Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Answer All Questions.: Section A (15 Marks)
Încărcat de
chee pin wongDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Answer All Questions.: Section A (15 Marks)
Încărcat de
chee pin wongDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CONFIDENTIAL*
2
Section A (15 marks)
Answer all questions.
1 The thermochemical equation for the formation of ethane-1,2-diol is shown below,
2C(s) + 3H2 (g) + O2 (g) → CH2 OHCH2 OH(l) ∆𝐻f° = 𝑥 kJ mol−1
Based on the enthalpies changes given in the Table 1 below, determine 𝑥.
Substance ∆𝐻c° / kJ mol−1
Ethane-1,2-diol −1180.0
Carbon −393.7
Hydrogen −285.9
Table 1
A +500.5 B −500.5 C +465.1 D −465.1
2 A student mixed 25.0 cm3 of 4.00 mol dm−3 hydrochloric acid with an equal volume of 4.00 mol dm−3
sodium hydroxide solution. The initial temperature of both solutions was 15.0 ℃ . The maximum
temperature recorded was 30.0 ℃.
Based on these results, what is the enthalpy change of neutralisation between hydrochloric acid and sodium
hydroxide solution?
A −62.7 kJ mol−1 B −57.3 kJ mol−1 C −31.4 kJ mol−1 D −15.7 kJ mol−1
3 Which of the following is correct about electrolytic cell and electrochemical cell?
Electrolytic cell Electrochemical cell
Anode Cathode The flow of electrons Anode Cathode The flow of electrons
A Positive Negative From negative electrode Negative Positive From positive electrode
to positive electrode to negative electrode
through external circuit through external circuit
B Positive Negative From positive electrode Negative Positive From negative electrode
to negative electrode to positive electrode
through external circuit through external circuit
C Negative Positive From negative electrode Positive Negative From positive electrode
to positive electrode to negative electrode
through external circuit through external circuit
D Negative Positive From positive electrode Positive Negative From negative electrode
to negative electrode to positive electrode
through external circuit through external circuit
4 The redox equation for the reaction in an electrochemical cell is shown below,
5Fe2+ (aq) + MnO− + 3+ 2+
4 (aq) + 8H (aq) → 5Fe (aq) + Mn (aq) + 4H2 O(l)
[Fe2+ ]
If the standard cell voltage is +0.75 V, the ratio of [Fe3+ ] = 0.10 and the concentrations of other ions are
maintained, what is the electromotive force at 25℃?
A +0.46 V B +0.69 V C +0.76 V D +0.81 V
STPM 2020 – 962/2
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over. CONFIDENTIAL*
CONFIDENTIAL*
3
5 X is a Period 3 element that could react with oxygen to form an oxide, Y which is insoluble in water.
Which of the following statement is correct based on the given information?
A X is aluminium.
B Atomic size of X is larger than sodium.
C Y can only react with acid but not alkali.
D Y can react with sodium hydroxide solution.
6 Which of the following element has the highest melting point?
A Phosphorus B Silicon C Sulphur D Sodium
7 P and Q are Group 2 elements. P shows a very slight reaction with water but it could react vigorously with
steam. Q cannot react with water but only can react with steam at very high temperature to form an oxide
which is insoluble in water. Which of the following are likely to be P and Q?
P Q
A Calcium Magnesium
B Beryllium Magnesium
C Magnesium Beryllium
D Magnesium Calcium
8 When 4.18 g of calcium nitrate is heated at room conditions, a brown gas P and a colourless Q are released.
What is the maximum total volume of gaseous products formed in the reaction?
[Molar volume =24 000 cm3 mol−1 at room conditions]
A 612 cm3 B 1224 cm3 C 1530 cm3 D 2448 cm3
9 X, Y and Z are elements of Group 14. What can be deduced about X, Y and Z based on the information
below?
• X is a metal whereas Y and Z are semimetals.
• The electrical conductivity of Y is higher than that of Z.
• The melting point of Y is lower than that of Z.
A The covalent bond of Y is weaker than that of Z.
B X, Y and Z have the same lattice structure.
C Y has a larger band gap compared to Z.
D The valence band of X has more electrons than that of Y and Z.
10 Which is a common property for germanium and lead compounds?
A Stability of +2 oxidation state of both compounds is due to the inert pair effect.
