Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Untitled 1
Încărcat de
Nazreen Latif0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
11 vizualizări2 paginiThrombophilia is the propensity to develop thrombosis (blood clots) It is due to an abnormality in the system of coagulation. The most common symptoms are DVT and pulmonary embolism.
Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
ODT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThrombophilia is the propensity to develop thrombosis (blood clots) It is due to an abnormality in the system of coagulation. The most common symptoms are DVT and pulmonary embolism.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca ODT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
11 vizualizări2 paginiUntitled 1
Încărcat de
Nazreen LatifThrombophilia is the propensity to develop thrombosis (blood clots) It is due to an abnormality in the system of coagulation. The most common symptoms are DVT and pulmonary embolism.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca ODT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
Abortion in the second trimester - from 13 to 24 weeks - is generally performed using a procedure
called Dilation & Evacuation (D&E). The D&E procedure is different from a 1st trimester abortion in a
number of ways.
Dilation and evacuation (D&E) is done in the second 12 weeks (second trimester) of pregnancy. It
usually includes a combination of vacuum aspiration, dilation and curettage (D&C), and the use of
surgical instruments (such as forceps).
Thrombophilia or hypercoagulability is the propensity to develop thrombosis (blood clots) due to an
abnormality in the system of coagulation.[1][2] Hereditary defects in one or more of the clotting factors
can cause the formation of potentially dangerous blood clots (thrombosis).
The most common symptoms of thrombophilia are deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary
embolism (PE), two conditions referred to together as venous thromboembolism (VTE). DVT usually
occurs in the legs, and is characterized by pain, swelling and redness of the limb. It may lead to long-
term swelling and heaviness in a proportion of cases due to damage to valves in the veins. The clot may
also break off and migrate (embolism) to the lungs. Depending on the size and the location of the
embolus this may lead to sudden-onset shortness of breath, chest pain, palpitations and may be
complicated by collapse, shock and cardiac arrest.[2] Venous thrombosis may also occur in more
unusual places: in the brain (cerebral venous sinus thrombosis), liver (portal vein thrombosis and
hepatic vein thrombosis), mesenteric vein, kidney (renal vein thrombosis) and possibly the veins of the
arms.[2] Whether thrombophilia also increases the risk of arterial thrombosis is less well established;
myocardial infarction (heart attack) and stroke are caused by arterial thrombosis.[2]
Thrombophilia has been linked to both recurrent miscarriage and possibly various complications of
pregnancy such as intrauterine growth restriction, stillbirth, severe pre-eclampsia and abruptio
placentae.[2]
Causes of thrombophilia can be acquired or congenital.
• Acquired refers to transient or acquired conditions that increase the tendency to clot. This
might include antiphospholipid antibodies or a temporary hypercoagulable state such as
pregnancy. Also, advanced carcinomas of the pancreas or lung may produce Trousseau
syndrome, which creates a hypercoagulable state.
• Congenital refers to hereditary conditions that increase the tendency to clot. These include
Factor V Leiden (see below); prothrombin G20210A; protein C, protein S and antithrombin
deficiencies.
An ovarian cyst is any collection of fluid, surrounded by a very thin wall, within an ovary. Any
ovarian follicle that is larger than about two centimeters is termed an ovarian cyst. An ovarian cyst can
be as small as a pea, or larger than an orange.
Most ovarian cysts are functional in nature, and harmless (benign).[1] In the US, ovarian cysts are
found in nearly all premenopausal women, and in up to 14.8% of postmenopausal women.[citation
needed]
Ovarian cysts affect women of all ages. They occur most often, however, during a woman's
childbearing years.
Some ovarian cysts cause problems, such as bleeding and pain. Surgery may be required to remove
cysts larger than 5 centimeters in diameter.
• Dull aching, or severe, sudden, and sharp pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen (one or both
sides), pelvis, vagina, lower back, or thighs; pain may be constant or intermittent—this is the
most common symptom
• Fullness, heaviness, pressure, swelling, or bloating in the abdomen
• Breast tenderness
• Pain during or shortly after beginning or end of menstrual period.
