Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Drug Study
Încărcat de
Jannine Bensi0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
1K vizualizări14 paginiHepatitis B vaccine is given to children as a series of three injections (shots) first shot is given to infants before leaving the hospital. Second shot is given between 1 and 2 months of age. Third shot is given at 6 months of Contraindication Recent cerebral hemorrhage.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
36781425-Drug-Study
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentHepatitis B vaccine is given to children as a series of three injections (shots) first shot is given to infants before leaving the hospital. Second shot is given between 1 and 2 months of age. Third shot is given at 6 months of Contraindication Recent cerebral hemorrhage.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
1K vizualizări14 paginiDrug Study
Încărcat de
Jannine BensiHepatitis B vaccine is given to children as a series of three injections (shots) first shot is given to infants before leaving the hospital. Second shot is given between 1 and 2 months of age. Third shot is given at 6 months of Contraindication Recent cerebral hemorrhage.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 14
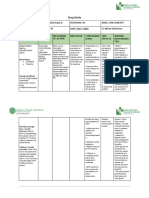
Generic Classification Mechanism of Indication Contraindication Nursing
name/Brand action Responsibility
name
Vaccine - hepatitis Vaccine Hepatitis The vaccine is The hepatitis B Most infants who
B; Immunization - B.. made from vaccine is given to receive the
hepatitis B inactivated whole children as a series hepatitis B vaccine
virus of hepatitis B. of three injections have no side
The inactive virus (shots). effects. Others may
Engerix-B, stimulates your have minor
Engerix-B body to produce • The first problems, such as
Pediatric, antibodies to fight shot is soreness and
the hepatitis B given to redness at the
virus. infants injection site or a
before mild fever. Serious
leaving the problems are rare
hospital. If and are mainly due
the baby's to allergic
mother reactions to a
carries the component of the
hepatitis B vaccine.
virus, the
baby
receives the
first vaccine
shortly after
birth.
• The second
shot is
given
between 1
and 2
months of
age.
• The third
shot is
given at 6
months of
age.
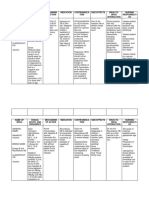
Generic Classification Mechanism of Indication Contraindication Nursing
name/Brand action Responsibility
name
Duvadilan Isoxsuprine HCl Prevention & Recent cerebral
(Isoxsoprine) treatment of hemorrhage
premature labour &
other undesired
uterine
contractions eg
surgical
intervention during
pregnancy &
cerclage.
Generic Classification Mechanism of Indication Contraindication Nursing
name/Brand action Responsibility
name
Erythromycin -Antibiotic Erythromycin - for prophylaxis of Recent cerebral
(Roymicin, displays ophthalmia hemorrhage
Ilotycin, -treat bacterial bacteriocidal neonatorum
Eyemycin) infections of the activity, caused by N.
eyes particularly at gonorrhoeae, C.
higher trachomatis, and
concentrations, but for chlamydial
the mechanism is conjunctivitis in
not fully neonates.
elucidated. By
binding to the 50s
subunit of the
bacterial 70s rRNA
complex, protein
synthesis and
subsequently
structure/function
processes critical
for life or
replication are
inhibited
Generic Classification Mechanism of Indication Contraindication Nursing
name/Brand action Responsibility
name
Ampicillin - Penicillins with They stop bacteria For treatment of Hypersensitivity;
extended from multiplying by infection infectious
spectrum. preventing bacteria (Respiratory, GI, mononucleosis.
-Antibiotics from forming the UTI and meningitis)
walls that surround due to E. coli, P.
them. The walls are mirabilis,
necessary to enterococci,
protect bacteria Shigella, S. typhosa
from their and other
environment and Salmonella,
to keep the nonpenicillinase-
contents of the producing N.
bacterial cell gononhoeae, H.
together. Bacteria influenzae,
cannot survive staphylococc
without a cell wall.
Ampicillin is
effective against
many bacteria
including H.
influenzae, N.
gonorrhoea, E. coli,
Salmonella, and
Shigella,
streptococci and
certain strains of
staphylococci.