B Tetrachlorides of both compounds are thermally stable.
C Dioxides of both compounds are amphoteric.
D Monoxides of both compounds are basic.
11 Aqueous K𝑋 reacts with aqueous AgNO3 to form a precipitate which does not dissolve in excess ammonia.
K𝑋 is
A KF B KCl C KBr D KI
STPM 2020 – 962/2
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over. CONFIDENTIAL*
CONFIDENTIAL*
4
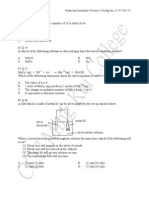
12 Variation of the enthalpy of vaporisation of three elements of Group 17 in the Periodic Table is shown in
the graph below.
The variation is due to an increase in
A covalent bond length B enthalpy of atomisation
C polarisability D intermolecular forces
13 Which of the following is true about transition elements?
A Transition elements are p-block elements.
B All d-block elements are transition elements.
C Transition elements are metals with high density and high conductivity but low melting point.
D Most of the transition elements have the valence electronic configuration of (𝑛 − 1)𝑑1 𝑛𝑠 2 to
(𝑛 − 1)𝑑10 𝑛𝑠 2 .
14 Tris(ethanedioato)nickelate(II) ion is a complex ion with chemical formula of [Ni(C2 O4 )3 ]4− .
Which of the following is correct about the complex ion?
A Its ligand is a bidentate ligand.
B The charge of the ligand is −4.
C It has a tetrahedral shape.
D There are three dative bonds between the centre metal ion and the ligand.
15 The structural formulae of platinum complexes are shown below.
I [Pt(SCN)2 (en)2 ]2+
II [PtCl(NO2 )(NH3 )2 ]
III [Pt(ox)Cl2 ]2−
IV [Pt(EDTA)]4−
Which platinum complexes are octahedral?
A I and II B I and IV C II and III D III and IV
STPM 2020 – 962/2
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over. CONFIDENTIAL*
CONFIDENTIAL*
5
Section B (15 marks)
Answer all questions.
16 Table 2 below shows information about some of the elements in the Period 3
Element Na Mg Al P S Cl
Atomic radius (nm) 0.186 0.160 0.143 0.110 0.104 0.099
Ionic radius (nm) 0.095 0.065 0.050 0.212 0.184 0.181
Highest oxidation number of
+1 +7
the element in its compound
Table 2
(a) Complete Table 2 to show the highest oxidation number of each element in its compounds. [1]
(b) Explain why the atomic radius of elements in Period 3 decreases from Na to Cl. [3]
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
(c) Compare the ionic radius of magnesium ion and sulphide ion. [2]
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
(d) Phosphorus could react readily in the presence of oxygen under different conditions to form different
products. Write equations to show the reaction between phosphorus and oxygen under the conditions
suggested below. [2]
Limited oxygen : …………………………………………………………………………………….
Excess oxygen : …………………………………………………………………………………….
STPM 2020 – 962/2
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over. CONFIDENTIAL*
CONFIDENTIAL*
6
17 Hydrogen halides are compounds formed when halogens (Group 17 elements) react with hydrogen.
The bond polarity of the hydrogen halides decreases from HF to HI.
Table 3 shows the boiling points of hydrogen halides and the bond enthalpies of H − X bonds.
Hydrogen halide HF HCl HBr HI
Boiling point (℃) 19 –85 –67 –35
H − X bond enthalpy (kJ mol−1 ) 562 431 366 299
Table 3
(a) Write the chemical equation for the reaction between chlorine gas and hydrogen gas. [1]
.................................................................................................................................................................
(b) Suggest why the boiling point of HF is much higher than the boiling points of the other hydrogen
halides. [2]
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
(c) Compare and explain the relative thermal stabilities of the hydrogen halides. [3]
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................................................
(d) Write an equation which is used to study the bond enthalpy of hydrogen halides, HX. [1]
.................................................................................................................................................................
STPM 2020 – 962/2
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over. CONFIDENTIAL*
CONFIDENTIAL*
7
Section C (30 marks)
Answer two questions only.
You may answer all the questions but only the first two answers will be marked.
