bioavailability Peripheral neuropathy Zidovudine may reduce
(synthetic thymidine analog) Readily crosses placenta Pancreatitis (stavudine + intracellular phosphorylation of
Active against HIV-1 and 2 Renal elimination didanosine) stavudine
Arthralgia
Elevated serum
transaminases
Lactic acidosis
Hepatic steatosis
Lipodystrophy
ANTIRETROVIRAL (HIV) AGENTS – NRTIS
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
Orally administered as
TENOFOVIR Tenofovir + Emtricitabine: pre-
prodrug:
(acyclic nucleotide phosphonate exposure prophylaxis to reduce
Tenofovir Disoproxil GI complaints (nausea,
analog of adenosine) HIV acquisition
Fumarate (TDF) diarrhea, vomiting,
Derivative of adenosine 5’
Tenofovir Alafenamide flatulence)
monophosphate lacking a Produces less mitochondrial
(TAF) Headache
complete ribose ring toxicity than NRTIs Mutation in K65R/N
Both converted intracellularly Asthenia
Active against HIV-1 and 2, HBV and K70E gene
to active moiety: Dizziness Increases tenofovir levels:
FDC: Tenofovir +Emtricitabine
Tenofovir Diphosphate Renal failure (Fanconi’s Atazanavir
Tenofovir +Efavirenz, Rilpivirine,
syndrome) Lopinavir
Elvitegravir+Cobicistat
- Water-soluble prodrug Osteomalacia
Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate for Ritonavir
- Low plasma-protein binding
pregnancy
- Not a substrate or inhibitor of
ZIDOVUDINE CYPs
(deoxythymidine analog) More active in Myelosuppression –
Increases zidovudine levels
Active against HIV-1 and 2, lymphocytes due to Oral bioavailable: 63% macrocytic anemia
Probenecid
HTLV-1 and 2 enhanced cellular Rapid first pass hepatic GI intolerance
Phenytoin Resistance:
HIV-associated dementia and proliferation metabolism Headache, insomnia,
Methadone M41L
thrombocytopenia Decreases rate of clinical Absorbed regardless food lipoatrophy
Fluconazole D67N
Reduce rate of vertical progression and prolongs intake Fatigue, malaise, myalgia,
Atovaquone K70R
transmission (first line agent for survival Detectable in breast milk, anorexia
Valproic acid T215F
pregnant) FDC: Zidovudine + semen, fetal tissue Nail hyperpigmentation
HIV infection in children and Lamivudine K219Q
Lamivudine High conc in male genital Muscle myopathy
adults Zidovudine + Lamivudine - Decreased when given with
tract Anxiety, confusion
Post-exposure prophylaxis in + Abacavir zidovudine: Phenytoin
Vaginal neoplasm
HIV-exposed healthcare workers - Competitive inhibition with
stavudine
ZALCITABINE More antiretroviral activity in High oral bioavailability Dose-dependent peripheral Increases zalcitabine levels
(synthetic cytosine analog) monocyte-macrophage cell Food has negligible effect neuropathy Probenecid
Active against HIV-1 and 2, HBV lines Oral and esophageal Cimetidine
ulcerations
Headache, nausea, rash,
arthralgia
Cardiomyopathy
Erythematous maculopapular
rash
Elevated hepatic
transaminases
ANTIRETROVIRAL (HIV) AGENTS – NNRTIS
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
Metabolized and induced
by CYP450 2-8% primary
Bind directly to HIV-1 First generation NNRTI resistance rates
NON-NUCLEOSIDE REVERSE reverse transcriptase (efavirenz, and nevirapine) K103N and Y181C:
TRANSCRIPTASE INHIBITORS allosteric inhibition of RNA All substrates are for CYP3A4 resistance to first
- Low barrier to Fat accumulation
(NNRTI) and DNA-dependent DNA Inducers (nevirapine) generation NNRTI
resistance Fatal hepatitis
Do not compete with nucleoside polymerase Inhibitors (delavirdine) L1001, Y188C,
- Require single mutation GI intolerance
triphosphates Non-competitively inhibits Mixed inducers-inhibitors G190A: cross-
Second generation NNRTI Skin rash (SJS)
Do not require phosphorylation viral reverse transcriptase (efavirenz, etravirine) resistance
(etravirine and rilpivirine)
for activation by binding its active site No cross-resistance
- Higher potency
enzyme inactivation between NRTI and
- Longer half-lives
NNRTI
- Reduced side effects
Skin rash (trunk and
Decreases delavirdine levels
dermatitis)
Fosamprenavir
Headache
High oral bioavailability Rifabutin
Fatigue
DELAVIRDINE Efficacy reduced by Didanosine
Nausea, diarrhea
(bisheteroarylpieperazine NNRTI) antacids, PPI, and H2 Lopinavir
Elevated serum
Active against HIV-1 blockers Nelfinavir
transaminases
Low CSF penetration Ritonavir
Severe dermatitis
Prolongs elimination half-life of
Neutropenia
