Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack)
Încărcat de
Christine Pialan SalimbagatTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack)
Încărcat de
Christine Pialan SalimbagatDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Cardio E (2nd) Injury: injuriST: ST segment elevation (at
least 1mm above isoelectric line) (secondary
Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack) to rapid repolarization)
(3rd) Ischemia: Tischemia: T wave inversion
Myo – Muscle - Cause of T wave inversion (ischemia) is
delayed repolarization
Cardial – Heart
- As the area of injury becomes ischemic,
Infarction – Death myocardial repolarization is altered and
delayed, causing the T wave to invert
= Death of the heart muscle 3. Echocardiography
- To evaluate ventricular function
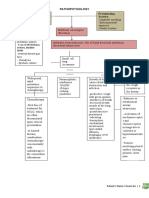
Pathophysiology 4. Cardiac Enzymes
- Myoglobin usually arises 1 hour after
- Complete obstruction of coronary arteries
myocardial infarctijn
leading to myocardial necrosis > arrhythmia
- Troponin arises 3 hours after MI (#1 most
(abnormal heart rhythm) > cardiogenic shock
specific, accurate indicator of MI)
Signs and Symptoms - Creatinine Kinase MB arises 4-6 hours after MI
- AST Alanine Serum Transferase: 8hrs
1. Chest pain - LDH Lactate dehydrogenase: 24hrs
- Unrelieved by rest or nitroglycerin 5. Blood chemistry
- #1 presenting symptom of myocardial Normal
infarction - Cholesterol : <200mg/dl
- Lasts for >20mins - Triclycerides: <150mg/dl
2. SNS (sympathetic nervous system) Stimulation - LDL (low density lipoprotein, bad chrolesterol
- Cool skin that carries fats and deposits it to the lining of
- Pallor blood vessels): <100mg/dl
- Diaphoresis (sweating) - HDL (high density lipoprotein , good
- Tachycardia cholesterol that carries fats from the blood
- Tachypnea vessels and deposits it to the liver): >60mg/dl
3. If with Diabetes Mellitus - vLDL (very low density lipoprotein): <40mg/dl
- No severe pain secondary to neuropathy (DM
is a condition characterized by hyper viscosity
of the blood secondary to higher than normal
blood sugar level, may cause micro occlusion
including small blood vessels which may
damage the nerve, thus DM pt may not feel
chest pain)
Diagnostic Tests
1. Patient history
- ssx
2. ECG
- performed within 10mins of pain onset or
upon arrival at emergency room
- ECG typically manifests the pathologic Q
wave, the elevated ST segment and inverted T
wave
When there’s infarction, the area of infarction will
be the one to register in pathologic Q wave
(1st) Infarction: InfarQtion: pathologic Q wave
The secondary injury will cause ST segment
elevation
Management - to reroute blood to bypass the occlusion
1. Oxygenation Uses:
2. Medication
(a) Greater saphenous vein – has least number of
>For pain relief tributaries
(b) Lesser saphenous vein – found in lower
Morphine Sulfate (drug of choice) extremity
Side effect > carotid endarderectomy
- Respiratory depression (most dangerous)
- Constipation (most common)
- Pruritus (idiosyncratic – uncommon)
(image) percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
>For reperfusion (restore blood flow to affected area)
Thrombolytic meds (tissue-plasminogen activator)
(urokinase, streptokinase, alteplase)
- Must be given within 3hours before there is
hardening or irreversible myocardial necrosis
- In case of bleeding: antidote – aminocaproic
acid – plasminogen inhibitor
- Watch out for cardiac arrhythmias (side effect
of antidote), it’s associated with reperfusion
of cardiac tissues
3. Hemodynamic Stability
- First 48 hours (very critical)
- Monitor VS (BP and HR)
- Look for possibility of
Arrhythmia (BP decreases)
Chemical
PTCA – tube with a balloon and a stent that is used to flatten /remove
Anti-arrhythmic drugs (Na channel blockers) atheroma, or restore the patency of occluded blood vessel.
