Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Hiller Plant Instructable
Încărcat de
sjsshipTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Hiller Plant Instructable
Încărcat de
sjsshipDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
342 2.
CHILLER PLANT INSTRUCTABLE
RATINGS
MEASURE 2.7.2 Maintain the proper New Facilities Retrofit O&M
refrigerant charge.
A
The efficiency of all chillers suffers if the system SUMMARY
has either too little or too much refrigerant charge. Also,
A fundamental chiller maintenance procedure
the compressor may suffer damage if the system is
overcharged. Some systems have only minimal reservoir with a significant effect on efficiency. Finding
capacity, making it important to charge the system the level of charge may be tricky. Some
precisely. Such systems are more vulnerable to loss of inexpensive accessories may help.
efficiency from small leaks. Other systems have a large SELECTION SCORECARD
amount of reservoir capacity. In these systems, a small
leak may persist for a long time before being noticed. Savings Potential ...................
Check the refrigerant charge in your cooling units Rate of Return .......................
often enough to keep the charge within proper limits. Reliability ...............................
This Measure gives you procedures for checking and
maintaining the proper refrigerant charge and explains Ease of Initiation ....................
the effects of improper refrigerant charge.
Bad Effects of Incorrect Refrigerant Charge In hermetic chillers, in which the motor is cooled
by the refrigerant gas, low charge can overheat the motor,
Both the COP and the capacity of a cooling unit
reducing its life.
suffer if the refrigerant charge is too low. When that
occurs, evaporator capacity is reduced because less of If there is too much refrigerant in the system, the
its surface is wetted, and the average evaporator excess may back up in the condenser, reducing its
temperature differential increases. The compressor must effective surface area and increasing the average
work harder to satisfy the same cooling load. temperature differential across the condenser. In chillers
that have a flooded cylindrical evaporator and no device
to regulate the refrigerant level in the evaporator, high
refrigerant level reduces the evaporation surface area.
In some types of systems, excess refrigerant can
travel through the evaporator in the liquid state,
continuing into the compressor. This can destroy a
positive displacement compressor immediately, and it
can destroy a centrifugal compressor gradually.
How to Measure Refrigerant Charge
The most difficult aspect of maintaining the proper
refrigerant charge may be measuring the charge that is
presently in the system. In some cases, this can be tricky,
tedious, or both. The best method of checking the
refrigerant charge depends on the type of system. Use
the best method or combination of methods for your
system. The following are the various methods that are
available.
Liquid Level Indicators and Sight Glasses
Some chiller units, and some vessels in a chiller
system, may have a means to indicate the refrigerant
WESINC quantity directly. These work only if a predictable
Fig. 1 Refrigerant level sight glass in a large chiller The quantity of refrigerant remains in one part of the system.
glass is located just below the center of the evaporator shell,
The most common liquid level indicator is a sight glass
to the right of the instrument panel. It is so small that it may
not line up with the liquid level. If so, you can’t tell whether the on the vessel where the refrigerant collects.
liquid level is above or below the glass. In this case, observe Refrigerant level sight glasses are common
the glass when the machine starts. accessories of packaged water chillers. They are useful
ENERGY EFFICIENCY MANUAL
2.7 REFRIGERANT CONDITION 343
on these machines because all the refrigerant remains pressure refrigerants, the blowout continues at full
within the shell of the machine and drains freely into pressure as long as there is liquid in the system, which
the evaporator. Figure 1 shows a typical sight glass. It is a dangerous situation.
can be used when the machine is running or turned off, Discharge and Suction Pressures
although the level is more stable when the machine is With all types of compression cooling equipment,
not running. you can check the state of refrigerant charge by
Many refrigerant level sight glasses are perversely measuring the discharge and suction pressures in the
small, making it difficult to check the level if it is above system. Do this while the compressor is operating and
or below the level of the sight glass. In such cases, it the system is in stable operation.