indinavir or saquinavir
Teratogenic
Inducer and inhibitor of
CYP3A4
Rash Decreased levels when given
EFAVIRENZ Moderately absorbed in with efavirenz
Neural tube defects
(dihydrobenzoxazinone NNRTI) GIT (take on empty
CNS toxicity Phenobarbital
Active against HIV-1 stomach)
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea Phenytoin
Recommended for pregnancy High fat meal improves
Crystalluria Carbamazepine
but should be initiated after first bioavailability
Elevated liver enzymes and Methadone
8 weeks Fecal elimination
serum cholesterol Indinavir
Saquinavir
Amprenavir
ETRAVIRINE Taken with meals Rash, nausea, diarrhea Substrate and inducer of Resistance to 1st gen
Alternative drug in patients with Highly protein-bound Increased levels of CYP3A4 NNRTIs d/t mutations
resistance to 1st gen NNRTI Fecal elimination cholesterol, glucose, Inhibitor of CYP2C9 and (efavirenz, nevirapine,
liver enzymes CYP2C19 delavirdine)
Not given with other NNRTI K103N
and NRTI (-navir) Y181C
ANTIRETROVIRAL (HIV) AGENTS – NNRTIS
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
NEVIRAPINE Moderate inducer of CYP3A
(dipyridodiazepinone NNRTI) system
Active against HIV-1 Well-absorbed Dose-limiting toxicity: rash
Lipophilic sparing the palms and soles Decreased levels when given
Decreases nevirapine Readily crosses placenta Pruritus, hepatitis with nevirapine
Rifampin Renal elimination Elevated transaminases Amprenavir
Rifabutin Metabolized by CYP3A Fever, headache, fatigue Indinavir
Increases nevirapine: isoform to hydroxylated SJS Lopinavir
Fluconazole metabolites Toxic epidermal necrolysis Saquinavir
Ketoconazole Efavirenz
Clarithromycin Methadone
RILPIVIRINE
Rash
Naïve patients with HIV-1 RNA
Depression
<100,000 copies/mL Preferably taken with high
Headache Caution when taking antacids
Used in combination with 2 other fat or >400 kcal meal
Insomnia and H2 receptor antagonist EI38K and M184I
ART agents Fecal elimination
Increased liver enzymes Contraindicated when taking substitution
FDC: Rilpivirine + Emtricitabine + and cholesterol PPI
Tenofovir Fat redistribution
Prolonged QT interval
ANTIRETROVIRAL (HIV) AGENTS – PROTEASE INHIBITORS
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
GI intolerance Ritonavir: most pronounced
Substitutions at 10,
Not need intracellular inhibitory effect
PROTEASE INHIBITOR Lipodystrophy 46, 54, 82, 84, 90
activation Act as pharmacokinetic
Peptide-like chemicals that Competitively inhibits PR and QT interval codons
High plasma protein enhancer
competitively inhibit aspartyl cleavage of Gag-Pol prolongation Atazanavir: I50L
binding Increases drug exposure and
protease required for production polyproteins in HIV-infected Drug-induced hepatitis Darunavir and
Limited CNS penetration prolong drug’s half life and
of mature infective virus cells Spontaneous bleeding tipranavir: used in
Active against HIV-1 and 2 Metabolized by CYP3A4 barrier to resistance
Sulfa allergy Saquinavir: least pronounced
px that are HIV-1
resistant to other PIs
inhibitory effect
ATAZANAVIR Other adverse effects: Increased absorption in an Central obesity/buffalo hump PPIs contraindicated
(azapeptide PI) GI disturbance, headache, acidic medium (pH- Peripheral and facial wasting CYP3A4, CYP2C9, and
Safe for pregnancy Peripheral neuropathy dependent solubility) Breast enlargement UGT1A1 inhibitor
Kidney stones, gallstones Taken with meals Not associated with Tenofovir and Efavirenz not
PR prolongation Antacids taken 12 hours dyslipidemia or given together unless
Decreased bone density apart hyperglycemia ritonavir is added I50L substitution
SJS Metabolism: liver Indirect hyperbilirubinemia Px with hepatic insufficiency
Elimination: Biliary
ANTIRETROVIRAL (HIV) AGENTS – PROTEASE INHIBITORS
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
DARUNAVIR Diarrhea, nausea
Increased bioavailability Contains sulfonamide moiety
Best tolerated PI in randomized Headache
when taken with meals (inc risk for hypersensitivity
studies Inc amylase and hepatic
Metabolism: liver rxn)
Given with ritonavir or cobicistat aminotransferase levels
Elimination: feces and urine CYP3A enzyme system
Darunavir/Ritonavir: safe for Liver toxicity
Highly protein bound (many drug-drug int)
pregnancy Hypersensitivity reaction
FOSAMPRENAVIR Amprenavir: disubstituted Can be taken with or Headache With sulfonamide moiety
