Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
When You Set Up Windows
Încărcat de
Reginald D. WhiteDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
When You Set Up Windows
Încărcat de
Reginald D. WhiteDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
When you set up Windows 2000, you have to provide information about how you want to install the
operating system. The procedures in this chapter help you provide necessary information. To ensure a successful installation, you should complete the following tasks-which are described in the sections that follow--before you install Windows 2000:
Make sure your hardware components meet the minimum requirements.
Obtain Windows 2000-compatible hardware and software, such as upgrade packs, new drivers, and so on. Obtain network information.
Back up your current files before upgrading, in case you need to restore your current operating system. Determine whether you want to perform an upgrade or install a new copy of Windows. If you're installing a new copy, identify and plan for any advanced Setup options you might want.
If You're Upgrading
The upgrade process is simple. The Setup wizard detects and installs the appropriate drivers, or it creates a report on devices that couldn't be upgraded so you can be sure your hardware and software are compatible with Windows 2000. Important You must uncompress any DriveSpace or DoubleSpace volumes before upgrading to Windows 2000.
To upgrade Windows 95, Windows 98, or Windows NT 4.0 from the CD
1. Start your computer by running your current operating system, and then insert the Windows 2000 Professional CD into your CD-ROM drive.
2.
If Windows automatically detects the CD and asks if you would like to upgrade your computer to Windows 2000 Professional, click Yes. Otherwise, click Start, and then click Run. At the prompt, type the following command, replacing d with the letter assigned to your CD-ROM drive: d:\i386\winnt32.exe 3. 4. Press ENTER. Follow the instructions that appear.
To upgrade Windows NT 3.51 from the CD
1. Start your computer by running your current operating system, and then insert the Windows 2000 Professional CD into your CD-ROM drive.
2.
In Program Manager, click File, and then click Run. At the prompt, type the following command, replacing d with the letter of your CD-ROM drive:
d:\i386\winnt32.exe 3. 4. Press ENTER. Follow the instructions that appear.
To upgrade from a network connection
1. Using your current operating system, establish a connection to the shared network folder that contains the Setup files. If you have an MS-DOS or network installation disk that contains network client software, you can use that disk to connect to the shared folder. Your network administrator will be able to provide you with this path.
2.
If your computer is currently running Windows 95, Windows 98, or a previous version of Windows NT, at the command prompt, type the path to the file winnt32.exe. 3. Press ENTER.
4.
5.
When you're asked if you would like to upgrade your computer to Windows 2000 Professional, click Yes. Follow the instructions that appear.
Collecting User and Computer Information
The Windows 2000 Setup wizard leads you through the process of gathering information about you and your computer. Although much of this installation process is automatic, you may need to provide information or select settings in the following screens, depending on the current configuration of your computer:
Licensing Agreement. If you agree with the terms, select I accept this agreement to continue with Setup. Select Special Options. Use this screen to customize Windows 2000 Setup, language, and accessibility settings for new installations. You can set up Windows 2000 to use multiple languages and regional settings. For more information, see Determining Advanced Setup Needs, earlier in this chapter. Upgrading to the Windows 2000 File System NTFS. Windows 2000 can automatically convert partitions on your hard disk to NTFS, or you can keep your existing file systems. If you're upgrading, Setup uses your current file system; however, you can change to NTFS, the recommended file system for Windows 2000. For more information, see NTFS in Chapter 3. Regional Settings. Change the system and user locale settings for different regions and languages.
Personalize Your Software. Enter the full name of the person and, optionally, the organization to whom this copy of Windows 2000 is licensed.
Computer Name and Administrator Password. Enter a unique computer name that differs from other computer, workgroup, or domain names on your network. Setup suggests a computer name, but you can change the name. Setup automatically creates an Administrator account during the installation. When you use this account, you have full rights over the computer's settings and can create user accounts on the computer. That is, logging on as an Administrator after you install Windows 2000 gives you administrative privileges that you need to log on and manage your computer. Specify a password for the Administrator account. For security reasons you should always assign a password to the Administrator account. Take care to remember and protect your password.
Date and Time Settings. Verify the date and time for your region, select the appropriate time zone, and then select whether you want Windows 2000 to automatically adjust for daylight savings time.
Networking Settings. Unless you're an advanced user, select the Typical settings option for your network configuration. Select the Custom settings option to manually configure network clients, services, and protocols.
