Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Reported Speech Chart Grammar Guide
Încărcat de
Mari OnofrioTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Reported Speech Chart Grammar Guide
Încărcat de
Mari OnofrioDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
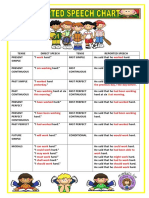
TENSE DIRECT SPEECH TENSE REPORTED SPEECH
PRESENT “I work hard.” PAST SIMPLE He said that he worked hard.
SIMPLE
PRESENT “I am working hard.” PAST He said that he was working hard.
CONTINUOUS CONTINUOUS
PAST SIMPLE “I worked hard PAST PERFECT He said that he had worked hard
yesterday.” the previous day / the day before.
PAST “I was working hard at PAST PERFECT He said that he had been working
CONTINUOUS six this morning.” CONTINUOUS hard at six that morning.
PRESENT “I have worked hard.” PAST PERFECT He said that he had worked hard.
PERFECT
PRESENT “I have been working PAST PERFECT He said that he had been working
PERFECT hard.” CONTINUOUS hard.
CONTINUOUS
PAST PERFECT “I had worked hard.” PAST PERFECT He said that
he had worked hard.
FUTURE “I will work hard.” CONDITIONAL He said that he would work hard.
SIMPLE
MODALS “I can work hard.” He said that he could work hard.
“I could work hard.” He said that he had been able to
“I may work hard.” work hard.
“I must work hard.” He said that he might work hard.
“I shall work hard.” He said that he had to work hard.
“I should work hard.” He said that he should work hard.
He said that he should work hard.
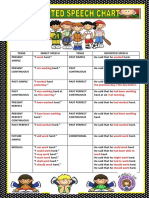
EXPRESSIONS OF TIME AND PLACE IN REPORTED SPEECH
Direct Speech Indirect Speech or Reported Speech
Pronouns and possessive We usually change from first or second to third person except
adjectives when the speaker is reporting his own words.
today that day
yesterday the day before (the previous day)
Tomorrow / the next day The following day
The day before
Two days before / earlier
yesterday
Yesterday morning The previous morning
A year / month / week
A year before / earlier
ago
The day after tomorrow In two days' time
Next week / month /
The following week / month / year
year
now then
tonight that night
here here / there
this that, it
these those
can could
will would
could could
may might
might might
have to / has to had to
must must
ought to / should ought to / should
[
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Read The Story and Answer The Questions BelowDocument4 paginiRead The Story and Answer The Questions BelowMari OnofrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading-Comprehension PossessivesDocument3 paginiReading-Comprehension PossessivesMari Onofrio100% (1)
- Present Perfect Tense Esl Dialogue Charlottes Birthday Exercises WorksheetDocument2 paginiPresent Perfect Tense Esl Dialogue Charlottes Birthday Exercises WorksheetMari Onofrio100% (1)
- Reading 1 What Do You Know About Giant PandasDocument4 paginiReading 1 What Do You Know About Giant PandasFadhla Diela100% (1)
- Short Stories British Tales Robin Hood WorksheetDocument2 paginiShort Stories British Tales Robin Hood WorksheetJiaying YoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech ChartDocument1 paginăReported Speech Chartririsky100% (1)
- Reported SpeechDocument4 paginiReported SpeechCECILIA SASTREÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech Chart PDFDocument1 paginăReported Speech Chart PDFMagdali MARTINEZ MARTINEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech Chart Grammar Guides - 11634Document1 paginăReported Speech Chart Grammar Guides - 11634Santiago CalderonÎncă nu există evaluări
- REPORTED SPEECH ChartDocument3 paginiREPORTED SPEECH Chartcristian solanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Reported Speech - StatementsDocument3 pagini1 - Reported Speech - StatementsJohnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech ChartDocument3 paginiReported Speech ChartLeonidas Miranda100% (1)
- Reported Speech 1. Tense Changes in Reported Speech Direct Speech Indrect SpeechDocument4 paginiReported Speech 1. Tense Changes in Reported Speech Direct Speech Indrect SpeechRECEP CANBOLATÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vocabulary: Read The ConversationDocument6 paginiVocabulary: Read The ConversationNoelia LorenzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wonder, Want To Know: Stilo NdirectoDocument2 paginiWonder, Want To Know: Stilo NdirectoTD ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument5 paginiReported SpeechNoelia LorenzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct and IndirectDocument11 paginiDirect and IndirectAssel SmagulovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech: Created by Gabriela Encheva 3 High School of Natural Sciences VarnaDocument29 paginiReported Speech: Created by Gabriela Encheva 3 High School of Natural Sciences VarnaEmiliya IvanovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review of The Passive: Be + Past Participle: NotesDocument3 paginiReview of The Passive: Be + Past Participle: NoteskvÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Reported SpeechDocument15 pagini6 Reported SpeechAndreea ManoliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech-StatementsDocument11 paginiReported Speech-StatementsMiss Ale PellizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument11 paginiReported Speechmis tarbiyatulmubtadiinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estilo Indirecto (Reported Speech) : 1º What Is It ? What Is It Used For ?Document6 paginiEstilo Indirecto (Reported Speech) : 1º What Is It ? What Is It Used For ?Patricia AbreuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Revision FCEDocument3 paginiGrammar Revision FCEeduappsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inglés PET 2 Segundo ParcialDocument2 paginiInglés PET 2 Segundo ParcialIng_Miguel_GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bài câu tường thuật (tự soạn)Document10 paginiBài câu tường thuật (tự soạn)SamÎncă nu există evaluări
- DirectIndirect Speech PPT 1Document17 paginiDirectIndirect Speech PPT 1Puja RatanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct and IndirectDocument11 paginiDirect and IndirectAssel SmagulovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech 124-140Document17 paginiReported Speech 124-140Ann WalterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reporte D Stateme Nts and Questio NSDocument14 paginiReporte D Stateme Nts and Questio NSDJ EDWÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech Is When You Tell Somebody What You or Another PersonDocument5 paginiReported Speech Is When You Tell Somebody What You or Another PersonRishit ChandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Grammar - SpeechDocument7 paginiEnglish Grammar - SpeechAisy AstarinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Change The Time When We Are ExplainingDocument5 paginiHow To Change The Time When We Are ExplainingOscarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument1 paginăReported Speechhajar enneyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech ChangesDocument1 paginăReported Speech ChangesEddie BaldwinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.indirect SpeechDocument7 pagini3.indirect SpeechzakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Luka KovacevicDocument8 paginiLuka KovacevicTeodora AndrijanicÎncă nu există evaluări
- "I'm Going To The Cinema Tonight". Later, Maybe We Want To Tell Someone Else What The First Person SaidDocument2 pagini"I'm Going To The Cinema Tonight". Later, Maybe We Want To Tell Someone Else What The First Person SaidCami PiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech Tec IIIDocument20 paginiReported Speech Tec IIIguardadobearÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech (Sentences)Document9 paginiReported Speech (Sentences)Hussain SamsadeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2022 09 23 HW 0Document13 pagini2022 09 23 HW 0Мария СеменоваÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reporting Statements: Reported Speech 10th GradeDocument5 paginiReporting Statements: Reported Speech 10th GradeThunder XÎncă nu există evaluări
- Use Quotation Marks in Direct Speech. Someone Said But Not The Exact Words. We Do Not Use Quotation Marks in Reported SpeechDocument4 paginiUse Quotation Marks in Direct Speech. Someone Said But Not The Exact Words. We Do Not Use Quotation Marks in Reported SpeechIeva VaičikauskaitėÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported-Speech 14996Document2 paginiReported-Speech 14996Carina ChicaizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument6 paginiReported SpeechEmma Colomé CasacubertaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech RulesDocument4 paginiReported Speech Rulesdino mujkicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument3 paginiDirect and Indirect SpeechCarlos Alfonzo CalderónÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument20 paginiDirect and Indirect SpeechChristian SiagianÎncă nu există evaluări
- CÂU TRỰC TIẾPDocument19 paginiCÂU TRỰC TIẾPPhan Huy HoàngÎncă nu există evaluări
- TM Reported Speech Change ListDocument1 paginăTM Reported Speech Change ListTeacher MonicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument10 paginiReported SpeechMilica DujakovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- St's HOW TO EXPLAIN CompletelyDocument5 paginiSt's HOW TO EXPLAIN Completelycarlos israel torres kleimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech 2º BachilleratoDocument4 paginiReported Speech 2º BachilleratoBlancaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct and Indirect Speech Grade 9 NewDocument6 paginiDirect and Indirect Speech Grade 9 NewRumesh MadusankaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech For FCEDocument4 paginiReported Speech For FCEMarinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument2 paginiDirect and Indirect SpeechDanielleOkÎncă nu există evaluări
