Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
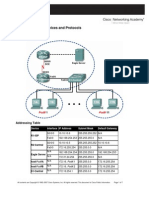
Namespaces and Assemblies: Contact
Încărcat de
Richard GonzalezDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Namespaces and Assemblies: Contact
Încărcat de
Richard GonzalezDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Rebex.NET: POP3 Tutorial http://www.rebex.net/mail.net/tutorial-pop3.
aspx
Login
Contact
About Rebex
Contact
Our customers
News
Jobs
Back to tutorial list...
Table of content
Namespaces and assemblies
POP3 basics - connecting, logging in and disconnecting
Authenticating to a POP3 server
Authentication using NTLM
Obtaining info about the mailbox
Sequence numbers and unique IDs
Retrieving the message list
Downloading message headers
Downloading messages
Deleting and undeleting messages
Using events and logging communication
# Namespaces and assemblies
There are two assemblies which have to be reference in your project to be able to use all features of Mail for .NET
described here. Rebex.Net.Pop3.dll is needed for any POP3 operations and contains the Pop3 class and others in
Rebex.Net namespace. Rebex.Mail.dll contains classes that make it possible to read, create and write e-mail
messages in MIME format and contains the MailMessage class in Rebex.Mail namespace and a number of classes
that represent mail message headers in Rebex.Mime.Headers namespace.
To gain access to all described functionality, reference the two assemblies from your project and import the following
namespaces in your source files:
C#
using Rebex.Net;
using Rebex.Mail;
using Rebex.Mime.Headers;
VB.NET
Imports Rebex.Net
Imports Rebex.Mail
Imports Rebex.Mime.Headers
back to top...
# POP3 basics - connecting, logging in and disconnecting
Typical POP3 session goes like this:
2 de 12 28/03/2011 09:54 a.m.
Rebex.NET: POP3 Tutorial http://www.rebex.net/mail.net/tutorial-pop3.aspx
Connect to the POP3 server
Login - authenticate with user name and password
Work with messages in your mailbox
Disconnect
POP3 is basically a single-session and single-folder protocol. While you are connected and authenticated, you are not
going to be informed when any new message arrives, and you only have access to messages that were available at the
time of authentication. Because of this, many POP3 servers only allow a single session for a single account at a time, so
don't forget to call Disconnect method when you are done with the mailbox, or you might experience problems
connecting again until the previous session either expires or the Ftp object is claimed by .NET's garbage collector. Also,
due to the nature of the POP3 protocol, you will need to connect periodically if you wish to check for new messages.
And now let's look at some sample code.
C#
using Rebex.Net;
...
// create client and connect
Pop3 client = new Pop3();
client.Connect("pop3.example.org");
// authenticate
client.Login("username", "password");
// work with messages
//...
// disconnect
client.Disconnect();
VB.NET
Imports Rebex.Net
...
'create client and connect
Dim client As New Pop3
client.Connect("pop3.example.org")
'authenticate
client.Login("username", "password")
'work with messages
'...
'disconnect
client.Disconnect()
back to top...
# Authenticating to a POP3 server
The POP3 protocol supports several authentication methods. Normally, you just have to supply your credentials to the
Login method. The component will automatically choose the best (most secure) authentication method available and log
you in.
Additionally, you can retrieve the list of supported authentication methods using the Pop3 object's
3 de 12 28/03/2011 09:54 a.m.
Rebex.NET: POP3 Tutorial http://www.rebex.net/mail.net/tutorial-pop3.aspx
GetSupportedAuthenticationMethods method, and specify which one is to be used for login. (Or specify
Pop3Authentication.Auto that will do this automatically.)
C#
using Rebex.Net;
...
Pop3 client = new Pop3();
client.Connect("pop3.example.org");
// authenticate - let the component choose the best method
client.Login("username", "password");
// or choose one yourself
// client.Login("username", "password", Pop3Authentication.Plain);
VB.NET
Imports Rebex.Net
...
'create client and connect
Dim client As New Pop3
client.Connect("pop3.example.org")
'authenticate - let the component choose the best method
client.Login("username", "password")
'or choose one yourself
'client.Login("username", "password", Pop3Authentication.Plain)
back to top...