Workgroup or Computer Domain. During Setup, you must join either a workgroup or a domain. For more information, see Providing Networking Information, later in this chapter.
Provide Upgrade Packs. Some software manufacturers provide upgrade packs that allow your programs to work with Windows 2000. If you don't have any upgrade packs, simply click Next to continue with Setup.
Network Identification Wizard. If your computer is participating on a network, this wizard prompts you to identify the users who will be using your computer. If you indicate that you're the only user, you're assigned Administrator privileges.
Providing Networking Information
During or after Setup, you need to join either a workgroup or a domain. If you won't be working on a network, specify that you want to join a workgroup. Joining a Workgroup A workgroup is one or more computers with the same workgroup name (for example, a "peer-to-peer" network). Any user can join a workgroup by simply specifying the workgroup name--you don't need special permissions to join a workgroup. You must provide an existing or new workgroup name, or you can use the workgroup name that Windows 2000 suggests during Setup
Logging on to Windows 2000
When your computer restarts after installation, you log on to Windows 2000 for the first time. If you upgraded from a previous version of Windows and already had an existing user account, you can log on using that account and password. If you don't have a user account, you need to log on using the Administrator account and the password you selected during Setup. Then you can create your user account. For more information, see Understanding Accounts in Chapter 5.
To log on to Windows 2000 using the Administrator account
1.
2.
In the Log on to Windows 2000 dialog box, type the Administrator password that you created during Setup. Press ENTER.
Windows 2000 starts, and the Welcome screen appears.
Creating a User Account
Your user account identifies your user name and password, the groups you're a member of, which network resources you have access to, and your personal files and settings. Each person who regularly uses the computer should have a user account. The user account is identified by a user name and a password, both of which the user types when logging on to the computer. You can create individual user accounts after logging on to the computer as Administrator.
To create your user account
1. 2. 3.
Click the Start button, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel. Double-click Users and Passwords. Click Add.
The Add New User wizard appears. 4. Follow the instructions that appear.
After you've added your user account, you're ready to log off as Administrator and log on using your user account.
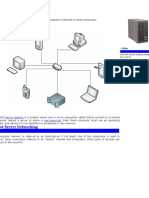
To make a local area connection
Typically, most Windows 2000 users belong to a local area network. When you start your computer, Windows 2000 detects your network adapter and automatically starts the local area connection. Unlike other types of connections, the local area connection is created automatically, and you do not have to click the local area connection in order to start it. Note
Windows 2000 automatically creates a local area connection for each network adapter that it detects. If more than one network adapter is installed, you can eliminate possible confusion by immediately renaming each local area connection to reflect the network that it connects to.
If your computer has one network adapter, but you need to connect to multiple LANs (for example, when traveling to a regional office), the network components for your local area connection need to be enabled or disabled each time you connect to a different LAN.
If more than one network adapter is installed, you need to add or enable the network clients, services, and protocols that are required for each local area connection. When you do so, the client, service, or protocol is added or enabled for all other network and dial-up connections.
To install TCP/IP
1. Open Network and Dial-up Connections Right-click the network connection for which you want to install and , and then click Properties.
2. 3.
enable TCP/IP
On the General tab (for a local area connection) or the Networking tab (all other connections), if Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is not in the list of installed components, then do the following:
a. b. c. 4.
Click Install. Click Protocol, and then click Add.
In the Select Network Protocol dialog box, click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click OK. Verify that the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) check box is selected, and then click OK. Note
To open Network and Dial-up Connections, click Start, point to Settings, and then click Network and Dial-up Connections. You must be logged on as an administrator or a member of the Administrators group in order to complete this procedure. TCP/IP is installed as the default network protocol if network adapter hardware was detected during Windows 2000 Setup. You only need to follow these instructions if the TCP/IP default selection was overridden during Setup
To configure TCP/IP for static addressing
1. Open Network and Dial-up Connections
2. 3.
Right-click the network connection you want to configure, and then click Properties. On the General tab (for a local area connection) or the Networking tab (all other connections), click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
4.
Click Use the following IP address, and do one of the following:
For a local area connection, in IP address, Subnet mask, and
Default gateway, type the IP address gateway addresses. , subnet mask, and default
For all other connections, in IP address, type the IP address.
5. 6. 7.