(phosphonooxy prodrug of hydroxyethyl without food Nausea CYP3A4 inducer and inhibitor
amprenavir) aminosulfonamide High fat meals decrease Diarrhea Oral suspension contains
Given with low dose ritonavir nonopeptide protease absorption Perioral paresthesias propylene glycol
inhibitor Metabolism: liver Depression contraindicated in children,
Highly protein bound Rash (sulfonamide moiety) women, etc
Unconjugated
hyperbilirubinemia
Needs acidic environment Nephrolithiasis
for optimum solubility CYP3A4 inhibitor
Acute renal failure
INDINAVIR Consumed on empty If given with ritonavir:
Interstitial fibrosis
(peptidomimetic hydroxyethylene stomach or with small, low- increased risk for
Nausea, diarrhea, headache
protease inhibitor) fat low-protein meal nephrolithiasis (give high
Sicca syndrome
More potent against HIV-1 Liver metabolism fluid)
Blurred vision
Fecal elimination
Insulin resistance
High level CSF
Higher risk for MI
Acute hemolytic anemia
GI disturbance
Rapidly absorbed after oral Increased serum lipids Contains propylene glycol
LOPINAVIR
administration Increased serum If given with lopinavir
(peptidomimetic protease inhibitor)
Liver metabolism aminotransferases (common Dec levels of lamotrigine and
Given with low-dose ritonavir
Low CSF penetration in HBV or HCV co-infection) methadone
Safe for pregnant women
Highly protein bound Prolonged PR or QT interval Inc levels of bosentant
Pancreatitis
NELFINAVIR Increased absorption in fed GI disturbance Inc dose of nelfinavir if given
(nonpeptidic protease inhibitor) state Glucose intolerance with rifabutin
Liver metabolism Hypercholesterolemia Dec dose of nelfinavir if given
Fecal elimination Hypertriglyceridemia with saquinavir
Highly protein bound Contraindicated if given with
drugs that contain
phenylalanine
ANTIRETROVIRAL (HIV) AGENTS – PROTEASE INHIBITORS
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
Full-dose ritonavir
Asthenia
GI disturbance Saquinavir/ritonavir:
RITONAVIR Hepatitis contraindicated due to
Increased bioavailability
(peptidomimetic protease inhibitor) Others increased risk of QT
with food intake
Safe for pregnant women Altered taste prolongation
Liver metabolism
Low doses of ritonavir + other PIs Paresthesia, headache
Biliary elimination
for lower dosing with greater Inc serum
Highly protein bound
tolerability and efficacy aminotransferase
Inc lipid levels
Inc serum creatine kinase
Pancreatitis
Taken 2 hours after a fatty
SAQUINAVIR meal for enhanced GI discomfort Increased saquinavir levels:
(peptidomimetic hydroxyethylamine absorption Low dose ritonavir: less omeprazole
protease inhibitor) Liver metabolism dyslipidemia or GI toxicity Saquinavir/delavirdine or
Reformulated and combined with Fecal elimination Increased risk for QT or PR rifampin: liver tests monitored
ritonavir Large Vd but negligible prolongation Not given with darunavir
CSF penetration Torsades de pointes
Highly protein bound
GI disturbance
Urticarial or maculopapular
rash Sulfonamide moiety – not
Liver toxicity given if with sulfa allergy
Poor absorption but
TIPRANAVIR Tipranavir/ritonavir: CYP3A4 system inducer and
increased when taken with
For those resistant to other PIs increased risk for inhibitor
high fat meal
Give with ritonavir intracranial hemorrhage Induces P-gp transporter
Liver metabolism
Depression Contraindicated use of
Elevated serum amylase supplemented vitamin E
Increased serum lipids
Decreased WBC
ANTIRETROVIRAL (HIV) AGENTS – FUSION INHIBITORS
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
FUSION INHIBITORS Inhibits viral attachment by
Inhibits HIV-1 entry into preventing binding of viral
host cells envelope glycoprotein
complex gp160 (gp120 and
gp41) to its cellular receptor
CD4
ANTIRETROVIRAL (HIV) AGENTS – FUSION INHIBITORS
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
ENFURVITIDE
(synthetic 36-amino acid peptide Local injection site reactions
FI) Binds gp41 subunit of Insomnia
SQ injection (only one
Only available HIV entry glycoprotein to prevent Headache
parenteral)
inhibitor conformational changes Dizziness No drug-drug interactions Mutations in gp41
Liver metabolism
Active only against HIV-1 required for fusion of viral Nausea
Given with other ART in px and cellular membrane Eosinophilia
with viral replication despite Bacterial pneumonia
