Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Endocrine System Chart
Încărcat de
Valeria Guadalupe Ramírez Moctezuma100%(2)100% au considerat acest document util (2 voturi)
1K vizualizări2 paginiThe document provides a chart of major hormones in the endocrine system, listing the organ that produces each hormone, its function, and an illustrative picture. Key hormones included are thyroxin from the thyroid gland which plays roles in digestion and development, leptin from adipose tissue which regulates food intake and energy, and insulin from the pancreas which maintains blood glucose levels. The chart also covers hormones like glucagon, testosterone, estrogen, and melatonin which regulate processes like sleep cycles, reproduction, and preventing low blood sugar.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
endocrine system chart
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThe document provides a chart of major hormones in the endocrine system, listing the organ that produces each hormone, its function, and an illustrative picture. Key hormones included are thyroxin from the thyroid gland which plays roles in digestion and development, leptin from adipose tissue which regulates food intake and energy, and insulin from the pancreas which maintains blood glucose levels. The chart also covers hormones like glucagon, testosterone, estrogen, and melatonin which regulate processes like sleep cycles, reproduction, and preventing low blood sugar.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
100%(2)100% au considerat acest document util (2 voturi)
1K vizualizări2 paginiEndocrine System Chart
Încărcat de
Valeria Guadalupe Ramírez MoctezumaThe document provides a chart of major hormones in the endocrine system, listing the organ that produces each hormone, its function, and an illustrative picture. Key hormones included are thyroxin from the thyroid gland which plays roles in digestion and development, leptin from adipose tissue which regulates food intake and energy, and insulin from the pancreas which maintains blood glucose levels. The chart also covers hormones like glucagon, testosterone, estrogen, and melatonin which regulate processes like sleep cycles, reproduction, and preventing low blood sugar.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
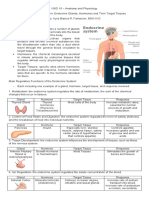
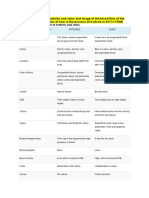
Chart of the endocrine system (done in ACT-2 FDM)
1. Complete the chart of the Endocrine system:
HORMONE ORGAN FUNCTION PICTURE
THAT
PRODUCES
IT
THYROXIN Thyroid It plays vital roles in
gland digestion, heart and
muscle function, brain
development and
maintenance of bones.
LEPTIN in the Leptin signals to the
adipocytes brain, in particular to
of white an area called the
adipose hypothalamus, it acts
to alter food intake
tissue.
and control energy
expenditure over the
long term.
MELATONIN pineal helps regulate
gland biological rhythms
such as sleep and
wake cycles.
INSULIN Pancreas To counter the
concerted actions of a
number of
hyperglycemia-generat
ing hormones and to
maintain low blood
glucose levels.
Stimulates lipogenesis,
diminishes lipolysis,
and increases amino
acid transport into
cells.
GLUCAGON Produced Prevent blood glucose
by the levels dropping too
alpha cells, low. Instructs the liver
found in to release stored
the islets of glucose, which causes
Langerhan blood sugar to rise.
s, in the
páncreas.
TESTOSTERONE Is Responsible for many
produced of the physical
by the characteristics specific
gonads to adult males. Plays a
key role in
reproduction and the
maintenance of bone
and muscle strength.
ESTROGEN Produced Usually travel through
primarily the bloodstream in
by the fluids, interact with
ovaries. cells in a variety of
tissues in the body,
and deliver a message
or instruction. It is one
of the most important
hormones for women.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Learn About the Endocrine System and Its DiseasesDocument14 paginiLearn About the Endocrine System and Its DiseasesNovie Jane HontiverosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine SystemDocument21 paginiEndocrine SystemMark DimarucutÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Can We Use Neurotransmitters in Emotion and Reward System To Study DepressionDocument22 paginiHow Can We Use Neurotransmitters in Emotion and Reward System To Study DepressionGlobal Research and Development ServicesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal IdentificationDocument13 paginiPersonal IdentificationJose Li ToÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2020-Biochem-Activity-16 - BIOCHEMISTRY OF HORMONESDocument32 pagini2020-Biochem-Activity-16 - BIOCHEMISTRY OF HORMONESGabrielle John HernaezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemDocument3 paginiNotes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemAlven ReyÎncă nu există evaluări
- DM Type 1Document4 paginiDM Type 1Adiel CalsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential Ayurveda BookDocument196 paginiEssential Ayurveda BookRoberto89% (9)
- Upper Limb MCQsDocument50 paginiUpper Limb MCQsstephen victory100% (1)
- The Endocrine SystemDocument18 paginiThe Endocrine SystemPhea VillarealÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radiation Biology: Presented By: Aarya.H.NairDocument83 paginiRadiation Biology: Presented By: Aarya.H.NairAARYAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine SystemDocument32 paginiEndocrine Systemlee bon hukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument23 paginiNucleic Acid MetabolismMSc Biotech/MicroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd Quarter Science Module 1Document13 pagini3rd Quarter Science Module 1Vincq100% (2)