- To Be Statements + To Be Statements - Questions ?: Simple Past TimelineDocument32 paginiTo Be Statements + To Be Statements - Questions ?: Simple Past TimelineMathialagan VeluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech 2020Document18 paginiReported Speech 2020ekaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 13Document2 paginiUnit 13Adrian González BlancoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech 2020Document17 paginiReported Speech 2020ekaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech-1Document34 paginiReported Speech-1sanchisanchita9Încă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech 1Document3 paginiReported Speech 1Luigi OliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chuyên Đề 5. Câu Trực Tiếp - Gián Tiếp - DONEDocument53 paginiChuyên Đề 5. Câu Trực Tiếp - Gián Tiếp - DONEThy Dương YênÎncă nu există evaluări
- See It & Say It! : Volume 1 | First (1st) Grade Sight WordsDe la EverandSee It & Say It! : Volume 1 | First (1st) Grade Sight WordsÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Guide to English Grammar: Conjugation of Verbs Volume 1De la EverandA Guide to English Grammar: Conjugation of Verbs Volume 1Încă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect Tense What A Busy Day Esl Reading Comprehension WorksheetDocument2 paginiPresent Perfect Tense What A Busy Day Esl Reading Comprehension WorksheetMari Onofrio100% (3)
- An Unexpected Holiday Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form 28786Document2 paginiAn Unexpected Holiday Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form 28786tomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Videos The Woolly Jumper WorksheetDocument2 paginiGrammar Videos The Woolly Jumper WorksheetMari OnofrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete The Reading. Use Present Simple, Past Simple or Present PerfectDocument3 paginiComplete The Reading. Use Present Simple, Past Simple or Present PerfectMari OnofrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Simple Daily Routines Esl Printable Speaking Cards WorksheetDocument1 paginăPresent Simple Daily Routines Esl Printable Speaking Cards Worksheetoussama bouallati100% (1)
- The Tragedy of Dr. FaustusDocument9 paginiThe Tragedy of Dr. FaustusMari OnofrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Food Festival Worksheet 1: Lesson PlanDocument4 paginiA Food Festival Worksheet 1: Lesson PlanMari OnofrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading Comprehension 2 Fun Activities Games Oneonone Activities Reading C 30087Document1 paginăReading Comprehension 2 Fun Activities Games Oneonone Activities Reading C 30087Ludy Copete Renteria67% (6)
- Past Simple Speaking Cards Set 1Document1 paginăPast Simple Speaking Cards Set 1Mari OnofrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Helping The Poor Fun Activities Games Reading Comprehension Exercis 19853Document1 paginăHelping The Poor Fun Activities Games Reading Comprehension Exercis 19853Mari Onofrio100% (1)
- Present Simple Peters Daily Routine Esl Reading Comprehension WorksheetDocument6 paginiPresent Simple Peters Daily Routine Esl Reading Comprehension WorksheetCelia CunhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect Tense What A Busy Day Esl Reading Comprehension WorksheetDocument3 paginiPresent Perfect Tense What A Busy Day Esl Reading Comprehension WorksheetMari Onofrio100% (2)
- Sophies Daily Routine Reading Comprehension Exercises 21729Document1 paginăSophies Daily Routine Reading Comprehension Exercises 21729Mari OnofrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Where Were You When ?: The Day MJ DiedDocument2 paginiWhere Were You When ?: The Day MJ DiedMari OnofrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conversation Questions Past Simple RecentDocument1 paginăConversation Questions Past Simple RecentMari OnofrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Simple Daily Routines Esl Printable Speaking Cards WorksheetDocument1 paginăPresent Simple Daily Routines Esl Printable Speaking Cards Worksheetoussama bouallati100% (1)
- Name: Date:: A) Took B) Take C) TakesDocument2 paginiName: Date:: A) Took B) Take C) TakesMari OnofrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Classroom and Personal Use Only. Not For Commercial: Answer KeyDocument2 paginiFor Classroom and Personal Use Only. Not For Commercial: Answer KeyMari OnofrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Helping The Poor Fun Activities Games Reading Comprehension Exercis 19853Document1 paginăHelping The Poor Fun Activities Games Reading Comprehension Exercis 19853Mari Onofrio100% (1)