- Lidocaine
- Procainamide
- Quinidine (image) coronary artery bypass graft
Electrical
- Defibrillation
*Cardiogenic Shock management
- drug of choice: Lidocaine (anti-arrhythmic effect)
- Dopamine (A1, B2)
- dobutamine (inotropic) (A1, B1, B2)
4. Surgery
> percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty: for
1-2 affected vessels
- balloon tipped catheter with stent
> coronary artery bypass graft: for >3 affected vessels
CABG – saphenous vein is used to connect blood vessels that are
obstructed by blockage and internal mammary artery graft that is
used to connect subclavian vein and another artery that has been
blocked
5.Maintenance medications
>Anticoagulants: to reduce circulation fibrinogen
- heparin
- warfarin
>angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: blocks the
conversion of angiotensin 1 (mild vasoconstrictor) to
angiotensin 2 (potent vasoconstrictor) in the
pulmonary circilation
- captopril
- enalapril
Side effect
- Cough (nonproductive): blocks the breakdown
of bradykinin (inflammatory mediator)
>Beta1 Blockers: decreases the heart rate (#1
determinant of cardiac metabolic demand)
> CCBS (calcium channel blockers)
- amlodipine
- nicardipine
>Antilipemics (statins): blocks enzyme HMG CoaA
(hydroxymetheylglutaryl coenzyme A), thus
decreasing cholesterol formation
Side Effect
- Muscle pain (myalgia – secondary to decrease
protein in muscles)
6.Nutritional support
- NPO first 24 hrs (for surgery)
- General liquid diet
- Soft diet (decreased fat, Na, calories)
- Prevent constipation: increase fluids, fibers
- Laxative: dulcolax
7.Sexual needs
resume if
- (a) the pt can climb stairs without shortness of
breathe (or 6weeks after surgery)
- Best time: early in the morning naol
- Do it in a familiar place with a familiar partner
(reduce anxiety)
- Prolong foreplays (for slow acceleration of
cardiac function)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cardiac Notes NursingDocument16 paginiCardiac Notes NursingYemaya8494% (17)
- Vascular Diseases (1 of 3)Document4 paginiVascular Diseases (1 of 3)Doctor GeneralÎncă nu există evaluări
- Textbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroDocument12 paginiTextbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroJica Marie Bandiola GicaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Surgical NursingDocument11 paginiMedical Surgical NursingMaria TagubaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest PainDocument50 paginiChest PainGrafu Andreea AlexandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes (1 To 6)Document21 paginiNotes (1 To 6)Justin EvansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathogenesis of Cardiac DisordersDocument28 paginiPathogenesis of Cardiac DisordersUdochukwu EnebeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiology-6 CADDocument20 paginiCardiology-6 CADMahmoud RamadanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument5 paginiAcute Coronary Syndromem3d1k100% (1)
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument62 paginiAcute Myocardial InfarctionJohn Alvin YoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument13 paginiAcute Myocardial InfarctionSajjad KabirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 7Document11 paginiLecture 7Grafu Andreea AlexandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac NotesDocument24 paginiCardiac NotesYary MayorÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANGINADocument3 paginiANGINAtalitha kumiÎncă nu există evaluări
- سريرية كمبيوتر-1Document11 paginiسريرية كمبيوتر-1مخلب كونوهاÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulation AssessmentDocument8 paginiCirculation AssessmentalhassanmohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myocardial Infarction NCLEX ReviewDocument4 paginiMyocardial Infarction NCLEX ReviewlhenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyDocument4 paginiAngina Pectoris Pathophysiologyteddydeclines1467% (6)
- Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument9 paginiCardiac ArrhythmiasRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 21 Muscle Blood FlowDocument17 paginiChapter 21 Muscle Blood Flowelmedina omeragicÎncă nu există evaluări
- PATH - Ischaemic Heart Disease (13p)Document13 paginiPATH - Ischaemic Heart Disease (13p)vikashchahal1987Încă nu există evaluări
