Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINE
Încărcat de
Mitu Miressa تDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINE
Încărcat de
Mitu Miressa تDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
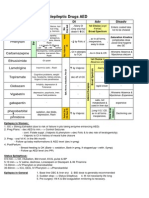
Page 1 Contraindictions/ Therapeutic Uses Mechanism of Action Pharmacokinetics Precautions Hypertension Block conversion of Absorption Contraindictions Heart Failure
Angiotensin I to Angiotensin II - Orally (except ENALAPRIL, IV -pregnancy (fetal injury, Myocardial Infarction aldosterone levels (reduce only) hypersenitivity, renal stenosis, Diabetic/Nondiabetic or inhibit agniotensin II) -Can be administered with food single kidney with stenosis Nephropathy Inhibit kinase II (ACE) (except CAPTOPRIL and (narrowing) Prevention of MI; stroke; and increase levels of bradykinin MOEXIPRIL) Precautions death in patients at high (vasodilator) -Long half-lives (except -renal and hepatic impairment, cardiovascular risk CAPTOPRIL, which is admin 2- hypovolemia (decreased blood IN HEART FAILURE: produce 3x a day) plasma volume), hyponatremia multiple benefits by lowering Distribution is well (Na concentration is low), arteriorlar tone, these drugs Metabolism breast feeding, aortic valve improve regional blood flow, -small intestine and liver insufficiency (leaking of valve) and by reducing cardiac Excretion afterload, they increase cardiac -by kidneys (can accumulate to output. dangerous levels in Pts with IN DIABETES: reduction of kidney disease, and hence glomerular filtration pressure. dosages must be reduced in Lower filtration pressure by these pts. Only one agent reducing levels of angiotensin FOSINOPRIL - does not require II, and thereby slow dosage reduction. development of renal injury. Side Effects/ Adverse Reactions Hypotension (1st dose hypotension) Cough (non productive) beacause increase in bradykinase hyperkalemia renal failure (renal stenosis) angioedema neutropenia loss of taste Nursing Implications/ Management
Assessment -Review client's medication history including allergies to medications, history of angioedema -Assess client's medical history -Ask if client is pregnant -Always obtain baseline BP prior drug administration -Monitor labs [CBC (WBC), electrolytes such as BUN, serum creatinine, K, urine for protein Nursing Diagnoses -Risk for injury related to hypotension (s.e. of ACEI is BP) -Potential complications of anaphylaxis, hyperkalemia -Alteration in comfort related to presistent dry cough (common side effect of ACEI) Implementation -Follow basic rights of medication administration -Instruct client to report signs of infection (due to possible neutropenia) -Monitor BP prior admin and 1 hr after admin esp. during initial therapy (BP may drop significantly) -Monitor for side effects and interactions -Monitor Labs -Admin captopril and moexipril on an empty stomach 1 hr before meals Education -Full benefits may not be apparent immediately -Drug compliance -Adverse reactions and side effects, when and how to report -Signs and symptoms of angioedema (Life threatening) -Don't use K supplements or substances containing large amounts of K (use salt substitute or low-Na milk) -Avoid taking OTC drugs without notifying prescriber Evaluation -Expected outcome of ACEI therapy in HTN: BP within normal limits without adverse reactions
Class
Generic Benazepril Captopril* Enalapril* Fosinopril Lisinopril* Moexipril Quinapril Ramipril Trandolapri
Brand Lotensin Capoten* Vasotec* Monopril Prinivil,Zestril* Univasc Accupril Altace Mavik
Drug Interactions Diuretics, such as spironolactone (Aldactone). May intensify 1st dose hypotension Antihypertensive Agents Drugs that increase K levels because ACEIs reduce excretion of K and will lead to hyperkalemia. Lithium (ACEIs can make lithium accumalte to toxic levels) Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) because they will reduce effect of antihypersenitivity of ACEIs
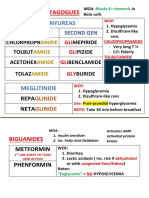
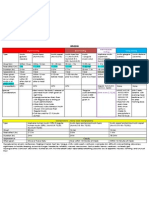
AngiotensinConverting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors "pril"
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs) "sartan"
Candesartan cilexetil Eprosartan Irbesartan Telmisartan Valsartan Losartan Olmesartan
Atacand Teveten Avapro Micardis Diovan Cozaar Benicar
Hypertension CHF (Diovan) Diabetic Nephropathy (Avapro, Cozaar) MI Stroke
Action Absorption - PO (with or -Blocks action of Angiotensin II without food) receptors on blood vessels, in Distribution heart, and adrenal glands Metabolism - liver Causes Excretion - kidneys -blood vessels vasodilation -heart prevent pathologic changes -adrenals decrease release of aldosterone No cough b/c no involvement with kinase
Similar to ACE Inhibitors
Same as ACE Inhibitors, but cough, dizziness and syncope have also been reported. Cough is commonly seen in ACE Inhibitors. Watch for Orthostatic Hypotension
Hypotensive effect of ARBs Same as ACE Inhibitors and with all other drugs are additive with those of other antihypertensive drugs. Side Note: -ARBs should be reserved for pts that cant tolerate ACEI b/c of cough -ARBs are used Diabetic Nephropathy due in part to reductions in BP, and in part to mechanisms that have not been determined. Although ARBs and ACEI can delay development of renal complications, only ACEI have been shown to reduce mortality.
