Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Inventory Management & Control Definition of Terms: Stocks and Inventories
Încărcat de
nda04030 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
25 vizualizări4 paginiStocks - consists of all the goods and materials that are stored by an organization for future use. Inventories - a list of all the items that are held in stock for future use by an organization. Economies of Scale - bulk buying, movement and storing brings in economies of scale.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Inventory Wk1
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentStocks - consists of all the goods and materials that are stored by an organization for future use. Inventories - a list of all the items that are held in stock for future use by an organization. Economies of Scale - bulk buying, movement and storing brings in economies of scale.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
25 vizualizări4 paginiInventory Management & Control Definition of Terms: Stocks and Inventories
Încărcat de
nda0403Stocks - consists of all the goods and materials that are stored by an organization for future use. Inventories - a list of all the items that are held in stock for future use by an organization. Economies of Scale - bulk buying, movement and storing brings in economies of scale.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 4
Definition of Terms
Inventory Management & Stocks
- consists of all the goods and materials
Control that are stored by an organization for
future use
Stocks and Inventories Inventory
- a list of all the items that are held in
stock for future use by an organization
- blocked working capital of an organization in
the form of materials
2
Definition of Terms Definition of Terms
Item (Stock Keeping Unit/SKU) Inventory Management
- a distinct product that is kept in stock - function responsible for all decisions
and is recorded as one entry in the about stock in an organization
inventory - sets policies, activities and procedures
Unit to make sure the right amount of each
- the standard size or quantity of an item item is held in stock at any time
3 4
Definition of Terms Classification of Stocks
Supply Chain Raw Materials
- consists of the series of activities and - materials and components scheduled for use
in making a product or in the performance of
organizations that materials move
a service
through on their journey from supplier
Work in Process (WIP)
to final consumer - materials and components that have begun
Supply Chain Management (Logistics) their transformation to finished goods
- function responsible for the flow of Finished Goods (Merchandise)
materials - goods which are ready for sale to the
5
consumers 6
Classification of Stocks Reasons for Holding Stocks
Goods in Transit (Pipeline Stock) Time
- goods which are in the process of distribution - time intervals present in the supply
Spare Parts (MRO Supplies) chain requires that a certain amount of
- for the maintenance, repair and operation of
inventory is maintained for use
machineries and equipments
Consumables Uncertainty
- items which are needed to support - inventories are used to cushion the
operations but do not form part of the final impact of uncertainties in demand,
product supply and movement of goods
7 8
Reasons for Holding Stocks Functions of Stocks
Economies of Scale To meet anticipated customer demand
- bulk buying, movement and storing To smooth production requirements
brings in economies of scale To decouple operations
To protect against stock outs
Underlying principle in holding stocks is To take advantage of order cycles
based on the need for a BUFFER To hedge against price increases
To permit operations
9 10
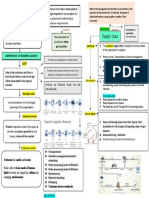
Importance of Stocks Stocks in the Supply Chain
Every organization on a supply chain holds its own stocks
Allows operations to become more Basic model of a supply chain for a product consists of:
efficient and productive a. Tiers of Suppliers
b. Tiers of Customers
Affects lead times and availability of Main Features of a Supply Chain are:
materials a. Length
- refers to the number of intermediaries that
Affect operating costs materials flow through
b. Breadth
Affect broader operations - refers to the number of parallel routes that materials can
move through
Risky
Driver of growth of other organizations
11 12
Cooperation within a Supply Cooperation within a Supply
Chain Chain
Organizations in a supply chain share a Ways to achieve cooperation
common overall objective, which is to get final
customer satisfaction a. Establishing an informal and valuable
Benefits working relationship with all
a. lower costs stakeholders
b. improved performance
c. improved material flow - no commitments
d. better customer service - flexible and non-binding
e. flexibility b. Establishing a formal arrangement
- obligations are clearly outlined
13 14
Trends affecting Stocks Trends affecting Stocks
Improving Communications Improving Customer Service
- EDI, E-Mail, E-Procurement
- customer demands drive organizations
a. efficient transfer of information
b. less paperwork to be more competitive
c. fewer errors Concentration of Ownership
d. more integration - realignment produces a shift of power
e. physical distances are becoming less
in the supply chain
significant
15 16
Trends affecting Stocks Trends affecting Stocks
Outsourcing Inventory Management (Vendor Managed Inventory) Cross-Docking (DC By-Pass)
- using TPL to take over logistics
- allows organizations to focus on their core activities - coordination of supply and delivery resulting
- benefits:
a. lower fixed costs
in materials being passed on for delivery the
b. use of experts, best practices moment it arrives at the receiving area
c. economies of scale
d. guaranteed levels of customer service
Postponement
e. flexible capacity - moves almost finished products into stock
f. lower exposure to risks
g. increased geographical coverage and delays final modification or customization
h. convenient way of entering and working in new markets - keeping stocks of the basic, standard
products only
17 18
Trends affecting Stocks Changing Views of Stock
Increasing Environmental Concerns Organizations have changed their
- cultural trend that has a significant attitude toward stocks over time
consequence on inventory The current view is that they are
management expensive and should be kept to a
- logistics is going “green” minimum
- significant investments on energy, Search for ways of removing uncertainty
reusable packaging, recycling, safety,
etc.
