Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
scription 1. Conwnlesw:R Ol: Comparison Sampling Techniques
Încărcat de
annfaiDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
scription 1. Conwnlesw:R Ol: Comparison Sampling Techniques
Încărcat de
annfaiDrepturi de autor:
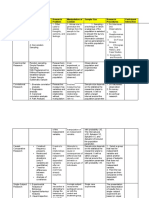
ilonprobabltlty $amptos
CoBt ond
&scription Dsgras ol Use Advanr.0Es Dlsadvantages
1. Conwnlesw:R* Very low cost, extensively No need lor list ol population Variatrility and bias of es&
searcher usos most con- used matss canrctbe
venient sample or most or conUolled ; projecling
economical sample. beyond sample
2. Judgment:An otpert or Moderate mst, averags usc Useful br certain types of Bhs due to 6xpsrts'
experienced researcher lorecasting; sample guaran- may make sample
selects the sample to ful- teed lo m6eta specific sentativs; projecting datr
lill a purpose, such as sn- obiqctitG yond SamBle
suring all members harre
a erlain characteristie.
3. O{rola; Researcher clas- Modsrate coEt, very odgh- lntroduc€s some stfntifica- lntroduces bias in re- I .,i
si{ies population b-y perd, siwly used tion of population; requires searcherb classification d
n6nt propertio$, no list ol population subiects; nonrandom
determines desired pro. tion wilhin classes mearx
portion of samplefrom
ermrfrom population
each elass, flxes quotas be estimatod; polecting
:1.:
!
br each interviewer. data beyo.nd sample
,15
inappropriate
4. $nowball: lnilial respon- Low cost, used.in special Useful in locating members High bias because sa
dents are eelected by situations of rars populalions unilB nol irdeperdent; :
probahility samples; addi- jecting data beyond
iional respondents are inappropriate
iic obtained'by rebrral lrom
,-,.€
lnitial re$pordents.
:,1::
::
!
,i
Figure 1 comparison of Nonprobability sampling Techniques
iii;.
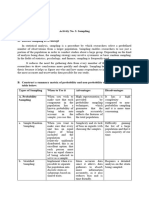
Prcbabltltf Sarpha
'ri:,
z' Coetano
i;\!
IlesJrlptlon Oeg*oe of U*e &vantager Dhdvant&ges
1- SimWnndom:Re- High cost, not fuquedty Only minimaladvance Bagulres sampling
searcher assigns oacfi used ln prac'tice (except knowledge of pop.rtation urcrk from; &es not use
t membsr of the sanpling
frame a number, then se-
random-digit dating) needed; easy to analyze
data and compute error
knordedge of
researcher may have;
lects samplo units by a
ran&m method. enors br same sampi*
lhan slratified
Qs:
jil 1
spondents may be
[a,,'
2. Systemattc: Hesearcher dlspersed, henee
fi,loderate cost, rnoderdety Simple to draiv sample;easy lf sampling intervat ls
uses natural ordering or used to chect to a periodic ordering d
ordarof sampling framg
population, may
selects an arbitrary start-
ing point, then selsc{s
increased variability
,:\.
items al a presolocted in-
terual.
3- $tratified: Researcher Ji- Hi'gh cost, moderately used Assures representation of all
vides the population inlo Hequires accurats
groups in sample; charac{er- tion on proportion in
istics of each stralum can be stratuml f $tratffted llsts
estimated and comparisons not already arrallable,
made; reduces varhbility br can be costly to prspare
clude proportional, dis-
same sample size
-.6ft portional, and optimal
fiocation of subsample
eizgs.
