Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Science Form 4 Annual Teaching Plan (2011)
Încărcat de
debbycley0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
79 vizualizări13 paginiannual plan
Titlu original
f4 2011
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentannual plan
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
79 vizualizări13 paginiScience Form 4 Annual Teaching Plan (2011)
Încărcat de
debbycleyannual plan
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 13
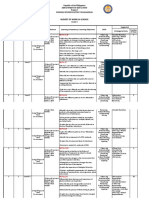
SCIENCE FORM 4 ANNUAL TEACHING PLAN (2011)
MONTH / THEME / LEARNING AREA / THINKING SKILLS SUGGESTE SCIENTIFIC
WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES / LEARNING OUTCOMES / THINKING D T&L ATTITUDES AND
STRATEGIES ACTIVITIES NOBLE VALUES
THEME : INTRODUCING SCIENCE
Week 1 – 2 LEARNING AREA : 1. SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION
(03/01 – • Analyzing • Being
• Making Discussion systematic
14/01) 1.1 : Analyzing method of scientific investigation
conclusions • Being
• explain the steps in scientific investigation objective
• Relating
• carry out a scientific investigation
• write a report on a scientific investigation
• explain the importance of scientific
investigation
1.2 : Realizing the need to practice scientific
attitudes and noble values when
carrying out scientific investigation
• identify scientific attitudes and noble values
practised by scientists
• explain the need to practise scientific
attitudes and
noble values when carrying out a scientific
investigation
• practise scientific attitudes and noble values
when
carrying out a scientific investigation
THEME : MAINTENANCE AND CONTINUITY OF LIFE
LEARNING AREA : 1. BODY COORDINATION
Week 3 – 7 1.1 : Understanding body coordination
• Analyzing Slide • Being
(17/01 – • describe what body coordination is presentation
• Making responsible
18/02) • identify the body systems that control and about the
conclusions
regulate coordination • Comparing Discussion safety of
• state the importance of body coordination and oneself,
contrasting Mind others and
1.2 : Understanding the human nervous system
• Synthesizin mapping/ the
• identify the component parts of the human concept environment
nervous system g
mapping • Being
• Visualizing
• state the function of each component part of thankful to
• Generating
the nervous system Groupwork & God
ideas
• state what a neurone is presentation • Thinking
• Evaluating
• identify the parts of a neurone rationally
• state the function of each part of the • Being
neurone confident
and
• identify the different types of the neurone independent
• state the function of each type of neurone
• compare and contrast different types of
neurone
1.3 : Analyzing nervous coordination
• state what receptors and effectors are
• state the functions of receptors and effectors
• explain with examples what a reflex action is
• describe a reflex arc
• illustrate the path taken by an impulse in the
reflex arc
1.4 : Understanding the role of proprioceptors in
maintaining balance and coordination
• explain what proprioceptors are
• explain the importance of proprioceptors
1.5 : Understanding the human brain and its
complexity
• identify the main parts of the human brain
• state the main functions of each part of the
THEME : MAINTENANCE AND CONTINUITY OF LIFE
Week 8 – 13 LEARNING AREA : 2. HEREDITY AND VARIATION
(21/02 –
• Analyzing Slide • Realizing
108/04) 2.1 : Understanding cell division
• Grouping presentation that science
• state what genes, deoxyribonucleic acids is a means to
and classifying
(DNA) and chromosomes are Group understand
• Comparing
• describe relationship between gene, DNA and discussion nature
and chromosome contrasting • Being
• state what mitosis is • Synthesizin Internet thankful to
research God
• describe the process of mitosis g
• state what meiosis is • Visualizing • Appreciati
• Generating ng the
• describe the process of meiosis contribution
ideas
• compare and contrast mitosis with meiosis of science
• explain the importance of mitosis and and
meiosis technology
2.2 : Understanding the principles and
mechanism of inheritance
• explain what dominnat genes and recessive
genes are
• identify dominant traits and recessive traits
in human
• illustrate the mechanism of inheritance of
traits using
a schematic diagram
