Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
EEEG215 Tut1
Încărcat de
Suroz AwalDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
EEEG215 Tut1
Încărcat de
Suroz AwalDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING KATHMANDU UNIVERSITY
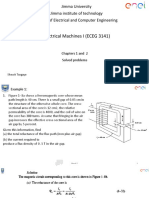
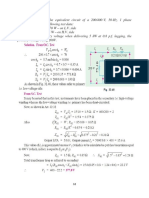
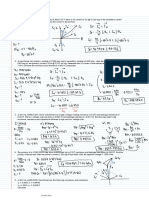
Tutorial Sheet 1 1. A 100 kVA, 2400/240 V, 50 Hz single phase transformer has an exciting current of 0.6A and a core loss of 700 watts, when its high-voltage side is energized at rated voltage and frequency. Calculate the two components of the exciting current. If the above transformer supplies a load current of 40 A at 0.8 power factor on its LV side, then calculate the primary current and its power factor. Ignore Leakage impedance drops. [Ans. 0.292 A; 0.569A; 4.584A, pf =0.762 lagging] 2. A 3300/1100 V, single phase transformer has leakage impedance of 4+j40 referred to its HV side. When unity power factor load of 20 kW is connected on the LV side, the secondary terminal voltage measured is 1050 V. Calculate the voltage and power factor as measured on its HV terminals considering exciting current negligible. [Ans. 3185.5 V; 0.9968 lag]. 3. A 50 kVA, 6600/230 V, single phase transformer has HV and LV winding resistances of 7 and 0.008 respectively. With LV winding open, a current of 0.3A at a pf of 0.3 lagging is recorded on HV side with the application of full rated voltage. Calculate efficiency at full load and 0.8pf lagging. Determine also the load current at which maximum efficiency occurs. [Ans. 96.56%; 189.74A] 4. A 100 kVA, 1100/230 V, 50 Hz transformer has an HV winding resistance of 0.1 and a leakage reactance of 0.4. The LV winding has a resistance of 0.006 and a leakage reactance of 0.01. Find the equivalent resistance, reactance and impedance referred to the HV and LV sides. Convert these into pu values. [Ans. (0.237+j0.629); (0.0104+j0.0275); (0.019+j0.052)pu] 5. A 20kVA, 2000/200V, 50 Hz transformer is operated at no load on rated voltage, the input being 150W (from HV side) at 0.12 power factor. When it is operated at rated load, the voltage drops in the total leakage reactance and the total resistances are 2% and 1% of the rated voltage respectively. Determine the input power and power factor when the transformer delivers at 200 V at 0.8pf lagging to a load on the LV side. [Ans. 10.23 kW; 0.753 lagging]. Hints: Refer load to HV side and Shift the shunt branches towards the HV source side) 6. Why are the open circuit and short circuit tests conducted on LV side and HV side respectively? 7. Why is the transformer rating given in Volt Amperes, not in Watts? 8. Explain why the core loss is taken constant for No load as well as Full load cases? 9. Describe the working principle of a transformer. Draw a phasor diagram for the transformer with load having lagging power factor. Draw its equivalent circuit. 10. Describe why the copper losses and core losses are neglected in the open circuit test and short circuit test respectively?
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Evaluare: 2.5 din 5 stele2.5/5 (3)
- Tutorial Problems 32.3Document2 paginiTutorial Problems 32.3Grace Joy Romias50% (4)
- Electrical QuestionDocument8 paginiElectrical QuestionMohd Radzi Kaki LimoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 1 (Transformers)Document5 paginiTutorial 1 (Transformers)Vishal GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer Pasar Am IDocument8 paginiTransformer Pasar Am IJennel BaringÎncă nu există evaluări
- A.C Powers and Power FactorDocument23 paginiA.C Powers and Power FactoremgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial - 2 - ELL203 - 07th August - 2023Document2 paginiTutorial - 2 - ELL203 - 07th August - 2023Ujjawal MeenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Sheet - 10Document2 paginiTutorial Sheet - 10Vishwas BabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 3Document4 paginiAssignment 3Lala's gamingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document1 paginăAssignment 1Vikash TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Sheet 05Document4 paginiTutorial Sheet 05Debdeep SamajdarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tut 2 emDocument1 paginăTut 2 emBishal TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- CaddDocument2 paginiCaddQuazi Warish AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved Problems (1&2)Document27 paginiSolved Problems (1&2)Eyosiyas BeleteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformers 17.7.14Document7 paginiTransformers 17.7.14TharinduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Exercises On Transformer: Introduction To Electrical Machine (Course Code-Emeg2261)Document2 paginiTutorial Exercises On Transformer: Introduction To Electrical Machine (Course Code-Emeg2261)Hanan Shayibo100% (1)
- TU2 TransformerDocument3 paginiTU2 TransformerLove Nepal Is BackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example 7Document5 paginiExample 7M7MD ACADEMIAÎncă nu există evaluări
- TransformersDocument1 paginăTransformersElormeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qs On TransformersDocument2 paginiQs On TransformersRoronoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open-Circuit or No-Load TestDocument13 paginiOpen-Circuit or No-Load TestNANDHAKUMAR AÎncă nu există evaluări