# Authentication using NTLM
By default, the Login method won't try NTLM authentication, because it might not work correctly in some situations.
However, if NTLM does work with your server, nothing stops you from using it. Just read the information on Microsoft
Exchange in the FAQ first if you use that server.
C#
// create client and connect
Pop3 client = new Pop3();
client.Connect("pop3.example.org");
// authenticate using NTLM
client.Login("domain\\username", "password", Pop3Authentication.Ntlm);
...
VB.NET
' create client and connect
Dim client As New Pop3()
client.Connect("pop3.example.org")
'authenticate using NTLM
client.Login("domain\username", "password", SmtpAuthentication.Ntlm)
4 de 12 28/03/2011 09:54 a.m.
Rebex.NET: POP3 Tutorial http://www.rebex.net/mail.net/tutorial-pop3.aspx
...
NTLM also makes it possible to authenticate as the user under whose context your application is running. This makes it
possible for the user to log in without the need to specify his or her password.
C#
// create client and connect
Pop3 client = new Pop3();
client.Connect("pop3.example.org");
// authenticate using NTLM
client.Login(Pop3Authentication.Ntlm);
...
VB.NET
' create client and connect
Dim client As New Pop3()
client.Connect("pop3.example.org")
' authenticate using NTLM's single-sign-on feature
client.Login(SmtpAuthentication.Ntlm)
...
back to top...
# Obtaining info about the mailbox
There are two pieces of information available - the number of messages in the mailbox can be obtained using the
GetMessageCount method and the total size of them using the GetMailboxSize method.
C#
// create client, connect and log in
Pop3 client = new Pop3();
client.Connect("pop3.example.org");
client.Login("username", "password");
Console.Write("Number of messages in the mailbox is: ");
Console.Write(client.GetMessageCount());
Console.WriteLine();
client.Disconnect();
VB.NET
'create client, connect and log in
Dim client As New Pop3
client.Connect("pop3.example.org")
client.Login("username", "password")
Console.Write("Number of messages in the mailbox is: ")
Console.Write(client.GetMessageCount())
Console.WriteLine()
5 de 12 28/03/2011 09:54 a.m.
Rebex.NET: POP3 Tutorial http://www.rebex.net/mail.net/tutorial-pop3.aspx
client.Disconnect()
back to top...
# Sequence numbers and unique IDs
The POP3 protocol uses two different IDs to identify messages.
ID type Description
A number between 1..[number of messages in the POP3 mailbox]. This number does
not change during POP3 session - even when one or more messages are deleted, the
int
remaining messages retaing their sequence number. However, these numbers are
sequenceNumber
specific to a single session - when you disconnect and log in again later, the same
sequence numbers will be assigned to different messages.
string Unlike sequence number, the message unique ID is permanent and does not change
uniqueID between sessions. A message will retain its unique ID until it is deleted.
Most POP3 methods that deal with messages only accept sequenceNumber as a parameter for message
identification. However, it is quite simple to map a given unique ID to a corresponding sequence number and vice-versa.
Just retrieve the message list using use GetMessageList method, use its Find method to get info about the given
message and read its UniqueId or SequenceNumber properties to get the required ID.
C#
string localPath = "";
// some valid unique ID we already retrieved in past
string uniqueId = "abcd13954986";
// create client, connect and log in
Pop3 client = new Pop3();
client.Connect("pop3.example.org");
client.Login("username", "password");
// get message list
Pop3MessageCollection messages = client.GetMessageList();
Pop3MessageInfo info = messages.Find(uniqueId);
if (info == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Message not found, probably deleted?");
}
else
{
// read the sequence number
int sequenceNumber = info.SequenceNumber;
// and use it to download the message
client.GetMessage(sequenceNumber, localPath);
}
client.Disconnect();
VB.NET
Dim localPath As String = ""
'some valid unique ID we already retrieved in past
6 de 12 28/03/2011 09:54 a.m.