• predict the genotype and phenotype ratios
of a monohybrid cross
2.3 : Understanding sex determination and the
occurrence of twins in human beings
• explain what sex chromosomes are
• explain how sex is determined
• explain the formation of identical and non-
identical twins
• compare and contrast between identical and
non-identical twins
• explain what siamese twins are
2.4 : Understanding mutation
• state what mutation is
• state the types of mutation
• list exampels of mutation
• identify causes of mutation
• state the advantages and disadvantages of
mutation
2.5 : Evaluating the effects of genetic research
on human life
• list the contributions of genetic research in
various fields
• explain selective breeding in plants and
livestock
• state the importance of selective breeding in
plants and livestock
• describe the technology used for selective
breeding
• present arguments for and against genetic
research
2.6 : Analyzing variation among living things
• state what variation is
• list variation in humans
• classify variation into continuos and
discontinuos variation
• compare and contrast continuous and
discontinuous variation
• identify factors that cause variation
• explain the importance of variation
2.7 : Realizing the need to adhere to a code of
ethics in genetic research
• explain how the misuse of knowledge in the
field of
• genetics can endanger life
• describe the importance of establishing and
adhering to
• ethics and morals in scientific research for the
benefit of mankind
March
Week 10 UJIAN GERAK MAHIR
(07/03 –
11/03)
Week 11 MID – SEM BREAK
(12/03 –
18/03)
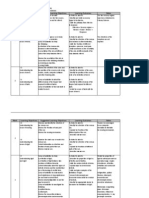
April - May THEME : MATTER IN NATURE
Week 14 – LEARNING AREA : 1. MATTER AND SUBSTANCE
18
• Analyzing Discussion • Realizing
(04/04 – 1.1 : Analyzing changes in the states of matter
• Grouping that science
06/05) • explain the kinetic theory of matter Experimentin
and classifying is a means to
(a) relate changes in the heat to changes in g understand
• Making
kinetic energy of the particles in matter inferences nature
(b) explain the interconversion of the three • Making • Appreciati
states hypothesis ng the
of matter based on the kinetic theory • Generating balance of
matter ideas nature
1.2 : Understanding the structure of an atom • Evaluating
• describe the structure of an atom
• identify the subatomic particles
• compare and contrast the subatomic
particles
1.3 : Applying the idea of proton number and
nucleon number in atoms of elements
• state what proton number is
• state what nucleon number is
• relate the number of protons, neutrons, and
electrons
in an atom to its proton number and nucleon
number
• deduce the number of protons, electrons and
neutrons in atoms of different elements
• make a generalisation on the numbers of
protons
and electrons in atoms of different elements
• state what isotops are
• give examples of isotopes
1.4 : Understanding the classification of elements
in the Periodic Table
• describe the arrangment of elements in the
Periodic Table
• describe what is meant by groups and
periods in
THEME : ENERGY IN LIFE
Week 19 – LEARNING AREA : 1. ENERGY AND CHEMICAL
27 CHANGES
• Analyzing Experimentin • Realizing
(09/05 –
• Making g that science
08/07) 1.1 : Understanding physical and chemical
hypothesis is a means to
changes Discussion understand
• Generating
• explain whqt physical change is ideas nature
• explain what chemical change is • Sequencing • Appreciati
• give examples of physical changes in daily • Evaluating ng the
life • Predicting contribution
• give examples of chemical changes in life of science
and
• compare and contrast physical changes and technology
chemical changes
1.2 : Analyzing heat change in chemical reactions
• state that chemical reactions involve heat
change
• identify reactions involving heat loss
• identify reactions involving heat gain
• relate changes in temperature of reactants
to exothermic reactions
• relate changes in temperature of reactants
to endothermic reactions
• explain through examples heat changes that
occur during industrial chemical reactions
1.3 : Synthesizing the reactivity series of metals
• describe the reactivity of metals with water
• describe the reactivity of metals with acids
• describe the reactivity of metals with oxygen
• compare and contrast the reactivity of
metals
with water, acids and oxygen