- Cardio 2Document9 paginiCardio 2Moon KillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Er FinalsDocument63 paginiEr FinalsNaren RaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- سريرية كمبيوترDocument11 paginiسريرية كمبيوترمخلب كونوهاÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3 - IHDDocument29 paginiLecture 3 - IHDقاسم اليوسفيÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8C - Antiarrythmic DrugsDocument76 pagini8C - Antiarrythmic DrugsShahpoor Ahmad ShirzadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiology BookletDocument30 paginiCardiology Bookletali.khanfariplsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Ministry of Health King Fahad Hofuf Hospital Nursing EducationDocument33 paginiAcute Coronary Syndrome: Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Ministry of Health King Fahad Hofuf Hospital Nursing EducationAqeelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of Angina PectorisDocument5 paginiDrugs Used in The Treatment of Angina PectorisPadmanabha T SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conduction System: Rhythm Identification and TreatmentDocument12 paginiConduction System: Rhythm Identification and Treatmenthops23Încă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular System: By: Marc Anthony Liao RNDocument59 paginiCardiovascular System: By: Marc Anthony Liao RNloveseeker06Încă nu există evaluări
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument9 paginiAcute Coronary SyndromeAnthony Philip Patawaran CalimagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument5 paginiAcute Coronary Syndromecotten joeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac Disorders Cardiac Drugs: Shair Muhammad HazaraDocument36 paginiCardiac Disorders Cardiac Drugs: Shair Muhammad HazaraJubil KurianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes For Responses To Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument12 paginiNotes For Responses To Altered Tissue Perfusiondivine armentonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology: Cardiovascular SystemDocument20 paginiPharmacology: Cardiovascular SystemCheryl OrtizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular System: DiseasesDocument6 paginiCardiovascular System: DiseasesEn ConejosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stroke: Cerebro Vascular Accident" (CVA)Document37 paginiStroke: Cerebro Vascular Accident" (CVA)Elfrida HaznaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Coronary Syndrome (Sindroma Koroner Akut) : Zulfikri MukhtarDocument32 paginiAcute Coronary Syndrome (Sindroma Koroner Akut) : Zulfikri MukhtarWina DeskyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: by Ho NisaDocument58 paginiAcute Coronary Syndrome: by Ho NisaShre RanjithamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardio I: Shock, CHF, HTN, ACS Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 paginiCardio I: Shock, CHF, HTN, ACS Cheat Sheet: by ViaMariana NannettiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac DisordersDocument80 paginiCardiac Disordersscan1993Încă nu există evaluări
- Heart FailureDocument35 paginiHeart FailureSanjeev Harry BudhooramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thea Laurene T. Tonelada BSN Iv-C Dysrhythmia: TachydysrhythmiasDocument5 paginiThea Laurene T. Tonelada BSN Iv-C Dysrhythmia: Tachydysrhythmiasscribd_lostandfoundÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology: - Hypertension - Angina Pectoris - Cardiac Arrhythmias - Heart FailureDocument31 paginiCardiovascular Pharmacology: - Hypertension - Angina Pectoris - Cardiac Arrhythmias - Heart Failurelynch775100% (2)
- Review On Cardiovascular Diseases: BY: Fidel G. Yongque III, RNDocument20 paginiReview On Cardiovascular Diseases: BY: Fidel G. Yongque III, RNFidel Gimotea Yongque IIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeDocument5 paginiPost-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeEben Ezar Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heart Failure: Dysfunction)Document5 paginiHeart Failure: Dysfunction)Christine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angina PectorisDocument10 paginiAngina Pectorissantoshd99Încă nu există evaluări
- ArrhythmiaDocument31 paginiArrhythmiaAbdallah Essam Al-ZireeniÎncă nu există evaluări