helps to look at the sight glass as the chiller is being Larger machines usually have gauges installed that
started. If the refrigerant surface is above the sight glass, indicate the evaporator and condenser pressures at all
you can probably see bubbles as the chiller starts, or the times. Figure 2 shows a typical example. Use portable
refrigerant level drops to the level of the sight glass. If gauges if the machine does not have gauges installed.
the refrigerant level is below the sight glass, you may
be able to see splatter on the sight glass, which indicates The normal discharge pressure depends on the
that the charge is low. condensing temperature. To check system charge, use
a table of refrigerant pressures and temperatures. This
Some older units have a liquid level test cock on tells you what the condensing pressure should be at the
the evaporator shell. However, these require venting current condensing temperature. If the discharge
some refrigerant to test the liquid level. This practice is pressure is lower than it should be at that temperature,
now considered very bad form, for environmental the system is low on charge.
reasons.
Refrigerant pressure gauges often have the
In chiller systems where the components are spread corresponding saturation temperatures printed right on
out, refrigerant quantity indicators do not work as well, the gauge dials. This saves you the trouble of finding a
or they may not work at all. The problem is that refrigerant pressure chart. Portable refrigerant gauges
refrigerant migrates from one part of the system to typically show the saturation pressures for several of
another. When the chiller is running, the distribution of the most common refrigerants. If you need to use a
refrigerant in the system varies with load. When the refrigerant table, you can find one in many reference
chiller is not running, refrigerant migrates to the coldest books. Also, refrigeration supply houses common give
part of the system. For example, the refrigerant might away refrigerant tables that are printed on handy cards.
accumulate in the condenser during winter and in the If the type of refrigerant used in the chiller system has
evaporators during summer. been changed, be sure to use a refrigerant table for the
If a spread-out chiller system has a receiver current refrigerant.
(refrigerant surge tank) or a shell-and-tube evaporator, If the refrigerant charge is low, both the discharge
it may be practical to use a level indicator in one of and suction pressures will be lower than normal. The
these vessels. In such cases, the level indicator provides discharge pressure is low because there is not enough
useful information only when the system is running and gas in the system for the compressor to squeeze to the
stabilized. Even then, the level of refrigerant varies with normal discharge pressure. The suction pressure drops
the cooling load. The refrigerant level indicator should
be readable anywhere within the acceptable charge
range. When the system is turned off, refrigerant pools
in the coldest parts of the system, and the level indicator
gives a false reading.
If your chiller system does not have an easy-to-read
refrigerant level indicator, consider adding one, if
possible. If you do, install a placard at the sight glass or
gauge that indicates the normal range of readings, and
the conditions under which the readings are valid. For
example, the placard might say, “Refrigerant level
indicator valid only if the compressor is running, or if
the receiver temperature is at least 10°F colder than the
outside air temperature.” (See Reference Note 12,
Placards, for tips on how to create an effective placard.) WESINC
Any kind of refrigerant level gauge or sight glass Fig. 2 Evaporator and condenser gauges These tell you
should be strong and well protected. A broken sight immediately whether the machine has the minimum amount
of refrigerant for efficient operation. They do not tell you the
glass or gauge connection would vent the entire
actual amount. The condenser pressure provides an uncertain
refrigerant charge into the surrounding space. With high- indication of excessive charge.
© D. R. Wulfinghoff 1999. All Rights Reserved.
344 2. CHILLER PLANT
because there is not enough liquid refrigerant in the normal, because the condenser is not rejecting as much
evaporator to boil off vapor at the normal vapor pressure. heat. However, this symptom is subtle.