Click Use the following DNS server addresses. In Preferred DNS server and Alternate DNS server, type the primary addresses.
and secondary DNS server
To configure advanced settings, click Advanced, and do one or more of the following:
To configure additional IP addresses:
1. 2. 3.
On the IP Settings tab, in IP addresses, click Add.
In IP Address and Subnet mask, type an IP address and subnet mask, and then click Add. Repeat step 1 for each IP address you want to add, and then click OK.
To configure additional default gateways:
1.
Add.
On the IP Settings tab, in Default gateways, click
2. 3.
In Gateway and Metric, type the IP address of the default gateway and the metric, and then click Add. Repeat step 1 for each default gateway you want to add, and then click OK
To configure TCP/IP to use DNS
1. Open Network and Dial-up Connections
2. 3.
Right-click the network connection you want to configure, and then click Properties. On the General tab (for a local area connection) or the Networking tab (all other connections), click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
4. 5.
If you want to obtain DNS server addresses from a DHCP server, click Obtain DNS server address automatically. If you want to manually configure DNS server addresses, click Use the following DNS server addresses, and in Preferred DNS server and Alternate DNS server, type the preferred DNS server and alternate DNS server IP addresses.
6.
To configure advanced DNS properties, click Advanced, click the DNS tab, and do one or more of the following:
To configure an additional DNS server IP address
1.
Under DNS server addresses, in order of use, click
Add.
2.
In DNS server, type the IP address of the DNS server, and then click Add.
To modify the resolution behavior for unqualified DNS names, do the
following:
To resolve an unqualified name by appending the primary DNS suffix and the DNS suffix of each connection (if configured), click Append primary and connection specific DNS suffixes. If you also want to search the parent suffixes of the primary DNS suffix up to the second level domain, select the Append parent suffixes of the primary DNS suffix check box.
To resolve an unqualified name by appending the suffixes from a list of configured suffixes, click Append these DNS suffixes (in order), and then click Add to add suffixes to the list.
To configure a connection-specific DNS suffix (local area connection
only), type the DNS suffix in DNS suffix for this connection. only), do the following:
To modify DNS dynamic update behavior (local area connection
To use a DNS dynamic update to register the IP addresses of this connection and the primary domain name of the computer, select the Register this connection's addresses in DNS check box. This option is enabled by default. The primary domain name of the computer is the primary DNS suffix appended to the computer name and can be viewed as the full computer name on the Network Identification tab (available in System in Control Panel).
To use a DNS dynamic update to register the IP addresses and the connection-specific domain name of this connection, select the Use this connection's DNS suffix in DNS registration check box. This option is disabled by default. The connection-specific domain name of this connection is the DNS suffix for this connection appended to the computer name.
No matter where you are working, your computer will be easier to use and to manage, because Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional is more compatible and more powerful than any workstation you've used before. Easier to use With Windows 2000 Professional, you have faster access to information, and you are able to accomplish tasks more quickly and easily. Windows 2000 Professional makes it easier to:
Work with files. Find information. Personalize your computing environment.
Work on the Web. Work remotely.
Easier to manage You and your network administrators can work more efficently now, because many of the most common computer-management tasks are automated and streamlined with Windows 2000 Professional. With Windows 2000, your workstation will be easier to:
Set up. Administer. Support.
More compatible Windows 2000 Professional offers increased compatibility with different types of networks and with a wide array of legacy hardware and software. Windows 2000 also provides:
Improved driver support.
Increased support for new-generation hardware and multimedia technologies. Integration of the new Euro currency symbol.