• arrangge metals in order of reactivity
• construct the reactivity series of metals
based on
reactivity of metals and oxygen
• identify the position of carbon in the
reactivity series
Week 20 –
21 FIRST SEMESTER EXAM
(16/05 –
27/05)
Week 22 – MID-YEAR BREAK
23
(30/05 –
10/06)
THEME : ENERGY IN LIFE
LEARNING AREA : 2. NUCLEAR ENERGY
• Analyzing Group • Thinking
2.1 : Understanding radioactive substances
• Predicting discussion rationally
• state what radioactive substances are
• Making • Having
Week 28 – • give examples of radioactive substances Slide
hypothesis critical and
29 • describe the process of radioactive decay presentation analytical
(11/07 – thinking
• name the three types of radioactive
22/07)
radiations
• describe the characteristics of each type of
radioactive radiations
• compare and contrast radioactive radiations
• explain what radioisotopes are
• give examples of radioisotopes
• explain the uses of radioactive substances
2.2 : Understanding the production of nuclear
energy and its uses
• describe the production of nuclear energy
through fission
• describe the production of nuclear energy
through fusion
• state the uses of nuclear energy
• describe the process of generating electricity
from nuclear energy
• explain the effects of nuclear energy
production
2.3 : Awareness of the need for proper handling
of radioactive substances
• state the effects of radioactive radiations on
living things
• describe the correct way of handling
radioactive
• substances and radioactive waste
• explain the need for proper handling in
radioactive
• substances and radioactive waste
THEME : ENERGY IN LIFE
LEARNING AREA : 3. LIGHT, COLOUR, SIGHT
• Synthesizin Discussion • Realizing
Week 30 – 3.1 : Synthesizing the formation of image by
g that science
33 plane mirrors and lenses Slide
• Visualizing is a means to
(25/07 – • state the characteristics of images formed presentation understand
• Attributing
19/08) by a plane mirror nature
• Making
• state the characteristics of images formed hypothesis Experimentin • Appreciati
by a convex lens g ng the
• Generating
• state the characteristics of images formed ideas contribution
by a concave lens • Relating of science
and
• compare and contrast images of distant technology
objects formed by convex • Being
lenses and concave lenses honest and
• draw a labelled ray diagram to show the accurate in
formation of recording
image by light rays passing through a convex and
lens validating
• draw a labelled ray diagram to show the data
formation of
image by light rays passing through a
concave lens
• draw a labelled ray diagram to explain how
characteristics
of images formed by convex lenses vary with
object distance
• determine the focal length of a convex lens
3.2 : Synthesizing the formation of image by
optical instruments
• identify the parts of optical instruments
involved in image formation
• draw ray diagrams for light rays passing
through an
optical instrument
• compare and contrast the mechanisms in
focusing and
controlling the amount of light that enters
human eyes and a camera
Week 35
(29/08 – MID-SEMESTER BREAK
02/09)
September THEME : TECHONOLOGICAL AND INDUSTRIAL
Week 34 – DEVELOPMENT IN SOCIETY
36 LEARNING AREA : 1. CHEMICALS IN INDUSTRY
(22/08 –
• Analyzing Slide • Realizing
08/09) 1.1 : Understanding the properties of alloys and presentation
• Predicting that science
their uses in industry is a means to
• Making
• state what an alloy is hypothesis Discussion understand
• give example of alloys • Generating nature
• explain how the formation of alloy can ideas Mind • Appreciati
change the mapping ng the
properties of metals balance of
nature
• relate the changes in the properties of
• Being
metals when they are
responsible
converted to alloys to the arrangment of about the
particles in the alloys safety of
• relate the properties of alloys to their uses in oneself,
daily life others and
• describe the importance of alloys in industry the
• state what superconductors alloys are environment
1.2 : Analyzing the production and uses of
ammonia in industry
• list the uses of ammonia and its compounds
in daily life
• describe how ammonia is produced in
industry
• state the factors which affect the production
of ammonia in industry
• state the industral uses of ammonia
• describe how ammonia is used to produce
ammonium salt fertilisers and urea
