Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
02-Infrastructure For Ict Implementation Including The Selection of Hardware and Software
Încărcat de
Annonymous963258Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
02-Infrastructure For Ict Implementation Including The Selection of Hardware and Software
Încărcat de
Annonymous963258Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
INFRASTRUCTURE FOR ICT
IMPLEMENTATION INCLUDING THE
SELECTION OF HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE
Aiswarya Vijayakrishnan
1 Sem MBA-IB
School of Management
Studies
CUSAT,kochi – 22
E-mail:smsmbaib@gmail.com
Abstract: Information and communication technology
implementation is very essential for economic
development. In this we discuss about the components,
elements, developments and life cycle of ICT. The major
types of hardware and software’s are also discussed.
Key Words : elements, components, ICT life cycle, types
of hardware and software’s.
1.0 INTRODUCTION
As defined by the Information
Technology Association of America
(ITAA), ICT is "the study, design,
development, implementation,
support or management of computer-
based Information Systems,
particularly software applications and
computer hardware.
ICT is an umbrella term that covers all
the means of processing and
communicating. The term has gained
popularity partially due to the
coveranges of Information technology
and telecom technology . ICT covers a
broad range of technologies, including
methods of communication
(communication protocols,
transmission techniques,
communication equipment as well as
the technique for storing and
processing information. ICT allows
users to participate in a rapidly
changing world in which work and
other activities are increasingly
transformed by access to varied and
developing technologies.ICT tools can
be used to find, explore, analyze,
exchange and present information
responsibly and without
discrimination. ICT can be employed
to give users quick access to ideas
and experiences from a wide range of
people, communities and cultures.
1.2 ELEMENTS IN ICT
The two definitions of ICT are IT and IS. IT means any form of technology to
organize information ( hardware and software). Eg windows, web publishing,
telecommunication network etc. Information system includes integrated
components of processing, storing and disseminating information ( study of
systems that provide information to the users).
1.3 COMPONENTS OF ICT
The main components of ICT are as given below:
a) personnel :ICT implementation offers the company an opportunity o
upgrade and promote personnel after training. Jobs may be restructured at
higher levels by using the computer to handle routine procedures that were
traditionally handled by people.
b) hardware : Hardware (computer) components, equipments involved in the
function of a computer. Computer hardware consists of the components that
can be physically handled. These parts of computer can be touched and
seen. The function of these components is typically divided into three main
categories: input, output, and storage.
c) software : software is the set of electronic instructions a computer uses to
manipulate data, such as a word-processing program or a video game. These
programs are usually stored and transferred via the computer's hardware to
and from the CPU. These instructions tell the hardware what to do.
d) telecommunication : Telecommunications, also called telecommunication,
is the exchange of information over significant distances by electronic means.
A complete, single telecommunications circuit consists of two stations, each
equipped with a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter and receiver at
any station may be combined into a single device called a transceiver. The
medium of signal transmission can be electrical wire or cable (also known as
"copper"), optical fiber or electromagnetic fields. The free-space transmission
and reception of data by means of electromagntetic fields is called wireless.
e) data : it’s a collection of raw facts. This data is processed to get
information.
ICT also includes
• Capturing technologies like camera’s ,tape recorders etc which are
used to capture data’s.
• Storage trechnologies like CD-ROMS, digital medias etc which is
used to store data’s and informations.
• Processing technologies which facilitate the transformation of raw
facts into meaningful information.
• Communication technologies like telephones, local area networks.
• Display technologies like monitors which displays the information.
1.4 BENEFITS OF ICT
There are many benefits of ICT implementations. Some of them are as given
below:
• ICT allows users to participate in a rapidly changing world in
which work and other activities are increasingly transformed by
access to varied and developing technologies
• . ICT tools can be used to find, explore, analyze, exchange and
present information responsibly and without discrimination. ICT
can be employed to give users quick access to ideas and
experiences from a wide range of people, communities and
cultures.
• It helps in the social and economic development of the country.
• It also support the central nervous system of complex societies.
