Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Coagulase
Încărcat de
Jiki LaluDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Coagulase
Încărcat de
Jiki LaluDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
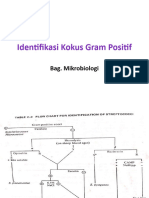
COAGULASE TEST
Staphylococcus aureus is known to produce coagulase, which can clot plama into gel in tube or agglutinate cocci in
slide. This test is useful in differentiating S.aureus from other coagulase-negative staphylococci. Most strains of
S.aureus produce two types of coagulase, free coagulase and bound coagulase. While free coagulase is an
enzyme that is secreted extracellularly, bound coagulase is a cell wall associated protein. Free coagulase is
detected in tube coagulase test and bound coagulase is detected in slide coagulase test. Slide coagulase test may
be used to screen isolates of S.aureus and tube coagulase may be used for confirmation. While there are seven
antigenic types of free coagulase, only one antigenic type of bound coagulase exists. Free coagulase is heat labile
while bound coagulase is heat stable.
SLIDE COAGULASE TEST:
Principle: The bound coagulase is also known as clumping factor. It cross-links the α and β chain of fibrinogen in
plasma to form fibrin clot that deposits on the cell wall. As a result, individual coccus stick to each other and
clumping is observed.
Procedure: Dense suspensions of Staphylococci from culture are made on two ends of clean glass slide. One
should be labeled as “test” and the other as “control”. The control suspension serves to rule out false positivity due
to autoagglutination. The test suspension is treated with a drop of citrated plasma and mixed well. Agglutination or
clumping of cocci within 5-10 seconds is taken as positive. Some strains of S.aureus may not produce bound
coagulase, and such strains must be identified by tube coagulase test.
TUBE COAGULASE TEST:
Principle: The free coagulase secreted by S.aureus reacts with coagulase reacting factor (CRF) in plasma to form
a complex, which is thrombin. This converts fibrinogen to fibrin resulting in clotting of plasma.
Procedure: Three test tubes are taken and labeled “test”, “negative control” and “positive control”. Each tube is
filled with 0.5 ml of 1 in 10 diluted rabbit plasma. To the tube labeled test, 0.1 ml of overnight broth culture of test
bacteria is added. To the tube labeled positive control, 0.1 ml of overnight broth culture of known S.aureus is added
and to the tube labeled negative control, 0.1 ml of sterile broth is added. All the tubes are incubated at 37oC and
observed up to four hours. Positive result is indicated by gelling of the plasma, which remains in place even after
inverting the tube. If the test remains negative until four hours at 37oC, the tube is kept at room temperature for
overnight incubation.
Application: Coagulase test is used to identify and differentiate S.aureus from coagulase negative staphylococci.
While slide coagulase test is useful in screening, tube coagulase test is useful in confirmation of coagulase test. Not
all S.aureus strains produce coagulase; such rare strains are identified by thermonuclease test. Some coagulase
negative staphylococci such as S.lugdensis and S.schleiferi are known to give positive slide coagulase test while
S.hyicus and S.intermedius are known to give positive tube coagulase test.
© Sridhar Rao P.N (www.microrao.com)
Last edited in June 2006
© Sridhar Rao P.N (www.microrao.com)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Essentials of ABO -Rh Grouping and Compatibility Testing: Theoretical Aspects and Practical ApplicationDe la EverandEssentials of ABO -Rh Grouping and Compatibility Testing: Theoretical Aspects and Practical ApplicationEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Blood Group Compatbility TestDocument46 paginiBlood Group Compatbility TestArslan ArshadÎncă nu există evaluări
- MicrobiologyDocument40 paginiMicrobiologyRasty Baku100% (1)
- Bacterial Identification Methods SummaryDocument12 paginiBacterial Identification Methods SummaryLarnie Alejandre100% (1)
- Blood AgarDocument4 paginiBlood Agarsyafa latifahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gram Positive CocciDocument21 paginiGram Positive CocciRedelle Mae Nini100% (2)
- Cross Matching-Wps OfficeDocument22 paginiCross Matching-Wps Officeashwini priyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gram-positive bacteria of medical importance overviewDocument58 paginiGram-positive bacteria of medical importance overviewGx NavinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compatibility TestingDocument36 paginiCompatibility TestingCharmaine Corpuz Granil100% (1)
- Microbiology Review HandoutDocument53 paginiMicrobiology Review HandoutAndrei Tumarong Angoluan100% (1)
- MicroLab Guide Questions #7 PDFDocument4 paginiMicroLab Guide Questions #7 PDFMILEN ANGELIE MEDALLAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbiology Sheet MCQ - Part 1Document12 paginiMicrobiology Sheet MCQ - Part 1MahmOod Gh100% (3)
- MTAP BACTE MIDTERMS MergedDocument26 paginiMTAP BACTE MIDTERMS MergedLea Juan100% (1)