1.3 : Analyzing the effects of industrial waste
disposal on the environment
• identify manufacturing activities which are
sources of pollution
• explain the effects of improper industrial
waste disposal
• relate the effects of improper industrial
waste
disposal to the survival of living things
• state with examples the methods of
controlling
industrial waste disposal to avoid pollution
1.4 : Realizing the need for preservation and
conservation of the environment from industrial
waste pollution for the well being of mankind
• describe the consequences of uncontrolled
and haphazard
• disposal of industrial waste
• explain the importance of practising
responsible
• way of disposing industrial waste
Week 37 – 42 REVISION
(12/09 –
22/10)
Week 43 – 44 SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION
(24/10 –
04/11)
November – YEAR END SCHOOL’S HOLIDAY
December
Prepared by, Verified by,
____________________ ___________________
(DEBBIE CLEMENT) (JANNIE A. ROMAN)
Head of Science Panel. Head of Department of Science and Mathematics.
SMK Tun Fuad Stephens, Kiulu. SMK Tun Fuad Stephens, Kiulu.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Constitutional Psychophysiology: Research in ReviewDe la EverandConstitutional Psychophysiology: Research in ReviewÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Triadic Structure of the Mind: Outlines of a Philosophical SystemDe la EverandThe Triadic Structure of the Mind: Outlines of a Philosophical SystemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Plan Science Form 4Document49 paginiYearly Plan Science Form 4Vikneswaran Gunahlan NeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Lesson Plan Science Form 4 2016Document21 paginiYearly Lesson Plan Science Form 4 2016Wani MesraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Curriculum Specifications Yearly Lesson Plan For Form Four 2011Document28 paginiScience Curriculum Specifications Yearly Lesson Plan For Form Four 2011姚方祥Încă nu există evaluări
- Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Pahang Science Curriculum Specifications Yearly Lesson Plan For Form Four 2010Document28 paginiJabatan Pelajaran Negeri Pahang Science Curriculum Specifications Yearly Lesson Plan For Form Four 2010Rodzila GhadziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Teaching Plan 2Document1 paginăYearly Teaching Plan 2Usop AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Lesson Plan Science Form 4 (201 )Document2 paginiYearly Lesson Plan Science Form 4 (201 )kudienaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Budget of Work Science 9Document3 paginiBudget of Work Science 9Abe JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revised Bloom's Taxonomy guideDocument17 paginiRevised Bloom's Taxonomy guideAaron DimaguilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes NotesDocument35 paginiWeek Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes NotesCatherine LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Vivekananda 2015 Yearly Lesson Plan Form 4Document32 paginiSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Vivekananda 2015 Yearly Lesson Plan Form 4Nurul FarhanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- K12 Science Curriculum Map Unit II: Living ThingsDocument10 paginiK12 Science Curriculum Map Unit II: Living ThingsMary Chriszle Domisiw100% (1)
- Scheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4, 2010Document28 paginiScheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4, 2010WanM.Syamim0% (1)
- SMK METHODIST TANJONG MALIM YEARLY SCIENCE PLANDocument33 paginiSMK METHODIST TANJONG MALIM YEARLY SCIENCE PLANZulkifli Bin JaafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Welcome To The World of PsychologyDocument7 pagini01 Welcome To The World of PsychologyTunahan OğuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychology Major PO CODocument10 paginiPsychology Major PO COaritrayeebarman05Încă nu există evaluări
- Finals Reviewer (UTS)Document3 paginiFinals Reviewer (UTS)Kimberly GuinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMK Slim Science Curriculum Specifications Yearly Lesson Plan For Form Four 2011Document29 paginiSMK Slim Science Curriculum Specifications Yearly Lesson Plan For Form Four 2011Zulkifli Bin JaafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analyzing Psychoanalysis ConceptsDocument22 paginiAnalyzing Psychoanalysis ConceptsRaiza CabreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 06-F2022 - Midterm#1 ReviewDocument6 pagini06-F2022 - Midterm#1 ReviewEmma MahoneyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teaching Guide 6 4Document88 paginiTeaching Guide 6 4Saleha Shoaib100% (2)