ART
ANTIRETROVIRAL (HIV) AGENTS – ENTRY INHIBITORS (CCR5 ANTAGONISTS)
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
Upper respiratory tract infect
Cough, pyrexia Dose varies according to
Rash, dizziness renal function and use of
Muscle and joint pain CYP3A inducers or inhibitors
Rapid but variable Diarrhea, sleep disturbance Substrate for P-glycoprotein
MARAVIROC
absorption Elevated serum Decrease dose of maraviroc:
Given with other ART in Blocks entry of CCR5-tropic Mutations in V3 loop
Liver metabolism aminotransferases when given with strong
adult px infected only with viruses into CD4 T-cell of gp120
Fecal > renal elimination Hepatotoxicity CYP3A inhibitors
CCR5-tropic HIV-1
Excellent tissue penetration Myocardial ischemia Increase dose of maraviroc:
Postural hypotension when given with CYP3A
No evidence of increased inducers
risk of malignancy or Not given with rifampin
infection
ANTIRETROVIRAL (HIV) AGENTS - INTEGRASE STRAND INHIBITORS (INSTIs)
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
INTEGRASE STRAND Prevent binding of pre- Well-tolerated Combination with cobicistat =
INHIBITORS integration complex to host Favorable effects upon lipid additional adverse events and
Active against HIV-1 and 2 cell DNA terminate metabolism drug-drug interactions
integration step of HIV Headache
replication GI effects
Systemic hypersensitivity
Rhadomyolysis
ANTIRETROVIRAL (HIV) AGENTS - INTEGRASE STRAND INHIBITORS (INSTIs)
Drug MOA Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effect Precaution/Drug Interaction Resistance
Not prescribed to any person
Taken 2 hours before or 6 of childbearing potential who
hours after Insomnia is sexually active and not
- cation-containing Headache using birth control method
DOLUTEGRAVIR antacids Increased serum Inhibits renal organic cation
Used in raltegravir and - laxatives aminotransferase levels transporter OCT2
elvitegravir resistance - sucralfate Fat redistribution syndrome increase plasma conc of
- oral iron and calcium Rash drugs eliminated via OCT2
supplements Hypersensitivity (dofetilide and metformin)
Taken with food Increased serum creatinine Not given with metabolic
(elvitegravir) inducers (oxcarbazepine,
Liver metabolism phenytoin, phenobarbital)
ELVITEGRAVIR Fecal elimination Not given with azole
Diarrhea
Used in treatment-naïve or (dolutegravir) antifungal drugs
Rash
treatment-experienced px Highly protein bound Increases rifabutin levels
Elevated hepatic
Given with a boosting agent Efavirenz or nevirapine
aminotransferases
(cobicistat or ritonavir) decreases elvitegravir
Nausea
Headache UGT1A1 inducers or
Fatigue inhibitors (rifampin or
Not food-dependent
RALVITEGRAVIR Muscle aches rifapentine) -> dosage
Taken at least 4 hours Single point mutatioin
(pyriminidone analog) Increased serum amylase adjustment
before antacids (codons 148 or 155)
Safe for pregnancy and aminotransferase levels Chewable tablets contain
SJS phenylalanine (harmful if with
Hypersensitivity phenylketonuria)
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
OTHER ANTIVIRAL AGENTS
INTERFERON Condyloma acuminate
IMIQUIMOD Topical agent of external genital warts
Nebulizing agents for infants and children w/ severe respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) bronchiolitis or pneumonia to reduce severity & duration of illness
RIBAVIRIN
Teratogenic and Embryotoxic
PALIZIVUMAN Prevents RSV infection in high-risk infants and children (premature infants and those with bronchopulmonary dysplasia or congenital heart disease)
SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS
PHARMACOKINETIC BOOSTING Usually wth low-dose ritonavir or cobicistat
TROUBLE SWALLING PILLS Some are available in liquid preparations (some are crushed or dissolved w/ or w/o losing potency)
TIMING OF DOSES IN
Take soon after dialysis
HEMODIALYSIS PATIENTS
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookDe la EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (9)
- Herpes Simplex Varicella and Zoster: Clinical Manifestations and TreatmentDe la EverandHerpes Simplex Varicella and Zoster: Clinical Manifestations and TreatmentEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (19)
