Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
1 2 Ist
Încărcat de
deepeshmathurDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1 2 Ist
Încărcat de
deepeshmathurDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Information Science and Technology, ISSN: 0976-917X & ISSN: 0976-9188, Vol.
1, Issue 1, 2010, PP-06-08
GPS (Global Positioning System) and its application in protection scheme
Anuashka Sharma*, Aakanksha Girolkar and Ankit Shrivastava
*Department of Electrical Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Raipur, G.E. Road, Raipur,
Chhatisgarh, 492010, India
Abstract- This is a new technique for the protection of transmission systems by using Global
Positioning Systems(GPS) and fault generated transients .In this scheme the relay contains a full
transient detection system together with a communication unit which is connected to the power line
through the high voltage coupling capacitor of the CVT(Capaitive Voltage Transformer). Relays are
installed at each busbar in transmission network. These detect the fault generated high frequency
voltage transient signal and record the time instant corresponding to when the initial travelling wave
generated by the fault arises at the busbar. The decision to trip is based on the components as they
propagate through the system.
Keywords- GPS, Fault detection, Transient analysis, Transient wave based protection scheme, fault
current, signal processing
INTRODUCTION
What is GPS:-The GPS is satellite based slower decaying tail. Composite waves have a
navigation system made up of a network of 24 propagation velocity and characteristic
satellites placed into orbit. Current GPS impedance and travel near the speed of light
enables users to determine their 3-D(Three away from the fault location towards line end.
Dimensional) differential position, velocity and They continue to travel throughout the power
time. By combining GPS with current and system until they diminish due to impedance
future computer mapping techniques we will and reflection waves and new power system
be better able to identify and manage our equilibrium is reached. The faults can be
natural resources. GPS satellite circles the located by precisely time-tagging the wave
earth twice a day and transmits signal fronts as they cross a known point typically in
information to earth. GPS receivers take this substations at line ends. Accuracy of 300 m
information and use triangulation to calculate can be obtained with time tagging the waves
the user’s exact location. Essentially the GPS with a resolution of 30m. Fault location can
receiver compares the time a signal was then be obtained by multiplying the wave
transmitted by a satellite with the time it was velocity by the time difference in line ends.
received. The time difference tells the GPS The master station performs the task of time
receiver how far away the satellite is. data collection and calculation.
DETECTION UNIT
Detection of fault current and current
transients:-During a fault on the transmission
line wide band voltage and current waves
travel throughout the transmission line away
from the fault point. When these signals reach
discontinuities on the transmission line some
of the signals are reflected back towards the
fault point. The characteristics of these waves
are determined by several factors such as
position of fault on the line, fault path
resistance and the characteristic impedance of
the transmission line. Relays located at each
substation in the power system independently
monitor the power system. The frequency
Dia. 1 range for monitoring these fault generated
high frequency signals is between 40-80 KHz
Travelling Wave Fault location and the signal processing unit is designed
Faults on the power transmission system accordingly to detect the arrival of a high
cause transients that propagate along the frequency transient characteristic of those
transmission line as waves. Each wave generated by a fault. At these frequencies ,
consists of several frequency components bus bars are dominated by their capacitive
ranging from a few kilohertz to several elements , and as a result, the incoming high
megahertz, having a fast rising front and a
Copyright © 2010, Bioinfo Publications
Information Science and Technology, ISSN: 0976-917X & ISSN: 0976-9188, Vol. 1, Issue 1, 2010
Anuashka Sharma, Aakanksha Girolkar and Ankit Shrivastava
frequency current signal is both inverted and away from the fault point in both directions
reflected .A resistive fault in this frequency along the transmission system with velocity
range will also reflect a current wave of the close to the speed of light. It has been long
opposite polarity. recognized that the actual faulted position can
be determined on line if the transient signals
Fault current transient detector are time tagged at key points on the power
A specially designed transient current detector system network. The global positioning
fed from the primary CTs(Current system, with its ability to provide
Transformers) is employed which extracts synchronization with an accuracy of
high frequency signals associated with the microsecond over the wide area, provides an
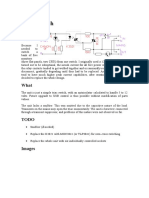
fault generated current transients. A simplified ideal tool for performing time tagging of the
block diagram of the detector arrangement is fault generated transients.
shown in the figure (1).The circuit comprises of Basic Principle:-The basic principle of the
an analogue input circuit for signal technique can be demonstrated by referring to
conditioning and a digital circuit for the 400KV, EHV(Electrical High Voltage)
determining the transients. Particular transmission network, shown in figure(2).