More powerful For all your computing needs, Windows 2000 Professional provides:
Industrial-strength reliability. The highest level of security. Powerful performance.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- How to Setup a Windows PC: A Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up and Configuring a New Computer: Location Independent Series, #4De la EverandHow to Setup a Windows PC: A Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up and Configuring a New Computer: Location Independent Series, #4Încă nu există evaluări
- Windows Operating System: Windows Operating System (OS) Installation, Basic Windows OS Operations, Disk Defragment, Disk Partitioning, Windows OS Upgrade, System Restore, and Disk FormattingDe la EverandWindows Operating System: Windows Operating System (OS) Installation, Basic Windows OS Operations, Disk Defragment, Disk Partitioning, Windows OS Upgrade, System Restore, and Disk FormattingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step by Step Procedure For Windows Server 2003 InstallationDocument26 paginiStep by Step Procedure For Windows Server 2003 InstallationGaurang Basarkar80% (5)
- A+ With Network Certification: Network Operating System (NOS)Document20 paginiA+ With Network Certification: Network Operating System (NOS)Dinesh RaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step by Step Guide To Setup Active Directory On Windows Server 2008Document397 paginiStep by Step Guide To Setup Active Directory On Windows Server 2008Ardian DharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- XP SetupDocument7 paginiXP SetupA R KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step-By-Step Guide For Setting Up VPN-Based Remote AccessDocument56 paginiStep-By-Step Guide For Setting Up VPN-Based Remote AccesskoolzfireÎncă nu există evaluări
- Setting Up Computer Servers (SUCS) Network Services and Its OperationDocument14 paginiSetting Up Computer Servers (SUCS) Network Services and Its Operationelmer riveroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Window ServerDocument25 paginiWindow ServersohaibchÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Install Active Directory On Windows 2003Document55 paginiHow To Install Active Directory On Windows 2003Ias Aspirant AbhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Install Windows Server 2003: Step #1: Plan Your InstallationDocument34 paginiInstall Windows Server 2003: Step #1: Plan Your InstallationgoniebisÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Can I Install Windows 2003 ServerDocument33 paginiHow Can I Install Windows 2003 ServerShaiful Bahari Abu BakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Server Instal at IonDocument6 paginiServer Instal at Ionpramod346Încă nu există evaluări
- Installing Windows Server 20031211Document7 paginiInstalling Windows Server 20031211Einho AicnegerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Remote Desktop: Administrator To Allow Other Users To Connect To Your ComputerDocument8 paginiRemote Desktop: Administrator To Allow Other Users To Connect To Your ComputerMin MCLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active Directory Directory Service Microsoft Windows Domain Windows Server Domain Controller Authenticates AuthorizesDocument3 paginiActive Directory Directory Service Microsoft Windows Domain Windows Server Domain Controller Authenticates AuthorizesJulius DollosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Client 2Document60 paginiIntroduction To Client 2Bernadeth Dusal GuiasilonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 3: 2003. Youtube Video Link: Https://Youtu - Be/FsprvgyajfmDocument2 paginiActivity 3: 2003. Youtube Video Link: Https://Youtu - Be/FsprvgyajfmMarjorie caldeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Computer Network Consists of Two or More Computers Intended To Share ResourcesDocument25 paginiA Computer Network Consists of Two or More Computers Intended To Share ResourcesGigi EspirituÎncă nu există evaluări
- CssDocument9 paginiCssSheng Suelto CarpenteroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Windows 2000 Server Installation OverviewDocument6 paginiWindows 2000 Server Installation OverviewAshish KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- UsefulTips Windows XPDocument123 paginiUsefulTips Windows XPpranithnambiar100% (3)
- Windows Server 2008 Active DirectoryDocument151 paginiWindows Server 2008 Active DirectoryPichai Ng-arnpairojhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam DumyDocument8 paginiExam Dumyapi-26530736Încă nu există evaluări
- Customer Release Notes Fiery Network Controller For Docucolor 250/240Document34 paginiCustomer Release Notes Fiery Network Controller For Docucolor 250/240jonnathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation Instructions For Manual Installation of Microsoft Windows Server 2003Document7 paginiInstallation Instructions For Manual Installation of Microsoft Windows Server 2003smart_eagle44Încă nu există evaluări
