Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Universe
Încărcat de
Dexter0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
25 vizualizări1 paginăTitlu original
universe
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
25 vizualizări1 paginăUniverse
Încărcat de
DexterDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
The
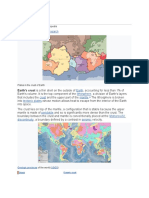
universe (Latin: universus) is all of space and time[a] and their contents,
[10]
including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is
the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. According to estimation
of this theory, space and time emerged together 13.799±0.021 billion years ago,[2] and the universe
has been expanding ever since. While the spatial size of the entire universe is unknown,[3] it is
possible to measure the size of the observable universe, which is currently estimated to be 93
billion light-years in diameter.
The earliest cosmological models of the universe were developed by ancient Greek and Indian
philosophers and were geocentric, placing Earth at the center.[11][12] Over the centuries, more precise
astronomical observations led Nicolaus Copernicus to develop the heliocentric model with the Sun at
the center of the Solar System. In developing the law of universal gravitation, Isaac Newton built
upon Copernicus's work as well as Johannes Kepler's laws of planetary motion and observations
by Tycho Brahe.
Further observational improvements led to the realization that the Sun is one of hundreds of billions
of stars in the Milky Way, which is one of a few hundred billion galaxies in the universe. Many of the
stars in our galaxy have planets. At the largest scale, galaxies are distributed uniformly and the
same in all directions, meaning that the universe has neither an edge nor a center. At smaller scales,
galaxies are distributed in clusters and superclusters which form immense filaments and voids in
space, creating a vast foam-like structure.[13] Discoveries in the early 20th century have suggested
that the universe had a beginning and that space has been expanding, since then,[14] and is currently
still expanding at an increasing rate.[15]
According to the Big Bang theory, the energy and matter initially present have become less dense as
the universe expanded. After an initial accelerated expansion called the inflationary epoch at around
10−32 seconds, and the separation of the four known fundamental forces, the universe gradually
cooled and continued to expand, allowing the first subatomic particles and simple atoms to
form. Dark matter gradually gathered, forming a foam-like structure of filaments and voids under the
influence of gravity. Giant clouds of hydrogen and helium were gradually drawn to the places where
dark matter was most dense, forming the first galaxies, stars, and everything else seen today.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Course Catalog: Graduation Requirements - Secondary Program Options Planning Guide For Katy ISD Students, Grades 6 - 12Document156 paginiCourse Catalog: Graduation Requirements - Secondary Program Options Planning Guide For Katy ISD Students, Grades 6 - 12Eddy YusufÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Modeling and Analysis With Induction Generators Third EditionDocument1 paginăModeling and Analysis With Induction Generators Third Editionzahid afzal thokerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glass: Definition of Glass (Entry 2 of 4)Document2 paginiGlass: Definition of Glass (Entry 2 of 4)DexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synonyms & Antonyms of Mop: Save Word To Save This Word, You'll Need To Log inDocument6 paginiSynonyms & Antonyms of Mop: Save Word To Save This Word, You'll Need To Log inDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Tectonic Plates: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument2 paginiList of Tectonic Plates: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- BottleDocument3 paginiBottleDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verb (1) : Synonyms & Antonyms of Wax (Entry 1 of 2)Document7 paginiVerb (1) : Synonyms & Antonyms of Wax (Entry 1 of 2)DexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jump To Navigation Jump To Search: For Other Uses, SeeDocument3 paginiJump To Navigation Jump To Search: For Other Uses, SeeDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth's Crust: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument2 paginiEarth's Crust: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gravitational Wave: General RelativityDocument3 paginiGravitational Wave: General RelativityDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inertia: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument5 paginiInertia: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- General RelativityDocument4 paginiGeneral RelativityDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metrology: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument4 paginiMetrology: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oxygen: Allotropes of Oxygen Oxygen (Disambiguation) O2 (Disambiguation)Document5 paginiOxygen: Allotropes of Oxygen Oxygen (Disambiguation) O2 (Disambiguation)DexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matter Mass (Liturgy) Mass (Disambiguation) : Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument4 paginiMatter Mass (Liturgy) Mass (Disambiguation) : Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- DDR Sdram: and TypesDocument13 paginiDDR Sdram: and TypesDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum: Etymology and DiscoveryDocument3 paginiQuantum: Etymology and DiscoveryDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semiconductor Memory: Computer Memory Data StorageDocument9 paginiSemiconductor Memory: Computer Memory Data StorageDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Backplane: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument4 paginiBackplane: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Buffer: ApplicationsDocument2 paginiData