- Mtap - BacteriologyDocument11 paginiMtap - BacteriologyMoira Pauline LibroraniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MTAP - 1.1 - BacteriologyDocument14 paginiMTAP - 1.1 - BacteriologyKassandra CordetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochemical Tests For Identification of Bacteria PDFDocument30 paginiBiochemical Tests For Identification of Bacteria PDFEmber BahianÎncă nu există evaluări
- II) Coagulase Test: ProcedureDocument4 paginiII) Coagulase Test: ProcedureMd Ahsanul HaqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coagulase PlasmaDocument2 paginiCoagulase PlasmaHà Anh Minh LêÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Staph TestsDocument33 paginiAll Staph Testsalhaitham alqmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coagulase Test Guide: Detecting S. aureusDocument2 paginiCoagulase Test Guide: Detecting S. aureusilyas9558Încă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Discussion Activity 5Document2 paginiLaboratory Discussion Activity 5carina smithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pratical Two ReportDocument13 paginiPratical Two ReportMUBIRU SAMUEL EDWARDÎncă nu există evaluări
- PL850 Rabbit-Coagulase-Plasma EnglishDocument2 paginiPL850 Rabbit-Coagulase-Plasma Englishzahramaulidi28Încă nu există evaluări
- Coagulase TestDocument10 paginiCoagulase Testlunaghilvin2026Încă nu există evaluări
- Practical-MSS1 - NEWDocument28 paginiPractical-MSS1 - NEWAsem AlhazmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab-5-Staphylococci: BY Dr. Shnyar Hamid QadirDocument24 paginiLab-5-Staphylococci: BY Dr. Shnyar Hamid QadirHanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coagulase Test ProtocolDocument12 paginiCoagulase Test ProtocolMaria DapkeviciusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instrucciones CoagulasaDocument1 paginăInstrucciones CoagulasashealockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coagulase TestDocument3 paginiCoagulase TestVanandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochemical Methods For Staphylococci IdentificationDocument12 paginiBiochemical Methods For Staphylococci IdentificationJuliannaViktoriiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- STAPHYLOCOCCUSDocument16 paginiSTAPHYLOCOCCUSSyed Mohsin NisarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coagulase Test Intended UseDocument1 paginăCoagulase Test Intended UseRidhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory 2 - Microflora of The SkinDocument13 paginiLaboratory 2 - Microflora of The SkinNur Ariff Bin HakimiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coagulase Test - Principle, Procedure, Types, Interpretation and ExamplesDocument10 paginiCoagulase Test - Principle, Procedure, Types, Interpretation and ExamplesJagruti KambaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coombs TestDocument17 paginiCoombs Testnativeman2221Încă nu există evaluări
- Differentiate Staph and Strep with Blood Agar and Catalase TestsDocument1 paginăDifferentiate Staph and Strep with Blood Agar and Catalase TestsNor ShasalbilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Praktikum MikrobiologiDocument54 paginiPraktikum MikrobiologilarasatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Bank Antibody Detection Test ProcedureDocument4 paginiBlood Bank Antibody Detection Test ProcedureAlfreah Jean TambasenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Microbiology Manual PDFDocument31 paginiDiagnostic Microbiology Manual PDFmajdi bilbisiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Column Agglutination Technology: The Antiglobulin Test: Agglutination of Red CellsDocument5 paginiColumn Agglutination Technology: The Antiglobulin Test: Agglutination of Red CellsOB3 Ortho Clinical DiagnosticsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment # 2 Venous Blood Collection: FinallyDocument8 paginiExperiment # 2 Venous Blood Collection: FinallyHasnat KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Dept: Hematology Test Name: Osmotic Fragility: General InformationDocument3 paginiLab Dept: Hematology Test Name: Osmotic Fragility: General InformationEvans HansenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sickle Cell TestDocument8 paginiSickle Cell Testcharutha gopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Bank Coombs ReportDocument5 paginiBlood Bank Coombs Reportleen.dimashkiehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Praktikum 3Document24 paginiPraktikum 3ALFEARA YUNIARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coagulase Plasma (Bactident Coagulase)Document10 paginiCoagulase Plasma (Bactident Coagulase)Verika AstrianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data and Observations:: Skin Swabs On Blood AgarDocument5 paginiData and Observations:: Skin Swabs On Blood AgarNor ShasalbilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penjelasan Praktikum KardiovaskulerDocument54 paginiPenjelasan Praktikum KardiovaskulerQuswah MaharaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABO and RH Blood Typing: AB ActsDocument4 paginiABO and RH Blood Typing: AB ActsRaja SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 3 BacteDocument7 paginiLec 3 BacteMitchee ZialcitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab.5 