- TutorialDocument18 paginiTutorialEllya Syahfitri 2108125983Încă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument27 paginiCardiovascular DiseaseKyrajane EsguerraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Management of Myocardial Infarction No PicturesDocument26 paginiAcute Management of Myocardial Infarction No PicturesSilvestri PurbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Competency AppraisalDocument43 paginiCompetency AppraisalErica Ruvie AgbayaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- NotesDocument6 paginiNotesCarl JuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument2 paginiMyocardial InfarctiongwynethntpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angina and MIDocument68 paginiAngina and MIAndrassy Twinkle AlineaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penyakit Kardiovaskular Yang Sering DijumpaiDocument121 paginiPenyakit Kardiovaskular Yang Sering Dijumpaiandikaagus13Încă nu există evaluări
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument23 paginiAcute Coronary SyndromeThanujaa UvarajÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY IN ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASEDe la EverandELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY IN ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Salimbagat - Legal Notes First BatchDocument8 paginiSalimbagat - Legal Notes First BatchChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Salimbagat - Legal Notes Second BatchDocument14 paginiSalimbagat - Legal Notes Second BatchChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 3 - Anatomy and Physiology - SalimbagatDocument4 paginiCase 3 - Anatomy and Physiology - SalimbagatChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 4 - Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresDocument7 paginiCase 4 - Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 5 - (Salimbagat) Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresDocument12 paginiCase 5 - (Salimbagat) Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- HTP - Supporting The Patient On DialysisDocument8 paginiHTP - Supporting The Patient On DialysisChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 5 - (Salimbagat) Drug StudyDocument4 paginiCase 5 - (Salimbagat) Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAWTON - BRODY I.A.D.L. - SalimbagatDocument2 paginiLAWTON - BRODY I.A.D.L. - SalimbagatChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment 8 - SalimbagatDocument2 paginiAssessment 8 - SalimbagatChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Katz Index of I.A.D.L - SalimbagatDocument1 paginăKatz Index of I.A.D.L - SalimbagatChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geriatric Depression Scale - SalimbagatDocument2 paginiGeriatric Depression Scale - SalimbagatChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection: Opening QuestionsDocument3 paginiReflection: Opening QuestionsChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPs - SalimbagatDocument6 paginiNCPs - SalimbagatChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrub and Circulating Practitioner Simulation Script - Salimbagat, UsmanDocument12 paginiScrub and Circulating Practitioner Simulation Script - Salimbagat, UsmanChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Socio 1 Midterm Exam: Answer. (CAPITAL LETTER)Document2 paginiSocio 1 Midterm Exam: Answer. (CAPITAL LETTER)Christine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP ImpairedSkinIntegDocument2 paginiNCP ImpairedSkinIntegChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: Salimbagat, Christine P. BSN Iii - CCC Group K Week 2 - Care of Older Adult Clinical RotationDocument3 paginiName: Salimbagat, Christine P. BSN Iii - CCC Group K Week 2 - Care of Older Adult Clinical RotationChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skill 12 Learning Feedback - SalimbagatDocument1 paginăSkill 12 Learning Feedback - SalimbagatChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsDocument2 paginiPathophysiology Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSU-Iligan Institute of Technology College of Nursing: Level II AACUP AccreditedDocument4 paginiMSU-Iligan Institute of Technology College of Nursing: Level II AACUP AccreditedChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsDocument2 paginiPathophysiology Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: Salimbagat, Christine P. BSN Iii - CCCDocument1 paginăName: Salimbagat, Christine P. BSN Iii - CCCChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mic Cabg Procedure PDFDocument12 paginiMic Cabg Procedure PDFprofarmah6150Încă nu există evaluări