- F4 Physics Yearly PlanDocument14 paginiF4 Physics Yearly PlansaizassrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology: Placement: First YearDocument68 paginiAnatomy and Physiology: Placement: First YearNandita Ghosh100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology: Placement: First YearDocument12 paginiAnatomy and Physiology: Placement: First YearJerin CyriacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding the Self and Psychological DevelopmentDocument75 paginiUnderstanding the Self and Psychological DevelopmentEllen ArboledaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Sains Ting 4Document33 paginiRancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Sains Ting 4Abdullah Yusof AzzamÎncă nu există evaluări
- YEARLY TEACHING PLAN OF FORM 4 SCIENCEDocument32 paginiYEARLY TEACHING PLAN OF FORM 4 SCIENCEHaffiuzdin Bin Abd AzizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scheme of Work f52006Document18 paginiScheme of Work f52006ediÎncă nu există evaluări
- RPT Science FRM 2 PZADocument12 paginiRPT Science FRM 2 PZAapeenakallÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 4 SequenceDocument5 paginiGrade 4 SequenceSarah ZaheerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weekly Lesson PlanDocument2 paginiWeekly Lesson PlanBea DoministoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIDTERM Pilar College Anatomy Physiology Final EditDocument41 paginiMIDTERM Pilar College Anatomy Physiology Final EditYeona BaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5º - Unit 1 NaturalDocument10 pagini5º - Unit 1 Naturalkarina guiradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 CLA PrinciplesDocument35 pagini1 CLA PrinciplesEira SethiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week Learning Objectives and Outcomes Learning ActivitiesDocument13 paginiWeek Learning Objectives and Outcomes Learning ActivitiesNorazla MustafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson: How Does The Brain Work?Document22 paginiLesson: How Does The Brain Work?yair Enrique Romero OspinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory - 60 HoursDocument7 paginiTheory - 60 HoursChenna KeshavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychology: PerceptionDocument4 paginiPsychology: Perceptionapi-3829364Încă nu există evaluări
- Midtermstudyguide2022!2!2 2 2Document4 paginiMidtermstudyguide2022!2!2 2 2Georgette AyazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maintenance and Continuity of Life 1. Body CoordinationDocument3 paginiMaintenance and Continuity of Life 1. Body Coordinationcyberbat2008Încă nu există evaluări
- Psychology Approaches and Research MethodsDocument1 paginăPsychology Approaches and Research MethodsemmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes - EDUC 154 Pres.Document6 paginiLearning Objectives Learning Outcomes - EDUC 154 Pres.Kerby Jean GumallaoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychology: Placement: First YearDocument8 paginiPsychology: Placement: First YearJerin CyriacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Yearly Lesson PlanDocument25 paginiScience Yearly Lesson PlanfordalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Reflexes: Psychology 372 Physiological PsychologyDocument4 paginiSpinal Reflexes: Psychology 372 Physiological PsychologylinaleenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1: Introduction: Learning Objective/sDocument11 paginiModule 1: Introduction: Learning Objective/sRoxie May Theresse AbagatnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bakai Yearly Plan 2011Document11 paginiBakai Yearly Plan 2011Nurul Shariza Mohd NasirÎncă nu există evaluări