Buffer: ApplicationsDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multi-Channel Memory Architecture: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument3 paginiMulti-Channel Memory Architecture: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument3 paginiComputer: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cientific Calculator: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument6 paginiCientific Calculator: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synchronization: TransportDocument3 paginiSynchronization: TransportDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Observable Universe: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument6 paginiObservable Universe: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ancient Egyptian Royal CubitDocument2 paginiAncient Egyptian Royal CubitDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument6 paginiMathematics: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Origins of Babylonian Mathematics: Babylonian Mathematics (Also Known As Assyro-Babylonian MathematicsDocument3 paginiOrigins of Babylonian Mathematics: Babylonian Mathematics (Also Known As Assyro-Babylonian MathematicsDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jump To Navigationjump To Search: This Article Is About The Astronomical Objects. For Other Uses, SeeDocument6 paginiJump To Navigationjump To Search: This Article Is About The Astronomical Objects. For Other Uses, SeeDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orbital Period: AstrodynamicsDocument5 paginiOrbital Period: AstrodynamicsDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculator: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument12 paginiCalculator: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDexterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal Ilmiah KKNDocument6 paginiJurnal Ilmiah KKNIlhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Australian Curriculum Correlation Grid: Pearson Science 9Document13 paginiAustralian Curriculum Correlation Grid: Pearson Science 9FlaaffyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Papers 2016 Balochistan University BA BSC EnglishPast PapersDocument3 paginiPast Papers 2016 Balochistan University BA BSC EnglishPast PapersJunaidAhmed saÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Copy Lesson 1Document3 paginiScience Copy Lesson 1Mhie RelatorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document17 paginiChapter 1Cassie CabidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5 - Knowledge and Expert SystemsDocument59 paginiLecture 5 - Knowledge and Expert SystemsBii PeterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theories of ChangeDocument20 paginiTheories of ChangeVictória Agelune MaiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PP 6Document7 paginiPP 6yuva rajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental EducationDocument3 paginiEnvironmental EducationKimberly Unice100% (1)
- A Physicist Experiments With Cultural StudiesDocument4 paginiA Physicist Experiments With Cultural StudiespaulicalejerÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Routledge Concise Histories of Literature) Mark Bould, Sherryl Vint - The Routledge Concise History of Science Fiction-Routledge (2011)Document260 pagini(Routledge Concise Histories of Literature) Mark Bould, Sherryl Vint - The Routledge Concise History of Science Fiction-Routledge (2011)lyn.ballegeerÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRACTICAL RESEARCH Midterm ExaminationDocument2 paginiPRACTICAL RESEARCH Midterm ExaminationValencia MyrhelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Evolution of Forces PDFDocument442 paginiThe Evolution of Forces PDFTodor RadovanovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Position Paper ABC FinalDocument13 paginiPosition Paper ABC FinalAdams IssakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Papers and Courses B.A (Honours) Political Science A) Core CourseDocument6 paginiList of Papers and Courses B.A (Honours) Political Science A) Core CourseBhoomika MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Ethics of Artificial Intelligence: Recommendation OnDocument44 paginiThe Ethics of Artificial Intelligence: Recommendation OnYohanes Adolf GusmoriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Claudio Galeno de PérgamoDocument2 paginiClaudio Galeno de PérgamoMade LascanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Home: Correspondence:: Ala N Aragon's Research Review - November 2020)Document24 paginiHome: Correspondence:: Ala N Aragon's Research Review - November 2020)Efrain SneiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human ConsciousnessDocument6 paginiHuman ConsciousnessBalasubramanian GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architectural Design 1 - Lecture 10 - Problem SeekingDocument24 paginiArchitectural Design 1 - Lecture 10 - Problem SeekingAL HAYUDINIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Course OutlineDocument6 paginiResearch Course Outlinenejib beharuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research 1Document125 paginiResearch 1VieDon Austria-FeranilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speciality Astrology BooksDocument5 paginiSpeciality Astrology BooksmoÎncă nu există evaluări
- P2015 List of StudsDocument5 paginiP2015 List of StudsAshish PÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alignment Tests On LatheDocument62 paginiAlignment Tests On LatheCharles OndiekiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pluto Press The Reform of Time Magic and Modernity Mar 2001 PDFDocument166 paginiPluto Press The Reform of Time Magic and Modernity Mar 2001 PDFJuan Sebastian Correa100% (1)
- Computers & Education: MD Abdullah Al Mamun, Gwendolyn Lawrie, Tony Wright TDocument17 paginiComputers & Education: MD Abdullah Al Mamun, Gwendolyn Lawrie, Tony Wright TBoi HendratmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ignou Dissertation SampleDocument5 paginiIgnou Dissertation SampleIWillPayYouToWriteMyPaperSingapore100% (1)