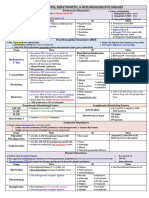
Nifedipine (prototype) Amlodipine Felodipine Isradipine Nicardipine Nimodipine Nisoldipine ____________________ Verapamil Diltiazem Calcium Channel Blockers (CCBs) "dipine"
Adalat, Procardia Norvasc Plendil DynaCirc Cardene Nimotop Sular _____________________ Calan Cardizem
Hypertension Vasodilation (decrease BP) Angina Pectoris Decrease HR Cardiac Dysrhytmias (admin Decrease force of contraction IV slow ventricular rate in pt with atrial flutter/fibrillation, Prevent Ca ions from entering and paroxysmal cells. Have greatest effect on supraventricular tachycardia) heart and blood vessels. Effect Blockage of Ca channels in the of Ca channel blockade is to heart can compromise cardiac decrease velocity of conduction function. through the AV node.
Absorption - PO (VERAPAMIL) and IV (DILTIAZEM or VERAPAMIL) Distribution - Well Metabolism - liver (doses must be reduced substantially in pt with hepatic impariment) Excretion - liver
Constipation Dizziness Facial flushing Dry Mouth Headache Edema of ankles and feet
Digoxin b/c it also suppresses Assessment impulse conduction of AV node -Also refer to Nursing Management for ACEIs -Review current health status, medical history, medication history including pregnancy = risk of AV block -Review baseline BP (donot admin if SBP is less than 90mm Hg), HR, ECG if possible Beta Blockers b/c also -Contraindicated in client's with heart block -Cautiously give to clients: elderly, history of kidney or liver disease decrease HR, AV conduction, Nursing Diagnosis and contractility = risk of -Risk for impaired oral mucous membrane (gingival hyperplasia) excessive cardiosuppression -Risk for impaired comfort (dry mouth, dizziness, headache, flushing) Side Note: -Like VERAPAMIL, DIGOXIN suppresses impulse conduction through AV node. When used together AV block is increased. -VERAMAPRIL increases plasma levels of digoxin by 60% thereby increasing risk of digoxin toxicity, If toxicity appear, digoxin dosage should be reduced.