- Chiildlabour With DataDocument31 paginiChiildlabour With DataprateekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paragraph Development ExerciseDocument6 paginiParagraph Development ExerciseSYAFINAS SALAM100% (1)
- Worksheet - Dna Protein SynthesisDocument2 paginiWorksheet - Dna Protein Synthesisapi-270403367100% (1)
- The Endocrine SystemDocument2 paginiThe Endocrine SystemKyra Bianca R. FamacionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine System Functions & GlandsDocument11 paginiEndocrine System Functions & Glandssaeed qurashiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 SexualQigongDocument6 pagini12 SexualQigongAnonymous r84IzwCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument13 paginiChronic Kidney DiseaseJobelle AcenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1Document10 paginiScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1RUTH PIANGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neet PG Mock 4Document65 paginiNeet PG Mock 4Diwakesh C B100% (1)
- Answer Key For Comprehensive Exam XVDocument18 paginiAnswer Key For Comprehensive Exam XVQharts SajiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- CV AkhyarDocument31 paginiCV AkhyarNaveed UR RehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toc PDFDocument12 paginiToc PDFSOURAV DAS100% (1)
- Biology 3 Tuto 1Document43 paginiBiology 3 Tuto 1Firdaus ZulkifliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hormone GroupDocument35 paginiHormone GroupNeph VargasÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Endocrine System: Hormones and Glands that Regulate the BodyDocument6 paginiThe Endocrine System: Hormones and Glands that Regulate the BodyLuiciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HarmonesDocument6 paginiHarmonesbaskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesDocument10 paginiEndocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesHabi JabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Endocrine System: Lesson 8.3Document21 paginiThe Endocrine System: Lesson 8.3K-yanVehraaYomomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hormone Table with Glands and ActionsDocument2 paginiHormone Table with Glands and ActionsFrancess Thea PascuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hormone Abbreviation Function Target Cell Related Diseases: Gland Which Secretes The HormoneDocument4 paginiHormone Abbreviation Function Target Cell Related Diseases: Gland Which Secretes The HormoneMarianne Jubille CataquisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine System ActivityDocument4 paginiEndocrine System ActivityPablo GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 +endocrine+systemDocument41 pagini3 +endocrine+systemDew JirawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine SystemDocument10 paginiEndocrine SystemMiguel FalfanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2ND Gen Bio Prelim NotesDocument8 pagini2ND Gen Bio Prelim NotesRalph RadazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap9 Endocrine Anaphy NotesDocument11 paginiChap9 Endocrine Anaphy NotesAxel Neil VidalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine System RevDocument3 paginiEndocrine System RevWena Grace NonanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 - Endocrine System (Summary of Hormones)Document3 paginiChapter 9 - Endocrine System (Summary of Hormones)Rishelle Mae Miñoza PilonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Article and Table - Peptide HormonesDocument3 paginiArticle and Table - Peptide HormonesZEBINA PIE GENORINGÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Endocrine PancreasDocument11 paginiThe Endocrine Pancreaspradeep pÎncă nu există evaluări
- EndocrineDocument1 paginăEndocrineDiwata DonatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- HormonesDocument3 paginiHormonesAdhara SalfarlieÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnaphyDocument3 paginiAnaphyArah PadillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Endocrine System NotesDocument11 paginiThe Endocrine System NotesArce JohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genbio2 ReviewerDocument4 paginiGenbio2 ReviewerLovely QuezonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7.1 Human Endocrine System - MEMO - ONE PAGER 2020Document1 pagină7.1 Human Endocrine System - MEMO - ONE PAGER 2020Rudzi UdziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Task 3Document15 paginiTask 3maryamshahzad489Încă nu există evaluări
- Control and Coordination in Plants and Hormones in AnimalsDocument4 paginiControl and Coordination in Plants and Hormones in AnimalsAceHunterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine System NotesDocument14 paginiEndocrine System NotesSteven100% (1)
- Biochemistry of Hormones and AgingDocument10 paginiBiochemistry of Hormones and AgingTushar ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochemistry of Hormones and AgingDocument10 paginiBiochemistry of Hormones and AgingTushar ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- q3 Module Edited w1-7Document21 paginiq3 Module Edited w1-7Regine DigamonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 UNIT IIDocument10 paginiChapter 2 UNIT IIAyen LatosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 paginiEndocrine SystemjakevcabauatanÎncă nu există evaluări