- B1M4L2-Anti Viral TherapyDocument8 paginiB1M4L2-Anti Viral TherapyRalph de la TorreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pcol Antiviral Agents - de La Cruz, M - Gangoso, K..Document101 paginiPcol Antiviral Agents - de La Cruz, M - Gangoso, K..Marienelle De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antivirals (Katzung)Document6 paginiAntivirals (Katzung)sarguss1467% (3)
- Antivirals Pharma Activity 08may23Document17 paginiAntivirals Pharma Activity 08may23Adrian CaballesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiviral AgentsDocument61 paginiAntiviral AgentsTES SENÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti-Viral Drugs: Mechanisms and Clinical UsesDocument47 paginiAnti-Viral Drugs: Mechanisms and Clinical UsesYani MulyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acyclovir Versus ValacyclovirDocument6 paginiAcyclovir Versus ValacyclovirOmar BernalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti-viral Drugs Mechanisms and Uses (39Document38 paginiAnti-viral Drugs Mechanisms and Uses (39Curex QAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti ViralsDocument14 paginiAnti ViralsparinitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANTIVIRAL DRUGS FOR HSV, CMV AND HIV INFECTIONSDocument14 paginiANTIVIRAL DRUGS FOR HSV, CMV AND HIV INFECTIONSshehranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharma NotesDocument9 paginiPharma NotesMayya FirdousÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti-Viral DrugsDocument53 paginiAnti-Viral DrugsClaudia SunshieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antivirals for Herpes and Cytomegalovirus InfectionsDocument10 paginiAntivirals for Herpes and Cytomegalovirus InfectionshectorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topical antiviral treatment optionsDocument15 paginiTopical antiviral treatment optionsHernando Gomez100% (1)
- AntivmariDocument3 paginiAntivmariMoliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4517anti Viral DrugsDocument45 pagini4517anti Viral DrugsBOsch VakilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiviral Drugs: Ana Khusnul Faizah Farmasi FK Uht 2020Document24 paginiAntiviral Drugs: Ana Khusnul Faizah Farmasi FK Uht 2020Muhammad Iqbal DarmansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug MOAs Uses Forms AEs Resistance CharacteristicsDocument2 paginiDrug MOAs Uses Forms AEs Resistance CharacteristicsKate Sarah GabasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virus DrugsDocument1 paginăVirus DrugsJoan ChoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antihsv-Vzv AgentsDocument35 paginiAntihsv-Vzv AgentsAulia Rahma NoviastutiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiviral Drugs: Novi Irwan Fauzi, M.Si., Apt. Maria Ulfah, M.Si., Apt Sekolah Tinggi Farmasi IndonesiaDocument40 paginiAntiviral Drugs: Novi Irwan Fauzi, M.Si., Apt. Maria Ulfah, M.Si., Apt Sekolah Tinggi Farmasi Indonesianetrall BMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Antiviral Drugs PDFDocument68 pagini6 Antiviral Drugs PDFIman SaksoukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti-Viral Agents: Dr. R. Deepak AnandDocument30 paginiAnti-Viral Agents: Dr. R. Deepak AnandDeepak AnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compilation of Antiviral Drug Leaflets: Project in PharmacologyDocument32 paginiCompilation of Antiviral Drug Leaflets: Project in PharmacologydaleascabanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiviral p1Document4 paginiAntiviral p1N Gv FcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiviral and Antifungal PharmacologyDocument13 paginiAntiviral and Antifungal Pharmacologymohsen mirdamadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti-Viral and Anti-Fungal AgentsDocument212 paginiAnti-Viral and Anti-Fungal Agentsmiguel cuevas100% (1)
