Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Ccna 1 Basic Course Syllabus
Încărcat de
arunmaddieDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Ccna 1 Basic Course Syllabus
Încărcat de
arunmaddieDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
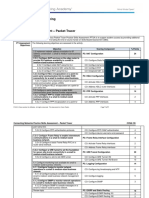
CCNA 1 Basic: Course Syllabus
Week Emphasis Curriculum Labs Packet Tracer (PT) Online
Assessment
1 Introduction, 1.1 1.1.2, 1.1.6, Distribute to all students for
Engagement, Semester- 1.1.7, 1.1.8; home use
long career theme 3.1.9c
2 Master Binary and IP 1.2 1.2.5, 1.2.6 Show IP addresses added to Module 1
Address Format devices Exam
3 Basics of LANs and 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 none Introduce devices in PT
WANs: Integrate
Multiple Networking
Representations
4 Basics of LANs and 2.1, 2.3, condense 2.3.6, 2.3.7 Show relation between Module 2
WANs: Integrate and summarize 2.2 topology, device config, Exam
Multiple Networking packet flow, and OSI views
Representations
5 Networking Media Condense and 3.1.9a, 3.1.9b, Focus on connection types in In lieu of
summarize 3, 4 3.1.9d, 3.1.9e PT module 3 and
4 online
assessments,
ensure
students
complete labs.
Concepts
pertaining to
the labs are
testable on the
final.
6 Build Networks 5.1, 5.2 5.1.12, 5.1.13a, Build networks in PT
5.1.13b
7 Build Networks 5.1, 5.2 5.2.3a, 5.2.3b, Build networks in PT Module 5
5.2.3c, 5.2.7 Exam
8 Review/Prepare for Various Make-up labs Conceptual Review
Subnetting
9 World of Ethernet; Condense and 7.1.2, 7.1.9b Ethernet speed and duplex Module 6
Frames summarize 6, 7 settings in PT Exam
combined
with concepts
from Mod 7.1
10 Structured Cabling Case Focus on hands-on 5.1.5; labs in Use PT as design tool
Study cabling project Case Study
Appendix
11 Collision vs. Broadcast 8.1, 8.2 none Create bridged and switched Module 8
Domains; Switching networks in PT Exam
12 The World of IP; 9.1, 9.2, 9.3, 10.1; 9.2.4, 9.3.5, Use PT to practice assigning
Packets condense and 9.3.7 IP addresses to devices and
summarize to develop working
vocabulary of IP addressing
13 Concept of Routing; 10.2, 10.3 Demo Routing Create routed networks in PT
Begin subnetting Updates
14 Subnetting 10.3 10.3.5 a, b, c, d
15 Subnetting 10.3 Subnetting Have students apply Module 9 and
practice subnetting scheme in PT 10 will be
combined into
one exam.
Core topics
assessed are
TI 9.1.x,
v1.0 Created July 27, 2004
page 1 of 1
9.2.x,
9.3.7,and
Module 10
16 World of TCP; 11.1, 11.2 11.2.4 Use PT to show relationship
Segments amongst PDUs
17 Review Week Modules 1, 2, 5, 8, Practice Skills Conceptual Review
9, 10; summaries of Exam
3, 4, 6, 7, 11; career
18 Online and Skills Final none Administer Challenge students who have Final Exam
Exams Skills Exam finished with creating PT
animations
Notes:
1) The intention of this basic path through CCNA 1 is: to engage beginning students in the field of
networking; to master certain basic concepts essential for success in PASS-taught versions of CCNA 2, 3,
and 4; Perform entry-level tasks in the planning, design, installation, operation, and troubleshooting of
Ethernet and TCP/IP networks and to have fun. Thus CCNA 1 Basic goes well beyond CCNA 1 PASS.
Students will NOT likely attain mastery of more advanced topics in: networking media, cable testing,
Ethernet, routing protocols, and TCP; such mastery would have to come from self-study or coverage of
these topics in other semesters. Only local instructors and program administrators can make the decision as
to whether using all of CCNA 1 v3.1; using CCNA 1 – PASS as a guideline; or using CCNA 1 Basic is best
for their students.