- PART 1 Health Assessment Lec Prelim TransesDocument11 paginiPART 1 Health Assessment Lec Prelim TransesLoLiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cerebrum AbdullaDocument16 paginiCerebrum AbdullaafssmowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Research 2 CS - RS12-If-J-4Document3 paginiPractical Research 2 CS - RS12-If-J-4Lei Lundai-CondinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ø Creative Presentation of A Neuron and Its PartsDocument12 paginiØ Creative Presentation of A Neuron and Its PartsBryant GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- INTELLIGENCE THEORY and WICS MODELDocument12 paginiINTELLIGENCE THEORY and WICS MODELEst LijÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Lesson Plan SC f4Document36 paginiYearly Lesson Plan SC f4Gula MelakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Lesson Plan Science Form 1Document7 paginiYearly Lesson Plan Science Form 1Lenny Verra JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYSIOPDocument23 paginiPHYSIOPAirame Dela RosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology of CognitionDocument67 paginiBiology of CognitionMarcusColacinoLicioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Senses and The Brain Lesson Plan GGDocument4 paginiSenses and The Brain Lesson Plan GGCindy Huerta CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- MI Theory and Learning StylesDocument5 paginiMI Theory and Learning StylesAshley Co TingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selfhood, Identity and Personality StylesDe la EverandSelfhood, Identity and Personality StylesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Locomotion ActivitiesDocument2 paginiLocomotion ActivitiesdebbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Variation MapDocument1 paginăVariation MapdebbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 4 Crossword 1-AnsDocument1 paginăScience Form 4 Crossword 1-AnsdebbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 5 Annual Plan 2010Document36 paginiScience Form 5 Annual Plan 2010debbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Paper 3 Experiment Checklists: Num. Form Activity NotesDocument1 paginăBiology Paper 3 Experiment Checklists: Num. Form Activity Notesdebbycley70% (10)
- Science Form 4 Annual Plan 2010Document38 paginiScience Form 4 Annual Plan 2010debbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Module 2010Document25 paginiScience Module 2010debbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantDocument10 paginiSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantdebbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - LocomotionDocument6 paginiChapter 2 - LocomotiondebbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 4 Crossword 1-AnsDocument1 paginăScience Form 4 Crossword 1-AnsdebbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 5 Annual Teaching Plan (2011)Document11 paginiScience Form 5 Annual Teaching Plan (2011)debbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annual Plan 2011 Gantt ChartDocument2 paginiAnnual Plan 2011 Gantt ChartdebbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Role of Hormones in HumanDocument2 paginiThe Role of Hormones in HumandebbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Betmo Sains 2009Document37 paginiBetmo Sains 2009debbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument5 paginiThe Lymphatic Systemdebbycley100% (1)
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantDocument10 paginiSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantdebbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- RespirationDocument11 paginiRespirationdebbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument4 paginiThe Lymphatic SystemdebbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8Document4 paginiChapter 8debbycley100% (3)
- Chapter 7Document3 paginiChapter 7debbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2009 Teaching Plan For Science Form 4Document4 pagini2009 Teaching Plan For Science Form 4debbycley100% (4)
- Chapter 6Document1 paginăChapter 6debbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2009 Science Form 5 Yearly Teaching PlanDocument3 pagini2009 Science Form 5 Yearly Teaching Plandebbycley100% (2)
- Chapter MotionDocument3 paginiChapter MotiondebbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2009 Teaching Plan For Science Form3Document4 pagini2009 Teaching Plan For Science Form3debbycley100% (11)
- Science Form 5 Synthetic Materials in IndustryDocument10 paginiScience Form 5 Synthetic Materials in Industrydebbycley100% (11)