18 (a) The electrode systems for several half-cells are given in Table 4 below,
Electrode system 𝐄° /𝐕
Fe2+ + 2e− ⇌ Fe −0.44
Fe3+ + 3e− ⇌ Fe −0.04
Fe3+ + e− ⇌ Fe2+ +0.77
Table 4
A student wants to determine the standard electrode potential of Fe3+ (aq)|Fe2+ (aq) half-cell.
Based on the electrode systems given in Table 4 and a suitable labelled diagram, explain how he could
do that. Show the calculation to obtain the standard electrode potential of the electrode system. [8]
(b) Sakthis wants to manufacture chlorine using a diaphragm cell in industry.
State the electrolyte he needs to use and describe the reactions that occur in the diaphragm cell.
Support your explanation with suitable equations. [7]
19 (a) (i) What is meant by transition element? [1]
(ii) Ti(III) compounds are coloured but Ti(IV) compounds are colourless. Based on the electron
configurations, explain why both compounds have different colours. [5]
(b) (i) Define the terms complex ion and ligand. [2]
(ii) The structure of an aqueous complex ion which is pale blue in colour is shown below.
Give the IUPAC name of this complex ion, and state its shape. Describe the type of ligand(s)
present(s) in this complex ion. [6]
(iii) Draw the structure of complex ion with formula of [Cu(H2 O)6 ]2+ . [1]
STPM 2020 – 962/2
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over. CONFIDENTIAL*
CONFIDENTIAL*
8
20 (a) Describe the chemical reaction of Group 2 elements with water. [5]
(b) Explain the solubility of sulphates of Group 2 elements. [3]
(c) Explain the acid-base property and the thermal stability of the oxides of silicon. [7]
STPM 2020 – 962/2
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over. CONFIDENTIAL*
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionDe la EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- 962/1 Trial STPM 2010: Confidential / SulitDocument15 pagini962/1 Trial STPM 2010: Confidential / SulitDiong JayhueyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersDe la EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersÎncă nu există evaluări
- STPM 2017 Sem 2Document7 paginiSTPM 2017 Sem 2Aprillia ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2020 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Ngee Ann SecondaryDocument35 pagini2020 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Ngee Ann SecondaryDORA SIN YU KWOKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer ALL The Questions in This Section in Space ProvidedDocument6 paginiAnswer ALL The Questions in This Section in Space ProvidedfaizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Redox Practice Test 2Document22 paginiRedox Practice Test 2Sam KothuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer All Question in This SectionDocument8 paginiAnswer All Question in This SectionMuhd FaiZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: Class: I/C NoDocument19 paginiName: Class: I/C NopermatasemarakÎncă nu există evaluări
- SULIT 4541/1 Chemistry Paper 1 Mei 2007Document22 paginiSULIT 4541/1 Chemistry Paper 1 Mei 2007AMINÎncă nu există evaluări
- TPJC H2chem Prelim p1 2009Document14 paginiTPJC H2chem Prelim p1 2009Amos YapÎncă nu există evaluări
- J1 Promos 2015 Paper 1Document11 paginiJ1 Promos 2015 Paper 1aliciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 3Document22 pagini12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 3Deepak PradhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 12 Practice QuestionsDocument10 paginiGrade 12 Practice Questionsnahil ahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Done Edu - Joshuatly.com) N9 STPM Trial 2010 Chemistry (W Ans) (8DB31AAC)Document0 pagini(Done Edu - Joshuatly.com) N9 STPM Trial 2010 Chemistry (W Ans) (8DB31AAC)BlaireÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem Sem 1 Percubaan SMK Pusat Bandar PuchongDocument12 paginiChem Sem 1 Percubaan SMK Pusat Bandar Puchongevacuate clashÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChemistryDocument11 paginiChemistrypandatrilochana784Încă nu există evaluări
- APEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFDocument2 paginiAPEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFMuhammad UsmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- APEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFDocument2 paginiAPEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFFirdausia Rahma PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- APEF - Electrochemistry - Multiple Choice Questions - Page 1 of 2Document2 paginiAPEF - Electrochemistry - Multiple Choice Questions - Page 1 of 2alyaa sheirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yr10 Chemistry Paper 2 YE22Document14 paginiYr10 Chemistry Paper 2 YE22Ern QiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endothermic.: A The Forward Reaction IsDocument9 paginiEndothermic.: A The Forward Reaction IsSatyrKuangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uppp2 Sem 2 2017Document5 paginiUppp2 Sem 2 2017Loh Wai YeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry - Test ElectrochemistryDocument12 paginiChemistry - Test Electrochemistrypolamraju100% (1)