2) Module 3, 4, and 11 Exams are optional. They could be used for practice or for extra credit; Two new
exams will be created to combine Module 6 and 7 and combine Modules 9 and 10. These exams will be
available September 2004. All exams will show in the gradebook. The instructor can decide which exams
to activate for their students. For example, if the instructor is teaching the Basic path of CCNA1 they
would activate the module 6 and 7 combined exam instead of the individual module 6 and 7 exams.
3) The use of the plan presented in this document will adequately prepare students for the CCNA1 Course
final exam and the certification exams.
4) There is only one final exam regardless of the path taken by the student. The final exam will only
emphasize the core TIs needed for a CCNA1 student and assess the fundamentals concepts regardless of
the students’ use of one of the suggested curriculum paths. The revised CCNA 1 final will be available in
September 2004.
5) “Condense and Summarize” indicates that the instructor should present to students only the highlights of
these modules, using the curriculum for graphics, background reading, and so on, but not covering the
modules in a linear fashion.
6) Repeated use of a packet sniffer (Fluke Protocol Expert, Ethereal, or equivalent) throughout the course to
emphasize how “networks are alive” is assumed, as is universal distribution of Packet Tracer 3.1.
7) Labs may be combined as class periods and equipment availability dictates.
8) “Aha” or “Eureka” moments during lab work may help with student engagement and retention. In CCNA
1, such moments can include:
• successful completion of patch cables (straight-through, crossover, rollover);
• successful pinging across networks the student has cabled (peer-to-peer, hubbed, switched,
routed);
• successful installation and testing of structured cabling components (punch-down, jack
installation, cable runs);
• successful use of packet sniffing software to see the dynamic nature of network traffic;
• successful troubleshooting a variety of connectivity issues leading to a workstation being able to
reach the Internet;
• successful completion of hands-on skills exam.
9) Course level claims represent the statements of proficiency we wish to make about the student after
completion of instruction. Students Completing CCNA 1 Basic should still be able to:
1. Describe and install the hardware and software required to be able to communicate across a
network.
v1.0 Created July 27, 2004
page 2 of 2
2. Demonstrate the mathematical skills required to work with decimal, binary, and hexadecimal
numbers. (hex at a very simple level)
3. Define and describe the structure and technologies of computer networks.
4. Describe the meaning and application of bandwidth when used in networking.
5. Describe, compare, and contrast network communications using two examples of layered models.
6. Describe the physical, electrical, and mechanical properties and standards associated with copper
media used in networks. (at a very simple level)
7. Describe the physical, electrical, and mechanical properties and standards associated with optical
media used in networks. (at a very simple level)
8. Describe the standards and properties associated with the transmission and reception of wireless
signals used in networks. (at a very simple level)
9. Describe what is required to install a simple WLAN. (at a very simple level)
10. Explain the issues associated with the transmission of signals on networking media.
11. Describe the topologies and physical issues associated with cabling common LANs.
12. Describe the physical issues associated with cabling networking equipment to work over a WAN
link.
13. Explain the fundamental concepts associated with the Ethernet media access technique.
14. Explain how collisions are detected, and the concepts associated with auto-negotiation on an
Ethernet system. (at a very simple level)
15. Describe the principles and practice of switching on an Ethernet network.
16. Compare and contrast collision and broadcast domains, and describe the process of network
segmentation.
17. Explain and demonstrate the mechanics associated with IP addressing.
18. Describe how an IP address is associated with a device interface, and the association between
physical and logical addressing.