As a result, the vapor expands into the compressor (If the discharge pressure is lower than normal and
suction, lowering its pressure. In other words, the the suction pressure is higher than normal, the
compressor starts to act like a vacuum pump. compressor may be worn out, or the compressor or
Low suction pressure also creates abnormally low system may have an internal leak from the discharge
suction temperature. This occurs because the refrigerant side to the suction side, or the system may have hot gas
gas is cooled below its saturation temperature by the bypass.)
greater expansion. The suction temperature can So, the suction and discharge pressures are a reliable
eventually fall enough to freeze the evaporator coil. In indicator of low charge, and the discharge pressure is a
a water chiller, this can cause major damage. less reliable indicator of excessive charge. However,
Suction pressure could be lower than normal for system pressure cannot tell how much refrigerant is in
other reasons, such as obstructed air flow through an the system within the normal range of charge. As long
air-cooled evaporator. For example, opening the as there is enough liquid within the system to keep the
evaporator coil access panel in an air handling unit short- evaporator supplied, the readings are normal. In systems
circuits the flow of air around the coil, causing its without refrigerant quantity indicators, you have to check
refrigerant pressure to drop. the refrigerant pressure at appropriate intervals to detect
Discharge pressure is much less reliable as a clue to the first sign of inadequate charge. When leakage finally
excessive refrigerant charge. If the condenser floods causes liquid starvation in the evaporator, pressures start
from excess charge, its cooling capacity is reduced, so to decline. The rate of decline depends on the leakage
the discharge pressure rises. A noticeable pressure rise rate and on the volume of refrigerant in the system.
occurs only under high load. A condenser that is heavily On the other hand, air in the system causes all
flooded with excess refrigerant will also cause cooling pressures to be higher than normal. This can mask a
water or cooling air temperatures that are lower than
Carrier Corporation
Fig. 3 Evaporator liquid line sight glass It is generally located as shown here, close to where the refrigerant
liquid enters the evaporator. Bubbles in the sight glass while the system is running probably indicate low
refrigerant charge, but they may also indicate an obstruction of the refrigerant line in the direction of the condenser.
ENERGY EFFICIENCY MANUAL
2.7 REFRIGERANT CONDITION 345
low refrigerant charge. Keep air out of the system at all lingers in the condenser long enough to become
times. This is covered by Measures 2.7.1 and 2.7.3. excessively subcooled.
Evaporator Liquid Line Sight Glass The difference in temperature between normal and
In chillers that use a throttling type of refrigerant subcooled refrigerant from a condenser is small. This
metering device (an “expansion valve,” capillary tubes, makes the test too subtle for any but experienced
etc.) to control the flow of refrigerant to the evaporator, technicians. Look for condenser subcooling as
a sight glass may be installed in the refrigerant line confirmation of excess charge if the discharge pressure
leading to the evaporator. Figure 3 shows where to look is too high.
for the sight glass. This symptom is accompanied by abnormally high
Bubbles in the sight glass indicate that there is not condenser pressure, especially at high cooling load.
enough liquid in the system to keep the line filled. Bleeding Refrigerant Pressure
Bubbles first appear under high cooling load, when As a last resort, you can bleed refrigerant from the
liquid is being drawn out of the line most rapidly. system until the operating pressures drop, and then add
Bubbles that occur when the system first starts may be the recommended amount of extra refrigerant. Do not
normal, and do not indicate low charge. use this method with any environmentally harmful
Bubbles in a sight glass are not a foolproof refrigerant unless you have the equipment to salvage
indication. If the sight glass is located upstream of a the refrigerant.
partially obstructed filter or dryer, the back pressure may
keep bubbles from forming even when the charge is low. Should You Add a Receiver?
Conversely, if the sight glass is downstream of a clogged All chiller systems have a certain amount of storage
filter or dryer, the reduced pressure at the sight glass volume for liquid refrigerant, but the amount varies
may cause bubbles to form even though the amount of widely. Ample refrigerant storage capacity ensures that
refrigerant in the system is proper. Adding more refrigerant is available to the evaporator. It compensates
refrigerant based on this false indication may overcharge for accumulation of refrigerant in different parts of the
the system and cause compressor damage. system under different operating conditions. It prevents
A liquid line sight glass cannot reveal excessive back-flooding of refrigerant into the condenser. And, it
refrigerant charge. provides a reserve to make up for leakage.
Suction Gas Superheat Some chillers inherently have large storage volume.