Figure 2 comparison of probability sampling Techniques
SSlPage
4le
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Sampling of Heterogeneous and Dynamic Material Systems: Theories of Heterogeneity, Sampling and HomogenizingDe la EverandSampling of Heterogeneous and Dynamic Material Systems: Theories of Heterogeneity, Sampling and HomogenizingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 7 Apple Case Study FinalDocument18 paginiWeek 7 Apple Case Study Finalgopika surendranathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch-3 Census and Sample Method of Collection of DataDocument12 paginiCh-3 Census and Sample Method of Collection of DataAadi SachdevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sampling MethodsDocument2 paginiSampling MethodsVernonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sampling DistributionDocument22 paginiSampling DistributionMaria Fe DomondonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 13 SamplingDocument24 paginiLecture 13 SamplingHadi RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 Week 1 Q2 Research-12Document4 paginiModule 1 Week 1 Q2 Research-12Lawrence Sean MotinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing CourseDocument5 paginiMarketing CourseGracezel Evangelista GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical ResearchDocument3 paginiPractical ResearchKathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 7Document32 paginiChap 7api-3763138100% (3)
- Eje 4 - Foro DebateDocument9 paginiEje 4 - Foro DebatealexandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- PR1 - Lesson 6 - Sample and Sampling TechniquesDocument2 paginiPR1 - Lesson 6 - Sample and Sampling TechniquesCharlotte Aspecto LladonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch.1 Data CollectionDocument1 paginăCh.1 Data CollectionLoretah SembeguyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8: Quantitative SamplingDocument5 paginiChapter 8: Quantitative SamplingWahyu HidayatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Submitted By: Gaurav Singla 0903271 3ME6 Submitted To: Lect. Luxmi ShankarDocument14 paginiSubmitted By: Gaurav Singla 0903271 3ME6 Submitted To: Lect. Luxmi Shankargaurav503050Încă nu există evaluări
- C GEMTH MidtermsDocument4 paginiC GEMTH MidtermsKarl LintanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SC, Part-ADocument7 paginiSC, Part-APrakasika .KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantitative ApproachesDocument2 paginiQuantitative ApproachesJoseph Mark BaldomarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sampling Method and Estimation: Statistics For Economics 1Document62 paginiSampling Method and Estimation: Statistics For Economics 1Benyamin DimasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Research Method: Census Vs SamplingDocument8 paginiBusiness Research Method: Census Vs SamplingPulkit AggarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.data CollectionDocument1 pagină1.data Collectionannabel.turner1412Încă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 4 Research PDFDocument5 paginiCHAPTER 4 Research PDFAviqa RizkyÎncă nu există evaluări
- S1-Chp1-DataCollection DrfrostDocument30 paginiS1-Chp1-DataCollection DrfrostNadeen KhalilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biostatistics Laboratory SAMPLINGDocument6 paginiBiostatistics Laboratory SAMPLINGTrisha Joy SicatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sampling Design: Basic Concepts and Procedure: Sampling Frame. Known. Random SamplesDocument18 paginiSampling Design: Basic Concepts and Procedure: Sampling Frame. Known. Random SamplesJohn Aaron MirabelÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 07Document20 paginiCH 07Abhijeet TripathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 4 Sampling and Sampling ProceduresDocument47 paginiWeek 4 Sampling and Sampling ProceduresNaym HardenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sampling Methods. Problems and Solutions: January 1991Document12 paginiSampling Methods. Problems and Solutions: January 1991anna starkÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 3: Data Collection and Basic Concepts in Sampling DesignDocument11 paginiCHAPTER 3: Data Collection and Basic Concepts in Sampling DesignDominique Anne BenozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Field Methods in Psychology MidtermsDocument12 paginiField Methods in Psychology Midtermsale.cristianÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Northeastern Philippines School of Graduate Studies Iriga CityDocument4 paginiUniversity of Northeastern Philippines School of Graduate Studies Iriga CityKim NoblezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Research 2 Participants of The StudyDocument3 paginiPractical Research 2 Participants of The StudyAbegail Decasa100% (7)