- Install Zentyal As PDC (Primary Domain Controller) and Integrate Windows System - Part 1Document48 paginiInstall Zentyal As PDC (Primary Domain Controller) and Integrate Windows System - Part 1Johann MalakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiery User GuideDocument36 paginiFiery User GuideCraig MusgravesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 7.3.1: Installation Demonstration of Windows 2000: Estimated Time: 90 Minutes ObjectiveDocument12 paginiLab 7.3.1: Installation Demonstration of Windows 2000: Estimated Time: 90 Minutes ObjectiveHamzaSpahijaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer CSS NCIIDocument43 paginiReviewer CSS NCIICartoon Collection100% (1)
- NW Admin LAB Exercise 1 SETUPDocument19 paginiNW Admin LAB Exercise 1 SETUPxyzalimohamed76Încă nu există evaluări
- XP TricksDocument124 paginiXP TrickssandeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer System Services NC IiDocument55 paginiComputer System Services NC IiJuris SucroÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Can I Install Windows Server 2003 On My ServerDocument9 paginiHow Can I Install Windows Server 2003 On My Serverjjs555729Încă nu există evaluări
- Inter QuesDocument6 paginiInter Quesambrish78659Încă nu există evaluări
- Installing Microsoft Windows Server 2003Document23 paginiInstalling Microsoft Windows Server 2003FH ChowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Setup Guide 98 367Document9 paginiLab Setup Guide 98 367Morfeo MunitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- P.C.T.E.: Report File OF Handling Operating SystemsDocument33 paginiP.C.T.E.: Report File OF Handling Operating SystemsArsh SainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DHCP Step by Step GuideDocument28 paginiDHCP Step by Step GuideruletriplexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course 2152 Module 1Document58 paginiCourse 2152 Module 1alterdcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assgnment of ServerDocument193 paginiAssgnment of Servernuri mohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networking Useful TipsDocument3 paginiComputer Networking Useful TipsSantosh RaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Informatica PowerCenter 9 Installation and Configuration Complete GuideDocument38 paginiInformatica PowerCenter 9 Installation and Configuration Complete Guideashish_s_6174Încă nu există evaluări
- CSS - Info Sheet 3.2-3 - Confirm Network Services To Be ConfiguredDocument26 paginiCSS - Info Sheet 3.2-3 - Confirm Network Services To Be ConfiguredomarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step by Step Additional Doimain Controller and Child DomainDocument4 paginiStep by Step Additional Doimain Controller and Child DomainRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rzbiconda Arerdusite Bayuitopek 239z382133e-1a110 - 15Document15 paginiRzbiconda Arerdusite Bayuitopek 239z382133e-1a110 - 15rpal2014Încă nu există evaluări
- Sample TextDocument39 paginiSample TextKent Erl Uson EmiuhcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rzbiconda Arerdusite Bayuitopek 239z382133e-1a110 - 7Document15 paginiRzbiconda Arerdusite Bayuitopek 239z382133e-1a110 - 7rpal2014Încă nu există evaluări
- CHS Module 4 - Maintaining Computer Systems and NetworksDocument46 paginiCHS Module 4 - Maintaining Computer Systems and NetworksLawrence Cada Nofies100% (7)
- Getting StartedDocument16 paginiGetting StartedmsiskatemwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Install Windows Server 2003Document9 paginiInstall Windows Server 2003Jayson GumbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Os Format TipsDocument9 paginiOs Format TipsVamsi Jayasimha KaranamÎncă nu există evaluări
- XP InstalltaionDocument90 paginiXP InstalltaionJaveed AhamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creating The Active DirectoryDocument24 paginiCreating The Active Directoryakr14febÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dec50103 PW6Document30 paginiDec50103 PW6aiman raraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation MagIC Net 2.xDocument17 paginiInstallation MagIC Net 2.xJuan Diego Aznar FernándezÎncă nu există evaluări
- DP2 V5127 New InstallDocument33 paginiDP2 V5127 New InstallMarck MarckzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Windows Vista Sp2 Install Guide English EditionDe la EverandWindows Vista Sp2 Install Guide English EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guilt and Responsibility in "Doctor Faustus" and "Paradise Lost"Document2 paginiGuilt and Responsibility in "Doctor Faustus" and "Paradise Lost"Reginald D. WhiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kuwaiti Oil Fires: Rachel White 3Rd PeriodDocument5 paginiKuwaiti Oil Fires: Rachel White 3Rd PeriodReginald D. WhiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Analysis of Themes in A Doll's HouseDocument5 paginiAn Analysis of Themes in A Doll's HouseReginald D. White100% (1)