Generic Classification Mechanism of Indication Contraindication Nursing
name/Brand action Responsibility
name
BCG vaccine Biologic response Live BCG vaccine is Hypersensitivity;
modifier an attenuated patients who are
strain of bacillus immunocompromis
Calmette-Guérin; ed, HIV-infected,
used for active have febrile illness
immunisation and burn patients.
against Active tuberculosis;
tuberculosis. It is urinary tract
also used as an infection, gross
active haematuria and
immunotherapy for recent (<7-14
the treatment of days) biopsy,
bladder carcinoma transurethral
in situ by causing a resection (TUR), or
local, chronic traumatic
inflammatory catheterisation.
response involving
macrophage and
leukocyte
infiltration of the
bladder. This local
inflammatory
response results in
destruction of
superficial tumor
cells of the
urothelium.
Generic Classification Mechanism of Indication Contraindication Nursing
name/Brand action Responsibility
name
Ampicillin - Penicillins with They stop bacteria For treatment of Hypersensitivity;
extended from multiplying by infection infectious
spectrum. preventing bacteria (Respiratory, GI, mononucleosis.
-Antibiotics from forming the UTI and meningitis)
walls that surround due to E. coli, P.
them. The walls are mirabilis,
necessary to enterococci,
protect bacteria Shigella, S. typhosa
from their and other
environment and Salmonella,
to keep the nonpenicillinase-
contents of the producing N.
bacterial cell gononhoeae, H.
together. Bacteria influenzae,
cannot survive staphylococc
without a cell wall.
Ampicillin is
effective against
many bacteria
including H.
influenzae, N.
gonorrhoea, E. coli,
Salmonella, and
Shigella,
streptococci and
certain strains of
staphylococci.
Generic Classification Mechanism of Indication Contraindication Nursing
name/Brand action Responsibility
name
Vit. K vaccine Coagualant Vitamin K Vitamin K is a fat Blood disorders,
(phytomenadione) promotes the soluble vitamin allergies. A
hepatic formation which plays an preservative
of active important role in (benzyl alcohol)
prothrombin (factor blood clotting. This which may be
II), proconvertin medication is used found in this
(factor VII), plasma to prevent and product or in the
thromboplastin treat liquid used to mix
component , which hypoprothrombine this product
are required for mia (low blood clot (diluent) can
normal blood factor levels) infrequently cause
clotting. Vitamin K caused by vitamin serious problems
is an essential K deficiency. (sometimes death)
cofactor for a if given by injection
hepatic microsomal to an infant during
enzyme that the first months of
catalyzes the post- life (neonatal
translational period). The risk is
carboxylation of greater with lower
multiple, specific, birth weight infants
peptide-bound and is greater with
glutamic acid increased amounts
residues in inactive of benzyl alcohol.
hepatic precursor Symptoms include
proteins of factors sudden gasping,
II, VII, IX, and X. low blood pressure,
The resulting or a very slow
gamma- heartbeat. Report
carboxyglutamic these symptoms to
acid residues the doctor
convert the immediately should
precursor proteins they occur. If
to active possible, a
coagulation factors preservative-free
that subsequently product should be
are secreted by used when treating
liver cells into the neonates. This
blood. medication should
be used as directed
during pregnancy
or while breast-
feeding. Consult
your doctor about
the risks and
benefits.
Generic Classification Mechanism of Indication Contraindication Nursing
name/Brand action Responsibility
name
Vitamin A Vitamin A is a fat- Vitamin A helps The Food and If you don't get
soluble vitamin. form and maintain Nutrition Board at enough vitamin A,
healthy teeth, the Institute of you are more
skeletal and soft Medicine susceptible to
tissue, mucous recommends the infectious diseases
membranes, and following: and vision
skin. It is also problems.
known as retinol Infants
because it If you get too much
produces the vitamin A, you can
• 0-6
pigments in the become sick. Large
months:
retina of the eye. doses of vitamin A
400
micrograms can also cause
Vitamin A per day birth defects. Acute
promotes good (mcg/day) vitamin A
vision, especially in • 7 - 12 poisoning usually
low light. It may months: occurs when an
also be needed for 500 adult takes several
reproduction and mcg/day hundred thousand
breast-feeding. IU. Babies and
children are more
Children
Retinol is an active sensitive and can
form of vitamin A. become sick after
It is found in • 1 - 3 years: taking smaller
animal liver, whole 300 doses of vitamin A
milk, and some mcg/day or vitamin A-
fortified foods. • 4 - 8 years: containing
400 products such as
mcg/day retinol
• 9 - 13
years: 600
mcg/day Hypervitaminosis
A.