- HormonesDocument55 paginiHormonesAvinashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment MetabolismDocument10 paginiAssignment MetabolismCherrylyn RaytosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sci-10 Q3 Pt-1-Hormonal Chart - IliganDocument4 paginiSci-10 Q3 Pt-1-Hormonal Chart - IliganILIGAN John Paul MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscular-Endocrine 1Document7 paginiMuscular-Endocrine 1JD BunielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Inquiry (Chapter 1)Document50 paginiScience Inquiry (Chapter 1)Nancy HastingÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Endocrine System: A Network of Hormone-Secreting GlandsDocument6 paginiThe Endocrine System: A Network of Hormone-Secreting GlandsLuiciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 paginiEndocrine SystemDearly Niña OsinsaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine System Feedback SystemsDocument25 paginiEndocrine System Feedback SystemsEthan Miles VigilanciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument6 paginiChemical Coordination and IntegrationRonaldÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSRN-id3309237Document10 paginiSSRN-id3309237Bima Anugrah WijayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Worksheets on Homeostasis, Excretory System, and Endocrine SystemDocument5 paginiBiology Worksheets on Homeostasis, Excretory System, and Endocrine SystemMaria Bettina DizonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine System Guide: Hormones and Their FunctionsDocument3 paginiEndocrine System Guide: Hormones and Their FunctionsKush KesharwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYDocument5 paginiChapter 10 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYAngela Mae MeriñoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Chart Virus and Bacteria PDFDocument1 paginăComparative Chart Virus and Bacteria PDFValeria Guadalupe Ramírez MoctezumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology PortfolioDocument28 paginiBiology PortfolioValeria Guadalupe Ramírez MoctezumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homologous Structure Chart PDFDocument1 paginăHomologous Structure Chart PDFValeria Guadalupe Ramírez MoctezumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolution of Species ChartDocument1 paginăEvolution of Species ChartValeria Guadalupe Ramírez MoctezumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproductive System ChartDocument2 paginiReproductive System ChartValeria Guadalupe Ramírez MoctezumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethical-Challenges-PDF-1-Elliott-1 (Arrastrado)Document5 paginiEthical-Challenges-PDF-1-Elliott-1 (Arrastrado)Valeria Guadalupe Ramírez MoctezumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arteries and Veins ChartDocument2 paginiArteries and Veins ChartValeria Guadalupe Ramírez MoctezumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Questions I MAY ASK AS A LEADERDocument1 pagină10 Questions I MAY ASK AS A LEADERValeria Guadalupe Ramírez MoctezumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Onomatopoeia Worksheet 1Document2 paginiOnomatopoeia Worksheet 1Valeria Guadalupe Ramírez Moctezuma100% (1)
- Magical RealismDocument2 paginiMagical RealismValeria Guadalupe Ramírez MoctezumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excretory System QuizDocument17 paginiExcretory System QuizShadab HanafiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 201305283en Capsurefix 5076Document2 pagini201305283en Capsurefix 5076Bian PurwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Anatomical Terms PPTDocument30 paginiBasic Anatomical Terms PPTInsatiable Clee100% (1)
- C5 - Metabolism and Enzyme Part 1Document20 paginiC5 - Metabolism and Enzyme Part 1Daniel LohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thalassemia: SymptomsDocument3 paginiThalassemia: SymptomsAndi BandotÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Layer Coursera Learning How To LearnDocument4 paginiFirst Layer Coursera Learning How To LearnSandy SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument89 paginiUntitledVladimir VešovićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blue Bio V DoH and HFMADocument21 paginiBlue Bio V DoH and HFMAShane StarlingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zoology: Zoology Previous Eamcet QuestionsDocument8 paginiZoology: Zoology Previous Eamcet QuestionsGaganpreetSingh100% (1)
- POLYGRAPHY: THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD OF DETECTING DECEPTIONDocument15 paginiPOLYGRAPHY: THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD OF DETECTING DECEPTIONEino DuldulaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 Biology Exercises For SPM (Chapter6 & Chapter7)Document15 pagini2018 Biology Exercises For SPM (Chapter6 & Chapter7)Kuen Jian LinÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Difference Between Toxic and Nontoxic GoiterDocument2 paginiThe Difference Between Toxic and Nontoxic GoiterJawad Rehman100% (1)
- q3 Sci10 Unit1 Feedback MechanismsDocument125 paginiq3 Sci10 Unit1 Feedback MechanismsIvann EboraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8Document6 pagini8rajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP PSYCHOLOGY EXAM REVIEW SHEETDocument6 paginiAP PSYCHOLOGY EXAM REVIEW SHEETNathan HudsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nanosep 1Document5 paginiNanosep 1MomÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 103 RLE NOTESDocument8 paginiNCM 103 RLE NOTESgallardo.bettinarose.iÎncă nu există evaluări
- Haemoglobin: DR Nilesh Kate MBBS, MD Associate ProfDocument31 paginiHaemoglobin: DR Nilesh Kate MBBS, MD Associate ProfMarcellia100% (1)
- Gavage FeedingDocument18 paginiGavage FeedingMena AmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- B CellDocument10 paginiB CellSonia Elizabeth SimonÎncă nu există evaluări