1.5 TYPES OF HARDWARE
Computer hardware is a physical part of a computer that executes within
the hardware. It is unlike computer software or data that can be frequently
changed, modified or erased on a computer. Computer hardware is not
frequently changed and so is stored in hardware devices such as read only
memory (ROM) where it is not readily changed.
Most computer hardware is embedded and so is not visible to normal
users.
Below are the different types of hardware’s found in a computer.
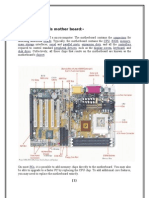
-- Motherboard: It is the central or primary circuit board making up a
complex electronic system such as a computer. A motherboard is also
known as a main board, logic board or system board.
-- Central processing Unit: A CPU is the main component of a digital
computer that interprets instructions and process data in computer
programs.
-- Random Access Memory: A RAM allows the stored data to be accessed
in any order. RAM is considered as the main memory of the computer
where the working area is used for displaying and manipulating data.
-- Basic Input Output System: BIOS prepares the software programs to
load, execute and control the computer.
-- Power Supply: Power Supply supplies electrical energy to an output load
or group of loads.
-- Video Display Controller: It converts the logical representation of visual
information into a signal that can be used as input for a display medium.
-- Computer Bus: It is used to transfer data or power between computer
components inside a computer or between computers.
-- CD-ROM drive: It contains data accessible by a computer
-- Floppy disk: It is a data storage device
-- Zip Drive: It is a medium capacity removable disk storage system.
-- Hard Disk: It is a non-volatile data storage system that stores data on a
magnetic surface layered unto hard disk platters.
1.6 TYPES OF SOFTWARES
Software, or program, enables a computer to perform specific tasks, as
opposed to the physical components of the system (hardware). This
includes application software such as a word processor, which enables a
user to perform a task, and system software such as an operating system,
which enables other software to run properly, by interfacing with hardware
and with other software or custom software made to user specifications.
Practical computer systems divide software into three major classes:
system software, programming software and application software, although
the distinction is arbitrary, and often blurred. System software helps run the
computer hardware and computer system. It includes operating systems,
device drivers, diagnostic tools, servers, windowing systems, utilities and
more. The purpose of systems software is to insulate the applications
programmer as much as possible from the details of the particular
computer complex being used, especially memory and other hardware
features, and such accessory devices as communications, printers,
readers, displays, keyboards, etc.
Programming software usually provides tools to assist a programmer in
writing computer programs and software using different programming
languages in a more convenient way. The tools include text editors,
compilers, interpreters, linkers, debuggers, and so on. An Integrated
development environment (IDE) merges those tools into a software bundle,
and a programmer may not need to type multiple commands for compiling,
interpreter, debugging, tracing, and etc., because the IDE usually has an
advanced graphical user interface, or GUI.
Application software allows end users to accomplish one or more specific
(non-computer related) tasks. Typical applications include industrial
automation, business software, educational software, medical software,
databases, and computer games. Businesses are probably the biggest
users of application software, but almost every field of human activity now
uses some form of application software. It is used to automate all sorts of
functions.
1.7 DEVELOPMENTS IN ICT
Before the last two decades mainframe computers were used. The users
used to work with terminals. But today decentralized computing and shared
database, at any location and at any time can access information. ICT is
very useful and is very essential in the present scenario. Its useful in job
training, health care, education etc.
1.8 INNOVATIONS IN ICT
1. Microelectronics : Microelectronics is a subfield of electronics.
Microelectronics, as the name suggests, is related to the study and
manufacture, or microfabrication, of electronic components which are very
small (usually micrometre-scale or smaller, but not always). These devices
are made from semiconductors. Many components of normal electronic
design are available in microelectronic equivalent: transistors, capacitors,
inductors, resistors, diodes and of course insulators and conductors can all
be found in microelectronic devices.
2. Telecommunication and electronics : Telecommunication is
transmission over a distance for the purpose of communication. In earlier
times, this may have involved the use of smoke signals, drums,
semaphore, flags or heliograph. In modern times, telecommunication
typically involves the use of electronic devices such as the
3. Microprocessors : A silicon chip that contains a CPU. In the world of
personal computers, the terms microprocessor and CPU are used
interchangeably. At the heart of all personal computers and most
workstations sits a microprocessor. Microprocessors also control the logic
of almost all digital devices, from clock radios to fuel-injection systems for
automobiles.