Rebex.NET: POP3 Tutorial http://www.rebex.net/mail.net/tutorial-pop3.aspx
Dim uniqueId As String = "abcd13954986"
'create client, connect and log in
Dim client As New Pop3
client.Connect("pop3.example.org")
client.Login("username", "password")
'get message list
Dim messages As Pop3MessageCollection = client.GetMessageList()
Dim info As Pop3MessageInfo = messages.Find(uniqueId)
If info Is Nothing Then
Console.WriteLine("Message not found, probably deleted?")
Else
'read the sequence number
Dim sequenceNumber As Integer = info.SequenceNumber
'and use it to download the message
client.GetMessage(sequenceNumber, localPath)
End If
client.Disconnect()
back to top...
# Retrieving the message list
To get a list of messages in the mailbox, call the GetMessageList method. It accepts an optional parameter that
specifies what information to retrieve from the server:
Parameter value Description
Pop3ListFields.SequenceNumber Message sequence number for current session.
Message unique ID that is permanent and does not change
Pop3ListFields.UniqueID
between sessions.
Pop3ListFields.Length Message data size in bytes.
Combination of SequenceNumber, UniqueId and Length. This
Pop3ListFields.Fast is the default for GetMessageList method if no fieldsargument
is specified.
Same as Fast, but also downloads the message headers of each
Pop3ListFields.FullHeaders message as Date, From, To, Subject or Message ID fields. This
variant is the most verbose, but also the slowest. See the next
section for more discussion about this.
These fields are bit flags, which means that combinations of SequenceNumber|Length and UniqueId|Length are
also possible - use bitwise or operator for this.
The following code shows how to download a message list and show a unique ID and From/Subject headers of each
message:
C#
// create client, connect and log in
Pop3 client = new Pop3();
client.Connect("pop3.example.org");
client.Login("username", "password");
7 de 12 28/03/2011 09:54 a.m.
Rebex.NET: POP3 Tutorial http://www.rebex.net/mail.net/tutorial-pop3.aspx
// get message list - full headers
Pop3MessageCollection messages =
client.GetMessageList(Pop3ListFields.FullHeaders);
// display info about each message
Console.WriteLine("UID | From | To | Subject");
foreach (Pop3MessageInfo message in messages)
{
Console.WriteLine
(
"{0} | {1} | {2} | {3}",
message.UniqueId,
message.From,
message.To,
message.Subject
);
}
client.Disconnect();
VB.NET
'create client, connect and log in
Dim client As New Pop3
client.Connect("pop3.example.org")
client.Login("username", "password")
'get message list - full headers
Dim messages As New Pop3MessageCollection
messages = client.GetMessageList(Pop3ListFields.FullHeaders)
'display info about each message
Console.WriteLine("UID | From | To | Subject")
Dim message As Pop3MessageInfo
For Each message In messages
Console.WriteLine( _
"{0} | {1} | {2} | {3}", _
message.UniqueId, _
message.From, _
message.To, _
message.Subject)
Next
client.Disconnect()
back to top...
# Downloading message headers
The simplest method for downloading all message headers is to call GetMessageList with parameter
Pop3ListFields.FullHeaders, as described in the Retrieving the message list tutorial. It retrieves headers for all
messages in the mailbox.
However, as mentioned earlier, this might take a very long time if there are too many messages in the mailbox or the
connection bandwidth is limited. If this is the case, it is advisable to only ask for the message list with the IDs and length
(Pop3ListFields.Fast) and retrieve message headers of each message separately using the GetMessageInfo
method - and this can even be done later or only when needed.
8 de 12 28/03/2011 09:54 a.m.
Rebex.NET: POP3 Tutorial http://www.rebex.net/mail.net/tutorial-pop3.aspx
C#
// create client, connect and log in
Pop3 client = new Pop3();
client.Connect("pop3.example.org");
client.Login("username", "password");
int sequenceNumber = 1; // the first message
Pop3MessageInfo info = client.GetMessageInfo
(
sequenceNumber,
Pop3ListFields.FullHeaders
);
Console.Write("Date: " + info.Date);
Console.Write("From: " + info.From);
Console.Write("Subject: " + info.Subject);
client.Disconnect();
VB.NET
'create client, connect and log in
Dim client As New Pop3
client.Connect("pop3.example.org")
client.Login("username", "password")
Dim sequenceNumber As Integer = 1 'the first message
Dim info As Pop3MessageInfo = client.GetMessageInfo( _
sequenceNumber, _
Pop3ListFields.FullHeaders)
Console.Write("Date: " & info.Date.ToString())
Console.Write("From: " & info.From.ToString())
Console.Write("Subject: " & info.Subject)
client.Disconnect()
back to top...