emphasis has been placed on the Relays are installed at the bus bars P,Q,R and
development of digital circuit. The detector is S and are responsible for the protection of the
designed to interrogate signals in the range of network . The protection of the network PQR
frequencies from 40-80KHz. Analog circuit and tripping of the breakers associated with
extracts the band of fault generated transient that network is studied. High frequency signals
current signal from the line by acting as a band are generated at the fault point and travel
pass filter. As a result, the response of the outward from that point along the network
scheme is not affected by the power frequency conductors. In time they reach the monitored
short circuit band at the busbar or the precise bus bar are detected by the relays connected
configuration of the source side networks. to them. Each relay record the arrival instant of
the signal generated by the fault. The recorded
Signal Processing unit arrival instant is then code with details of their
The signal is decoupled into its respective identification by the relays and transmits this to
aerial modes by using model transformation. their neighboring relays. All relays are
The signal mixing circuit is fed from the 3 continuously ready to receive the coded
phase CTs continue to form mode2 and messages send by other devices. Data
mode3 signals. There are filters to remove any protocols are used to avoid conflict between
spurious noise. The outputs of the analog information sent by different devices along the
circuit are then passed to the digital circuit. same line. The relays compare the fault
The sampling frequency of the analog to digital transient arrival time recorded at its sight with
A/D converter is 1 MHz and the speed of those send by other relays and determine
propagation of the high frequency transient is whether the fault is within the protected zone.
similar to the speed of light. The digital Appropriate tripping instructions are then send
processing unit includes filters sequence to the relevant local circuit breakers. The
recording, ampldoitude comparison, counters actual location where the fault occurs can be
and decision logic. clearly identified at each relay location by this
method.
Relay design:- A simplified block diagram of
PRINCIPLE AND DESIGNING the relay unit is shown in fig(3). Three CVTs
Basic principle and relay design:- A short connect the transient detector unit to the line
circuit fault on a power transmission line and detect the voltage signal level. The
generates voltages and current signals of communication unit also uses CVTs and a
several frequency range which propagate
Copyright © 2010, Bioinfo Publications 7
Information Science and Technology, ISSN: 0976-917X & ISSN: 0976-9188, Vol. 1, Issue 1, 2010
GPS (Global Positioning System) and its application in protection scheme
hybrid unit to connect the two circuits i.e., ABBREVIATIONS
Transmitter and Receiver circuits. GPS- Global Positioning System
The transient detector is used to detect the CVT-Capacitive Voltage Transformer
fault generated signals and to record the time 3-D- Three Dimensional
tag obtained from the GPS receiver. All the KHz-Kilo Hertz
relays connected to the system receive this CT- Current Transformer
time tag information from the transmitter A/D Convertor- Analog to Digital Convertor
circuit. Previous research has investigated the MHz- Mega Hertz
use of digital filters to detect the high KV- Kilo Volt
frequency signals generated by the fault and EHV- Extra High Voltage
had shown that the accuracy of fault location CB- Circuit Breaker
was a function of the sampling rate used to GPS CLK – Global Positioning System Clock
digitalize the measured signal. The accuracy
was directly related to the sampling rate and REFERENCES
higher the sampling rate, the more accurate [1] http://www.seminarprojects.com
the measureme. Hence continuous sampling [2] http://en.wikipedia.org
has an upperhand i.e., an analog system and [3] http://www.howstuffworks.com
a pass band filter tuned to operate between 40 [4] http://www.gpsmagazine.com
and 80 KHz. The protection technique is [5] http://www.tycho.usno.org
therefore divorced from the power system [6] http://www.google.co.in
frequency. The decision to trip the local [7] Bo Z.Q. Waller G. Lomas, T. Redfern
breaker depends on the comparison between M.A. (2000) Power delivery,IEEE
the times measured by the GPS system at that transations, 15(4), 1163-1168.
location and those measured by other relays.
Unlike the conventional protection scheme,
where each relay associates with one circuit
breaker on that line section, this relaying
scheme protects several lines connected to
the bus bar where it is installed. For e.g., as
shown in fig. the relay at bus bar “R”
responsible for the protection of both line
section , connected to the busbar, by
controlling both circuit breakers CB-RP and
CB-RQ. Therefore the technique offers a
network protection scheme rather than than
one which concentrates on specific units of
plant. This provides several technical
advantages over conventional relaying [1].
CONCLUSION
The positional protection using GPS is a high
speed protection system and offers a high
accuracy in fault location. The protection
system monitors the network to which it is
connected and is not limited to individual unit
plant as in traditional protection scheme.