19 20
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Unit 2 - Basic of Procurement PDFDocument11 paginiUnit 2 - Basic of Procurement PDFDudyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre-Read OperationsDocument16 paginiPre-Read OperationsSIDDHI KANSAL MBA 2021-23 (Delhi)Încă nu există evaluări
- NOTES - Operation and Supply Chain ManagementDocument6 paginiNOTES - Operation and Supply Chain ManagementKarel Shane KamensaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LSCM M1 ReviewerDocument3 paginiLSCM M1 ReviewerBENJAMEN AMPOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 013Document15 paginiChap 013بكرة جاىÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logistics Notes Chapter 5Document1 paginăLogistics Notes Chapter 5banÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supply Chain Reviewer MidtermDocument6 paginiSupply Chain Reviewer MidtermColeen PayongayongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 - Opman TQM: Chapter 1 - Operations and ProductivityDocument4 paginiModule 1 - Opman TQM: Chapter 1 - Operations and ProductivityApril GumiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- CoursePacket02 STRAMADocument8 paginiCoursePacket02 STRAMAFourenhyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 5 Operation Management With TQMDocument9 paginiModule 5 Operation Management With TQMポーラ・ メイガトンÎncă nu există evaluări
- Key Concepts of Physical DistributionDocument21 paginiKey Concepts of Physical DistributionRataÎncă nu există evaluări
- OM CP 1 - ReviewerDocument4 paginiOM CP 1 - ReviewerELLYSSA MAE CLEMENTEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yellow Modern The Building PresentationDocument24 paginiYellow Modern The Building Presentationkingfearless27Încă nu există evaluări
- Supply Chain Management: Logistics/SC CompetencyDocument4 paginiSupply Chain Management: Logistics/SC CompetencyhassanlibraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inventory PDFDocument7 paginiInventory PDFJose De CuentasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materials Managemen TDocument21 paginiMaterials Managemen TAkash NiwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enterprise System Week09Document20 paginiEnterprise System Week09Muhammad Fajar PamungkasÎncă nu există evaluări
- F23 Week 06 OPER8340 Lecture KHDocument37 paginiF23 Week 06 OPER8340 Lecture KHMurtuza SajidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logistic Notes Chapter 1Document1 paginăLogistic Notes Chapter 1banÎncă nu există evaluări
- OM - ReviewerDocument5 paginiOM - ReviewerELLYSSA MAE CLEMENTEÎncă nu există evaluări
- IMRP HandoutDocument91 paginiIMRP Handoutbullfinch2Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Facilities PlanningDocument3 paginiChapter 1: Introduction To Facilities PlanningHazel MosotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum Syllabus Template Level - 7 Retail Store ManagerDocument14 paginiCurriculum Syllabus Template Level - 7 Retail Store ManagerDinesh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 - INVENTORY MANAGEMENTDocument11 paginiChapter 7 - INVENTORY MANAGEMENTLong Đoàn PhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pertemuan 3 - SCM - SDL - Genap - 19 - 20 - Lec4Document23 paginiPertemuan 3 - SCM - SDL - Genap - 19 - 20 - Lec4DivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 010Document41 paginiChap 010tb7976sk100% (1)
- Inventory Management - PPTDocument46 paginiInventory Management - PPTMuneeb KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Om 4Document36 paginiOm 4Charles MedallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 1: Supply Chain ManagementDocument17 paginiTopic 1: Supply Chain ManagementRoyce DenolanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SUB158963Document8 paginiSUB158963karen leonÎncă nu există evaluări
- OMTQM FinalsDocument4 paginiOMTQM FinalsChristian De GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCM - SDL - Gasal 18 - 19 - Lec3 - T1Document24 paginiSCM - SDL - Gasal 18 - 19 - Lec3 - T1nirwan cokÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supply Chain Management Review: Your Company NameDocument77 paginiSupply Chain Management Review: Your Company Namekcprakash26Încă nu există evaluări