• Irregular periods, or abnormal uterine bleeding or spotting
• Change in frequency or ease of urination (such as inability to fully empty the bladder), or
difficulty with bowel movements due to pressure on adjacent pelvic anatomy
• Weight gain
• Nausea or vomiting
• Fatigue
• Infertility
• Increased level of hair growth
• Increased facial hair or body hair
• Headaches
• Strange pains in ribs, which feel muscular
• Bloating
• Strange nodules that feel like bruises under the layer of skin
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Pharma MCQ214324324325Document17 paginiPharma MCQ214324324325rab yoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5795)
- Liver As Endocrine - Stuart WhiteDocument53 paginiLiver As Endocrine - Stuart WhitechicanahenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Pathology MnemonicsDocument18 paginiPathology MnemonicsMamoorLatef100% (3)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
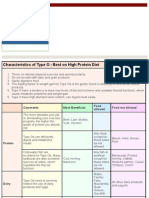
- Blood Type Diet - Type O - DrLam® - Body. Mind. Nutrition®Document5 paginiBlood Type Diet - Type O - DrLam® - Body. Mind. Nutrition®Namkha Nyingpo100% (2)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Muhammad LawalDocument6 paginiMuhammad LawalMuhammad LawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- 99 Symptoms One Root CauseDocument74 pagini99 Symptoms One Root CauseIONUT GRIGOROVÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- HipotiroidDocument27 paginiHipotiroidJuwitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Medication in PregnancyDocument11 paginiMedication in Pregnancyhussain AltaherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Minimal Packaging.Document14 paginiMinimal Packaging.AkÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Cholesterol MythDocument6 paginiThe Cholesterol MythSurendranÎncă nu există evaluări
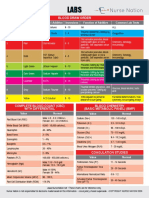
- 2 Labs Cheat Sheets Nurse NationDocument2 pagini2 Labs Cheat Sheets Nurse NationkÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Menstrual BrochureDocument2 paginiMenstrual BrochureMacrina Patoc100% (1)
- IJPI's Journal of Pharmacognosy and Herbal Formulations VisitDocument5 paginiIJPI's Journal of Pharmacognosy and Herbal Formulations VisitBean GemboelzÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Clinical Microscopy Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument5 paginiClinical Microscopy Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersGlazel TulaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Reproduction WorksheetDocument5 paginiReproduction WorksheetJENY VEV GAYOMAÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Bio ChemistryDocument16 paginiBio ChemistryDamini MandhoryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study MannitolDocument2 paginiDrug Study Mannitoljasielle80% (5)
- Wk. 1 - GlucoseDocument5 paginiWk. 1 - GlucoseChie HisuganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Engineering Living Therapeutics With Synthetic BiologyDocument20 paginiEngineering Living Therapeutics With Synthetic BiologyGabriel LohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Online-Self-Paced (OSP) Course Offering: The Study by Enderun - 4Document4 paginiOnline-Self-Paced (OSP) Course Offering: The Study by Enderun - 4jeznerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metabolic Responses To ExerciseDocument16 paginiMetabolic Responses To ExerciseKanyakorn AnothipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motivation Group B MCQS Fiza Sattar-1Document8 paginiMotivation Group B MCQS Fiza Sattar-1Intzar HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- اسئلة جراحة فصل ثانيDocument9 paginiاسئلة جراحة فصل ثانيبلال محمدÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Sifat Fisik Daging Sapi Dark Firm Dry (DFD) Hasil Fermentasi Bakteri Asam Laktat Lactobacillus PlantarumDocument7 paginiSifat Fisik Daging Sapi Dark Firm Dry (DFD) Hasil Fermentasi Bakteri Asam Laktat Lactobacillus PlantarumDebby YuvlindaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Nutrition: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionDocument53 paginiAnimal Nutrition: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionAfifaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutritional StatusDocument5 paginiNutritional StatusBern Nerquit100% (1)
- Case Study/Presentation: I. Patient ProfileDocument5 paginiCase Study/Presentation: I. Patient ProfileFatimah Sherina HussamÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Nur 194 Mod 2Document5 paginiNur 194 Mod 2Mendoza Winchelle Kyla R.Încă nu există evaluări
- MetoprololDocument15 paginiMetoprololMahavir SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sistem Klasifikasi Palm CoeinDocument11 paginiSistem Klasifikasi Palm CoeinCaca SahaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)