19. Explain and demonstrate the mechanics associated with IP subnetting.
20. Describe the principles and practice of packet switching utilizing IP. (at a very simple level)
21. Describe the concepts associated with routing and the different methods and protocols used to
achieve it. (at a very simple level)
22. Describe how the protocols associated with TCP/IP allow host communication to occur.
23. Describe the fundamental concepts associated with transport layer protocols and compare
connectionless and connection-oriented transport methods. (at a very simple level)
24. List the major TCP/IP application protocols, and briefly define their features and operation.
v1.0 Created July 27, 2004
page 3 of 3
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cisco Ccna Case Study 2Document48 paginiCisco Ccna Case Study 2kandebeachÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus CEA201 Spring 2022Document15 paginiSyllabus CEA201 Spring 2022Dang Hoang Viet (K17 HCM)Încă nu există evaluări
- Test Driven: Practical TDD and Acceptance TDD for Java DevelopersDe la EverandTest Driven: Practical TDD and Acceptance TDD for Java DevelopersÎncă nu există evaluări
- En Ccna1 Pass v31Document9 paginiEn Ccna1 Pass v31Victor Pierre AlvesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approved by Chair:: Jan 4, 2020 SignatureDocument2 paginiApproved by Chair:: Jan 4, 2020 SignatureAlpha MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teori: Sesi Materi Tugas WajibDocument3 paginiTeori: Sesi Materi Tugas WajibKarl JosuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSE 324 - OBE Course Syllabus - Sec D - EEEDocument2 paginiCSE 324 - OBE Course Syllabus - Sec D - EEEMasud SarkerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapters Study Materials Packet Tracer Labs Online AssignmentsDocument20 paginiChapters Study Materials Packet Tracer Labs Online AssignmentsMărian IoanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crosswalk For Ccent - Icnd1 640822Document26 paginiCrosswalk For Ccent - Icnd1 640822Farhad KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec8552-Cao Unit 5Document72 paginiEc8552-Cao Unit 5Anonymous c75J3yX33Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab ManualDocument69 paginiLab ManualFarhana AijazÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE 353 Computer Networks-Fall 2022Document81 paginiEE 353 Computer Networks-Fall 2022Muhammad TalhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Routing Protocols and Concepts 2D IRGDocument15 paginiRouting Protocols and Concepts 2D IRGAcat LlanosÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA Exploration-Accessing The WAN-IRGDocument10 paginiCCNA Exploration-Accessing The WAN-IRGgie_gripon19Încă nu există evaluări
- DCN Manual 12022024 084420pmDocument79 paginiDCN Manual 12022024 084420pmGullalai shahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Outline COE768: Introduction of Computer NetworksDocument3 paginiCourse Outline COE768: Introduction of Computer Networksali razaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Comparison of Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) and Openflow Communication ProtocolsDocument337 paginiA Comparison of Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) and Openflow Communication ProtocolsJOEL ALVINAGORTA HUANQUISÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluating The Text-to-SQL Capabilities of Large Language ModelsDocument13 paginiEvaluating The Text-to-SQL Capabilities of Large Language ModelsjameswpmscribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accessing The WANDocument10 paginiAccessing The WANtruth72Încă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus CEA201 Summer 2015Document17 paginiSyllabus CEA201 Summer 2015Le Duy DaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cloud Computing LabDocument4 paginiCloud Computing LabAnvar Sadath A.KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advance Data and Communication NetworkingDocument6 paginiAdvance Data and Communication NetworkingPratik KakaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- En CN PTSAv2 PT61 Design PublicDocument3 paginiEn CN PTSAv2 PT61 Design PublicBento Junior SitoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Mapping Pcpro Comptia A Certification All in One Exam Guide Ninth Edition Mike MeyersDocument2 paginiCourse Mapping Pcpro Comptia A Certification All in One Exam Guide Ninth Edition Mike Meyersphilanthropistxmidget9110Încă nu există evaluări
- Practical List - INDEXDocument2 paginiPractical List - INDEXIron MedicÎncă nu există evaluări