8 Information Science and Technology, ISSN: 0976-917X & ISSN: 0976-9188, Vol. 1, Issue 1, 2010
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Amateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileDe la EverandAmateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- HP An1285Document12 paginiHP An1285Mohamed TalebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detection of Fault Location in Transmission Line Using Internet of Things (Iot)Document3 paginiDetection of Fault Location in Transmission Line Using Internet of Things (Iot)Journal 4 ResearchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learn Amateur Radio Electronics on Your SmartphoneDe la EverandLearn Amateur Radio Electronics on Your SmartphoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protection of Transmission Line Using GPSDocument11 paginiProtection of Transmission Line Using GPSRajeswari Vayugundla100% (6)
- Trilogy of Wireless Power: Basic principles, WPT Systems and ApplicationsDe la EverandTrilogy of Wireless Power: Basic principles, WPT Systems and ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protection of Transmission Lines Using GPS: by G.S.Ramya Krishna B080614EEDocument36 paginiProtection of Transmission Lines Using GPS: by G.S.Ramya Krishna B080614EERamya Gajjarapu100% (2)
- Protection of Transmission Lines Using Gps Full ReportDocument28 paginiProtection of Transmission Lines Using Gps Full ReportRamya GajjarapuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsDe la EverandSignal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On: Digital Protection of Power SystemDocument19 paginiPresentation On: Digital Protection of Power SystemRachna JuyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protection of Transmission Line Using GPSDocument13 paginiProtection of Transmission Line Using GPSAnurag VyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fault Location in Transmission Lines Using GpsDocument15 paginiFault Location in Transmission Lines Using GpsDeepak KargetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global Position System (GPS) in Power SystemDocument17 paginiGlobal Position System (GPS) in Power Systemk rajendraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protection of Transmission Line Using GPSDocument24 paginiProtection of Transmission Line Using GPSerfan0909100% (1)
- Multipath Propagation and Its Influence On DigitalDocument19 paginiMultipath Propagation and Its Influence On Digitalthabiso.moropaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traveling WaveDocument59 paginiTraveling WaveMohit Kumar ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Measurement System For Very Fast Transients in GIS Power SubstationsDocument4 paginiA Measurement System For Very Fast Transients in GIS Power SubstationsRommel DestacamentoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protectionoftransmissionlinesusing GPSDocument19 paginiProtectionoftransmissionlinesusing GPSChaithra BRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glossary: (N K) Called A Codeword, Using AnDocument6 paginiGlossary: (N K) Called A Codeword, Using AnAliÎncă nu există evaluări
- T, Then The Range May Be Determined by The SimpleDocument5 paginiT, Then The Range May Be Determined by The SimpleSathiya NarayananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fault Location in Ehv Transmission Lines Using Artificial Neural NetworksDocument10 paginiFault Location in Ehv Transmission Lines Using Artificial Neural NetworkssahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transmission LinesDocument19 paginiTransmission LinesNavarshi VishnubhotlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subburaj+Et+Al 2018 Monitoring+Architecture+for+a+76-81GHz+Radar+Front+EndDocument4 paginiSubburaj+Et+Al 2018 Monitoring+Architecture+for+a+76-81GHz+Radar+Front+Endzx DÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation and Analysis of Transmission Line Fault Detection and Location Using Fuzzy LogicDocument8 paginiSimulation and Analysis of Transmission Line Fault Detection and Location Using Fuzzy LogicFocus OnÎncă nu există evaluări
- 192 202 SamDocument10 pagini192 202 SamLinwan AbadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Partial Discharge Detection by Using ComDocument21 paginiPartial Discharge Detection by Using ComsunilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 453Document10 paginiPaper 453Aleksa SaricÎncă nu există evaluări
- SeminarDocument31 paginiSeminarDhivya GunasekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Passive Telemetric Readout System: Sajeeda and Todd J. Kaiser, Member, IEEEDocument6 paginiPassive Telemetric Readout System: Sajeeda and Todd J. Kaiser, Member, IEEEPhong Đào Văn HoàngÎncă nu există evaluări