- 4 Surgical Anatomy of The HeartDocument79 pagini4 Surgical Anatomy of The HeartKacper DaraszkiewiczÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maria Citcos: Cap. 1 Cap. 1 Cap. 1 Cap. 1 Cap. 1 Cap. 2 Cap. 3 Cap. 6 Cap. 7 Cap. 1 Cap. 5 Cap. 4 Cap. 3 Cap. 4 Cap. 4Document11 paginiMaria Citcos: Cap. 1 Cap. 1 Cap. 1 Cap. 1 Cap. 1 Cap. 2 Cap. 3 Cap. 6 Cap. 7 Cap. 1 Cap. 5 Cap. 4 Cap. 3 Cap. 4 Cap. 4Smaranda-Elena MateiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac CTDocument7 paginiCardiac CTdaniel7pintiliiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Cabg SurgeryDocument26 paginiCoronary Artery Bypass Graft Cabg SurgeryNogra CarlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arterial Clamping Leads To Stenosis at Clamp Sites After Femoropopliteal Bypass SurgeryDocument9 paginiArterial Clamping Leads To Stenosis at Clamp Sites After Femoropopliteal Bypass SurgeryAyhan ComertÎncă nu există evaluări
- NivaBupa 2023Document83 paginiNivaBupa 2023Aniket Yadav100% (1)
- Panvascular Disease - Diagnosis and Management: SciencedirectDocument9 paginiPanvascular Disease - Diagnosis and Management: SciencedirectAndikaputra Brahma WidiantoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medicine, Evaluation and Management Services CPT CODES 90000 - 99999Document39 paginiMedicine, Evaluation and Management Services CPT CODES 90000 - 99999Asha RubyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CABGDocument3 paginiCABGprofarmahÎncă nu există evaluări
- CABG (Repaired)Document31 paginiCABG (Repaired)preet kaur100% (2)
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument43 paginiMyocardial InfarctiondeeptiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Raju B Soma Ed Clinical Methods in Cardiology PDFDocument522 paginiRaju B Soma Ed Clinical Methods in Cardiology PDFAshishsanjay Munoli0% (1)
- Oracle Healthcare Data ModelDocument258 paginiOracle Healthcare Data ModelSrinivas KankanampatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kode ICD XDocument764 paginiKode ICD XMade Surya DinathaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surgery ReviewDocument12 paginiSurgery ReviewJo AnneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Austin Journal of Cardiovascular Disease and AtherosclerosisDocument4 paginiAustin Journal of Cardiovascular Disease and AtherosclerosisAustin Publishing GroupÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anesthesia QuestionsDocument8 paginiAnesthesia QuestionsDurga RaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.best Insight Cardio Metabolic TeamDocument61 pagini2.best Insight Cardio Metabolic TeamSaQlain BalochÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular Surgery QuizDocument4 paginiCardiovascular Surgery Quizjeevan more100% (2)
- Trends in Nmangement and Outcomes of Patients With Acute Myocardil Infarction Complicated by Cardiogenic ShockDocument7 paginiTrends in Nmangement and Outcomes of Patients With Acute Myocardil Infarction Complicated by Cardiogenic ShockVICTOR EUCLIDES BRIONES MORALESÎncă nu există evaluări
- F1000research 7 16443Document8 paginiF1000research 7 16443Muhammad AzamÎncă nu există evaluări
- History and Background of Quality Measurement: Jonathan Chun, MD Andrea Chao Bafford, MD, FACSDocument5 paginiHistory and Background of Quality Measurement: Jonathan Chun, MD Andrea Chao Bafford, MD, FACSSara MezianeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychology of Women 401 807Document407 paginiPsychology of Women 401 807Alessio TinerviaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angiographic Views of Coronary ArteriesDocument60 paginiAngiographic Views of Coronary Arteriesreshma somarajan100% (3)
- Cardiac TransplantDocument44 paginiCardiac TransplantMavi SaldevarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Timing of Revascularization in Patients With Transient ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction A Randomized Clinical TrialDocument9 paginiTiming of Revascularization in Patients With Transient ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction A Randomized Clinical TrialWelly WijayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Percutaneous Intervention For Coronary Chronic Total Occlusion 2016 PDFDocument238 paginiPercutaneous Intervention For Coronary Chronic Total Occlusion 2016 PDFmepimplolabotellasÎncă nu există evaluări
- CABGDocument4 paginiCABGMaria Janet BasalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- CABGDocument31 paginiCABGRiya PhilipÎncă nu există evaluări