- EEE 203 Energy Conversion I - Problems For Assignments - PrintDocument20 paginiEEE 203 Energy Conversion I - Problems For Assignments - PrintthiagoomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document1 paginăAssignment 1Pra GoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Bombay EE111: Introduction To Electrical Systems Assignment 5555555555Document2 paginiDepartment of Electrical Engineering, IIT Bombay EE111: Introduction To Electrical Systems Assignment 5555555555K paritoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheet 2Document2 paginiSheet 2meminna99Încă nu există evaluări
- King Fahd University of Petroleum & MineralsDocument3 paginiKing Fahd University of Petroleum & MineralsAly AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aim of The Experiment:: Sl. No. Name of Apparatus Specification QuantityDocument4 paginiAim of The Experiment:: Sl. No. Name of Apparatus Specification QuantityDevansh MankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical MachinesDocument54 paginiElectrical MachinesAhmed MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE2029 - Introduction To Electrical Energy Systems Tutorial # 1 TransformersDocument2 paginiEE2029 - Introduction To Electrical Energy Systems Tutorial # 1 TransformersToh Wei WenÎncă nu există evaluări
- SFBVSFBSFDocument2 paginiSFBVSFBSFTiongJingYinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exact Equivalent Circuit of A Loaded TransformerDocument8 paginiExact Equivalent Circuit of A Loaded TransformerM7MD ACADEMIAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 TransformerDocument2 paginiAssignment 1 TransformerGayatri Vedula50% (2)
- Ece5377 6377 HW02 (20150211)Document1 paginăEce5377 6377 HW02 (20150211)bilalhanjra246Încă nu există evaluări
- Tut 2Document3 paginiTut 2MOHIT SINGHALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examples - For - Transformer - On - Load - and - NLDocument2 paginiExamples - For - Transformer - On - Load - and - NLEpi FanioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 2 - Uncontrolled Rectifier Circuits RevisedDocument2 paginiTutorial 2 - Uncontrolled Rectifier Circuits RevisedAyhan AbdulAzizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EEN-112: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 05Document1 paginăDepartment of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EEN-112: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 05Kumar ShivamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 6 Solution - 21955Document9 paginiTutorial 6 Solution - 21955Sahil GalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE-307 Assignment-2Document2 paginiEE-307 Assignment-2123Încă nu există evaluări
- 1 Tutorial TranformerDocument1 pagină1 Tutorial TranformerNitin NarangÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLB 10402 - July 2012Document2 paginiCLB 10402 - July 2012xargahÎncă nu există evaluări
- TUTO 5 TransformerDocument2 paginiTUTO 5 TransformerVievie Le BluewberrietrufflesÎncă nu există evaluări
- LECTUERE 6 E 1530 High Voltage EngineeringDocument30 paginiLECTUERE 6 E 1530 High Voltage Engineeringahmed372416Încă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Sheet EEC2110 - Electrical Machines-I Unit - I and II (Transformers)Document2 paginiTutorial Sheet EEC2110 - Electrical Machines-I Unit - I and II (Transformers)SunilkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machines AssignmentDocument3 paginiMachines AssignmentBolisetti DheerajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machine LabDocument7 paginiMachine LabNurjahan-Ara StudentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 2 - Fa16-Bet-056 - Muneeb UllahDocument9 paginiLab 2 - Fa16-Bet-056 - Muneeb UllahPel Colour onÎncă nu există evaluări
- TransformerDocument2 paginiTransformerBsal SokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machines Tutorial Sheet #1Document4 paginiMachines Tutorial Sheet #1Shruthi reddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC Machine Apparatus CONTACT2Document15 paginiAC Machine Apparatus CONTACT2Jayven Q. VillamaterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report 1 Power eDocument12 paginiReport 1 Power eMuhd HafizzudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- ET Tut5 AUT2016-17Document4 paginiET Tut5 AUT2016-17gebreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recitation#3Document4 paginiRecitation#3William AlikisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 03Document2 paginiExperiment 03micuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 6Document2 paginiTutorial 6Shubham KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer SheetDocument5 paginiTransformer Sheetمحمد عليÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer Questions-1Document2 paginiTransformer Questions-1EmmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oc SC PDFDocument5 paginiOc SC PDFVenkatasairamreddy KandulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- mohanCV PDFDocument3 paginimohanCV PDFSuroz AwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gid1548Pdf Hi3516DV100Document36 paginiGid1548Pdf Hi3516DV100Suroz AwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- mohanCV PDFDocument3 paginimohanCV PDFSuroz AwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hi 3516 DDocument7 paginiHi 3516 Dco_stel817842Încă nu există evaluări
- Imx290 291lqr FlyerDocument2 paginiImx290 291lqr FlyerSuroz AwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Voice Commander PDFDocument2 paginiVoice Commander PDFSuroz AwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- NodeDocument240 paginiNodeSuroz AwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Load Shedding Schedule Kathmandu 5-Dec-2011Document2 paginiLoad Shedding Schedule Kathmandu 5-Dec-2011Geshan ManandharÎncă nu există evaluări
- GrpreportDocument14 paginiGrpreportSuroz AwalÎncă nu există evaluări