- UPFC Based Distance Relays For Protection of Transmission Systems Employing FACTSDocument4 paginiUPFC Based Distance Relays For Protection of Transmission Systems Employing FACTSShiv TripathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Phase Fault Detection System in Transmission Line Using ArduinoDocument10 paginiThree Phase Fault Detection System in Transmission Line Using ArduinoKusha SatapathyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instrumentation and Measurement (Chapter 4)Document10 paginiInstrumentation and Measurement (Chapter 4)regassa rajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traveling Wave Fault Location in Protective RelaysDocument14 paginiTraveling Wave Fault Location in Protective RelaysFJRVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Telemetry Encoder PDFDocument5 paginiTelemetry Encoder PDFAleem AzharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peterson CoilDocument6 paginiPeterson CoilDeepika GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- A New Algorithm To Prevent Maloperation of Distance Protection Zone 3 During Wide Are DisturbancesDocument13 paginiA New Algorithm To Prevent Maloperation of Distance Protection Zone 3 During Wide Are DisturbanceskponramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protectoin of Transmission Lines Using GPS: Submitted By: Monalisha Dash Branch: Electrical Regd No: 0701208143Document21 paginiProtectoin of Transmission Lines Using GPS: Submitted By: Monalisha Dash Branch: Electrical Regd No: 0701208143Monalisha Dash100% (1)
- Microwave Sensor Technology HFE0407 - PolivkaDocument8 paginiMicrowave Sensor Technology HFE0407 - Polivkatecnolectronica890Încă nu există evaluări
- New Technique For The Protection of A Transmission Line NetworkDocument1 paginăNew Technique For The Protection of A Transmission Line Networksagar9117Încă nu există evaluări
- Vibration and Monitoring Terms GlossaryDocument12 paginiVibration and Monitoring Terms Glossaryyaniprasetyo12Încă nu există evaluări
- Transmission Line Fault Detection Using Phasor Measurement UnitDocument13 paginiTransmission Line Fault Detection Using Phasor Measurement Unitjorbol827Încă nu există evaluări
- Protection of Transmission Line Using GPSDocument19 paginiProtection of Transmission Line Using GPSNittin BennyÎncă nu există evaluări
- S.MANJU (09E58) J.JANANI (09E32) : Submitted byDocument8 paginiS.MANJU (09E58) J.JANANI (09E32) : Submitted bysssampleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Superimposed Components Based Sub-Cycle Protection of Transmission LinesDocument6 paginiSuperimposed Components Based Sub-Cycle Protection of Transmission LinesFabien CallodÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELF Earthquake PredictionDocument8 paginiELF Earthquake PredictionRasoul KhajaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peterson Coil PDFDocument6 paginiPeterson Coil PDFDeepika GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- A New Approach Distance Protection Using: FOR Artificial Neural NetworkDocument5 paginiA New Approach Distance Protection Using: FOR Artificial Neural NetworkMedo PriensÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traveling Wave Fault Location On HVDC LinesDocument16 paginiTraveling Wave Fault Location On HVDC LinesJonathan ManzakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Improving Relay Reach and Speed Through A Hybrid AlgorithmDocument6 paginiImproving Relay Reach and Speed Through A Hybrid AlgorithmGokul DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Power System ProtectionDocument22 paginiFundamentals of Power System ProtectionKGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Load Switching MonitoringDocument4 paginiPower System Load Switching MonitoringChowdhury, A HasibÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Wavelet Multiresolution Analysis For Location of Faults On Transmission LinesDocument11 paginiA Wavelet Multiresolution Analysis For Location of Faults On Transmission LinesengshimaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual on-Cellular-Mobile-CommunicationDocument42 paginiManual on-Cellular-Mobile-CommunicationAnonymous 1XnVQmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time Domain Reflectometry Theory: Application NoteDocument16 paginiTime Domain Reflectometry Theory: Application NoteyadamyugandharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec 71 QBDocument16 paginiEc 71 QBepregithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 2 - Vector Network Analyzer MeasurementDocument25 paginiExperiment 2 - Vector Network Analyzer MeasurementBadut234Încă nu există evaluări
- Cognitive Transceiver ArchitectureDocument7 paginiCognitive Transceiver ArchitectureGaurav MorghareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calibration of Linear Displacement Sensor Systems Used To Measure MicromotionDocument4 paginiCalibration of Linear Displacement Sensor Systems Used To Measure MicromotionAhmad Zubair RasulyÎncă nu există evaluări
- M48T02 M48T12: 5.0 V, 16 Kbit (2 KB X 8) TIMEKEEPER SramDocument26 paginiM48T02 M48T12: 5.0 V, 16 Kbit (2 KB X 8) TIMEKEEPER SramMgc ElektronikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research PaperDocument11 paginiResearch Paperapi-466416222Încă nu există evaluări