4. semiconductors : A semiconductor is a solid whose electrical
conductivity can be controlled by adding impurities. A semiconductor is a
material that has an electrical resistivity between that of a conductor and an
insulator.
These innovations enable processing and storage of enormous amounts of
information, plus rapid distribution of information through communication
networks.
1.9 REFERENCES
1. Robert G Murdick, Joel E Ross, James R Claggett 1988,
Information systems for modern management
2.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Inspiron 15 7577 Laptop Service Manual en UsDocument142 paginiInspiron 15 7577 Laptop Service Manual en UsPhlomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sparcengine™Ultra™Axi: Oem Technical Reference Manual July 1 9 9 8Document181 paginiSparcengine™Ultra™Axi: Oem Technical Reference Manual July 1 9 9 8Jaxon Mosfet100% (1)
- ROYAL DUTCH/SHELL: Human Rights in NigeriaDocument5 paginiROYAL DUTCH/SHELL: Human Rights in NigeriaAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Gulf Cooperation CouncilDocument7 paginiGulf Cooperation CouncilAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- India-Asean Free Trade Agreement: Submitted To Dr. James ManalelDocument16 paginiIndia-Asean Free Trade Agreement: Submitted To Dr. James ManalelAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Framework For FDI in India and Foreign Investment PolicyDocument35 paginiFramework For FDI in India and Foreign Investment PolicyAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Ariel Excel Gel: Project ReportDocument10 paginiAriel Excel Gel: Project ReportAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Financial Statement Analysis of Carborundum Universal LTDDocument5 paginiFinancial Statement Analysis of Carborundum Universal LTDAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Article 11Document2 paginiArticle 11Annonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Virtual Keyboard: Yuben JosephDocument10 paginiVirtual Keyboard: Yuben JosephAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Tata MotorsDocument2 paginiTata MotorsAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Asean Future ProspectsDocument3 paginiAsean Future ProspectsAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Greenpeace Says Global Cos Have Double Standards When It ComesDocument4 paginiGreenpeace Says Global Cos Have Double Standards When It ComesAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Presented by Arun T. Ravindran Neethu Sunny Sudeep V P Reeba Mary JoseDocument63 paginiPresented by Arun T. Ravindran Neethu Sunny Sudeep V P Reeba Mary JoseAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Witricity Seminar ReortDocument15 paginiWitricity Seminar ReortAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Wireless USBDocument6 paginiWireless USBAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Virtual Keyboard: Yuben JosephDocument11 paginiVirtual Keyboard: Yuben JosephAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Telepresence - Arun T RaviDocument7 paginiTelepresence - Arun T RaviAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Tina Technical PaperDocument6 paginiTina Technical PaperAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Ms Office Assignment: Sudeep PeterDocument3 paginiMs Office Assignment: Sudeep PeterAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Michael Eisner: Early LifeDocument23 paginiMichael Eisner: Early LifeAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- TelemedicineDocument7 paginiTelemedicineAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- It Implementation-Issues, Opportunities, Challenges, ProblemsDocument9 paginiIt Implementation-Issues, Opportunities, Challenges, ProblemsAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Bioinformatics: Tina Elizabeth VargheseDocument9 paginiBioinformatics: Tina Elizabeth VargheseAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- Smart Dust: Ansu Elizabeth PhilipDocument9 paginiSmart Dust: Ansu Elizabeth PhilipAnnonymous963258Încă nu există evaluări