# Downloading messages
Finally, let's start downloading some messages! It is very simple - just call the GetMailMessage method and you
retrieve an instance of the MailMessage class that contains the message corresponding to the supplied sequence
number. You can read message headers, body and attachments from it, modify it, save it to disk or send it again using
our Smtp class. For more info about this, check out our MailMessage class tutorial.
Alternatively, if all you need is to download the message data and save it to disk or write it into a stream, and you don't
need to access the message content in any way at the moment, just call the GetMessage method instead. This won't
return an instance of MailMessage and just writes the message data into the supplied local path or stream.
C#
// create client, connect and log in
Pop3 client = new Pop3();
client.Connect("pop3.example.org");
client.Login("username", "password");
9 de 12 28/03/2011 09:54 a.m.
Rebex.NET: POP3 Tutorial http://www.rebex.net/mail.net/tutorial-pop3.aspx
// get message list
Pop3MessageCollection list = client.GetMessageList();
if (list.Count == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("There are no messages in the mailbox.");
}
else
{
// download the first message
MailMessage message = client.GetMailMessage(list[0].SequenceNumber);
//...
}
client.Disconnect();
VB.NET
'create client, connect and log in
Dim client As New Pop3
client.Connect("pop3.example.org")
client.Login("username", "password")
'get message list
Dim list As Pop3MessageCollection = client.GetMessageList()
If list.Count = 0 Then
Console.WriteLine("There are no messages in the mailbox.")
Else
'download the first message
Dim message As MailMessage = client.GetMailMessage(list(0).SequenceNumber)
'...
End If
client.Disconnect()
back to top...
# Deleting and undeleting messages
Deleting messages in POP3 is quite straightforward, but might seem a bit awkward at first. To delete a message, call
the Delete method with message sequence number as an argument.
The Delete method marks a message as deleted. These won't appear in subsequent message lists, but will actually
only be removed from the mailbox after a call to Disconnect method. You can "undelete" messages that were not yet
removed using one of the following methods:
Calling Undelete method. This recovers messages marked as deleted. It will appear in message lists again and
won't be removed when the session ends.
Calling Disconnect(true). This will undelete all deleted messages and disconnect from the server. No deleted
messages will be removed, and the next time you connect to this mailbox, they will be there again. Calling
Disconnect() without parameter will commit all changes and remove all messages marked as deleted.
C#
// create client, connect and log in
Pop3 client = new Pop3();
10 de 12 28/03/2011 09:54 a.m.
Rebex.NET: POP3 Tutorial http://www.rebex.net/mail.net/tutorial-pop3.aspx
client.Connect("pop3.example.org");
client.Login("username", "password");
int sequenceNumber = 1;
// delete the first message
client.Delete(sequenceNumber);
// undo the delete operation
client.Undelete();
// and delete it again
client.Delete(sequenceNumber);
// commit changes and disconnect
client.Disconnect();
VB.NET
'create client, connect and log in
Dim client As New Pop3
client.Connect("pop3.example.org")
client.Login("username", "password")
Dim sequenceNumber As Integer = 1
'delete the first message
client.Delete(sequenceNumber)
'undo the delete operation
client.Undelete()
'and delete it again
client.Delete(sequenceNumber)
'commit changes and disconnect
client.Disconnect()
back to top...
# Using events and logging communication
In case something goes wrong, it is very useful to have a log of commands sent to the server and responses received
from it for diagnostics purposes. To make this possible, the Pop3 class declares the following events:
Event name Description
CommandSent Occurs when a command (e.g. CAPA or RETR) is sent to the server.
ResponseRead Occurs when response is received from the server.
Occurs when the session state changes, such as from Disconnected to Ready, from
StateChanged
Ready to Sending or from Sending to Reading.