- Infineon ICE2QS03 DS v02 - 02 en PDFDocument19 paginiInfineon ICE2QS03 DS v02 - 02 en PDFWilliam Rodriguez BermudezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalog 2010Document23 paginiCatalog 2010fernanguedes2071Încă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Circuits - 1 Unit - 3 Small Signal Analysis of JFET and MOSFET Amplifiers Biasing of Fet Amplifiers Fixed BiasDocument17 paginiElectronic Circuits - 1 Unit - 3 Small Signal Analysis of JFET and MOSFET Amplifiers Biasing of Fet Amplifiers Fixed BiasMutharasu SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time Delay CircuitDocument3 paginiTime Delay CircuitKarina DovigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DL413 Rev 1 Motorola Radio RF and Video Applications 1994Document474 paginiDL413 Rev 1 Motorola Radio RF and Video Applications 1994kopcicleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Riviera RLCD 32pafDocument45 paginiRiviera RLCD 32pafJohan MantuanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flip FlopDocument26 paginiFlip FlopFrancesco De FlorenceÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Health Informatics) Morris F. Collen, Marion J. Ball (Eds.) - The History of Medical Informatics in The United States-Springer-Verlag London (2015)Document769 pagini(Health Informatics) Morris F. Collen, Marion J. Ball (Eds.) - The History of Medical Informatics in The United States-Springer-Verlag London (2015)atikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Triac SwitchDocument19 paginiTriac SwitchFernando SotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skiip Complete Data SheetDocument27 paginiSkiip Complete Data Sheetjmgyuyu0% (1)
- TX6CRX6C New PDFDocument9 paginiTX6CRX6C New PDFbilalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edge Detection (RC and NAND)Document6 paginiEdge Detection (RC and NAND)librian_30005821Încă nu există evaluări
- Current Sensor Ic 4017Document55 paginiCurrent Sensor Ic 4017Alan RejiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Depletion Mode MosfetDocument19 paginiDepletion Mode MosfetSunil PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- FINAL - DLOG LABORATORY MANUAL v.11Document143 paginiFINAL - DLOG LABORATORY MANUAL v.11Blessa BernabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDC Lab ManualDocument71 paginiPDC Lab Manualswapnadeepika100% (3)
- Features Description: D D D D D D D D D D D DDocument19 paginiFeatures Description: D D D D D D D D D D D DCarlos ReisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pair Task Activity #03-00-05 555 LED Flasher: ComponentsDocument3 paginiPair Task Activity #03-00-05 555 LED Flasher: ComponentsRissy Kh XhieÎncă nu există evaluări
- UcD Patent US20050162228A1Document9 paginiUcD Patent US20050162228A1Luis ValerianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Digi Encoder E5n-D0360-5m0mcDocument17 paginiManual Digi Encoder E5n-D0360-5m0mcAlejandra PadillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data SheetDocument8 paginiData SheetmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power SytemsDocument6 paginiPower SytemsAshwin RaghavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Over and Under Voltage Protection RelayDocument44 paginiOver and Under Voltage Protection RelaySeven Hills100% (3)
- Logic GatesDocument29 paginiLogic Gatesamit meelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multisim Fundamentals PDFDocument51 paginiMultisim Fundamentals PDFDulshan DulshannÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7VE6xxx Manual A2 V041003 enDocument314 pagini7VE6xxx Manual A2 V041003 enArnab DeÎncă nu există evaluări
- SyllDocument16 paginiSyllraj8bhondÎncă nu există evaluări
- RLC 1st ManualDocument141 paginiRLC 1st Manualjaved shaikh chaandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNDe la EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsDe la EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Hacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.De la EverandHacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsDe la EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA Certification Study Guide, Volume 2: Exam 200-301De la EverandCCNA Certification Study Guide, Volume 2: Exam 200-301Încă nu există evaluări
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityDe la EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (13)
- PHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZDe la EverandPHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsDe la EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksDe la EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- Cybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringDe la EverandCybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (40)
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionDe la EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamDe la EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataDe la EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (22)
- Microsoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900De la EverandMicrosoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900Încă nu există evaluări
- Designing and Building Security Operations CenterDe la EverandDesigning and Building Security Operations CenterEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (3)
- Unlock Any Roku Device: Watch Shows, TV, & Download AppsDe la EverandUnlock Any Roku Device: Watch Shows, TV, & Download AppsÎncă nu există evaluări
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamDe la EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachDe la EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Hacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxDe la EverandHacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (67)
- Kali Linux Network Scanning Cookbook - Second EditionDe la EverandKali Linux Network Scanning Cookbook - Second EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationDe la EverandPractical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Mastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionDe la EverandMastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionÎncă nu există evaluări