In direct-expansion chiller systems (which send the For example, packaged centrifugal water chillers store
refrigerant directly into the cooling coils), low charge a large amount of refrigerant in their evaporator shells.
is indicated by high superheat in the gas leaving the On the other hand, direct-expansion chillers may have
evaporator, especially when the compressor is operating little storage capacity, because air coils have small liquid
at full load. Superheat is the excess of the gas suction volumes. In the past, it was common practice to install
temperature above the gas saturation temperature. When a “receiver” in such systems, which is simply a storage
the evaporator becomes “starved” for refrigerant, the tank, or surge tank. Different chiller system designs
available refrigerant boils off quickly and the unsatisfied may have receivers in different parts of the system.
heat load of the evaporator superheats the refrigerant It has become commonplace to eliminate the
gas excessively. receiver from chiller systems as a cost saving measure.
In systems that use a thermostatic expansion valve, In such systems, storage volume is limited to the
the valve is designed to maintain a fixed amount of condenser itself and to the piping downstream of the
superheat. The purpose of the superheat is to ensure condenser. Therefore, a relatively small overcharge may
that liquid refrigerant does not enter the compressor. cause refrigerant to back up into the condenser, and a
Do not let this superheat fool you into believing that the relatively small undercharge may starve the evaporator
charge is low. If the superheat setting of the valve is of refrigerant. For example, a difference of a few ounces
unknown (it is typically 10°F to 20°F, or 5°C to 11°C), of refrigerant charge may affect chiller performance in
the charge is probably not low if the superheat remains a small split system.
essentially the same at all loads. In systems that lack refrigerant storage capacity, it
Condensate Subcooling may be desirable to add a receiver to the system. The
mechanical installation is usually not complicated, but
In systems with air-cooled condensers, excessive
it should be done by a refrigeration specialist familiar
charge is indicated by excessive subcooling of the
with proper piping practices and other aspects of
refrigerant. Subcooling is cooling of the liquid
assembling cooling systems. Finding the proper location
refrigerant below its saturation temperature. When the
for the receiver in the system requires a clear
system is overcharged, the condenser fills with liquid
understanding of chiller system design.
refrigerant, the condenser capacity drops, and the liquid
© D. R. Wulfinghoff 1999. All Rights Reserved.
346 2. CHILLER PLANT
Installing a receiver is not a substitute for keeping recharging. Don’t try this without training. Chiller
the system free of leaks. If the system operates properly servicing should be done only by technicians who fully
when it is properly charged, it probably does not need a understand what they are doing. Inadequate training of
receiver. Instead, put your emphasis on proper charging maintenance personnel is a common cause of chiller
procedure and checking for leaks. damage and inefficiency.
How to Add Refrigerant ECONOMICS
Follow the refrigerant charging procedures specified SAVINGS POTENTIAL: Up to 20 percent of chiller
by the manufacturer. If your system does let you operating cost.
measure the refrigerant charge directly, find the point
of minimum charge as described previously. Then, add COST: Usually minimal.
refrigerant in the amount specified by the manufacturer. PAYBACK PERIOD: Short.
If you use a large bulk container of refrigerant, put it on
a portable scale as you charge the system. Calculate TRAPS & TRICKS
the amount of refrigerant added from the change in SKILLS AND TRAINING: Understand how refrigerant
weight. travels in your chiller system. Know the best methods
Be careful to keep air from entering the system when of checking the charge in that type of system. Invest in
you recharge it. This requires great care if the refrigerant training the right person for this responsibility. Keep
in the chiller is below atmospheric pressure. Even with unqualified people from messing with refrigerant charge.
high-pressure refrigerants, be careful to purge all the They can do a lot of harm.
refrigerant gauge and filling hoses before opening the SCHEDULING: This is another function that tends to
chiller service ports. be forgotten. If the charge in your chillers can be checked
If you are filling a chiller system that has been easily, put a column for refrigerant level on the chiller
opened to the atmosphere, you have to use a vacuum operating log. Otherwise, schedule checks in your
pump to remove all air and vapor from the system before maintenance calendar. (You do have a chiller operating
log and a maintenance calendar, right?)