-Risk for injury related to dizziness -Risk for excess fluid volume related to Na and H2O retention aeb swelling of feet, ankles, lower legs -Risk for constipation -Potential for complications (skin, rash, dysrhytimias) Implementations (Also refer to ACEIs) -Monitor BP, HR -Monitor electrocardiogram rhythm -Monitor I&O and weight, edema -Avoid abrupt withdrawal -Avoid OTC, herbal or other medications (unless they have been discussed with clinician) -Admin on an empty stomach to promote rapid absorption, if nausea occurs may admin with meals or at bedtime -Take client's BP and pulse before each dose, if pulse is less than 50bpm, hold the dose and notify clinician -For IV injection (diltiazem or verapamil) inspect IV site for swelling, redness, tenderness, and inspect drug preparation- if cloudy, discard -Admin drug via IV injection (IV push) slowly over 2 minutes (over 3min in older adults) and monitor BP and telemetry frequently -Not to double up on doses if doses are missed Education (Similar to ACEIs) Evaluation -BP, HR, and EKG are within normal limits without experiencing adverse effects from CCBs -Knowledgeable on disease process and therapy
Atenolol* Acebutolol Metoprolol* Carvediolol Labetalol Nadolol Propranolol Sotalol Pindolol Penbutolol
Tenormin* Sectral Lopressor, Toprop XL* Coreg Normodyne, Trandate Corgard Inderal, Inderal LA Betapace Visken Levatol
Beta Blockers (Beta-Adrenergic Antagonist) "lol"
Hypertension (suppress cardiac output and renin release) Angina Pectoris (block heart b1 to decrease cardiac work, thus bringing oxygen demand back into balance with oxygen supply and prevents pain) Cardiac Dysrhytmias (decrease rate of sinus nodal discharge and suppress conduction of atrial impulses through AV node, thus preventing ventricles being driven at excessive rate) MI CHF Migraine
Non-Selective: Blocks B1 & B2 Cardioselective: Blocks B1 Blockade of heart beta 1 receptors in the heart. Result with (1) HR, (2) force of contraction, and (3) velocity of impulse conduction through the atrioventricular (AV) node. Blockade of renal B1 receptors, propranolol can suppress secretion of renin Blockade of B2 receptors, propranolol = (1) bronchoconstriction (in lungs), (2) vasoconstriction (blood vessels), and (3) glycogenolysis (in skeletal muscle and liver)
Absorption - PO Distribution Metabolism - Liver (b/c extensive metabolism on it first pass through the liver, less than 30% reaches the systemic circulation Excretion ******
Hypersensitivity, bradycardia, heartblocks, lung disease such as COPD & asthma, impotence, dizziness Precautions: Diabetes
Bradycardia, impotence, heart block (AV block), dizziness B1 Blockade: Bradycardia, Reduced Cardiac Output, Precipitation of Heart Failure, AV Heart Block, Rebound Cardiac Excitation B2 Blockade: Bronchoconstriction, Inhibition of Glycogenolysis
Assessment May cause additive -Monitor blood pressure and pulse frequently during dosage adjustment and periodically throughout therapy. myocardial depression and -Monitor intake and output ratios and daily weight. Assess patient routinely for signs and symptoms of CHF (dyspnea, rales/crackles, weight gain, peripheral edema, jugular venous distention). bradycardia when used with -Angina: Assess frequency and severity of episodes of chest pain periodically throughout therapy. other agents having these -Migraine Prophylaxis: Assess frequency and severity of migraine headaches periodically throughout therapy. effects (digoxin and some Nursing Diagnoses -Ineffective tissue perfusion (Indications) antiarrhythmics). -Deficient knowledge , related to disease process and medication regimen (Patient/Family Teaching) May antagonize the -Noncompliance (Patient/Family Teaching) therapeutic effects of Implementation -Take apical pulse prior to administering. If heart rate is <50 bpm or if arrhythmias occur, hold medication and notify health care professional. bronchodilators. -Many beta blockers are available in combination products to enhance compliance (see combination drugs). May alter the requirements for Education insulin or hypoglyemic agents -Instruct patient to continue taking medication, even if feeling well. Abrupt withdrawal may cause life-threatening arrhythmias, hypertension, or does not cure, hypertension. in diabetics. Cimetidine may myocardial ischemia. Medication controls, butinterventions for hypertension (weight reduction, low-sodium diet, regular exercise, smoking -Encourage patient to comply with additional decrease the metabolism and cessation, moderation of alcohol consumption, and stress management). -Instruct patient and family on proper technique for monitoring blood pressure. Advise them to check blood pressure weekly and report significant increase the effects of some changes to health care professional. beta blockers. -Caution patient to make position changes slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension. Advise patient that exercising or hot weather may enhance hypotensive effects. -Advise patient to consult health care professional before taking any OTC medications or herbal/alternative therapies, especially cold remedies. -Caution patient that these medications may cause increased sensitivity to cold. -Diabetics should monitor blood glucose closely, especially if weakness, malaise, irritability, or fatigue occurs. Evaluation -Decrease in blood pressure. -Decrease in frequency and severity of anginal attacks. -Control of arrhythmias. -Prevention of myocardial reinfarction. -Prevention of migraine headaches. -Decrease in tremors. -Lowering of intraocular pressure.