Adolescents and
Adults Increased amounts
of beta-carotene
• Males age can turn the color
14 and of skin to yellow or
older: 900 orange. The skin
mcg/day color returns to
normal once the
Females age 14 increased intake of
and older: 700 beta-carotene is
mcg/day reduced.
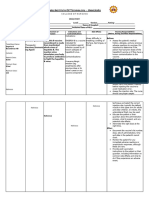
Generic Classification Mechanism of Indication Contraindication Nursing
name/Brand action Responsibility
name
Tetanus toxoid Immunizing • It provides • For booster • NOT indicated • Intramuscular
agent longer injection only for primary immu injections should be
protection than for persons 7 nization. given with great
antitoxin of years of age • HYPERSENSITIVIT care in patients
animal origin or older Y TO ANY suffering from
and causes few against COMPONENT OF thrombocytopenia
adverse tetanus. THE VACCINE, or other coagulation
reactions. The • For the INCLUDING disorders
currently prevention THIMEROSAL, A • Special care should
recommended of neonatal te MERCURY be taken to ensure
prophylactic tanus in DERIVATIVE, IS that the injection
dose of TIG unvaccinated ACONTRAINDICA does not enter a
(Human) for pregnant wo TION FOR blood vessel.
wounds of men FURTHER USE OF • Immunosuppressive
average THIS VACCINE. therapies including
• to protect
severity is 250 • Contraindication radiation,
(immunize)
units to use this or any corticosteroids, ant
against
intramuscularly tetanus other related metabolites,
. infection vaccine after a alkylating agents,
Generic Classification Mechanism of Indication Contraindication
serious adverse Nursing Responsibility
and cytotoxic drugs
name/Brand action event temporally may reduce the
name associated with a immune response
D5lr Lactated Ringer's • Produces a • Source of • Should
previousnot dose
be • Monitor changes in fluid
to vaccines
in 5% Dextrose metabolic water, administered
including an balance, electrolyte
alkalinizing electrolytes simultaneously
anaphylactic concentrations, and
effect. with blood
reaction. acid base balance
and calories
Lactate ions through the
• A history of during
are or as an same
alkalinizing systemic allergic prolonged parenteral th
metabolized administration
or neurologic erapy or whenever the
ultimately to agent. set because of condition of the patient
reactions
carbon • for fluid and the likelihood
following a warrants such
dioxide and electrolyte ofprevious
coagulation.
dose of evaluation.
water, which • Not for useToxoid
Tetanus in •is Should be used with
replenishmen
requires the the
antreatment
absolute caution. Excess
consumption t and caloric
ofcontraindication
lactic administration may
of hydrogen supply in a acidosis. result in metabolic
for further use.
cations. single dose • Contraindicate alkalosis.
• Capable of container for d in patients • Caution must be
inducing intravenous with known exercised in the
diuresis administratio allergy to corn administration of
depending on n or corn Lactated Ringer's and
the clinical products. 5% Dextrose Injection,
condition of USP to patients
the patient. receiving
corticosteroids or
corticotropin.