ENERGY EFFICIENCY MANUAL
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Advanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionDe la EverandAdvanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refrigerator Revelations: A User's Guide to Operation and MaintenanceDe la EverandRefrigerator Revelations: A User's Guide to Operation and MaintenanceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Servico Serie MDFDocument50 paginiManual Servico Serie MDFflavio fontesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Component Balancing in Refrigeration SystemsDocument4 paginiComponent Balancing in Refrigeration SystemsBryan VertuodasoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LADDER Program Solution For Multi-Probe Monitoring and Control in Simple Cooling ProcessDocument10 paginiLADDER Program Solution For Multi-Probe Monitoring and Control in Simple Cooling ProcessShivam SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- 320C Causas de RecalentamientoDocument4 pagini320C Causas de RecalentamientoEdin Raul Yalle RafaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ascott Service Manual Iss - Part 2Document42 paginiAscott Service Manual Iss - Part 2Le BachÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSC Information Sheet 608: What's The Big Deal About Refrigerant ChargeDocument2 paginiBSC Information Sheet 608: What's The Big Deal About Refrigerant ChargeSvetoslav VlashkiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Component Balancing in Refrigeration Systems: Related Commercial ResourcesDocument4 paginiComponent Balancing in Refrigeration Systems: Related Commercial Resourcesalialavi2Încă nu există evaluări
- 3ureohp 3Rvvleoh&Dxvh 5hsdlu &RPPHQWV: Lmportant: Adequate Air Circulation Around The DryerDocument3 pagini3ureohp 3Rvvleoh&Dxvh 5hsdlu &RPPHQWV: Lmportant: Adequate Air Circulation Around The DryerMatthew MhlongoÎncă nu există evaluări
- System Practices For Ammonia RefrigerantDocument27 paginiSystem Practices For Ammonia RefrigerantLuis Carlos PardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ashrae Handbook98.r44stxt Component Balancing in Refrigeration SystemsDocument4 paginiAshrae Handbook98.r44stxt Component Balancing in Refrigeration SystemsGiang ĐàoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCR Instruction Manual For Refrigeration Dryer (R407C)Document13 paginiSCR Instruction Manual For Refrigeration Dryer (R407C)Yaroslav100% (1)
- ML-Engine: COMPETENCE 3 - Operation, Surveillance, Performance Assessment and Maintaining Safety of Propulsion Plant and Auxilliary MachineryDocument9 paginiML-Engine: COMPETENCE 3 - Operation, Surveillance, Performance Assessment and Maintaining Safety of Propulsion Plant and Auxilliary Machineryjohn aldrinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aire AcondicionadoV5Document78 paginiAire AcondicionadoV5Bruno PompilioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refeer Air CompressorDocument12 paginiRefeer Air CompressorSantharam MarinerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 Vapour Compression Ref Systems 1 06Document11 pagini04 Vapour Compression Ref Systems 1 06scarpredator5Încă nu există evaluări
- Fordson Major ManualDocument47 paginiFordson Major ManualHassan GDOURAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free Cooling Without Refrigeration ProcessDocument9 paginiFree Cooling Without Refrigeration Processsaif aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Valves: For Refrigerant ControlDocument16 paginiElectric Valves: For Refrigerant ControlMohamed HamadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liquid Overfeed Systems: TerminologyDocument9 paginiLiquid Overfeed Systems: TerminologyFlorin OnucÎncă nu există evaluări
- System Practices For Ammonia and Carbon Dioxide RefrigerantsDocument27 paginiSystem Practices For Ammonia and Carbon Dioxide Refrigerants1940LaSalleÎncă nu există evaluări
- System Design For Efficient Low-Load Cooling: SubsectionDocument12 paginiSystem Design For Efficient Low-Load Cooling: SubsectionRajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20 2020-03-27 Refrigerant Cycle ATEEDocument3 pagini20 2020-03-27 Refrigerant Cycle ATEEعبير ابوصالحهÎncă nu există evaluări
