Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pneumothorax Concept Map: Diagnostic Tests
Încărcat de
Joshua VillarbaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pneumothorax Concept Map: Diagnostic Tests
Încărcat de
Joshua VillarbaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
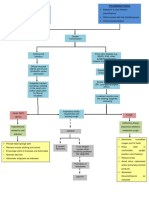
Diagnostic Tests Definition
Thoracic CT: detects thoracic injuries, PNEUMOTHORAX CONCEPT MAP Presence of air or gas in the
lung contusion, hemothorax, and cavity between the lungs and
pneumothorax. the chest wall, causing collapse
Chest x-ray: Reveals air and/or fluid of the lung.
accumulation in the pleural space; may
show shift of mediastinal structures.
Arterial Blood Gas test: variable
depending on the degree of compro- TRAUMATIC PNEUMOTHORAX
mised lung function, altered breathing
Traumatic Pneumothorax
mechanics, and oxygen saturation.
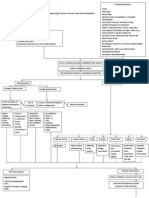
occurs after some type of
PNEUMOTHORAX trauma or injury has
Management happened to the chest or
lung wall.
Chest tube. A small chest tube is inserted Examples of injuries include:
near the second intercostal space to drain
TYPES
the fluid and air. A stab wound or
Maintain a closed chest drainage system. bullet wound to the
Monitor a chest tube unit for any kinks or chest.
bubbling. These could indicate an air leak, Broken ribs
but do not clamp a chest tube without a
physician’s order because clamping may
SYMPTOMS
NON-TRAUMATIC PNEUMOTHORAX
lead to tension pneumothorax. Pleuratic Pain
Autotransfusion involves taking the patient’s Increase in RR Primary Secondary
own blood that has been drained from the Dyspnea Spontaneous Spontaneous
chest, filtering it, and then transfusing it Asymmetry of chest wall Pneumothorax Pneumothorax
back into the vascular system. Trachea deviated to the Abnormal accumulation of Occurs in people with a wide
Antibiotics. Antibiotics are usually affected side air in the space between variety of parenchymal lung
prescribed to combat infection from Hyperresonant the lungs and the chest diseases. These individuals
contamination. V breath sound at the cavity that can result to have underlying pulmonary
Oxygen therapy. The patient with possible affected side partial or complete collapse pathology that alters normal
tension pneumothorax should immediately Mediasternal structure of a lung. lung structure. Air enters the
be given a high concentration of shift to unaffected side Occurs in people who have pleural space via distended,
supplemental oxygen to treat the no known lung disease. damaged or compromised
hypoxemia. alveoli.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For InjuryDocument1 paginăNursing Care Plan Risk For InjuryAce Dioso TubascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 paginiNursing Care PlanAnnahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manage Bronchiectasis Nursing Care PlanDocument5 paginiManage Bronchiectasis Nursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for Billy Admitted with Ear and Throat InfectionsDocument6 paginiNursing Care Plan for Billy Admitted with Ear and Throat InfectionsNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Pleural EffusionDocument5 paginiPleural EffusionTerizla MobileÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effectiveness of Planned Teaching Programme On Knowledge Regarding Needle Stick Injury Among The Staff NursesDocument3 paginiEffectiveness of Planned Teaching Programme On Knowledge Regarding Needle Stick Injury Among The Staff NursesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For Swine FluDocument3 paginiNCP For Swine FluGiana CalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Infection OB University of Santo Tomas College of NursingDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Risk For Infection OB University of Santo Tomas College of NursingKaren ValdezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pcap Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 paginiPcap Pathophysiology PDFMikaela RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan For Patient With PNEUMONIA (Geriatrics)Document4 paginiNursing Care Plan For Patient With PNEUMONIA (Geriatrics)CHRISTIE MONTANO0% (1)
- NCP (BPH)Document8 paginiNCP (BPH)NataCo50% (2)
- Generic Name: Classification Indication:: Hema KDocument2 paginiGeneric Name: Classification Indication:: Hema KKristine YoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan On SepsisDocument6 paginiNursing Care Plan On SepsisleoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Self Task For English Lesson Part 2THDocument1 paginăSelf Task For English Lesson Part 2THistiningrum0% (1)
- FNCP TB As A Health DeficitDocument5 paginiFNCP TB As A Health Deficitkuu faalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study SARAHDocument2 paginiDrug Study SARAHirene Joy DigaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument4 paginiDrug StudyPam RomeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teething:diaper Dermatitis NCPDocument2 paginiTeething:diaper Dermatitis NCPMARK OLVIER E. MELCHORÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk For InfectionDocument2 paginiRisk For InfectionSuzette Rae Tate0% (1)
- Clinical Nursing Malpractice Case StudiesDocument3 paginiClinical Nursing Malpractice Case StudiesPaul RichardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionDocument50 paginiPathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionPryo UtamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk For InfectionDocument3 paginiRisk For Infectionprickybiik100% (1)
- Acute Pain Nursing Diagnosis and InterventionsDocument2 paginiAcute Pain Nursing Diagnosis and InterventionsSheril Sularte CasanesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tpo Eo Poa LFDDocument4 paginiTpo Eo Poa LFDEzra Miguel DarundayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 55 BPHDocument4 paginiCase 55 BPHGetachew Addis75% (12)
- Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1Document8 paginiRisk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1kint manlangitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tarasoff CaseDocument2 paginiTarasoff Casealyssa marie salcedo100% (1)
- Reducing Anxiety in a Client with Health ConcernsDocument3 paginiReducing Anxiety in a Client with Health ConcernsTimothy Joseph F. RosalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iloilo Doctors' College Nursing Care Plan for Anaphylactic ShockDocument7 paginiIloilo Doctors' College Nursing Care Plan for Anaphylactic ShockAbie Jean BalbontinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Posterior Mold: PurposeDocument3 paginiPosterior Mold: PurposeSheryl Ann Barit PedinesÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP PTBDocument2 paginiNCP PTBKath TalubanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Precipitating and predisposing factors of croupDocument3 paginiPrecipitating and predisposing factors of croupingrid50% (2)
- Journal Pcap CDocument3 paginiJournal Pcap CKit Lara50% (2)
- Gallbladder Cancer Drugs and Nursing Care PlanDocument14 paginiGallbladder Cancer Drugs and Nursing Care Planlady_crucial22100% (1)
- Student Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisDocument2 paginiStudent Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisPanJan BalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nepafenac Drug StudyDocument3 paginiNepafenac Drug StudyLucky Rius0% (1)
- Risk For InjuryDocument1 paginăRisk For Injuryandycamille7Încă nu există evaluări
- University of Negros Occidental Student Clinical Training ReportDocument3 paginiUniversity of Negros Occidental Student Clinical Training ReportAzhly AntenorÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceDocument8 paginiNCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceWyen Cabatbat100% (1)
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Document4 paginiAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child - ImmunizationsDocument1 paginăChild - ImmunizationsJOHN100% (1)
- NCP TBDocument7 paginiNCP TBLorraine CilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP KoDocument1 paginăNCP Kojiellianemae100% (1)
- HyperthermiaDocument2 paginiHyperthermiapamgee100% (11)
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 paginiAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Idoc - Pub Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPDocument2 paginiIdoc - Pub Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPACERET, IVAN LAURENTINE G.Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP .Postoperative.Document5 paginiNCP .Postoperative.Jerome GazmenÎncă nu există evaluări
- CefotaximeDocument3 paginiCefotaximeMargotÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP MRMDocument2 paginiNCP MRMKhloe Cristel Llanes Torres100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Status EpilepticusDocument6 paginiPathophysiology of Status EpilepticusKysha Ruth SevillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument19 paginiCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationEmeEmeka100% (1)
- Activity intolerance, fear, infection risks in thalassemiaDocument1 paginăActivity intolerance, fear, infection risks in thalassemiaHannah Clarisse Monge IgniÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument6 paginiNCP Risk For InfectionCazze SunioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Intervention and Evaluation of a Client with Increased Airway SecretionsDocument3 paginiAssessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Intervention and Evaluation of a Client with Increased Airway SecretionsNicholas TagleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seizure NCPDocument2 paginiSeizure NCPChristine Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Pneumothorax PathophysiologyDocument8 paginiUnderstanding Pneumothorax PathophysiologyKyle FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest DrainDocument4 paginiChest DrainGALINDO PE?A JOSE EDUARDOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest Trauma Pneumothorax - TensionDocument5 paginiChest Trauma Pneumothorax - Tensionmita susantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congestive Heart Failure: EtiologyDocument3 paginiCongestive Heart Failure: EtiologyJoshua VillarbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prioritized Nursing For Problem For Rheumatic Fever Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention RationaleDocument3 paginiPrioritized Nursing For Problem For Rheumatic Fever Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention RationaleJoshua VillarbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prioritized Nursing Problem For Pneumothorax Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention RationaleDocument3 paginiPrioritized Nursing Problem For Pneumothorax Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention RationaleJoshua VillarbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prioritized Nursing for Bacterial Infection ProblemsDocument2 paginiPrioritized Nursing for Bacterial Infection ProblemsJoshua VillarbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Bacterial Sinusitis Pathophysiology: Obstruction of Sinus OstiaDocument1 paginăAcute Bacterial Sinusitis Pathophysiology: Obstruction of Sinus OstiaJoshua VillarbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment in MHCNDocument7 paginiAssignment in MHCNJoshua VillarbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 paginiNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Ineffective Airway ClearanceJoshua VillarbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuberculosis Concept Map PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiTuberculosis Concept Map PathophysiologyJoshua VillarbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Social functions of artworksDocument1 paginăSocial functions of artworksJoshua Villarba83% (30)