- Materials GCDocument42 paginiMaterials GCNUR ADLINA ATIQAH ANUARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adobe Scan 03-Aug-2023Document3 paginiAdobe Scan 03-Aug-2023RajeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- OSCM FullDocument180 paginiOSCM Fullhien ngothanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eng Management First Sem Finals ReviewerDocument7 paginiEng Management First Sem Finals ReviewerJohn Carlo EdejerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operations Management ReviwerDocument5 paginiOperations Management ReviwerAshianna KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of InventoryDocument8 paginiManagement of InventoryNavjot SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Achieving Operational Excellence by Implementing An Erp (Enterprise Resource Planning) System (A Case Study of A Large Scale Industry)Document8 paginiAchieving Operational Excellence by Implementing An Erp (Enterprise Resource Planning) System (A Case Study of A Large Scale Industry)Raffay MaqboolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment 2 Guide OSCMDocument5 paginiAssessment 2 Guide OSCMKùshwåhã Mãhêsh BábüÎncă nu există evaluări
- GVC 2 Inventory Mangement FinalDocument59 paginiGVC 2 Inventory Mangement Finalnoname920134Încă nu există evaluări
- Inventory ManagementDocument17 paginiInventory ManagementSanthosh PrabhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supply Chain Management: Obstacles To Achieving Strategic FitDocument20 paginiSupply Chain Management: Obstacles To Achieving Strategic FitpavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- S221. 5 Managing Inventory Throughout The Supply ChainDocument30 paginiS221. 5 Managing Inventory Throughout The Supply ChainANH TRẦN TIẾNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 5 Inventory Management - Ikea (Final 2)Document36 paginiGroup 5 Inventory Management - Ikea (Final 2)triyono kuncoroaji100% (1)
- Week 8Document38 paginiWeek 8hanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supply Chain Responsiveness-1Document12 paginiSupply Chain Responsiveness-1Tarun ChopraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision - in (AutoRecovered)Document24 paginiRevision - in (AutoRecovered)thamnguyen304Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument3 paginiChapter 1 NotesRorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch20 Quản trị tồn kho OSCMDocument7 paginiCh20 Quản trị tồn kho OSCMThanhHuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prelims - Org. ManDocument11 paginiPrelims - Org. ManLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weeklysummary7group ADocument8 paginiWeeklysummary7group AOlivio CampanerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 - Buy MakeDocument68 paginiChapter 4 - Buy MakeYassine AzzaouiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Production and Operations Management Systems: Chapter 9: Supply Chain Management Sushil K. Gupta Martin K. Starr 2014Document57 paginiProduction and Operations Management Systems: Chapter 9: Supply Chain Management Sushil K. Gupta Martin K. Starr 2014Homeq RealestateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supply Chain Drivers and MetricsDocument21 paginiSupply Chain Drivers and MetricsLira ByunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finals - Org. Man.Document30 paginiFinals - Org. Man.LEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bac0n1b Prelim ReviewerDocument2 paginiBac0n1b Prelim ReviewerAprel Praise Morada TravenioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conversion CycleDocument3 paginiConversion CycleLil ConicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benchmarking Best Practices for Maintenance, Reliability and Asset ManagementDe la EverandBenchmarking Best Practices for Maintenance, Reliability and Asset ManagementÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Accounting Multiple ChoiceDocument4 paginiBasic Accounting Multiple Choicenda04030% (1)
- Auditing Theory Quiz Final PrintDocument6 paginiAuditing Theory Quiz Final Printnda0403Încă nu există evaluări
- Ms ConsultancyDocument3 paginiMs Consultancynda0403Încă nu există evaluări