- System PracticesDocument27 paginiSystem PracticesMechanicalÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Review On Performance Comparison of VCRs &VARsDocument7 paginiA Review On Performance Comparison of VCRs &VARsdbpublicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2010-04-15 023718 File PDFDocument27 pagini2010-04-15 023718 File PDFBrayan paredesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Absorption Refrigeration SystemsDocument33 paginiAbsorption Refrigeration SystemsAdedire FisayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZG Cooling System 7 - 1Document26 paginiZG Cooling System 7 - 1Dalton WiseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supervisory Control For Resilient Chiller Plants Under Condenser FoulingDocument19 paginiSupervisory Control For Resilient Chiller Plants Under Condenser FoulingAnupriya GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Simple Air Conditioning Circuit and Cycle Diagram That You Might Find UsefulDocument6 paginiA Simple Air Conditioning Circuit and Cycle Diagram That You Might Find UsefulTEUKUÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4VOL R01ipDocument9 pagini4VOL R01ipzhyhhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Fluid ChillersDocument7 paginiPrinciples of Fluid ChillersAzim AdamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - Chap 9Document35 paginiChapter - Chap 9SimphiweÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liquid Subcooling: The Case For RefrigerantDocument4 paginiLiquid Subcooling: The Case For RefrigeranttaupiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boletin Ae1182 - Carga de RefrigeranteDocument7 paginiBoletin Ae1182 - Carga de Refrigeranteanton baxterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process-Insights MBW 373 Datasheet v22-1Document7 paginiProcess-Insights MBW 373 Datasheet v22-1Mido AzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 Expansion Devices Refrigerants 06Document13 pagini03 Expansion Devices Refrigerants 06scarpredator5Încă nu există evaluări
- IMI HB-3-Balancing of Radiator SystemsDocument56 paginiIMI HB-3-Balancing of Radiator SystemsAbey VettoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sabp K 002Document49 paginiSabp K 002Erol DAĞÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refrigerant Charging Procedure For Air Conditioner or Heat Pump Repair or Refrigeration Equipment RepairDocument10 paginiRefrigerant Charging Procedure For Air Conditioner or Heat Pump Repair or Refrigeration Equipment RepairJeevanandam ShanmugasundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Screw Chiller Water Cooled PDFDocument76 paginiManual Screw Chiller Water Cooled PDFAbhinav Sai100% (1)
- Secondary RefrigerantsDocument15 paginiSecondary Refrigerantse4erkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Superheat Demystified FieldpieceDocument5 paginiSuperheat Demystified FieldpieceInsoluperez FPÎncă nu există evaluări
- CTV-PRB006-EN (New Pressure Differential For Refrigerant Pump Chillers)Document12 paginiCTV-PRB006-EN (New Pressure Differential For Refrigerant Pump Chillers)Emerson PenaforteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 1Document47 paginiTopic 1sasi taranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Development of Vapour Compression Refrigeration System Using Liquid Heat ExchangerDocument4 paginiDesign and Development of Vapour Compression Refrigeration System Using Liquid Heat Exchangersmruti katwaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finding Problems in HVAC R Refrigeration CycleDocument4 paginiFinding Problems in HVAC R Refrigeration CyclejotalopecincoÎncă nu există evaluări
- System Practices For Ammonia and Carbon Dioxide RefrigerantsDocument27 paginiSystem Practices For Ammonia and Carbon Dioxide RefrigerantsAndrés Felipe NaranjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamic Performance Analysis of Cascade Refrigeration System - A ReviewDocument5 paginiThermodynamic Performance Analysis of Cascade Refrigeration System - A ReviewOnofreÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Properly Interpret Liquid Subcooling in The Condenser NEWS - August 09, 2021Document7 paginiHow To Properly Interpret Liquid Subcooling in The Condenser NEWS - August 09, 2021Insoluperez FPÎncă nu există evaluări
- IJEAS0204012Document3 paginiIJEAS0204012erpublicationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amonia Energy PDFDocument10 paginiAmonia Energy PDFLeonardo PachecoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refrigeration EquipmentDocument71 paginiRefrigeration EquipmentmarleythejckrssllÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Conditioning System: PrecautionDocument94 paginiAir Conditioning System: Precautionsungjoo75Încă nu există evaluări