TransferProgress Occurs when a block of message data is received from the server.
The CommandSent or ResponseRead events are particularly useful for the purpose of generating a communication log
and the TransferProgress event can be used by a GUI application to display amount of transfered data or a progress
11 de 12 28/03/2011 09:54 a.m.
Rebex.NET: POP3 Tutorial http://www.rebex.net/mail.net/tutorial-pop3.aspx
bar.
C#
Pop3 client = new Pop3();
client.CommandSent += new Pop3CommandSentEventHandler(client_CommandSent);
client.ResponseRead += new Pop3ResponseReadEventHandler(client_ResponseRead);
client.Connect("pop3.example.org");
...
private void client_CommandSent(object sender, Pop3CommandSentEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Command: {0}", e.Command);
}
private void client_ResponseRead(object sender, Pop3ResponseReadEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Response: {0}", e.Response);
}
VB.NET
Dim client As New Pop3
AddHandler client.CommandSent, AddressOf client_CommandSent
AddHandler client.ResponseRead, AddressOf client_ResponseRead
client.Connect("pop3.example.org")
...
Public Sub client_CommandSent(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As _
Pop3CommandSentEventArgs)
Console.WriteLine("Command: {0}", e.Command)
End Sub
Public Sub client_ResponseRead(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As _
Pop3ResponseReadEventArgs)
Console.WriteLine("Response: {0}", e.Response)
End Sub
back to top...
Back to tutorial list...
12 de 12 28/03/2011 09:54 a.m.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- JCL RefresherDocument50 paginiJCL RefresherCosta48100% (1)
- ANSI B4.1-1967 Preferred Limits and Fits For Cylindrical PartsDocument25 paginiANSI B4.1-1967 Preferred Limits and Fits For Cylindrical Partsgiaphongn100% (5)
- Construction Vibrations and Their Impact On Vibration-Sensitive FacilitiesDocument10 paginiConstruction Vibrations and Their Impact On Vibration-Sensitive FacilitiesKwan Hau LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alphabet of LinesDocument46 paginiAlphabet of LinesNancy Cordero AmbradÎncă nu există evaluări
- Python Sending EmailDocument3 paginiPython Sending EmailWelsinsin Kevin SinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Best Practice for BDoc Message AnalysisDocument27 paginiBest Practice for BDoc Message AnalysisChandra SekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Python Network Programming: Two LevelsDocument36 paginiPython Network Programming: Two LevelsFetene BeleteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spam and Phishing: CAP6135: Malware and Software Vulnerability AnalysisDocument46 paginiSpam and Phishing: CAP6135: Malware and Software Vulnerability Analysisraed messaoudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accellos - Guide - V60WebDispatch PDFDocument112 paginiAccellos - Guide - V60WebDispatch PDFcaplusinc100% (1)
- Web Based Mail ClientDocument11 paginiWeb Based Mail ClientUmesh WaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pineapple Peel Extract vs Calamansi Extract Stain RemoverDocument13 paginiPineapple Peel Extract vs Calamansi Extract Stain RemoverShebbah MadronaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Setup of FortiMail Mail ServerDe la EverandBasic Setup of FortiMail Mail ServerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Python Networking PDFDocument4 paginiPython Networking PDFBharathi RajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning The POP3 ProtocolDocument13 paginiLearning The POP3 ProtocolKristijan ZbiljskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A POP3 Client in C# .NET - Code ProjectDocument6 paginiA POP3 Client in C# .NET - Code ProjectRupak GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab3 3Document7 paginiLab3 3ruksandradÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sending Email With PythonDocument17 paginiSending Email With PythonDeepak GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pop3, Imap and SMTPDocument9 paginiPop3, Imap and SMTPyashthummar003Încă nu există evaluări
- C# Chat ClientDocument19 paginiC# Chat Clientjoe_kaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding TCP/IP: PC Network AdvisorDocument6 paginiUnderstanding TCP/IP: PC Network AdvisormiladÎncă nu există evaluări