• aution
in pediatric patients,
particularly neonates
and low weight infants,
because of the
increased risk of
hyperglycemia/hypogly
cemia.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Drug Study Baby and MotherDocument9 paginiDrug Study Baby and MotherLyra Mae E. MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expanded Program On Immunization and Reproductive Health DOH Programs PDFDocument24 paginiExpanded Program On Immunization and Reproductive Health DOH Programs PDFMiss GÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSU-Iligan Institute of TechnologyDocument9 paginiMSU-Iligan Institute of TechnologyNathanielle Keith PENASOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patient 6 Drug Study Day 1 BCGDocument4 paginiPatient 6 Drug Study Day 1 BCGJackieMae100% (1)
- Immunizations To Be Taken On Gandako'S First VisitDocument5 paginiImmunizations To Be Taken On Gandako'S First VisitKryzza LeizellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study PDFDocument14 paginiDrug Study PDFsretirado02Încă nu există evaluări
- Mandatory Infants and Children Health Immunization Act of 2011 Compulsory ImmunizationDocument3 paginiMandatory Infants and Children Health Immunization Act of 2011 Compulsory Immunizationbunso padilla100% (2)
- Brocure ImmunizationDocument3 paginiBrocure ImmunizationGil AswiguiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Community Health Nursing Expanded Program For Immunization (EPI)Document2 paginiCommunity Health Nursing Expanded Program For Immunization (EPI)ronaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vaccine Minimum Age at 1st Dose Number of Doses Dose Minimum Interval Between Doses Route Site ReasonDocument3 paginiVaccine Minimum Age at 1st Dose Number of Doses Dose Minimum Interval Between Doses Route Site ReasonMaui LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Talk Format.Document7 paginiHealth Talk Format.Manoj LaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impetigo Rare FindingDocument2 paginiImpetigo Rare FindingMeniscoOctaviandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- National Immunization Program (NIP) : Mary Ann E. Lopez MAN RN LPTDocument26 paginiNational Immunization Program (NIP) : Mary Ann E. Lopez MAN RN LPTJanaica JuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of EPI: Community Health Nursing Expanded Program For Immunization (EPI)Document2 paginiPrinciples of EPI: Community Health Nursing Expanded Program For Immunization (EPI)Rona Pie100% (1)
- Principles of EPI: Community Health Nursing Expanded Program For Immunization (EPI)Document2 paginiPrinciples of EPI: Community Health Nursing Expanded Program For Immunization (EPI)ronaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topics For Oral Exam EPIDocument3 paginiTopics For Oral Exam EPIPCRMÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument8 paginiUntitledMohamed MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk For Infection - NCPDocument5 paginiRisk For Infection - NCPmatcha.ganacheÎncă nu există evaluări
- EPI Vaccines HandoutsDocument14 paginiEPI Vaccines HandoutsStephen Pilar PortilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- EPI Vaccines HandoutsDocument14 paginiEPI Vaccines HandoutsBurhan uddin100% (11)
- Lecture 3.2 ImmunizationDocument10 paginiLecture 3.2 ImmunizationMoonyeen Jann Casera BalicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Potential Nursing Diagnosis Problem Fdar / NCP: Activity # 2Document2 paginiPotential Nursing Diagnosis Problem Fdar / NCP: Activity # 2Karl KiwisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viral Exanthem in PregnancyDocument3 paginiViral Exanthem in PregnancyCatherine Blanche LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- E5-Case Analysis 3M Responsible ParenthoodDocument21 paginiE5-Case Analysis 3M Responsible ParenthoodAubrey Justine GaleonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyyyyDocument3 paginiDrug StudyyyyNathalie kate petallarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 paginiName of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesMinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VaccineDocument1 paginăVaccinexmitchxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunize Your ChildDocument1 paginăImmunize Your ChildIntan NurulLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vaccination PDF.'''''Document14 paginiVaccination PDF.'''''Ompriya SÎncă nu există evaluări
- SL No. Time Specific Objective Content AV Aids Teachers's Activity Group Activit y EvaluationDocument14 paginiSL No. Time Specific Objective Content AV Aids Teachers's Activity Group Activit y EvaluationETCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expanded Program On ImmunizationDocument8 paginiExpanded Program On Immunizationjanine_valdezÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - Yeast InfectionDocument2 paginiNCP - Yeast InfectionChelzie Laserna100% (2)
