Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
The Cardiovascular System
Încărcat de
RachelHatcher1230 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
105 vizualizări3 paginiCardiovascular system is responsible for carrying essential products to tissue cells. It is also responsible for removing waste products such as carbon dioxide. The respiratory system takes in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide in the lungs. The systemic circuit involves the left ventricle and the right atrium and links to the rest of the body.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
The Cardiovascular system
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentCardiovascular system is responsible for carrying essential products to tissue cells. It is also responsible for removing waste products such as carbon dioxide. The respiratory system takes in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide in the lungs. The systemic circuit involves the left ventricle and the right atrium and links to the rest of the body.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
105 vizualizări3 paginiThe Cardiovascular System
Încărcat de
RachelHatcher123Cardiovascular system is responsible for carrying essential products to tissue cells. It is also responsible for removing waste products such as carbon dioxide. The respiratory system takes in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide in the lungs. The systemic circuit involves the left ventricle and the right atrium and links to the rest of the body.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
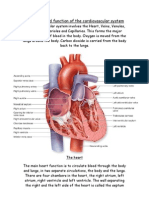
The Cardiovascular system
The cardiovascular system is responsible for carrying essential
products to tissue cells such as food, oxygen and other
nutrients. It is also responsible for removing waste products
such as carbon dioxide. There are two cycles that we refer to
when talking about the
cardiovascular system, the
pulmonary and the systemic.
Pulmonary circuit involves the left
atrium and the right ventricle and
links to the lungs. The systemic
circuit involves the left ventricle and
the right atrium and links to the
rest of the body. The respiratory
system is the stage that will take in
oxygen and remove carbon dioxide in
the lungs. As we breathe in we fill
our lungs with oxygen, as we breathe out we get rid of the
carbon dioxide. Oxygen moves from the lungs into the blood by
diffusion. The newly oxygenated blood travels through the
capillaries into the arterioles and then into the artery. The
artery carrying the oxygenated blood links to the left atrium in
the heart. The atrium is at the relaxed stage which is referred
to as atrial diastole. This oxygen rich blood fills up the left
atrium, the only thing stopping this blood moving into the
ventricle is the mitral valve. An increases pressure in the
atrium will cause the mitral valve to open, the atrium will now
contract to remove all the blood and allow the blood through
into the left ventricle once the blood is through the mitral
valve shuts. This means the blood is now increasing the
pressure in the left ventricle. The left ventricle now contains
the oxygenated blood which needs to be pumped around the
rest of the body. The ventricle forces the blood out through
the aortic valve, the blood will then travel through
the aorta. The aorta is the largest artery in the
body, it carries the blood to the rest of the body
and has many arteries branching off it. Blood and
blood vessels transport oxygen to the tissues and
muscles and then removes the carbon dioxide and
other waste products from the muscles and
tissues. Once the oxygen in the blood has been
used up by the muscles and tissues the blood now
need to travel
back to the lungs to collect
more oxygen and remove
the carbon dioxide. The
blood travels through the
vena cava and other veins
and venules back to the
heart. The vena cava links
to the right atrium. There
are two parts to the vena
cava, the superior and the
inferior. The superior
returns blood from the top
half of the body and the
inferior from the bottom half of the body. The deoxygenated
blood will fill up the right atrium and will increase the pressure
until the tricuspid valve is forced open. A contraction to
remove all blood from the atrium occurs and pumps the blood
through to the right ventricle. The right ventricle fills up with
the deoxygenated blood and now must force the blood up
through the pulmonary valve in the pulmonary artery to the
lungs. The carbon dioxide will be removed and the oxygen rich
blood will then start the cycle again. This is a continuous cycle,
we need our body to supply our muscles and tissue cells with