Mixed - Adrenergic Antagonists
Labetalol Carvediolol
Normodyne, Trandate Coreg
Act at catecholamines receptors and peripheral -1 receptors
Hepatocellular damage, postural hypotension, lupus-like syndrome, tremore
Page 1
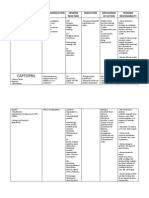
Page 2 Hydralazine Apresoline Hypertension (PO) Heart Failure (reduce afterload) Hypersentivie crisis (IV) Dilation of Arterioles = BP -peripheral resistance and arterial BP fall. -HR and myocardial contractility increase. Absorption- PO within 45min Hypersensitivity, and persist for 6hrs, with cardiovascular/cerebrovascular PARENTARAL ADMIN within disease, renal/hepatic disease 10min, and last for 2-4hrs Distribution - well Metabolism- Acetylation, to avoid hydralazine accumulation dosae should be reduced in slow acetylators. Excretion - kidneys Postrual Hypotension (problem BP meds such as Beta is vasodilator acts on veins) Blockers Refelx Tachycardia Combined with BETA Expansion of Blood Volume BLOCKERS to protect against Dizziness reflux tachycardia and diuretics Headache to prevent sodium and water Fatigue retention and expansion of Systemic Lupus blood volume. Erythematosus-like Syndrome: acute rheumatoid syndrome closely resembles lupus muscle pain, joint pain, fever, nephritis, pericarditis reversible within 6 hours or more months Assessment -Monitor BP, CBC, and electrolytes Nursing Diagnosis -ineffective tissure perfusion and non compliance Implementation -PO with meals Education -Importance of continuing to take medication even if feeling well Evaluation -Decrease BP and Decrease afterload in CHF
Hydralazine (Apresoline) Vasodilator
Nitroglycerin
Drug of choice for relieving acute angina attacks
Vasodilation of Veins Vasodilation of Vascular Smooth Muscle
Organic Nitrates (Anti-Angina Drugs, MI)
Absorption - Highly lipid soluble sublingual, buccal, transdermal and (IV/Oral). No PO b/c 1st Pass Effect (it first goes to liver to metabolize and reduces bioavailability of drug before reaching rest of body). -Sublingual tablet - store in dark, tightly closed bottle & give max of 3 tablets with acute attack. Distribution - unknown Metabolism - liver rapidly and by enzymes in bloodstream Excretion -
Headache (common) Orthostatic Hypotension (dizziness) Tachycardia (body tries to accommodate for low BP by beating faster)
Other BP meds (to not cause Baseline on frequency of angina attacks and location and factors hypotension as well as alcohol) Hairless area for patch Viagra (intensifies Upper lip and gum - for buccal - or cheek and gum nitroglycerin induced vasodilation - can cause life threatening hypotension - all blood to the penis - then heart attack)
Loop Diuretics -Furosemide -Bumetanide -Torsemide
Loop Diuretics -Lasix -Bumex -Demadex
Diuretics
Powerful drug that is generally The high-ceiling agents are Absorption- PO, IM, IV (IV in reserved for situations that the most effective diuretics critical situation only require rapid/massive available. Produce more loss of (pulmonary edema) - effects mobilzation of fluid fluid and electrolytes than any begin within 5min and lasts Pulmonary edema associated other diuretics b/c site of action 2hrs) with CHF is in the loop of Henle. Distribution - Widely Edema of hepatic, cardiac, or Inhibits reabsorption of Na and distributed renal origin that has been chloride from loop of Henle and Metabolism - Liver unresponsive to leff efficacious distal renal tubule. Excretion - Kidneys diuretics Increases renal excretion of Hypertension that cannot be H2O, Na, Cl, Mg, K, Ca controlled with other diuretics Effectiveness persists in Hyperaldosteronism (too much impaired renal function aldosterone produced by adrenal gland, can K in blood.) (spironolactone)
Other diuretics Side Note: BP meds (ACEI) -SPECIALLY USEFUL IN PTs WITH SEVERE RENAL IMPAIRMENT, since, unlike thiazides, this drug can Digoxin - in presence of low K promote diureis even when renal blood flow and glomerular filtratin rate are low. levels, the risk of serious -FUROSEMIDE affects preload b/c one of its side effects is substantial drop in BP (hypotension). At least 2 digoxin induced toxicity mechanism are involved: 1. Loss of Volume, and 2. Relaxation of Venous Smooth Muscle, which reduces (ventricular dysrhythmias) is venous return to heart. greatly increased. -Poor return of blood to heart in inadequate preload (filling of heart) Lithium
Thiazides -Chlorothizide -Hydrochlorothiazide
Thiazides -Diuril, Diurigen -HydroDiuril
Diuretics
Essential hypertension (drug of 1st choice) Edema associated with mild to moderate heart failure and hepatic or renal disease Diabetes insipidus (excessive thirst and excretion of large amounts of severely diluted urine)
Promotes urine production by blocking the reabsorption of Na and Cl in the early segment of the distal convoluted tubule.