- Algebra QuizDocument1 paginăAlgebra Quiznda0403Încă nu există evaluări
- Manuscript - Batallantes &Lalong-Isip (2021) Research (Chapter 1 To Chapter 3)Document46 paginiManuscript - Batallantes &Lalong-Isip (2021) Research (Chapter 1 To Chapter 3)Franzis Jayke BatallantesÎncă nu există evaluări
- CNG Fabrication Certificate16217Document1 paginăCNG Fabrication Certificate16217pune2019officeÎncă nu există evaluări
- AkDocument7 paginiAkDavid BakcyumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ticket Udupi To MumbaiDocument2 paginiTicket Udupi To MumbaikittushuklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jetweigh BrochureDocument7 paginiJetweigh BrochureYudi ErwantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Job Number EngineerDocument2 paginiProject Job Number Engineertekno plus banatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algorithm - WikipediaDocument34 paginiAlgorithm - WikipediaGilbertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flow Chart For SiFUS Strata Title ApplicationDocument5 paginiFlow Chart For SiFUS Strata Title ApplicationPhang Han XiangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Load Sharing Strategies in Multiple Compressor Refrigeration SystemsDocument8 paginiLoad Sharing Strategies in Multiple Compressor Refrigeration SystemsLiu YangtzeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACM2002D (Display 20x2)Document12 paginiACM2002D (Display 20x2)Marcelo ArtolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TT Class XII PDFDocument96 paginiTT Class XII PDFUday Beer100% (2)
- Computer System Architecture: Pamantasan NG CabuyaoDocument12 paginiComputer System Architecture: Pamantasan NG CabuyaoBien MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lenskart SheetDocument1 paginăLenskart SheetThink School libraryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vicente, Vieyah Angela A.-HG-G11-Q4-Mod-9Document10 paginiVicente, Vieyah Angela A.-HG-G11-Q4-Mod-9Vieyah Angela VicenteÎncă nu există evaluări
- HP Sustainability Impact Report 2018Document147 paginiHP Sustainability Impact Report 2018Rinaldo loboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tendernotice 1Document42 paginiTendernotice 1Hanu MittalÎncă nu există evaluări
- United States v. Manuel Sosa, 959 F.2d 232, 4th Cir. (1992)Document2 paginiUnited States v. Manuel Sosa, 959 F.2d 232, 4th Cir. (1992)Scribd Government DocsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design & Construction of New River Bridge On Mula RiverDocument133 paginiDesign & Construction of New River Bridge On Mula RiverJalal TamboliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Li Li Prof. Feng Wu Beijing Institute of TechnologyDocument20 paginiDr. Li Li Prof. Feng Wu Beijing Institute of TechnologyNarasimman NarayananÎncă nu există evaluări
- VP Construction Real Estate Development in NY NJ Resume Edward CondolonDocument4 paginiVP Construction Real Estate Development in NY NJ Resume Edward CondolonEdwardCondolonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power For All - Myth or RealityDocument11 paginiPower For All - Myth or RealityAshutosh BhaktaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WHO Partograph Study Lancet 1994Document6 paginiWHO Partograph Study Lancet 1994Dewi PradnyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scope: Provisional Method - 1994 © 1984 TAPPIDocument3 paginiScope: Provisional Method - 1994 © 1984 TAPPIМаркус СилваÎncă nu există evaluări
- C Sharp Logical TestDocument6 paginiC Sharp Logical TestBogor0251Încă nu există evaluări
- Income Tax Calculator 2023Document50 paginiIncome Tax Calculator 2023TARUN PRASADÎncă nu există evaluări
- BreezeAIR 8000 Data SheetDocument2 paginiBreezeAIR 8000 Data Sheetalfasukarno100% (1)
- Huawei Core Roadmap TRM10 Dec 14 2011 FinalDocument70 paginiHuawei Core Roadmap TRM10 Dec 14 2011 Finalfirasibraheem100% (1)
- BACE Marketing Presentation FINALDocument14 paginiBACE Marketing Presentation FINALcarlosfelix810% (1)
- Between:-Mr. Pedro Jose de Vasconcelos, of Address 14 CrombieDocument2 paginiBetween:-Mr. Pedro Jose de Vasconcelos, of Address 14 Crombiednd offiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bea Form 7 - Natg6 PMDocument2 paginiBea Form 7 - Natg6 PMgoeb72100% (1)