- A Case Presentation: Ectopic PregnancyDocument10 paginiA Case Presentation: Ectopic PregnancyJoshua VillarbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Doh ProgramsDocument3 pagini5 Doh ProgramsJoshua VillarbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patient Education on Anemia and Iron-Rich FoodsDocument3 paginiPatient Education on Anemia and Iron-Rich FoodsJoshua Villarba100% (2)
- Gestational DiabetesDocument3 paginiGestational DiabetesJoshua VillarbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Route and Site of Administration: Age of The ChildDocument2 paginiRoute and Site of Administration: Age of The ChildJoshua VillarbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug ManualDocument1 paginăDrug ManualJoshua VillarbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument8 paginiDrug StudyJoshua VillarbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daikin AP Catalogue Digital1Document32 paginiDaikin AP Catalogue Digital1Sowham ChatterjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Partial Glossectomy: Oxford Centre For Head and Neck OncologyDocument4 paginiPartial Glossectomy: Oxford Centre For Head and Neck OncologyromzikerenzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arthritis PowerpointDocument25 paginiArthritis PowerpointAnnalesa BarkerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enfermedad Inflamatoria IntestinalDocument14 paginiEnfermedad Inflamatoria IntestinalMi5kaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HDL CholesterolDocument2 paginiHDL Cholesteroldwi riskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parasitology Material Book (Medical.360°)Document320 paginiParasitology Material Book (Medical.360°)Muhammad Javed Gaba100% (1)
- Health8 - q3 - Mod5 - Misconceptions, Myths, and Beliefs About Common Communicable DiseasesDocument14 paginiHealth8 - q3 - Mod5 - Misconceptions, Myths, and Beliefs About Common Communicable DiseasesElla Jane Manolos PaguioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cholinergic agents: mechanisms, clinical uses and anticholinergic drugsDocument13 paginiCholinergic agents: mechanisms, clinical uses and anticholinergic drugsمحمد علي حميدÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of Gastrointestinal Cancer Through Explainable AI and Ensemble LearningDocument6 paginiClassification of Gastrointestinal Cancer Through Explainable AI and Ensemble LearningAdhiraj SaxenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FIRST AID EDUCATION Part 1 and 2-DESKTOP-MTDTU1RDocument14 paginiFIRST AID EDUCATION Part 1 and 2-DESKTOP-MTDTU1RMary Ann VALLECERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eating Disorders Are Not An Illness Eating Disorders Are UncommonDocument5 paginiEating Disorders Are Not An Illness Eating Disorders Are UncommonRahi PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ilovepdf Merged 2 PDFDocument307 paginiIlovepdf Merged 2 PDFAhmed ZidanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Read & Writing BDocument13 paginiRead & Writing BPenang Home TuitionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Red Markets PDFDocument351 paginiRed Markets PDFdaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bazaar DrugsDocument104 paginiBazaar DrugsKartik Vashishta100% (1)
- NMES Electrode Placement GuideDocument2 paginiNMES Electrode Placement GuideSkye EllisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trauma of EyeDocument4 paginiTrauma of Eyeyadavreethu40Încă nu există evaluări
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit6Document2 paginiEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit6Băng Di TrầnÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Literature Review On Hypertensive Crisis: European Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medical ResearchDocument6 paginiA Literature Review On Hypertensive Crisis: European Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medical ResearchCindy MaslagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes Resp DiseaseDocument28 paginiLecture Notes Resp DiseaseWan Razin Wan HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical cariology and operative dentistry in the 21st centuryDocument4 paginiClinical cariology and operative dentistry in the 21st centuryDavid MonroyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Borne DiseaseDocument21 paginiWater Borne DiseaseJassimarSinghWahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benefits of Dark Chocolate PDFDocument4 paginiBenefits of Dark Chocolate PDFzulaikha fatinÎncă nu există evaluări
- KDIGO GD Guideline Key Takeaways For Clinicians Lupus NephritisDocument1 paginăKDIGO GD Guideline Key Takeaways For Clinicians Lupus Nephritisadamu mohammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Left-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Case PresentationDocument64 paginiLeft-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Case PresentationNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Becker - Shaffer Diagnosis and Therapy of Glaucomas (8ed, 2009)Document576 paginiBecker - Shaffer Diagnosis and Therapy of Glaucomas (8ed, 2009)Anggie Pradetya Maharani88% (8)
- Overview of The Immune System 2020Document31 paginiOverview of The Immune System 2020mehakÎncă nu există evaluări
- PALS Provider Manual PDFDocument57 paginiPALS Provider Manual PDFtimie_reyes90% (21)
- Mechanical InjuriesDocument40 paginiMechanical InjuriesProBot7Încă nu există evaluări
- Aconite Napellus: Short-Acting Remedy for Sudden, Violent SymptomsDocument18 paginiAconite Napellus: Short-Acting Remedy for Sudden, Violent Symptomskattarsys1Încă nu există evaluări