Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pressure Management Mind Map
Încărcat de
GAVIN TELFERDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pressure Management Mind Map
Încărcat de
GAVIN TELFERDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
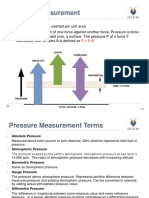
CHAPTER 5 : PRESSURE MEASUREMENT
Absolute pressure : fluid pressure above the reference value of a perfect vacuum or the absolute zero pressure.
Gauge pressure : pressure above the reference value of atmospheric pressure.
Atmospheric pressure : at sea level is nearly 1.013x105 N/m2 (101kPa) or 760 mm of Hg. (Pressure in the surrounding air)
Gravitional-type Thermal Conductivty Gauges
>= 1000 atm : very high
<= 1 mm Hg : very low
Elastic-type Ionization Gauges
Gauge, vacuum, &
absolute pressure
Bourdon tube (Elastic type)
High Pressure Measurement Elastic element will get deformed when
To be used for pressure above 1000 atm pressure applied. Deformation can be
Electrical resistance change of measured mechanically or electrically.
amanganin (alloy of Cu, Ni, Mn) or gold Diaphragm
chrome wire, with hydrostatic pressure Bellows
to accommodate a bulk compression Capsule
effect. Helical tube
Diaphragm PRESSURE Manometer
Pressure Gauge
MEASUREMENT
Bourdon gauge common been used to Manometer (Gravitational-type)
measure pressure. Difference height level between limbs is an
Pressure been measured by amplified indication of pressure different (p1-p2)
the motion of tube end and indicated by U-tube manometer
a moving pointer on a calibrated scale. Mercury manometer
Cistern manometer
Inclined tube manometer
Hydrostatic Bellows pressure
Pressure Gauge gauge
Hydrostatic pressure created by a liquid is Pressure is applied to one side of bellows and
directly related to the height of the liquid resulting deflection is counter balanced by a
column (P = pgh) spring = gauge pressure.
The rise and fall of the liquid level causes a Pressure is applied to inside of one sealed bellow
corresponding increase/decrease in P which while other pressure is applied to the inside of
is directly proportional to the liquid level h. another sealed bellow = pointer on the scale
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 02-MEC441-Fluid Statics-Part 1-v.1.1Document24 pagini02-MEC441-Fluid Statics-Part 1-v.1.1belÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Measuring Devices: Experiment No: 01 Fluid MechanicsDocument12 paginiPressure Measuring Devices: Experiment No: 01 Fluid MechanicsGayantha Induwara RanasinghaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure MeasurementDocument22 paginiPressure Measurement21UME003 TUSHAR DEBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Engineering Pressure APIDocument74 paginiChemical Engineering Pressure APIAsadMalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure MeasurementDocument31 paginiPressure MeasurementMusa MohammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 008 Pressure MeasurementDocument3 pagini008 Pressure MeasurementJayson Ca-ongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Melab ReviewrDocument9 paginiMelab ReviewrMissy ForlajeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressuremeasurement 150729093220 Lva1 App6892Document20 paginiPressuremeasurement 150729093220 Lva1 App6892Athira SivanandhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Module 1 Pressure 04-08-2021 (04 Aug 2021) Material - I - 04 Aug 2021 - Module1PressureDocument64 pagini1 Module 1 Pressure 04-08-2021 (04 Aug 2021) Material - I - 04 Aug 2021 - Module1Pressurebikki sahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment Level Control: 1. Objectives of The ExperimentDocument17 paginiExperiment Level Control: 1. Objectives of The ExperimentAnonymous mvM7yzsfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Is It Important?: Pressure MeasurementDocument28 paginiWhy Is It Important?: Pressure MeasurementMd MohinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Measurement: Objective of LessonDocument49 paginiPressure Measurement: Objective of LessonMohammad TahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tekanan Fluida Dan FlowrateDocument17 paginiTekanan Fluida Dan FlowrateFathuzaky SetyawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unidad II Termo I PDFDocument60 paginiUnidad II Termo I PDFRoutine Of Nepal BandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measurement of PressureDocument9 paginiMeasurement of PressureVICTORÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Fluid Pressure and Its MeasurementDocument20 paginiChapter 2 - Fluid Pressure and Its MeasurementGSaurav DahalÎncă nu există evaluări