- Exam Chew 1Document7 paginiExam Chew 1ThilagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Redox II (Multiple Choice) QPDocument25 paginiRedox II (Multiple Choice) QPAysu AÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMK Dato Jaafar, JohorDocument8 paginiSMK Dato Jaafar, JohorJun Hao ChongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer All Questions in This Section: Electrode System EDocument9 paginiAnswer All Questions in This Section: Electrode System EChang DiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test4 Ch19 Electrochemistry Practice ProblemsDocument13 paginiTest4 Ch19 Electrochemistry Practice ProblemsPhysiochemo Chemical100% (1)
- General Chemistry II Jasperse Electrochemistry. Extra Practice ProblemsDocument4 paginiGeneral Chemistry II Jasperse Electrochemistry. Extra Practice ProblemsYash BhattÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrochemistry Q & ADocument8 paginiElectrochemistry Q & AYash JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- H1, MCQ, Oct 2022Document8 paginiH1, MCQ, Oct 2022school of schoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- STPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Paper 1 (Pahang)Document12 paginiSTPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Paper 1 (Pahang)Looi Chui YeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jar 1 Jar 1 Lid Air: A B C DDocument7 paginiJar 1 Jar 1 Lid Air: A B C DaaryavaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision-2 - On ElectrochemistryDocument12 paginiRevision-2 - On ElectrochemistryKiro RemonÎncă nu există evaluări
- STPM 2019 Sem 2uDocument7 paginiSTPM 2019 Sem 2uAprillia ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang STPM Trial Exam Term 2 2019 (Chemistry)Document7 paginiSMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang STPM Trial Exam Term 2 2019 (Chemistry)AlyciaLeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPP Electrochemistry L-1 (Harsh Sir) (03-05-2021)Document77 paginiDPP Electrochemistry L-1 (Harsh Sir) (03-05-2021)Tejasvi MahuleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Redox QuizDocument5 paginiRedox QuizSherey FathimathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Victoria Junior College JC 2 Preliminary Examinations Higher 2Document20 paginiVictoria Junior College JC 2 Preliminary Examinations Higher 2saffronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Singles 11Document4 paginiSingles 11Nagendra BharadwazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre IG 0.14 (Night), Chemistry, Monthly TestDocument8 paginiPre IG 0.14 (Night), Chemistry, Monthly TestHtet Wai Yan AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXCEL G-12 Chemistry MODEL-1Document4 paginiEXCEL G-12 Chemistry MODEL-1henotech HDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Structure HL Multiple Choice Questions AnswersDocument3 paginiAtomic Structure HL Multiple Choice Questions AnswersMalak AlqaidoomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combined Prelim MCQDocument372 paginiCombined Prelim MCQVincent VetterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Trial STPM P1 2010Document18 paginiChemistry Trial STPM P1 2010sherry_christyÎncă nu există evaluări
- STPM Trial 2009 Che Q&A KelantanDocument37 paginiSTPM Trial 2009 Che Q&A KelantanSimPorÎncă nu există evaluări
- RedoxDocument6 paginiRedoxparth ladaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- There Are 50 Questions in This Paper. Choose The Best Answer For Each QuestionDocument21 paginiThere Are 50 Questions in This Paper. Choose The Best Answer For Each Questionapi-19650882Încă nu există evaluări
- STPM Trial 2012 Chemistry Qa KelantanDocument42 paginiSTPM Trial 2012 Chemistry Qa Kelantanteoh6234100% (2)
- 10chemistry General Trial Test AnsDocument6 pagini10chemistry General Trial Test AnsMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - Redox and Electrolysis (Pp2)Document36 pagini3 - Redox and Electrolysis (Pp2)api-3700944100% (1)
- Klks 9 Test-LatihanDocument6 paginiKlks 9 Test-LatihankrisnuÎncă nu există evaluări
- NSS Chemistry Part 7 Redox Reactions Chemical Cells and Electrolysis - MCDocument37 paginiNSS Chemistry Part 7 Redox Reactions Chemical Cells and Electrolysis - MCFelix YueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year End Paper 1 ChemDocument9 paginiYear End Paper 1 ChemNOR ATIKAH BINTI TAKRUDDIN MoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2009 RI Prelims Chem H2 P1 QPDocument16 pagini2009 RI Prelims Chem H2 P1 QPniveumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- STPM 2013 Sem 2Document5 paginiSTPM 2013 Sem 2m-4306022Încă nu există evaluări
- ElectrochemistryDocument21 paginiElectrochemistrypremathangam807Încă nu există evaluări