- It Unit4Document13 paginiIt Unit4rogithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Squeakymail Chapter Demonstrates Email FilteringDocument26 paginiSqueakymail Chapter Demonstrates Email FilteringWinifer HcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 - Providing E-Mail Services: at A GlanceDocument9 paginiChapter 8 - Providing E-Mail Services: at A Glanceghar_dashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comenzi Linux 2017 EmailDocument6 paginiComenzi Linux 2017 EmailGabriel AvasiloaeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Send Mail With SMTPDocument95 paginiSend Mail With SMTPdvartaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sending and Receiving Email via TelnetDocument16 paginiSending and Receiving Email via TelnetKrizzie Mae CastillonÎncă nu există evaluări
- zOS ConnectEE DB2 Lab-06682kDocument15 paginizOS ConnectEE DB2 Lab-06682kKumar AbhishekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 07Document9 paginiLab 07نیان سیف باٹھÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction To The Windows 2003 POP3 ServiceDocument8 paginiAn Introduction To The Windows 2003 POP3 ServicehtnlinnÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE353 Lab 4: Network Programming Using PythonDocument19 paginiEE353 Lab 4: Network Programming Using PythonBama DamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 Client - Server Model & Network SecurityDocument18 paginiUnit 5 Client - Server Model & Network Securityall thinks waseÎncă nu există evaluări
- HowTo POP3 in CDocument6 paginiHowTo POP3 in CrydonerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Casestudy 3rdIA Mail ArchitectureDocument8 paginiCasestudy 3rdIA Mail ArchitectureARYA MURALI ECE-2020-24Încă nu există evaluări
- Software Requirements Specification: Version 1.0 ApprovedDocument25 paginiSoftware Requirements Specification: Version 1.0 ApprovedUday SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Socket Programming Socket Timeouts Interruptible Sockets Half-Close Internet Address Java Mail Messaging SystemDocument33 paginiAdvanced Socket Programming Socket Timeouts Interruptible Sockets Half-Close Internet Address Java Mail Messaging SystemAchint KhanijoÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT V - Application LayerDocument46 paginiUNIT V - Application LayerSenthilkumar SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application Layer Functions and ProtocolsDocument24 paginiApplication Layer Functions and ProtocolsAshutosh SaraswatÎncă nu există evaluări
- The question arDocument10 paginiThe question arhwx8nckbnqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Socket Programming With Python - OdtDocument42 paginiSocket Programming With Python - Odtukakkad2011Încă nu există evaluări
- 63ae89ec850baCCN Lab12 Fall2022Document16 pagini63ae89ec850baCCN Lab12 Fall2022Farah khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dasar Network Programming dengan VB NETDocument11 paginiDasar Network Programming dengan VB NETGatot GanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pop3s & SMTPSDocument9 paginiPop3s & SMTPSKolawole OgundareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit - 2 - 2module - 2 - 2Document15 paginiUnit - 2 - 2module - 2 - 2Rony BinoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pop3s & SMTPSDocument6 paginiPop3s & SMTPSKolawole OgundareÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Bit of HistoryDocument13 paginiA Bit of HistoryPavan KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer:: Browser Add-Ons and ExtensionsDocument5 paginiAnswer:: Browser Add-Ons and ExtensionsLexy Ira CapaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post Office Protocol POPDocument9 paginiPost Office Protocol POPdr34m5Încă nu există evaluări
- FTP Server and Client Project ListDocument11 paginiFTP Server and Client Project ListdracoorlockÎncă nu există evaluări
- COEN 445 Communication Networks and Protocols Lab 4: Socket Programming With Python: Web ServerDocument10 paginiCOEN 445 Communication Networks and Protocols Lab 4: Socket Programming With Python: Web ServerSouad OtmaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2013 RegulationDocument29 pagini2013 RegulationfencyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 22Document45 paginiChapter 22Thanh Van DaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMTP and ImapDocument31 paginiSMTP and ImapSunitha ManamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Networking in SchemeDocument3 paginiNetworking in SchemeAnupam MalakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fun With XMPP and Google Talk: The BasicsDocument19 paginiFun With XMPP and Google Talk: The BasicsFrengki SimatupangÎncă nu există evaluări
- G52APR Coursework - Part 2: Steven R. Bagley, Colin Higgins & Stephen NutbrownDocument6 paginiG52APR Coursework - Part 2: Steven R. Bagley, Colin Higgins & Stephen NutbrownJevans70Încă nu există evaluări