- INSTRUMENTATION & CONTROL (Presentation)Document33 paginiINSTRUMENTATION & CONTROL (Presentation)Abdul RehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tinywow UNIT 3 5331119Document17 paginiTinywow UNIT 3 5331119take careÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Pressure MeasurementDocument28 pagini5 Pressure MeasurementMorshedul IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit III NotesDocument73 paginiUnit III NotesShubham SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presuure & Temperature MeasurementDocument48 paginiPresuure & Temperature MeasurementGourab MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nptel: Chemical Process InstrumentationDocument76 paginiNptel: Chemical Process InstrumentationSaurav SatyarthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- LU2 - Fluid Pressure ManometerDocument27 paginiLU2 - Fluid Pressure ManometerlabshitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Delivered By:: Rahat SarwarDocument39 paginiDelivered By:: Rahat SarwarinamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extract Total MeasurementDocument18 paginiExtract Total MeasurementBien MLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas On A Body or Surface, With The Force Acting at Right Angles To The Surface Uniformly in All DirectionsDocument4 paginiGas On A Body or Surface, With The Force Acting at Right Angles To The Surface Uniformly in All DirectionsGerardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Procedures 1 Spreadsheet 10.02.12 PMDocument24 paginiProcedures 1 Spreadsheet 10.02.12 PMulka07Încă nu există evaluări
- Slide Chapter 2 Measurement of PressureDocument29 paginiSlide Chapter 2 Measurement of PressureMuhd FareezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Measurement: Gauge CompoundDocument35 paginiPressure Measurement: Gauge CompoundTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aspecte Generale de PresiuDocument2 paginiAspecte Generale de PresiuAurelia AlexandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3Document74 paginiLecture 3Alhaj MassoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4156342Document19 pagini4156342Th GmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presented By: Ahmed Ali Ahmed ElmesiryDocument35 paginiPresented By: Ahmed Ali Ahmed ElmesiryghghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 2 - ReconDocument5 paginiAssignment 2 - ReconReyven ReconÎncă nu există evaluări
- 06 Pressure MeasurementsDocument47 pagini06 Pressure MeasurementsNikhil Kumar - 35Încă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Measurement: Muhajir Ab. RahimDocument19 paginiPressure Measurement: Muhajir Ab. RahimHadiqa KiyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mekanika Fluida: Pressure and Fluid StaticsDocument63 paginiMekanika Fluida: Pressure and Fluid StaticsMarfizalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.3.pressure SensorsDocument44 pagini2.3.pressure SensorsIroshiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manometer Basics SensorsDocument6 paginiManometer Basics SensorsgilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic HydraulicsDocument30 paginiBasic HydraulicsPremangshu SahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure and It's MeasurementDocument25 paginiPressure and It's Measurementsuyash.2022.awasthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture No - 2 Pressure - FinalDocument56 paginiLecture No - 2 Pressure - FinalresearchditÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 5 - Pressure Measurements StudentsDocument57 paginiChapter - 5 - Pressure Measurements Studentsprasaad0893% (14)
- Fluid Pressure MeasurementDocument7 paginiFluid Pressure MeasurementPurvesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1-1 Process Measurement and Devices Pressure MeasurementDocument81 paginiChapter 1-1 Process Measurement and Devices Pressure Measurementamin shukriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Measurement 2022-1Document38 paginiPressure Measurement 2022-1Varun VelrajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Measurement and Control InstrumentDocument121 paginiProcess Measurement and Control InstrumentEvans HopeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic Name:Pressure Gauge: Guided By:-Prof. Ankit V Sata Prof. Ravi K ParagdaDocument14 paginiTopic Name:Pressure Gauge: Guided By:-Prof. Ankit V Sata Prof. Ravi K Paragdakiran babyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure SensorsDocument14 paginiPressure SensorsDanish Ur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week - 09 - Pressure and Velocity MeasurementsDocument21 paginiWeek - 09 - Pressure and Velocity MeasurementsMohammad MohiuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3Document14 paginiLecture 3William DsouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture No - 2 PressureDocument86 paginiLecture No - 2 PressureresearchditÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Measurement S12Document45 paginiPressure Measurement S12anuopgame3030Încă nu există evaluări