- Sem 2 Uppp 1 2017Document7 paginiSem 2 Uppp 1 2017Wong Lee FongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bachelor of Computer Science (Multimedia) With HonoursDocument3 paginiBachelor of Computer Science (Multimedia) With Honourschee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Synopsis Department of Management and MarketingDocument7 paginiCourse Synopsis Department of Management and Marketingchee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Centre For Graduate Studies Universiti Tun Hussein Onn MalaysiaDocument1 paginăCentre For Graduate Studies Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysiachee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Should I Major in Environmental Science or Computer Science - QuoraDocument2 paginiShould I Major in Environmental Science or Computer Science - Quorachee pin wong100% (1)
- UPM FKEUR1 - Bacheloro - of - EconomicsDocument10 paginiUPM FKEUR1 - Bacheloro - of - Economicschee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Undergraduate Studies Regulations UMS Amendment 2019 PG 13-15-17Document42 paginiUndergraduate Studies Regulations UMS Amendment 2019 PG 13-15-17chee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faculty of Engineering: The Ability To Think, Analyze and Evaluate'Document23 paginiFaculty of Engineering: The Ability To Think, Analyze and Evaluate'chee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sabah U International MarketingDocument1 paginăSabah U International Marketingchee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faculty of Humanities, Arts and Heritage: ServingDocument72 paginiFaculty of Humanities, Arts and Heritage: Servingchee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Takwim Bpa 2019 Updated (7.2.2019)Document2 paginiTakwim Bpa 2019 Updated (7.2.2019)chee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Years Programme Course Structure (6 Semesters) : He19 International FinanceDocument12 pagini3 Years Programme Course Structure (6 Semesters) : He19 International Financechee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Academic Calendar SEM 2Document2 paginiAcademic Calendar SEM 2chee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- He09 - International BusinessDocument3 paginiHe09 - International Businesschee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Academic Calendar Semester 1 2019 - 2020 SessionDocument2 paginiAcademic Calendar Semester 1 2019 - 2020 Sessionchee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- He10 Marketing: (Except UC01002 Corporate Communication)Document1 paginăHe10 Marketing: (Except UC01002 Corporate Communication)chee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sabah U EntrepreneurshipDocument1 paginăSabah U Entrepreneurshipchee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Academic Calendar SEM 2Document2 paginiAcademic Calendar SEM 2chee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPA - Advanced Certificate - SyllabusDocument3 paginiIPA - Advanced Certificate - Syllabuschee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- UM BBA StructureDocument8 paginiUM BBA Structurechee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immig and Asylum Examination Guidelines - v8 February 17Document32 paginiImmig and Asylum Examination Guidelines - v8 February 17chee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diploma in Building Services EngineeringDocument3 paginiDiploma in Building Services Engineeringchee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPB5043-Business FinanceDocument18 paginiDPB5043-Business Financechee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPM Handbook - Latest For October 2018Document35 paginiCPM Handbook - Latest For October 2018chee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPA Foundation Certificate Qualification Policies 2019/2020 UK IntakeDocument7 paginiIPA Foundation Certificate Qualification Policies 2019/2020 UK Intakechee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook-2016 - 2017 PG 41 - 49Document110 paginiHandbook-2016 - 2017 PG 41 - 49chee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- BookDocument362 paginiBookchee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diploma in Building Services Engineering PDFDocument3 paginiDiploma in Building Services Engineering PDFchee pin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 56-MT-2 ChemistryDocument15 pagini56-MT-2 ChemistryalexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mendeleev For Chemistry 3rd SecondaryDocument41 paginiMendeleev For Chemistry 3rd SecondarySP DevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Upper Sixth 2016 First SequenceDocument7 paginiChemistry Upper Sixth 2016 First SequenceNgah Lilwaine MÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChemistryDocument23 paginiChemistryM KamranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council (Zimsec) : Advanced Level SyllabusDocument72 paginiZimbabwe School Examinations Council (Zimsec) : Advanced Level Syllabusnyasha chanetsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHM 101 - General Chemistry-1-Lecture Note - 2023Document36 paginiCHM 101 - General Chemistry-1-Lecture Note - 2023bangysmashiÎncă nu există evaluări
- D-Block NotesDocument19 paginiD-Block NotesRenu KumariÎncă nu există evaluări