- Penciclovir: Herpes and Varicella Zoster Herpes Zoster/shinglesDocument2 paginiPenciclovir: Herpes and Varicella Zoster Herpes Zoster/shinglesBeatrice SalgadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiviral Agents for Treating Herpes Simplex Virus and Varicella Zoster Virus InfectionsDocument41 paginiAntiviral Agents for Treating Herpes Simplex Virus and Varicella Zoster Virus InfectionsMae Lislie Canonigo - FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Antiviral1Document34 pagini5 Antiviral1Amr KhayyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti viral drug flash cardDocument12 paginiAnti viral drug flash cardSamqureshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agents to Treat Herpes Simplex Virus & Varicella-Zoster Virus InfectionsDocument35 paginiAgents to Treat Herpes Simplex Virus & Varicella-Zoster Virus InfectionsHera Julia GaraminaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti viral flash cardDocument11 paginiAnti viral flash cardSamqureshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study CEFAZOLINDocument6 paginiDrug Study CEFAZOLINAicelle Love Sampat LapenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti ViralsDocument4 paginiAnti ViralsJas GandingcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inhibition of Intracellular Synthesis byDocument1 paginăInhibition of Intracellular Synthesis byFalaq2Încă nu există evaluări
- Antiviral and Antifungal Drugs: "An Ounce of Prevention Worth Pound of Cure"Document21 paginiAntiviral and Antifungal Drugs: "An Ounce of Prevention Worth Pound of Cure"Jayendiran JaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viral Replicatio N Cycle: Target Antiviral DrugDocument8 paginiViral Replicatio N Cycle: Target Antiviral DrugMike GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antihsv-Vzv AgentsDocument35 paginiAntihsv-Vzv AgentsDhita Dwi NandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manage medications and monitor effectsDocument1 paginăManage medications and monitor effectsgeorgeloto12Încă nu există evaluări
- Ampicillin - Drug StudyDocument2 paginiAmpicillin - Drug StudyLegendX100% (4)
- USMLE Flashcards: Pharmacology - Side by SideDocument178 paginiUSMLE Flashcards: Pharmacology - Side by SideMedSchoolStuff67% (3)
- Acyclovir Mechanism of Action Acyclovir, 9 - ( (2-Hydroxyethoxy) Methyl) Guanine, Is ADocument6 paginiAcyclovir Mechanism of Action Acyclovir, 9 - ( (2-Hydroxyethoxy) Methyl) Guanine, Is AChe CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti Viral DrugsDocument3 paginiAnti Viral Drugsbilal ahmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiviral DrugsDocument25 paginiAntiviral Drugss.k. kubraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiviral DrugsDocument75 paginiAntiviral DrugsluamsmarinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- HC2017 - New Drugs Approved by Health Canada in 2017Document2 paginiHC2017 - New Drugs Approved by Health Canada in 2017BhushanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infectious Diseases IDocument7 paginiInfectious Diseases ITiff VoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiviral Agents: Jason J. Schafer, Pharmd, MPH, BCPS, Aahivp Associate Professor, Jefferson College of PharmacyDocument73 paginiAntiviral Agents: Jason J. Schafer, Pharmd, MPH, BCPS, Aahivp Associate Professor, Jefferson College of PharmacyJeffrey LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRUG STUDY AmoxicillinDocument2 paginiDRUG STUDY AmoxicillinKhylamarie VillalunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infectious Disease Board Review: HIV/AIDS ManagementDocument27 paginiInfectious Disease Board Review: HIV/AIDS ManagementrehanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AcyclovirDocument4 paginiAcyclovirJanhwi DwivediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiviral Drugs CologyDocument10 paginiAntiviral Drugs CologyManthan ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviews: Strategies in The Design of Antiviral DrugsDocument13 paginiReviews: Strategies in The Design of Antiviral Drugsapi-19793040Încă nu există evaluări
- Antiviral Agents: Dr. Roshna Sh. Aziz Department of Pharmacology School of Medicine University of SulaimaniDocument72 paginiAntiviral Agents: Dr. Roshna Sh. Aziz Department of Pharmacology School of Medicine University of Sulaimaniheta aprianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Trends in the Identification and Development of Antimicrobial AgentsDe la EverandCurrent Trends in the Identification and Development of Antimicrobial AgentsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIIDe la EverandAlert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neonatal Formulary: Drug Use in Pregnancy and the First Year of LifeDe la EverandNeonatal Formulary: Drug Use in Pregnancy and the First Year of LifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autonomics