- Past Simple Speaking Cards - Set 2Document1 paginăPast Simple Speaking Cards - Set 2Ксения СкрыльÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short Stories British Tales Nessie The Loch Ness Monster WorksheetDocument2 paginiShort Stories British Tales Nessie The Loch Ness Monster WorksheetMaria StaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Can You Spell Your Name? What Is Your FavouriteDocument2 paginiCan You Spell Your Name? What Is Your FavouriteMari OnofrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparatives ReadingDocument1 paginăComparatives ReadingMauricio AguilónÎncă nu există evaluări
- John Krasinski: Movie Small Group Discussion QuestionsDocument1 paginăJohn Krasinski: Movie Small Group Discussion QuestionsMari OnofrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Be Past ExercisesDocument2 paginiBe Past ExercisesElaine OliveiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generic Structure and Purpose of AnnouncementDocument3 paginiGeneric Structure and Purpose of AnnouncementMuhammad Haekal Muhyidin Al-ArabyÎncă nu există evaluări
- English 6 - Learning Material AAA1Document7 paginiEnglish 6 - Learning Material AAA1MARIA CASTRO SAUCEDOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prepositional Phrase: by Windawati M.PDDocument10 paginiPrepositional Phrase: by Windawati M.PDalan subagioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 3 Possessive Nouns BDocument2 paginiGrade 3 Possessive Nouns BBrendaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guia Inglés Semana 1 - Tercero MedioDocument6 paginiGuia Inglés Semana 1 - Tercero MedioAndrea Villegas FigueroaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crimes - English Intermediate VocabularyDocument10 paginiCrimes - English Intermediate VocabularyJorge Andrés100% (1)
- Administration of Postgraduates Studies and Training University of Zawia Department of English - Applied LinguisticsDocument8 paginiAdministration of Postgraduates Studies and Training University of Zawia Department of English - Applied LinguisticsIceMaster MinatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar and Correct UsageDocument8 paginiGrammar and Correct UsageRica de GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investigate The Problems of Using Punctuation Among Secondary School StudentsDocument68 paginiInvestigate The Problems of Using Punctuation Among Secondary School StudentsBhaskar AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bahan Ajar Report Text (Materi)Document8 paginiBahan Ajar Report Text (Materi)Ganthus Herprama SatyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs ChartDocument3 paginiIrregular Verbs ChartEvelyn JoséÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept of VerbDocument28 paginiConcept of VerbSayeed Akbar NobelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Textbookofbaloch00damerich PDFDocument234 paginiTextbookofbaloch00damerich PDFثاقبہ مزاریÎncă nu există evaluări
- CST Test Preparation and Review: Tere Lopez PER. 6Document13 paginiCST Test Preparation and Review: Tere Lopez PER. 6tere12345Încă nu există evaluări
- Vocabulary Hand Out: 1. Words Classes, Families, and FormationDocument24 paginiVocabulary Hand Out: 1. Words Classes, Families, and FormationFira Yunika100% (1)
- Pre-Starter GrammarDocument4 paginiPre-Starter Grammarjanmohammadrahimi439Încă nu există evaluări
- III. Subject-Verb AgreementDocument4 paginiIII. Subject-Verb AgreementAni Pearl PanganibanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Content Guide 2nd. BGU U1Document8 paginiContent Guide 2nd. BGU U1NARCISA ESTEFANIA NIEVES HENIQUEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Language Test 10: (20 Points)Document2 paginiLanguage Test 10: (20 Points)amalÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Appendix Simple Present PDFDocument2 paginiEnglish Appendix Simple Present PDFSatrio WibowoÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Verbs, Nouns, Adjectives and AdverbsDocument19 paginiList of Verbs, Nouns, Adjectives and AdverbsAmar PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non Finite ClausesDocument29 paginiNon Finite Clausesmourad0% (1)
- Task 3 HERBIE Short Written Response 2022 2Document3 paginiTask 3 HERBIE Short Written Response 2022 2aliullah jamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mock Exam 2º Eso - 3rd TermDocument1 paginăMock Exam 2º Eso - 3rd TermMaríaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of WritingDocument30 paginiMechanics of Writingakash lachhwani94% (16)
- C S ' U E: Left Entences Ndoubted XistenceDocument4 paginiC S ' U E: Left Entences Ndoubted XistenceNani DndÎncă nu există evaluări
- Talk Speak Say TellDocument4 paginiTalk Speak Say TellstatsenkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coordinating Conjunction LPDocument6 paginiCoordinating Conjunction LPjha RoxasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lexical and Functional Categories Auxiliaries Theta RolesDocument3 paginiLexical and Functional Categories Auxiliaries Theta RolesLaura DorobanțuÎncă nu există evaluări