- Doh Programs Related To Family Health - Expanded Programs On ImmunizationDocument3 paginiDoh Programs Related To Family Health - Expanded Programs On ImmunizationPatrisha Bianca Paige BadillesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expanded Program On Immunization Philippines)Document8 paginiExpanded Program On Immunization Philippines)Mark AcuzarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunization: Expanded Program On Immunization (EPI)Document4 paginiImmunization: Expanded Program On Immunization (EPI)3amabelle arevaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- ImmunizationDocument6 paginiImmunizationNIKAH PAULINE ALCANTARAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2B Diana - BCG Drug StudyDocument3 pagini2B Diana - BCG Drug Studymerry100% (1)
- Drug Study - Hepatitis B VaccineDocument2 paginiDrug Study - Hepatitis B VaccineJustin AncogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Illness Prevention Activities Are Designed To HelpDocument2 paginiIllness Prevention Activities Are Designed To HelpAlleya SheeneÎncă nu există evaluări
- EPI Vaccines HandoutsDocument14 paginiEPI Vaccines HandoutsMeryville JacildoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious DisorderDocument12 paginiChapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious DisorderAlyssaGrandeMontimorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vaccination in Pregnancy PDFDocument7 paginiVaccination in Pregnancy PDFNoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expanded Program On ImmunizationDocument10 paginiExpanded Program On ImmunizationHoneylouAzOpondaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communicable Disease (Introduction Part 2) : Period of DeclineDocument6 paginiCommunicable Disease (Introduction Part 2) : Period of Declinefiel borataÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Cord Prolapse Frias Ea Lissandra CDocument2 paginiNCP Cord Prolapse Frias Ea Lissandra CFatima Medriza Duran0% (1)
- Ob Topic 1 - Pprom - NCPDocument2 paginiOb Topic 1 - Pprom - NCPThelly MargalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discussion 2.editedDocument13 paginiDiscussion 2.editedmutisya johnboscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- National Childhood Vaccine Injury ActDocument2 paginiNational Childhood Vaccine Injury ActYovita100% (1)
- Hep BDocument4 paginiHep BHanniel MontecalboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Maintenance of InfantDocument59 paginiHealth Maintenance of InfantMohamed Na3eemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Childhood Immunization & Catch Up Immunization-2Document53 paginiChildhood Immunization & Catch Up Immunization-2Haters ExterminatorÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Health Workers) Booklet EnglishDocument72 pagini(Health Workers) Booklet EnglishdrpklalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study For Polio Vaccine Vaccine Trade Name: Indications Side Effects/Adverse Reactions Nursing Responsibilities or ConsiderationsDocument3 paginiDrug Study For Polio Vaccine Vaccine Trade Name: Indications Side Effects/Adverse Reactions Nursing Responsibilities or ConsiderationsZyra Jazmine JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- DOH Programs Group 1 BSN 2L 1Document19 paginiDOH Programs Group 1 BSN 2L 1Jocelyn AtisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 953b SIPConsentFormSeptember29ENDocument2 pagini953b SIPConsentFormSeptember29ENMani MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Old Diseases Are Coming Back:: Courtesy Of Anti-VaccinatorsDe la EverandOld Diseases Are Coming Back:: Courtesy Of Anti-VaccinatorsEvaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (1)
- Vaccines: Does herd immunity justify permanent impairment for a few?De la EverandVaccines: Does herd immunity justify permanent impairment for a few?Încă nu există evaluări
- Immunization Information: The Benefits and The RisksDe la EverandImmunization Information: The Benefits and The RisksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Severe Combined Immune Deficiency: Early Hospitalisation and IsolationDe la EverandSevere Combined Immune Deficiency: Early Hospitalisation and IsolationÎncă nu există evaluări
- B - Gordon'sDocument1 paginăB - Gordon'sJannine BensiÎncă nu există evaluări
- I Miss YouDocument1 paginăI Miss YouJannine BensiÎncă nu există evaluări