- Self and Personality Psychology Research Paper 2 (1) DraftDocument6 paginiSelf and Personality Psychology Research Paper 2 (1) DraftReginald D. WhiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Doll House - Character Analysis EssayDocument1 paginăA Doll House - Character Analysis EssayReginald D. White100% (1)
- CVM Lab 12Document4 paginiCVM Lab 12AdedayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tech Note - PAN Vwire Eval InstallDocument16 paginiTech Note - PAN Vwire Eval InstallJhonnySinatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- S2300&S3300 V100R006C05 Configuration Guide - IP Multicast PDFDocument276 paginiS2300&S3300 V100R006C05 Configuration Guide - IP Multicast PDFAlexander PischulinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2017 v51v60 Introduction To NetworksDocument65 paginiCCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2017 v51v60 Introduction To NetworksÐâvid Ĵesus Morales SeguraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sabp Z 080Document21 paginiSabp Z 080Hassan MokhtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- User Guide: For TP-Link Omada Access PointsDocument104 paginiUser Guide: For TP-Link Omada Access Pointsabul abbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- BX-Y08 User ManualDocument57 paginiBX-Y08 User Manualghatevinod9360Încă nu există evaluări
- Vesda: Application Note 001/03Document2 paginiVesda: Application Note 001/03eduardo gonzalezavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tew 310apbx ManualDocument47 paginiTew 310apbx ManualMarceloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Docslide - Us 1217 Packet Tracer Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches Instructions 56847ae83fed6Document3 paginiDocslide - Us 1217 Packet Tracer Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches Instructions 56847ae83fed6Christian EspinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 5: Creating Secure Architectures: A ChallengeDocument14 paginiLab 5: Creating Secure Architectures: A ChallengeLêDương AnhTuấnÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16.4.6 Packet Tracer - Configure Secure Passwords and SSHDocument3 pagini16.4.6 Packet Tracer - Configure Secure Passwords and SSHkds20850Încă nu există evaluări
- Comcast Xfinity 2012 Law Enforcement Handbook v022112Document33 paginiComcast Xfinity 2012 Law Enforcement Handbook v022112DonnieZunigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- F2008 Instruction Manual English - 131 AmadaDocument68 paginiF2008 Instruction Manual English - 131 AmadaJuanJo ToGoÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSC EXchange Data BestDocument22 paginiBSC EXchange Data BestAbebe SharewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fanuc Data Server &mitsubishi Ethernet USER MANUAL (Cesarftp Software)Document28 paginiFanuc Data Server &mitsubishi Ethernet USER MANUAL (Cesarftp Software)Rogério PereiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Array User Guide PDFDocument305 paginiArray User Guide PDFsanna agarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chatsworth, Inc. Power Management CatalogDocument26 paginiChatsworth, Inc. Power Management CatalogJuicy69MannÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summit x670 g2 Data Sheet PDFDocument10 paginiSummit x670 g2 Data Sheet PDFRahul RajputÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9: Multiarea OSPF: CCNA Routing and Switching Scaling Networks v6.0Document27 paginiChapter 9: Multiarea OSPF: CCNA Routing and Switching Scaling Networks v6.0Richard C CheccaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison With vCloudPoint V1 and NComputing RX300Document4 paginiComparison With vCloudPoint V1 and NComputing RX300Girish JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- NetperfDocument39 paginiNetperfDhiraj SuranaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AN5116-06B Optical Line Terminal Equipment GPON Service-CLI Quick Start Guide (Version A)Document62 paginiAN5116-06B Optical Line Terminal Equipment GPON Service-CLI Quick Start Guide (Version A)Luan Benato100% (1)
- SRX Cluster Monitoring Best PracticesDocument94 paginiSRX Cluster Monitoring Best PracticesHaider AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schleibinger ASTM C1581 Shrinkage-RingDocument32 paginiSchleibinger ASTM C1581 Shrinkage-RingJayachandranÎncă nu există evaluări
- V1600G Series OLT CLI User Manual - v1.1Document115 paginiV1600G Series OLT CLI User Manual - v1.1Krlos Andres PulgarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- RunningConfig 172.16.1.1Document3 paginiRunningConfig 172.16.1.1Sarah MerchantÎncă nu există evaluări
- CP Plus IP - Finder - User's ManualDocument13 paginiCP Plus IP - Finder - User's ManualvishwajitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spirent TestCenter Software and Hardware Release Notes 4 49Document28 paginiSpirent TestCenter Software and Hardware Release Notes 4 49pmo79Încă nu există evaluări
- JNCIA-Junos Study Guide-Part 2: Worldwide Education Services Worldwide Education ServicesDocument64 paginiJNCIA-Junos Study Guide-Part 2: Worldwide Education Services Worldwide Education Serviceswerna samÎncă nu există evaluări