- 03 Refrigeration&Air Conditioning-1Document50 pagini03 Refrigeration&Air Conditioning-1AmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2009-08 EMOs For Cooling SystemsDocument4 pagini2009-08 EMOs For Cooling Systemsnikola ilicÎncă nu există evaluări
- 30gx082 CarrierDocument12 pagini30gx082 CarrierRicardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Information: 1 - IntroductionDocument3 paginiTechnical Information: 1 - IntroductionJOSE CAMPOSÎncă nu există evaluări
- PL Cooling System 7 - 1Document0 paginiPL Cooling System 7 - 1Luis Alberto OrtegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- D48877F DEIF Control PanelDocument1 paginăD48877F DEIF Control PanelsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Easter Egg SearchDocument1 paginăEaster Egg SearchsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- D48877F DEIF Control PanelDocument1 paginăD48877F DEIF Control PanelsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norme Istallaz. Serie DLX 03-04Document1 paginăNorme Istallaz. Serie DLX 03-04sjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ratio Exam QuestionsDocument2 paginiRatio Exam QuestionssjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Backhoe Range: For Tractors From 15HPDocument8 paginiBackhoe Range: For Tractors From 15HPsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler Low Level Control Electrical DrawingDocument1 paginăBoiler Low Level Control Electrical DrawingsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Egg 3Document3 paginiEgg 3sjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1000 Ideas About Easter Riddles On Pinterest Scavenger HuntDocument1 pagină1000 Ideas About Easter Riddles On Pinterest Scavenger HuntsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Egg 1Document2 paginiEgg 1sjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clue Map For Egg HiderDocument2 paginiClue Map For Egg HidersjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1000 Ideas About Easter Riddles On Pinterest Scavenger HuntDocument1 pagină1000 Ideas About Easter Riddles On Pinterest Scavenger HuntsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- UT-Vessel GH SpecificationDocument3 paginiUT-Vessel GH SpecificationsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- MOSS-Vessel GH SpecificationDocument3 paginiMOSS-Vessel GH SpecificationsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- 164 Service Sheet4 PDFDocument4 pagini164 Service Sheet4 PDFsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- 164 Service Sheet4 PDFDocument4 pagini164 Service Sheet4 PDFsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- 164 Service Sheet6 PDFDocument4 pagini164 Service Sheet6 PDFsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- 164 Service Sheet6 PDFDocument4 pagini164 Service Sheet6 PDFsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- 164 Service Sheet5 PDFDocument4 pagini164 Service Sheet5 PDFsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- 164 Service Sheet5 PDFDocument4 pagini164 Service Sheet5 PDFsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- 164 Service Sheet TesterDocument4 pagini164 Service Sheet TesterJill WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 164 Service Sheet6 PDFDocument4 pagini164 Service Sheet6 PDFsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- 164 Service Sheet5 PDFDocument4 pagini164 Service Sheet5 PDFsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- 164 Service Sheet TesterDocument4 pagini164 Service Sheet TesterJill WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
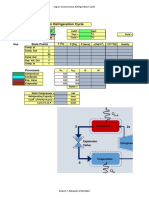
- Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle: State PointsDocument6 paginiVapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle: State PointssjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- 164 Service Sheet TesterDocument4 pagini164 Service Sheet TesterJill WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- R134aaa PDFDocument5 paginiR134aaa PDFsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recharge FeonDocument8 paginiRecharge FeonsjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequently Asked Questions: " (Type Subject of Faqs) " Rulefinder User GuideDocument1 paginăFrequently Asked Questions: " (Type Subject of Faqs) " Rulefinder User GuidesjsshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project - Charter1 Template-1Document5 paginiProject - Charter1 Template-1Jwaone KosiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Procedure Qualification Record - Page 1 of 2Document3 paginiProcedure Qualification Record - Page 1 of 2Rohit KambleÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIST HARGA Agustus 2023Document1 paginăLIST HARGA Agustus 2023AzwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scope Split Matrix For Agitator (Project-A010-HIIPL)Document6 paginiScope Split Matrix For Agitator (Project-A010-HIIPL)Tushar MangratiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Namsung 2015 CatalogueDocument10 paginiNamsung 2015 CataloguekimsonvuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gesture Control CarDocument39 paginiGesture Control CarSAMBE SRUJAN KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Program Manager Vs Project Manager Salary & ResponsibilitiesDocument2 paginiProgram Manager Vs Project Manager Salary & Responsibilities1105195794Încă nu există evaluări
- Understanding HTMLDocument11 paginiUnderstanding HTMLPriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- APQP Timing PlanDocument2 paginiAPQP Timing PlandanielsasikumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Craft Certicate and Diploma Solar Installation Scheme of WorkDocument3 paginiCraft Certicate and Diploma Solar Installation Scheme of WorkSharon AmondiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logging and AuditingDocument3 paginiLogging and AuditingJamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ao Sheet FinalDocument1 paginăAo Sheet FinalKreepa TimsinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gujarat Technological University (Established Under Gujarat Act No. 20 of 2007)Document23 paginiGujarat Technological University (Established Under Gujarat Act No. 20 of 2007)SVKP KADIÎncă nu există evaluări
- CATALOG. Baotou Steel Seamless ProductsDocument8 paginiCATALOG. Baotou Steel Seamless ProductsEdward R KaolinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3530 3533 BrochureDocument14 pagini3530 3533 Brochureganeshemmadi1987Încă nu există evaluări
- Answers: Warm-Up 1 Workout 1Document29 paginiAnswers: Warm-Up 1 Workout 1Hassan mouslmaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- MDCG 2018-4: Medical DevicesDocument3 paginiMDCG 2018-4: Medical Devicesjeeves_31Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab - 03 Task On 2D ArrayDocument3 paginiLab - 03 Task On 2D ArrayShantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DP610SACB ManualDocument24 paginiDP610SACB ManualChase SmytheÎncă nu există evaluări
- NPBC-V3C-1 Rev1 1 ENDocument36 paginiNPBC-V3C-1 Rev1 1 ENeddixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Report 4 ZARYAB RAUF FA17-ECE-046Document17 paginiLab Report 4 ZARYAB RAUF FA17-ECE-046HAMZA ALIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angular FrameworkDocument9 paginiAngular Frameworkvarsha dixitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 2Document4 paginiQuiz 2Viraj BhosaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machine Safety: PreventaDocument30 paginiMachine Safety: PreventaDouglasÎncă nu există evaluări
- DocumentDocument7 paginiDocumentHarsh ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examples For Feature 14EST (For Reference Only)Document12 paginiExamples For Feature 14EST (For Reference Only)Rojen LangatÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Novel Three-Phase Software Phase-Locked Loop Based On Frequency-Locked Loop and Initial Phase Angle Detection Phase-Locked LoopDocument6 paginiA Novel Three-Phase Software Phase-Locked Loop Based On Frequency-Locked Loop and Initial Phase Angle Detection Phase-Locked LoopjunyeolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q1) What Are The Primary Functions of Cyberark?Document8 paginiQ1) What Are The Primary Functions of Cyberark?santoshs2002848Încă nu există evaluări
- Couesera Python On OsDocument3 paginiCouesera Python On OsJashwanth REddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Information:: ACECOMS GEAR: RC Column Section Design Version: 3.0 (Rev. 1)Document3 paginiProject Information:: ACECOMS GEAR: RC Column Section Design Version: 3.0 (Rev. 1)Maria Rose Giltendez - BartianaÎncă nu există evaluări