- Process Instrumentation - Module 3Document100 paginiProcess Instrumentation - Module 3ibuddhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LC 2&3 Pressure Measurment DevicesDocument96 paginiLC 2&3 Pressure Measurment DevicesAli MoustafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me-3115 3Document17 paginiMe-3115 3Amit PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Measurement Apparatus: Operating Instruction Manual ofDocument10 paginiPressure Measurement Apparatus: Operating Instruction Manual ofRavi ParikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instrument Technology: Measurement of Pressure, Level, Flow and TemperatureDe la EverandInstrument Technology: Measurement of Pressure, Level, Flow and TemperatureEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Transducer Handbook: User's Directory of Electrical TransducersDe la EverandTransducer Handbook: User's Directory of Electrical TransducersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Globalization: Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument17 paginiGlobalization: Advantages and DisadvantagesJeselle Bagsican100% (1)
- Plastic Waste Management: Modern College of Arts, Commerce & Science Shivajinagar, PuneDocument16 paginiPlastic Waste Management: Modern College of Arts, Commerce & Science Shivajinagar, Punetanmay kothawadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Dependence of Cross SectionsDocument23 paginiEnergy Dependence of Cross SectionsSparsh ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- EtymologyDocument1 paginăEtymologyYekitaSÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChemistryDocument5 paginiChemistryapi-248750786Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1.3 WeatheringDocument6 paginiUnit 1.3 WeatheringJoshua John JulioÎncă nu există evaluări
- 托福阅读 - Arrival of Plant Life in HawaiiDocument5 pagini托福阅读 - Arrival of Plant Life in HawaiiYongchang ChenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global Warming Mouful 9 LectureDocument64 paginiGlobal Warming Mouful 9 LectureMohibul IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- 17 WEP SpringsDocument8 pagini17 WEP SpringseltytanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Born-Haber Cycles: AQA Chemistry A2 Stretch and Challenge © Nelson Thornes LTD 2009 1Document2 paginiBorn-Haber Cycles: AQA Chemistry A2 Stretch and Challenge © Nelson Thornes LTD 2009 1Paul MurrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Journal 2.1 Atomic TheoryDocument5 paginiChemistry Journal 2.1 Atomic TheoryKaylee LambertÎncă nu există evaluări
- PS PSSA Prep Physics ReviewDocument30 paginiPS PSSA Prep Physics ReviewflyingmsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essay Topics-ON TAPDocument20 paginiEssay Topics-ON TAPBích NgọcÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Review of Aging Models For Electrical Insulation in Power CablesDocument20 paginiA Review of Aging Models For Electrical Insulation in Power CablesPhilippe SingletonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module: Geologic Time ScaleDocument25 paginiScience: Quarter 1 - Module: Geologic Time ScaleLebz RicaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model Test-2 Class: IX (EV) Subject: Chemistry Creative SectionDocument2 paginiModel Test-2 Class: IX (EV) Subject: Chemistry Creative SectionLUBNA AKTERÎncă nu există evaluări
- OceanographyDocument24 paginiOceanographyAnkit Sundriyal100% (1)
- 4.5 M SBCDocument3 pagini4.5 M SBCvivekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Palm Oil BiomassDocument7 paginiPalm Oil Biomassnhalieza1067Încă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Transmission and Distribution System and DesignDocument67 paginiElectrical Transmission and Distribution System and DesignAdrian Toribio100% (3)
- Thermal Analysis of The Heat Exchanger Tubes Using Ansys PDFDocument4 paginiThermal Analysis of The Heat Exchanger Tubes Using Ansys PDFMuhammadBarrylAnggriawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- M. Cuney and K. Kayser - 2008, Recent and Not-So-Recent Developments in Uranium Deposits and Implications For ExplorationDocument259 paginiM. Cuney and K. Kayser - 2008, Recent and Not-So-Recent Developments in Uranium Deposits and Implications For ExplorationDomenik Elizabeth Calderon VÎncă nu există evaluări
- One-Step Synthesis of A 12CaO7Al2O3 Electride Via The SparkDocument3 paginiOne-Step Synthesis of A 12CaO7Al2O3 Electride Via The Sparkshazna203Încă nu există evaluări
- Igneous PetrologyDocument16 paginiIgneous PetrologyianmooneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safe Operation of Reboilers/Condensers in Air Separation UnitsDocument30 paginiSafe Operation of Reboilers/Condensers in Air Separation UnitsAmit BiswasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sea of Souls Volume V (Extra Content)Document51 paginiSea of Souls Volume V (Extra Content)Rafael Severino NomebostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MerDocument264 paginiMerkoloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Natural Convection Heat Transfer in Vertical Internally Finned TubeDocument10 paginiNatural Convection Heat Transfer in Vertical Internally Finned TubeAdarsh Kumar AngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - ExerciseDocument15 paginiChapter 1 - Exerciseحسن كميت hassankomeit lÎncă nu există evaluări