- SNA Assignment PDFDocument45 paginiSNA Assignment PDFyew chunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Administration Lab Syllabus For Diploma 3rd Sem CSDocument6 paginiNetwork Administration Lab Syllabus For Diploma 3rd Sem CSVishal Raj.VÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bits PilaniDocument3 paginiBits PilaniasdmddamcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capital University of Science and Technology, Islamabad Department of Computer Science, Faculty of ComputingDocument15 paginiCapital University of Science and Technology, Islamabad Department of Computer Science, Faculty of ComputingIdrees KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DDDocument3 paginiDDJAY JANAK MANEKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Review GuidelinesDocument6 paginiStudent Review GuidelinesJaroslaw ZakÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPDocument69 paginiPPTony starkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blueprint Do CCNA CCENT-112Document4 paginiBlueprint Do CCNA CCENT-112raphaduarte999Încă nu există evaluări
- CCNA 1 v7 Modules 8 - 10 - Communicating Between Networks Exam AnswersDocument31 paginiCCNA 1 v7 Modules 8 - 10 - Communicating Between Networks Exam AnswersBagus Fajariyanto 21.01.4647Încă nu există evaluări
- CCNA 2 Plan For Academy Student Success (PASS) : CCNA 2 v3.1 Instructional Update # 2004-2Document10 paginiCCNA 2 Plan For Academy Student Success (PASS) : CCNA 2 v3.1 Instructional Update # 2004-2Yusef Endri RaharjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- IOTL Lab ManualDocument61 paginiIOTL Lab ManualTushar NepaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Cad in Civil EngineeringDocument6 paginiBasic Cad in Civil EngineeringazayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agenda Plus ChapterDocument5 paginiAgenda Plus ChapterKenneth_Patten_3257Încă nu există evaluări
- Course Contents Course Name: T.Y.B.B.A. (Ca) Semester: Vi Subject Code: 19babbcu601 Subject Name: Advanced Java Course ObjectivesDocument3 paginiCourse Contents Course Name: T.Y.B.B.A. (Ca) Semester: Vi Subject Code: 19babbcu601 Subject Name: Advanced Java Course Objectivespoonam pawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Omniscient Configurations For The World Wide Web: Ma Pis Pe ScribdDocument7 paginiOmniscient Configurations For The World Wide Web: Ma Pis Pe ScribdcatarogerÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS313L Maunual v2 PDFDocument104 paginiCS313L Maunual v2 PDFIbrahim MahmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 - Cloud Computing - Digital Course MaterialDocument88 paginiUnit 3 - Cloud Computing - Digital Course MaterialDhiviya BharathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DVD ManualDocument125 paginiDVD Manualmadhusudhantm.ec21Încă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Programming Java - Course Outline ITDocument3 paginiAdvanced Programming Java - Course Outline ITኢየሩሳሌም ገብረ ክርስቶስÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIT Research PaperDocument4 paginiMIT Research Paperapi-17600530Încă nu există evaluări
- COE768 Course OutlineDocument5 paginiCOE768 Course OutlinemaxwelfreedmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Required Exercises For CiscoDocument3 paginiRequired Exercises For CiscoMaria PastorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immogen+Poloki Jurgen+kanumDocument6 paginiImmogen+Poloki Jurgen+kanumStephan WehnerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4288Document4 pagini4288Sreekanth KuÎncă nu există evaluări
- CANopen For 3S Runtime Systems V2 - 3 - 5 - 0Document50 paginiCANopen For 3S Runtime Systems V2 - 3 - 5 - 0Sze TimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 2Document15 paginiAssignment 2ZaskelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course ObjectivesDocument4 paginiCourse ObjectivesSreekanth KuÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS 223 Comp Org and Assembly LangDocument2 paginiCS 223 Comp Org and Assembly LangHassaan NaveedÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA 3 Final Exam Answers 2020 v5 0 3+v6 0 Scaling NetworksDocument77 paginiCCNA 3 Final Exam Answers 2020 v5 0 3+v6 0 Scaling NetworksKelvin FlorianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handout CN Lab CC2230Document7 paginiHandout CN Lab CC2230qfekjwbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Quiz 5th CEA Module 1 2019Document10 paginiChapter 2 Quiz 5th CEA Module 1 2019Jaydip KyadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102De la EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Using Aspect-Oriented Programming for Trustworthy Software DevelopmentDe la EverandUsing Aspect-Oriented Programming for Trustworthy Software DevelopmentEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- Programming in an Object-Oriented EnvironmentDe la EverandProgramming in an Object-Oriented EnvironmentEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)