- Ne Sug 89011Document7 paginiNe Sug 89011christopherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Research SummaryDocument33 paginiFinal Research SummaryFatamii IiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- L07 07-Sampling-2 PageDocument13 paginiL07 07-Sampling-2 PageUyên VũÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-7-Sampling & Sampling DistributionsDocument5 paginiChapter-7-Sampling & Sampling DistributionsAbenezer NegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 BiostatDocument5 pagini05 BiostatDavid MangawilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Permeability Determination From Well Log Data: W, For Both The Saturation Exponent, N, and Cementation Exponent, MDocument5 paginiPermeability Determination From Well Log Data: W, For Both The Saturation Exponent, N, and Cementation Exponent, Mdaniel.fadokunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blotting Techniques2 PDFDocument3 paginiBlotting Techniques2 PDFLolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 12: Selecting A SampleDocument2 paginiCHAPTER 12: Selecting A Samplealia.delareineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - Sampling & Sampling TechiqueDocument4 paginiChapter - Sampling & Sampling TechiqueRamadan NureeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pros and Cons of Different Sampling Techniques: Gaganpreet SharmaDocument4 paginiPros and Cons of Different Sampling Techniques: Gaganpreet SharmaKyla RodriguezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SimplingDocument3 paginiSimplingajaramilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- MRM-Unit 3Document14 paginiMRM-Unit 3Rakshith gowda H DÎncă nu există evaluări
- SamplingDocument34 paginiSamplingPulkit Sharma100% (1)
- Research Midterms ReviewerDocument11 paginiResearch Midterms ReviewerAxcel ChristianÎncă nu există evaluări
- StandardTechniquesforInventoryandMonitoring PDFDocument68 paginiStandardTechniquesforInventoryandMonitoring PDFThi AgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sampling: Census or A SampleDocument5 paginiSampling: Census or A SampleHeba MahmoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stats ReviewerDocument4 paginiStats ReviewerJao CodmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gec410 Note VDocument25 paginiGec410 Note VOsan ThorpeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maney PublishingDocument17 paginiManey PublishingAlberto Duran IniestraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sampling Methods and The Central Limit TheoremDocument20 paginiSampling Methods and The Central Limit TheoremTrainee 5482Încă nu există evaluări
- CTM 201 Sep1998 A11yDocument6 paginiCTM 201 Sep1998 A11ySai Teja ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- GEA1000 Final CSDocument3 paginiGEA1000 Final CSSherman LiamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-7-Sampling & Sampling DistributionsDocument5 paginiChapter-7-Sampling & Sampling DistributionsSimeon solomonÎncă nu există evaluări
- C H A P T e R 7Document5 paginiC H A P T e R 7claudine nyampingaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAMPLING TECHNIQUES HandoutsDocument1 paginăSAMPLING TECHNIQUES HandoutsMORENO BACOÎncă nu există evaluări
- POLSCI 105 SamplingDocument3 paginiPOLSCI 105 SamplingcmaryjanuaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 6 - Sampling DistributionsDocument7 paginiLesson 6 - Sampling DistributionsEdward NjorogeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statics Chapter 7777Document5 paginiStatics Chapter 7777tarekegnworku5Încă nu există evaluări