oxygen and remove the carbon dioxide.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Structure and Function of Sports Development ProvidersDocument1 paginăStructure and Function of Sports Development ProvidersRachelHatcher123Încă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Function of The Respiratory SystemDocument5 paginiFunction of The Respiratory SystemRachelHatcher123Încă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Barriers To Participation Sport DevDocument6 paginiBarriers To Participation Sport DevRachelHatcher12371% (7)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 paginiStructure and Function of The Cardiovascular SystemRachelHatcher123Încă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Sports DevelopmentDocument11 paginiSports DevelopmentRachelHatcher123Încă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in SportDocument20 paginiPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology in SportRachelHatcher123Încă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Techniques Used by Coaches To Improve The PerformanceDocument7 paginiTechniques Used by Coaches To Improve The PerformanceRachelHatcher123Încă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- 9700:MJ:23:2014Document12 pagini9700:MJ:23:20147yvgnjjjm2Încă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Mark Scheme (Results) : January 2017Document23 paginiMark Scheme (Results) : January 2017Raashed RamzanÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Scientech 2357: Scope of LearningDocument1 paginăScientech 2357: Scope of LearningSudip KunduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Form 5 Biology Chapter 1 TransportDocument12 paginiForm 5 Biology Chapter 1 TransportMohdAmerAhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- LP On 9.2 - HeartDocument3 paginiLP On 9.2 - Heartibrahim khalilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Alterations in Oxygenation 1Document15 paginiAlterations in Oxygenation 1alejandrino_leoaugustoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Golden File 3, September, Oct, November 2016 All Papers PDFDocument219 paginiGolden File 3, September, Oct, November 2016 All Papers PDFDr gigglesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Biology Notes Paper 1 (Finnished)Document92 paginiBiology Notes Paper 1 (Finnished)michaela menzelÎncă nu există evaluări
- A&P Cardiovascular System PowerPoint (Nursing)Document34 paginiA&P Cardiovascular System PowerPoint (Nursing)Linsey Bowen67% (6)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Silk Worm Enzymes For Carotid Artery BlockageDocument2 paginiSilk Worm Enzymes For Carotid Artery BlockageRoger-Peter Weizenegger100% (2)
- Medical Terms Related To Cardiovascular SystemDocument2 paginiMedical Terms Related To Cardiovascular SystemFarah AninditaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sim 2015Document16 paginiSim 2015Mary Grace A. BarridaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYS 3616E Chap91Document15 paginiPHYS 3616E Chap91johnÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Animals SurviveDocument69 paginiHow Animals SurviveMichael Daryl GalsimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Animals: Don't GetDocument308 paginiWhy Animals: Don't Getioan ispasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory & Circulatory SystemDocument6 paginiRespiratory & Circulatory SystemJanelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemodynamic Disorders: BY Dr. Birhane H (MD)Document88 paginiHemodynamic Disorders: BY Dr. Birhane H (MD)Biruck BirhanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Rol HPNDocument5 paginiRol HPNOamaga NajlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PAL: Cadaver Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels Lab Practical Question 2Document44 paginiPAL: Cadaver Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels Lab Practical Question 2Mariam DuhainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulation. Lec On HemodynamicsDocument30 paginiCirculation. Lec On HemodynamicsMudassar RoomiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathology - Cardiovascular SystemDocument17 paginiPathology - Cardiovascular SystemNdegwa Jesse100% (2)
- Gambaran Radiologi Anatomi Sistem Peredaran Darah Dan JantungDocument26 paginiGambaran Radiologi Anatomi Sistem Peredaran Darah Dan JantungBocah nakalÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Body Fluids and CirculatoinDocument34 paginiBody Fluids and CirculatoinPrasmita BeheraÎncă nu există evaluări
- McDonald John - Chinese Versus French Perspectives On The Channel SystemDocument17 paginiMcDonald John - Chinese Versus French Perspectives On The Channel SystemAssaf FeldmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summarized Notes Core 1 Health Priorities in AustraliaDocument21 paginiSummarized Notes Core 1 Health Priorities in AustraliaHaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Umbilical Artery CatheterizationDocument11 paginiUmbilical Artery CatheterizationRhaq Sheldon-CoelhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dáp An AvDocument32 paginiDáp An AvDũngNguyễnHữu100% (1)
- Enteral Nutrition Support Assignment 72618Document8 paginiEnteral Nutrition Support Assignment 72618api-341835458100% (1)
- 8 PHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES IN AGING AFFECTING VARIOUS SYSTEMS 2nd PartDocument9 pagini8 PHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES IN AGING AFFECTING VARIOUS SYSTEMS 2nd Partgwen manalonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- COPD Case StudyDocument10 paginiCOPD Case Studyskylineco4Încă nu există evaluări