Absorption - PO except CHLOROTHIZIDE (IV) Distribution - widely Metabolism Excretion - unchanged by kidneys
Contraindications -Pregnancy Precautions -Pt with gout (loop diuretics retain uric acid), diabetes (loop diuretics inhibit insulin production), renal & hepatic impairment.
Hyponatremia Hypokalemia - K is lost through increased secreation in the distal nephron Ototoxicity Dehydration Hyperglycemia Increase levels of Ca, uric acid, Mg, and lipids/cholesterol
Always give in the morning Usually given with K Hypokalemia can be minimized by consuming, K-rich foods (dried fruits, nuts, spinach, citrus fruits, potatoes, bananas. Side Note: Thiazides a.k.a benzothiadiazides have effects similar to loop diuretics. They both increase renal excretion of Na, Cl, K, and H2O. Thiazides elevate plasma level of uric acid and glucose. Principal difference between thiazides and loop is considerably lower than the maximum diuresis produced by loop drugs. Loops can be effective when urine flow is low, thiazides cannot.
K+ Sparing -Spironolactone -Triamterene
K+ Sparing -Aldactone -Dyrenium
Diuretics
Hypertension and edema CHF (Spironolactone) Hyperaldosteronism (Spironolactone) Conservation of K Weak diuretic & antihypertensive response compared to other diuretics Purpose of K+ sparing when used with thiazide or loop is to counteract the K wasting effects of the more powerful diuretics
Blocks action of aldosterone (spironolactone) in the distal nephon. Since aldosterone acts to promote Na uptake in exchange for K secretion, inhibition of aldosterone has the opposite effect: retention of K and increased excretion of Na.
Absorption - PO Distribution - widely Metabolism - liver Excretion - kidney
Hyperkalemia
Side Note: -B/c of the risk of hyperkalemia, K+ sparing diuretics must NEVER be combined with K supplements, salt substitutes (which contain KCl), with another K+ sparing diuretic or ACE (can also elevate K levels by suppressing aldosterone secretion, should be combined only when clearly necessary).