- KeysDocument1 paginăKeysJannine BensiÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Types of Abortion": A Reading ONDocument3 pagini"Types of Abortion": A Reading ONJannine BensiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cover PageDocument1 paginăCover PageJannine BensiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSN Level III Clinical InstructorDocument33 paginiBSN Level III Clinical InstructorChristine Bell JapitanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ivf StudyDocument2 paginiIvf StudyJannine Bensi100% (1)
- Helping Psychiatry Residents Cope With Patient SuicideDocument5 paginiHelping Psychiatry Residents Cope With Patient SuicidedrguillermomedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Times Sit To Stand TestDocument7 pagini5 Times Sit To Stand TestMelany PenagosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cps-Pg-Admission-2019 First Selection Round of Neet Eligible Candidates For The State of MaharashtraDocument93 paginiCps-Pg-Admission-2019 First Selection Round of Neet Eligible Candidates For The State of MaharashtrarohankananiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ludwig Heinrich Bojanus (1776-1827) On Gall's Craniognomic System, Zoology - UnlockedDocument20 paginiLudwig Heinrich Bojanus (1776-1827) On Gall's Craniognomic System, Zoology - UnlockedJaime JaimexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crowd Management PolicyDocument3 paginiCrowd Management PolicyAffan sami rayeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Permintaan Lab 2023Document9 paginiPermintaan Lab 2023imanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 1Document11 paginiPaper 1api-499574410Încă nu există evaluări
- Argumentative EssayDocument7 paginiArgumentative EssayHuy BuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas Case ReportDocument5 paginiTugas Case ReportNida ChoerunnisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument14 paginiUntitledsyntacs skÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) : R.Varidianto Yudo T., Dr.,MkesDocument21 paginiCytomegalovirus (CMV) : R.Varidianto Yudo T., Dr.,MkesIndah WahyuningtyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Louis Kuhne - Neo-Naturopathy (New Science of Healing) (1917)Document313 paginiLouis Kuhne - Neo-Naturopathy (New Science of Healing) (1917)Școala Solomonară / The Solomonary School100% (16)
- All India Hospital ListDocument303 paginiAll India Hospital ListwittyadityaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piis1036731421001144 PDFDocument7 paginiPiis1036731421001144 PDFvaloranthakam10Încă nu există evaluări
- Homoeopathy in Breast Cancer: AbstractsDocument5 paginiHomoeopathy in Breast Cancer: Abstractskathir_cÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refractive Surgery Standards Dec 2004Document7 paginiRefractive Surgery Standards Dec 2004dr_jrcÎncă nu există evaluări
- BeraDocument20 paginiBeraMuhamad SyaifulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nurs 3020 Midterm EvaluationDocument8 paginiNurs 3020 Midterm Evaluationapi-372418362Încă nu există evaluări
- CEO COO Behavioral Health in ST Louis MO Resume David LeeDocument2 paginiCEO COO Behavioral Health in ST Louis MO Resume David LeeDavidLee2Încă nu există evaluări
- Unik Group-1Document10 paginiUnik Group-1Different PointÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aron FinalDocument70 paginiAron FinalJaime Pastrana Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- HEPADNAVIRIDAEDocument14 paginiHEPADNAVIRIDAEnur qistina humaira zulkarshamsiÎncă nu există evaluări
- FP Form ItrDocument2 paginiFP Form ItrAlibasher Macalnas100% (1)
- Approach To Nursing Assessment 1Document5 paginiApproach To Nursing Assessment 1Taiye OkondoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gynera: Coated TabletsDocument67 paginiGynera: Coated TabletsOdeke VascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- FDG PET - CT-based Response AssessmentDocument17 paginiFDG PET - CT-based Response AssessmentHelen MejiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Placenta PreviaDocument12 paginiPlacenta Previapatriciagchiu100% (3)
- Indications and Short-Term Outcome of Major Lower Extremity Amputations in Khartoum Teaching HospitalDocument8 paginiIndications and Short-Term Outcome of Major Lower Extremity Amputations in Khartoum Teaching Hospitaljean vargasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edwards Hemodynamic Monitoring For COVID Critically Ill PatientsDocument3 paginiEdwards Hemodynamic Monitoring For COVID Critically Ill PatientsblanquishemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Las - Mapeh - Health Module 1Document5 paginiLas - Mapeh - Health Module 1Analiza SantosÎncă nu există evaluări