CaseDocument2 paginiAutonomics CaseJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cares NotesDocument2 paginiCares NotesJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GYNECOLOGY Chief ComplaintsDocument3 paginiGYNECOLOGY Chief ComplaintsJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embryogenesis Hypoxia (1-3-1-2-1)Document3 paginiEmbryogenesis Hypoxia (1-3-1-2-1)Jennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 24 MICRO B2022 SO2 General Properties of VirusesDocument6 pagini24 MICRO B2022 SO2 General Properties of VirusesJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retninopathy of Prematurity Notes From Vaughan & AsburyDocument5 paginiRetninopathy of Prematurity Notes From Vaughan & AsburyJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adolescent Case March 27 2020Document3 paginiAdolescent Case March 27 2020Jennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autonomics CaseDocument2 paginiAutonomics CaseJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ? Yes No Yes: Telemedicine EthicsDocument11 pagini? Yes No Yes: Telemedicine EthicsJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TMC OrientationDocument4 paginiTMC OrientationJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sodium Disorders NotesDocument1 paginăSodium Disorders NotesJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sodium Disorders NotesDocument1 paginăSodium Disorders NotesJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd Shift CompilationDocument7 pagini3rd Shift CompilationJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ebola Handout QuizDocument5 paginiEbola Handout QuizJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SerologyDocument34 paginiSerologyJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RRL of ABO Blood GroupDocument2 paginiRRL of ABO Blood GroupJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1400 Update of Status of Standardisation of TFTs - DR Paul WilliamsDocument64 pagini1400 Update of Status of Standardisation of TFTs - DR Paul WilliamsJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Los Angeles Rail Map SystemDocument1 paginăLos Angeles Rail Map SystemJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crosstabs Male Smokers RBCDocument7 paginiCrosstabs Male Smokers RBCJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of MicrobiologyDocument20 paginiHistory of MicrobiologyJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mohr Pipet Serologic Al Pipet Volumet Ric Pipet Ostwald-Folin Pipet Pasteur Pipet Automatic PipetDocument1 paginăMohr Pipet Serologic Al Pipet Volumet Ric Pipet Ostwald-Folin Pipet Pasteur Pipet Automatic PipetJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Botany BasicsDocument34 pagini1 Botany BasicsAnonymous RY91UFyQÎncă nu există evaluări
- New MusicDocument2 paginiNew MusicJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Clinical Parasitology - Study of Parasites & Their Life CyclesDocument6 paginiIntroduction to Clinical Parasitology - Study of Parasites & Their Life CyclesJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parasitology UST Resource ListDocument3 paginiParasitology UST Resource ListJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hematology AcronymsDocument1 paginăHematology AcronymsJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ust Resource List For Clinical ChemistryDocument2 paginiUst Resource List For Clinical ChemistryJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualitative Tests For CarbohydratesDocument6 paginiQualitative Tests For CarbohydratesJennifer Heredia0% (1)
- Qualitative Color Reactions of AlbuminDocument6 paginiQualitative Color Reactions of AlbuminJennifer HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mapeh 10 2nd PrelimsDocument4 paginiMapeh 10 2nd PrelimsBlaize PascualÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflective Essay: Writing in The Genetics DiscourseDocument5 paginiReflective Essay: Writing in The Genetics DiscourseAnonymous AY6XDZHBxPÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cancer Lesson Plan For High SchoolDocument7 paginiCancer Lesson Plan For High SchoolUm IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 18Document36 paginiChapter 18hussein harbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evidence