- IMMUNISATIONDocument1 paginăIMMUNISATIONdebbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 5 Conceptual QuestionDocument8 paginiScience Form 5 Conceptual QuestiondebbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 5 Problem Solving QuestionsDocument4 paginiScience Form 5 Problem Solving QuestionsdebbycleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Animal Science - 1Document14 paginiIntroduction To Animal Science - 1Jesus Gomez Cortizzo100% (1)
- Sex Linked Inheritance ExplainedDocument37 paginiSex Linked Inheritance ExplainedJacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Genetics: Biology-KirbyDocument27 paginiIntroduction To Genetics: Biology-KirbyAli SeenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IBO 2011 Theory Part ADocument47 paginiIBO 2011 Theory Part Apdbiocomp100% (1)
- Aakash Rank Booster Test Series For NEET Aakash Rank Booster Test Series For NEET-2020 2020Document12 paginiAakash Rank Booster Test Series For NEET Aakash Rank Booster Test Series For NEET-2020 2020VedÎncă nu există evaluări
- BLOOD TYPE INHERITANCEDocument4 paginiBLOOD TYPE INHERITANCETaylorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetic Algorithms in Induction Motor Efficiency DeterminationDocument78 paginiGenetic Algorithms in Induction Motor Efficiency DeterminationKean PagnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Punnett Square Packet 2012Document13 paginiBiology Punnett Square Packet 2012api-241528754Încă nu există evaluări
- Ncma219 Lec PrelimDocument59 paginiNcma219 Lec PrelimJillian Danielle GalvezÎncă nu există evaluări
- InheritanceDocument230 paginiInheritancebiologi88Încă nu există evaluări
- 6-4 Study GuideDocument2 pagini6-4 Study GuideKirryn ParsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1stQ G9 Test QuestionsDocument5 pagini1stQ G9 Test QuestionsMichÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blueprint of LifeDocument42 paginiBlueprint of Lifesophiehee1234Încă nu există evaluări
- 10 Science English 2020 21Document296 pagini10 Science English 2020 21Daksh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essentials of Molecular Genetics: Understanding Gene FunctionsDocument47 paginiEssentials of Molecular Genetics: Understanding Gene Functionsn1123581321Încă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation - Revision WorksheetDocument5 paginiPrinciples of Inheritance and Variation - Revision Worksheetafsheenfatima2006Încă nu există evaluări
- A Closer Look at Genes and Genetic Engineering (2012) PDFDocument89 paginiA Closer Look at Genes and Genetic Engineering (2012) PDFlacisagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetic Materia Medica - Vol-1 - by Parful Vijayakar - Typed PDFDocument278 paginiGenetic Materia Medica - Vol-1 - by Parful Vijayakar - Typed PDFvirag.patil100% (2)
- Biology Exploring The Diversity of Life Canadian 3Rd Edition Russell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument22 paginiBiology Exploring The Diversity of Life Canadian 3Rd Edition Russell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFbierbalkgeorge3f17100% (13)
- 3.7.1 InheritanceDocument7 pagini3.7.1 InheritanceNaimah ShakeelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evo BioDocument20 paginiEvo BioKlea Francheska SembranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LS7B Week 2 Lab WorksheetDocument4 paginiLS7B Week 2 Lab WorksheetYemberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Life Sciences Fundamentals and Practice - IIDocument161 paginiLife Sciences Fundamentals and Practice - IIPathifnder Publication81% (21)
- UPCAT Genetics and Biology With AnswersDocument2 paginiUPCAT Genetics and Biology With AnswersOlivaa Wilder100% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument4 paginiLesson Planapi-295212770Încă nu există evaluări
- My LP Revised For DemoDocument4 paginiMy LP Revised For DemoJonas CabusbusanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Video Recap of Alleles and Genes by Amoeba SistersDocument3 paginiVideo Recap of Alleles and Genes by Amoeba Sistersur100% (2)
- Namma Kalvi 12th Botany Question Bank em 218759Document25 paginiNamma Kalvi 12th Botany Question Bank em 218759sharanentrepreneur045Încă nu există evaluări
- 1st Periodical Test Grade 9Document4 pagini1st Periodical Test Grade 9Adrian FromPHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mendel 3keyDocument20 paginiMendel 3keyJames KnowellÎncă nu există evaluări