- Network ApplicationDocument65 paginiNetwork ApplicationakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tech Ques2Document2 paginiTech Ques2Sukhminder RajbharÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 - Mail ServicesDocument61 pagini03 - Mail ServicesridaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Email ServiceDocument10 paginiTutorial Email ServiceSYED AHMAD SHAUQI BIN SYED SHUHAIMIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zoha Afzal 035 PDFDocument30 paginiZoha Afzal 035 PDFayesha siddiqaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT 5 Final CNDocument20 paginiUNIT 5 Final CNShivamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Programming Assignment 1: E-Mail Client: POP3 CommandsDocument6 paginiProgramming Assignment 1: E-Mail Client: POP3 CommandsAli TopçuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distinguish Between Application Programs and Application ProtocolDocument13 paginiDistinguish Between Application Programs and Application ProtocolvgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit V Application Layer Traditional ApplicationsDocument29 paginiUnit V Application Layer Traditional ApplicationsakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- E-Mail: One of The Most Popular Internet Services Is E-MailDocument40 paginiE-Mail: One of The Most Popular Internet Services Is E-MailJayaprasannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- E Mail TutorialDocument7 paginiE Mail TutorialMani KandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- How to configure SMTP in PeopleTools 7.5x, 8.1x, 8.4xDocument8 paginiHow to configure SMTP in PeopleTools 7.5x, 8.1x, 8.4xCharles GermanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER II: Review of Related Literature I. Legal ReferencesDocument2 paginiCHAPTER II: Review of Related Literature I. Legal ReferencesChaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forensic psychology: false confessions exposedDocument19 paginiForensic psychology: false confessions exposedBoÎncă nu există evaluări
- OracleDocument26 paginiOracleДелије НикшићÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equipment BrochureDocument60 paginiEquipment BrochureAmar BeheraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Political Philosophy of J S MillDocument9 paginiPolitical Philosophy of J S MillRajkumar SunnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7949 37085 3 PBDocument11 pagini7949 37085 3 PBAman ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- INGLESDocument20 paginiINGLESNikollay PeñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTM C186 - 15a Standard Test Method For Heat of Hydration of Hydraulic CementDocument3 paginiASTM C186 - 15a Standard Test Method For Heat of Hydration of Hydraulic CementKalindaMadusankaDasanayakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Difference Between Private and Public Nuisance": Law of TortsDocument4 pagini"Difference Between Private and Public Nuisance": Law of Tortsaridaman raghuvanshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Components of GMP - Pharma UptodayDocument3 paginiComponents of GMP - Pharma UptodaySathish VemulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lpi - 101-500Document6 paginiLpi - 101-500Jon0% (1)
- Compiled XiiDocument34 paginiCompiled XiiMridul VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document9 paginiChapter 1Ibrahim A. MistrahÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Benefits of Radio Broadcasting As Perceived by The People in Rural AreasDocument10 paginiThe Benefits of Radio Broadcasting As Perceived by The People in Rural AreasMaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test October ADocument2 paginiTest October AAna Paula CarlãoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computational Chunking in Chess PDFDocument211 paginiComputational Chunking in Chess PDFTran VuÎncă nu există evaluări
- LoyalDocument20 paginiLoyalSteng LiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdul Azim Resume NewDocument9 paginiAbdul Azim Resume NewSayed WafiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fractions, Decimals and Percent Conversion GuideDocument84 paginiFractions, Decimals and Percent Conversion GuideSassie LadyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dry Docking Ships Training Course for DockmastersDocument7 paginiDry Docking Ships Training Course for DockmastersSunil Kumar P GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes On Unit - 4 - Employees Roles in Service MarketingDocument3 paginiNotes On Unit - 4 - Employees Roles in Service MarketingSridhar Gowda67% (3)
- Object Oriented Assignment GuideDocument10 paginiObject Oriented Assignment GuideThiviyaa DarshiniÎncă nu există evaluări