Based Practices For Young Children With AutismDocument11 paginiEvidence Based Practices For Young Children With Autismkonyicska_kingaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SWP-23 Maintenance Machinery Regime DaimanDocument1 paginăSWP-23 Maintenance Machinery Regime DaimanHassan AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types and Causes of Medication Errors From A Nurse'S ViewpointDocument3 paginiTypes and Causes of Medication Errors From A Nurse'S ViewpointMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions For RefugeesDocument24 paginiSolutions For RefugeesjacquelineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planning and Design of A Cell and Tissue Culture Laboratory: Christopher B. MorrisDocument2 paginiPlanning and Design of A Cell and Tissue Culture Laboratory: Christopher B. MorrisSubaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Name: Clinical Chemistry Alkaline WashDocument11 paginiProduct Name: Clinical Chemistry Alkaline WashАндрей ФедуловÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Diagnosis of Diarrheal DiseasesDocument37 paginiLab Diagnosis of Diarrheal DiseasesGIST (Gujarat Institute of Science & Technology)Încă nu există evaluări
- Tun Razak Exchange, Retail Plot 1: APPENDIX 5 - Incident Reporting ProcedureDocument5 paginiTun Razak Exchange, Retail Plot 1: APPENDIX 5 - Incident Reporting ProcedureMatthew Mohan PerumalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pq-Unocal Csms '03Document15 paginiPq-Unocal Csms '03Ismail Hamzah Azmatkhan Al-husainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assisted SuicideDocument30 paginiAssisted SuicideAlex Mini AndraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHN Assignment (Community Health Nursing)Document21 paginiCHN Assignment (Community Health Nursing)binjuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing Mental Health and Stress Online CourseDocument2 paginiManaging Mental Health and Stress Online CourseDakota624Încă nu există evaluări
- High Yield Surgery Compatible VersionDocument77 paginiHigh Yield Surgery Compatible Version17kimpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Less Adaptive or More Maladaptive? A Meta-Analytic Investigation of Procrastination and CopingDocument12 paginiLess Adaptive or More Maladaptive? A Meta-Analytic Investigation of Procrastination and CopingVALERIA BUSTAMANTE ALBERCOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of GuidanceDocument13 paginiTypes of GuidanceJomar Gasilla Navarro100% (1)
- 2-1-2021 Response To LandlordDocument2 pagini2-1-2021 Response To LandlordJessica SwarnerÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Classic" Technique Guide: Niti Rotary Instrumentation SystemDocument12 pagini"Classic" Technique Guide: Niti Rotary Instrumentation SystemdrnikhilbobadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Igem ListDocument9 paginiIgem ListMilad YadollahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Typing PDFDocument3 paginiBlood Typing PDFFrances Lau Yee ChinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adhaota Vasica (Malabar Nut)Document7 paginiAdhaota Vasica (Malabar Nut)ABHINABA GUPTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interim Saligan Supreme Student Council: Official List of Players of ArchangelsDocument2 paginiInterim Saligan Supreme Student Council: Official List of Players of ArchangelsMark Luigi M. LazaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education Solutions, Edunsol@gmail - Com, 09996522162Document170 paginiEducation Solutions, Edunsol@gmail - Com, 09996522162edphrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Steroid Analgesic, Antipyretic, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Allergy DrugsDocument217 paginiNon-Steroid Analgesic, Antipyretic, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Allergy DrugsAstri DesmayantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trends, issues, and magnitude of psychiatric nursingDocument4 paginiTrends, issues, and magnitude of psychiatric nursingsona0% (1)
- PALLIATIVE CARE SYMPTOM MANAGEMENTDocument153 paginiPALLIATIVE CARE SYMPTOM MANAGEMENTrlinao100% (3)
- Umesh Pharma 1507821908 - 365Document22 paginiUmesh Pharma 1507821908 - 365Training and PlacementÎncă nu există evaluări