- D and F Block-1Document52 paginiD and F Block-1Sachin YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normal 64253934112bdDocument2 paginiNormal 64253934112bdsomethingis2857100% (1)
- D Block Elements WorksheetDocument2 paginiD Block Elements WorksheetsushiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practica 8 INOR II PDFDocument2 paginiPractica 8 INOR II PDFmmmmmmmmmmmmmmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flashcards - Topic 9 The Periodic Table - CAIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument101 paginiFlashcards - Topic 9 The Periodic Table - CAIE Chemistry IGCSEkush pÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHM 303Document2 paginiCHM 303Vincent AmobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018SU B.SC Chemistry SyllabusDocument22 pagini2018SU B.SC Chemistry Syllabussachin81185Încă nu există evaluări
- 3.1 Classification If ElementsDocument19 pagini3.1 Classification If ElementsSharon RamaiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transition Elements AND COORDINATION CHEMISTRY PDFDocument50 paginiTransition Elements AND COORDINATION CHEMISTRY PDFAniruddha KawadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inorganic Chemistry 2-1Document48 paginiInorganic Chemistry 2-1Oliver JumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Chemistry 2017 Notes Stud.Document44 paginiGeneral Chemistry 2017 Notes Stud.victorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Helpful For CAPE U1 Chemistry Transition Elements PDFDocument30 paginiHelpful For CAPE U1 Chemistry Transition Elements PDFXia U Rong100% (1)
- HKDSE CHEMISTRY - Book 4B AnsDocument47 paginiHKDSE CHEMISTRY - Book 4B AnsSteven Chu100% (2)
- Pioneer Junior College H2 Chemistry (9647) An Introduction To The Chemistry of Transition ElementsDocument31 paginiPioneer Junior College H2 Chemistry (9647) An Introduction To The Chemistry of Transition ElementsTimothy HandokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- D-F-Block IIT JEEDocument26 paginiD-F-Block IIT JEEThe Rock89% (9)
- Transition Elements Final 1Document44 paginiTransition Elements Final 1Venkatesh MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Metals CoreDocument6 paginiTest Metals CoreRuqia ZahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Em+2 Qrtly Exam Chem Imp Questions-2023Document6 paginiEm+2 Qrtly Exam Chem Imp Questions-2023Azees AzeesÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Chemical Map of Nasicon Electrode Materials For Sodium-Ion BatteriesDocument37 paginiA Chemical Map of Nasicon Electrode Materials For Sodium-Ion BatteriesNikitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FL53215 Chemical Analysis Brass Lesson Plan Uv VisDocument6 paginiFL53215 Chemical Analysis Brass Lesson Plan Uv VisNaeem RehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 11 KEMPRN1Document94 paginiLecture 11 KEMPRN1Ina RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hard and Soft Acids and BasesDocument17 paginiHard and Soft Acids and BasesSalmi Seprianti100% (2)
- 3 Chapter Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties - Class 11Document32 pagini3 Chapter Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties - Class 11Vaibhav KargetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityDe la EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDe la EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (14)
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideDe la EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDe la EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (137)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeDe la EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDe la EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDe la EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (3)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingDe la EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (10)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeDe la EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsDe la EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (10)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDe la EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeDe la EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDe la EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideDe la EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsDe la EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- The Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesDe la EverandThe Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsDe la EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsDe la EverandPiping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisDe la EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyDe la EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (21)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDe la EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (90)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodDe la EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (20)