- 865GM3/865PEM2 Series: MS-6763 (v1.X) M-ATX MainboardDocument70 pagini865GM3/865PEM2 Series: MS-6763 (v1.X) M-ATX MainboardveryfoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atx and p4 Power SuppliesDocument6 paginiAtx and p4 Power SuppliesSantosh DevadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dell Optiplex GX 620 UGDocument352 paginiDell Optiplex GX 620 UGcehrenbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pegatron VA70 - VG70 CR Rev2.1Document83 paginiPegatron VA70 - VG70 CR Rev2.1Taras KrasinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asus P5QL-EM ManualDocument112 paginiAsus P5QL-EM Manualmsb210Încă nu există evaluări
- The Main Circuit Board of A MicrocomputerDocument16 paginiThe Main Circuit Board of A Microcomputeramandeep123Încă nu există evaluări
- G41D3C 7 XDocument3 paginiG41D3C 7 XIqbal NurhadiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Da0hk1mb6e0 Rev e MBX-247 PDFDocument39 paginiDa0hk1mb6e0 Rev e MBX-247 PDFmohamadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foxcon 45GMX ManualDocument73 paginiFoxcon 45GMX Manualelcayman276Încă nu există evaluări
- Gigabyte GA H110M DS2Document38 paginiGigabyte GA H110M DS2Jack KramerÎncă nu există evaluări
- ARK - Intel® Core™ i7-3630QM Processor (6M Cache, Up To 3Document3 paginiARK - Intel® Core™ i7-3630QM Processor (6M Cache, Up To 3OtonielCardenasÎncă nu există evaluări
- F1A55-M LX PLUS CPU Compatibles Placas Madre ASUSDocument2 paginiF1A55-M LX PLUS CPU Compatibles Placas Madre ASUSCiroCardozoAlfonzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laptop Level-1 Service Training - Course Syllabus: Tools and Testing EquipmentsDocument12 paginiLaptop Level-1 Service Training - Course Syllabus: Tools and Testing EquipmentsHari HargovindÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mini ATX Micro ATX: AT Motherboard ATX MotherboardDocument1 paginăMini ATX Micro ATX: AT Motherboard ATX MotherboardErric MarquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- HP Xw8600 Configuration Guide June 08 RevCDocument4 paginiHP Xw8600 Configuration Guide June 08 RevCidosterenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Msi ms-7204 Rev 1A SCHDocument33 paginiMsi ms-7204 Rev 1A SCHТарас ІщакÎncă nu există evaluări
- Second Periodical Test in Information and Communications Technology (For Grade 8 and 10)Document3 paginiSecond Periodical Test in Information and Communications Technology (For Grade 8 and 10)DennisEstrellosoAlbisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compaq Presario SR5160IL Desktop PC Product Specifications Compaq Presario SR5160IL Desktop PC - HP Customer Care (United States - English)Document6 paginiCompaq Presario SR5160IL Desktop PC Product Specifications Compaq Presario SR5160IL Desktop PC - HP Customer Care (United States - English)Chhavi ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 110 Building Blocks of Nursing Informatics Concep 1aDocument23 pagini110 Building Blocks of Nursing Informatics Concep 1adeborahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dialog+ SW9.xx Service Manual, Chapter 3 Repair Instructions, Edition 1-2010Document107 paginiDialog+ SW9.xx Service Manual, Chapter 3 Repair Instructions, Edition 1-2010Ser GiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tavi 5 Specialuri Danisnulebis Interfeisebi: Ata/Atapi (Ide)Document14 paginiTavi 5 Specialuri Danisnulebis Interfeisebi: Ata/Atapi (Ide)avto sepashviliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Hardware ServicingDocument6 paginiComputer Hardware ServicingRy Cacatian KakuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Debug 1214Document7 paginiDebug 1214Anas ChokieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gigabyte Ga-b85m-Ds3h Rev 3.0Document30 paginiGigabyte Ga-b85m-Ds3h Rev 3.0YosbelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motherboard Manual Ga-8siml eDocument75 paginiMotherboard Manual Ga-8siml eReza Maliki AkbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intel Mobile CPU: Project Code: 91.4W101.001 PCB P/N: 48.4W101.011 PCB No.: 07212 Revision: - 1Document57 paginiIntel Mobile CPU: Project Code: 91.4W101.001 PCB P/N: 48.4W101.011 PCB No.: 07212 Revision: - 1kasimkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DownloadDocument4 paginiDownloadunknown_0303Încă nu există evaluări