- Lec 10 NotesDocument3 paginiLec 10 NotesNehal SalemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Page 13Document1 paginăPage 13annfaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Page 15Document1 paginăPage 15annfaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Page 14Document1 paginăPage 14annfaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Page 4Document1 paginăPage 4annfaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Ofa: A A The BeDocument1 paginăA Ofa: A A The BeannfaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Page 3Document1 paginăPage 3annfaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Page 5Document1 paginăPage 5annfaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workshop1: No. Variable Name Variable Label Value and Value Label Coding InstructionsDocument3 paginiWorkshop1: No. Variable Name Variable Label Value and Value Label Coding InstructionsannfaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CouponsDocument1 paginăCouponsannfaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Page2 PDFDocument1 paginăPage2 PDFannfaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers To Online Review Questions: The Classical Long-Run ModelDocument6 paginiAnswers To Online Review Questions: The Classical Long-Run ModelannfaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SOLUTION of EnthymemeDocument3 paginiSOLUTION of EnthymemeannfaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- RGGRDGSTDocument25 paginiRGGRDGSTannfaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Minor Ailments Services: A Starting Point For PharmacistsDocument49 paginiMinor Ailments Services: A Starting Point For PharmacistsacvavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sealant Solutions: Nitoseal Thioflex FlamexDocument16 paginiSealant Solutions: Nitoseal Thioflex FlamexBhagwat PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drill String DesignDocument118 paginiDrill String DesignMohamed Ahmed AlyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liga NG Mga Barangay: Resolution No. 30Document2 paginiLiga NG Mga Barangay: Resolution No. 30Rey PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure 2017Document44 paginiBrochure 2017bibiana8593Încă nu există evaluări
- HandbookDocument194 paginiHandbookSofia AgonalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1980WB58Document167 pagini1980WB58AKSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bismillah SpeechDocument2 paginiBismillah SpeechanggiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acevac Catalogue VCD - R3Document6 paginiAcevac Catalogue VCD - R3Santhosh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shopnil Tower 45KVA EicherDocument4 paginiShopnil Tower 45KVA EicherBrown builderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Between:-Mr. Pedro Jose de Vasconcelos, of Address 14 CrombieDocument2 paginiBetween:-Mr. Pedro Jose de Vasconcelos, of Address 14 Crombiednd offiÎncă nu există evaluări
- VoLTE KPI Performance - E2EDocument20 paginiVoLTE KPI Performance - E2EAnway Mohanty100% (1)
- Creative Thinking (2) : Dr. Sarah Elsayed ElshazlyDocument38 paginiCreative Thinking (2) : Dr. Sarah Elsayed ElshazlyNehal AbdellatifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hierarchy of The Inchoate Crimes: Conspiracy Substantive CrimeDocument18 paginiHierarchy of The Inchoate Crimes: Conspiracy Substantive CrimeEmely AlmonteÎncă nu există evaluări
- QG To AIS 2017 PDFDocument135 paginiQG To AIS 2017 PDFMangoStarr Aibelle VegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entrep Q4 - Module 7Document5 paginiEntrep Q4 - Module 7Paula DT PelitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPB 3193 Operation Management - Group 10Document11 paginiPPB 3193 Operation Management - Group 10树荫世界Încă nu există evaluări
- Amel Forms & Logging SheetsDocument4 paginiAmel Forms & Logging SheetsisaacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surface CareDocument18 paginiSurface CareChristi ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- LICDocument82 paginiLICTinu Burmi Anand100% (2)
- Accounting II SyllabusDocument4 paginiAccounting II SyllabusRyan Busch100% (2)
- 6 AsianregionalismDocument32 pagini6 AsianregionalismChandria Ford100% (1)
- Nat Law 2 - CasesDocument12 paginiNat Law 2 - CasesLylo BesaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- PE Range Moulded Case Current Transformers: Energy DivisionDocument7 paginiPE Range Moulded Case Current Transformers: Energy DivisionUlfran MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PanasonicDocument35 paginiPanasonicAsif Shaikh0% (1)
- KrauseDocument3 paginiKrauseVasile CuprianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Admissibility of Whatsapp Messages in Court For Family MattersDocument3 paginiAdmissibility of Whatsapp Messages in Court For Family Mattersnajihah adeliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modulation and Frequency Synthesis X Digital Wireless RadioDocument233 paginiModulation and Frequency Synthesis X Digital Wireless Radiolcnblzr3877Încă nu există evaluări
- MWG Installation 7.6.2 IG INSTALLATION 0516 en - PDDocument64 paginiMWG Installation 7.6.2 IG INSTALLATION 0516 en - PDjbondsrÎncă nu există evaluări