Biochemical Test-1Document13 paginiLab.5 Biochemical Test-1zainab6112003Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab 6Document5 paginiLab 6moodyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1496-Article Text-7538-1-10-20230917Document9 pagini1496-Article Text-7538-1-10-20230917anastasyagerant2ndÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Experiment Group 6Document57 paginiBlood Experiment Group 6Melissa SalayogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interpretation of The Tube Coagulase Test Identification Of: StaphylococcusDocument4 paginiInterpretation of The Tube Coagulase Test Identification Of: StaphylococcusFina RahmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BloodDocument3 paginiBloodnamithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spermogram Specimen CollectionDocument5 paginiSpermogram Specimen CollectionKatiasalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elution and Adsorption TechniquesDocument23 paginiElution and Adsorption TechniquesBromance H.Încă nu există evaluări
- Enjelasan Praktikum Mikrobiologi Blok KardiovaskulerDocument56 paginiEnjelasan Praktikum Mikrobiologi Blok KardiovaskulerAtik LestariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Bank - Pretransfusion Compatibility TestingDocument4 paginiBlood Bank - Pretransfusion Compatibility TestingWayne VillalunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 4.5.6. ABODocument22 paginiLab 4.5.6. ABOAhmed AssafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specimen Collection GuidelinesDocument4 paginiSpecimen Collection GuidelinesFathi MesoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF 4Document26 paginiPDF 4Dhruv Raj 9 B 24Încă nu există evaluări
- PDF 5Document25 paginiPDF 5Dhruv Raj 9 B 24100% (1)
- Pulse - Serum or Plasma-2Document2 paginiPulse - Serum or Plasma-2Raghad AlansariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Report #2 MicrobioDocument18 paginiLab Report #2 Microbioariana villarrealÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Session Two Guide-1Document9 paginiPractical Session Two Guide-1Andrease WandazÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4BMT Ortho1Document4 pagini4BMT Ortho1jay primaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPEAKER: Dr. Subhajit Das MODERATOR: Prof. Jyoti ShuklaDocument25 paginiSPEAKER: Dr. Subhajit Das MODERATOR: Prof. Jyoti Shuklaswaraj sharma100% (2)
- Blood GroupingDocument16 paginiBlood Groupinglubna aloshibiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bacteriological Analysis of Salad Vegetable in Eke Awka Market, Anambra State, NigeriaDocument8 paginiBacteriological Analysis of Salad Vegetable in Eke Awka Market, Anambra State, NigeriaJASH MATHEWÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uses of Carbohydrate Fermentation Test: EnterobacteriaceaeDocument12 paginiUses of Carbohydrate Fermentation Test: EnterobacteriaceaeChristyl JoÎncă nu există evaluări
- BBL CrystalDocument9 paginiBBL CrystalYsrad Dante RmzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbial Limit TestDocument33 paginiMicrobial Limit TestSurendar KesavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- C995 12 PDFDocument14 paginiC995 12 PDFdanzan1Încă nu există evaluări
- Rationale in Microbiology and Parasitology: Prepared By: Ralf LadreraDocument4 paginiRationale in Microbiology and Parasitology: Prepared By: Ralf LadreraralfÎncă nu există evaluări
- CoagulaseDocument2 paginiCoagulaseJiki LaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Identificacion Staphy MicrobiologíaDocument17 paginiIdentificacion Staphy MicrobiologíaLAURA VANESSA REYES ROMEROÎncă nu există evaluări
- Staining TechniqueDocument2 paginiStaining TechniqueClaire MayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbiology CapsuleDocument167 paginiMicrobiology Capsulecryptoblockchain116Încă nu există evaluări
- Bacte Midterm Di TaposDocument9 paginiBacte Midterm Di TaposAL-HUSSEIN NAWABÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture PP5&6 StaphylococcusDocument44 paginiLecture PP5&6 StaphylococcusVera AkmiliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BBL Coagulase Plasmas: Marcescens, Enterococcus Faecalis and Strains of Streptococcus Will Clot Citrated PlasmaDocument16 paginiBBL Coagulase Plasmas: Marcescens, Enterococcus Faecalis and Strains of Streptococcus Will Clot Citrated Plasmaseb2008Încă nu există evaluări
- MARY@SLT12 ProjectDocument48 paginiMARY@SLT12 ProjectsantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Testes de Microbiologia - BAM - FDADocument16 paginiTestes de Microbiologia - BAM - FDAAlessandra FerreiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochemical Tests and Culture Media PDF+AsperigillusDocument242 paginiBiochemical Tests and Culture Media PDF+Asperigillushamody662002100% (1)
- Medical Bacteriology, Henrys Laboratory MedicineDocument43 paginiMedical Bacteriology, Henrys Laboratory MedicineRikkachuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions ExplanationDocument63 paginiQuestions ExplanationnomintmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Staphylococci PDFDocument9 paginiStaphylococci PDFGianina YlnÎncă nu există evaluări