Page 2
Page 3 Digoxin** Dopamine Dobutamine Lanoxin Lanoxicaps Digitex CHF Dysrhythimia Exerts positive inotropic action Absorption - PO tablets 60%- Ventricular fibrilation, on heart. (Increases force of 80%, capsules 90%- 100% ventricular tachycardia, digoxin ventricular contraction, and (more expensive) - if HR < toxicity Digoxin Levels: 0.5-0.8 ng/mL thereby increase cardiac 60bpm or if change in rhythm Hypokalemia, partial AV block, output.) is detected, withhold digoxin advanced HF or renal As a result of increase CO: and notify physician. impairment 1. Sympathetic tone IV (monitor Ca status closely for 2. Urine output 1-2hrs following IV injection. 3. Renin release Distribution Affects electical activity of Metabolism - Liver, minimal heart Excretion - Kidney Dysrhythmias - most serious Diuretics - thiazide and loop adverse effect, atrioventricular promote K, increase risk of block with escape beast is most digoxin-induced dysrythmias. common, ventricular flutter and ACEI - can K lvls, ventricular fibrilation is most therapeutic response of dangerous. digoxin. N/V, anorexia - most common Verapamil - plasma lvls of GI side effect, due to digoxin (suppress myocardial stimulation of chemoreceptors contractility) trigger zone of the medulla. Quinidine - can cause plasma Fatigue - most common CNS lvls of digoxin to effect. Visual Disturbances - CNS digoxin lvl in presence of hypokalemia Assessment -S/S of HF including fatigue, weakness, cough, breathing difficulty, jugular distension, edema. Nursing Diagnosis - CO Implementation -Avoid excessive fluids, reduce caloric diet, drink alcohol no more than one drink a day. Education -Early signs of hypokalemia (muscle weakness) Evaluation -Reductions in orthopnea, dyspnea on exertion, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, neck vein distention, edema and rales, increased capacity for physical activity
Cardiac Glycosides
CHOLESTEROL REDUCING DRUGS Atorvastatin Fluvastatin Lovastatin Simvatatin Pravastatin
(Hyperlipidemia is #1 cause of CHD) Lipitor Lescol Mevacor Zocor Pravachol Hyperlipidemia Serum cholesterol and LDL Hypercholesterolemia Levels Coronary Heart Disease (CAD) Increasing # of LDL Post-MI Therapy receptors on hypatocytes (inhibition of cholesterol Lowering of total and LDL and synthesis cause hepatocytes tryglycerides. Slightly increases to synthesize more LDL HDL receptors)**More receptors = Reduction of lipids/cholesterol more removal of LDLs from reduces risk of MI and Stroke blood Sequelae HDL Cholesterol Slows progession of coronary Triglyceride Levels atherosclerosis with resultant Nonlipid Beneficial decrease in coronary heart Cardiovascular Actions disease-related events promote plaque stability, reduce inflammation at plaque site, slow progression of coronary artery calcification, improve endothelial function, enhance ability of vasodilation, reduce risk of atrial fibrillation , and reduce thrombosis Site of action - LIVER Absorption - Oral 30%- 90% absorbed Distribution - low, action at liver Metabolism - liver, rapid Excretion - liver, in the bile -LOVASTATIN, PRAVASTATIN, SIMVASTATIN (10%-20% excreted in urine) Hypersensitivity Active liver disease (viral/ alcoholic hepatitis) Category X: NOT for pregnant women Precautions: -history of liver disease -alcoholism -renal impairment Hepatotoxicity Myopathy Rhabdomylysis - muscle cell destructions that can lead to renal failure Grapefruit Check for hepatomegly and Liver Function Test (LFT) TB Drugs Monitor labs fro LDL and HDL Alcohol Exercise, diet, smoking, drinking Other hepatoxic drugs (Tylenol) Other statins (muscle weakness/injury, liver injury, kidney injury) With drugs that Inhibit CYP3A4
Hydroxymethylgl utaryl Coenzyme (HMG-CoA) Reductase Inhibitors: "Statins"
Water Soluable Vitamin/ Lipid Lowering Agent
Nicotinic Acid, Niacin
Vitamin B3
LDL and Triglyceride levels treat hypercholesterolemia
Cause hyperglycemea and hyperuricemia
Intense flushing - take Alpha Blockers 325mg aspirin 30min before Diabetes Meds each dose Abdominal discomfort Nausea Consipation Bloating Indigestion Nausea GAS Thiazide Digoxin Warfarin Antibiotics Drugs above b/c bile-acid sequestrants can form complexes with other drugs
Hepatotoxic - Monitor Liver Function with long acting Niacin
Cholestyramine Colestipol Colesevelam* Bile-Acid Sequestrants/ Lipid Lowering Agent
Questran Colestid Welchol*
Used as an adjunct to diet and exercise Hypercholesterolemia Usually combined with STATIN
Bind with Bile Acids excretion in feces LDL by increasing LDL receptors on hepatocytes
Absorption - PO (insoluble in H2O, can't be absorbed in GI). Simply pass through intestine and become excreted in feces Distribution Metabolism - GI Excretion - feces
Grapefruit Antiacids Milk Beans Cabbage INCREASE GAS (foods above)
Assessment -Obtain lab values for total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, triglycerides (TG) (Very Low Density Lipoprotein(VLDL)) Nursing Diagnosis -Compliance, non compliance Implementation -Mix cholestyramin powder and colestipol granules with H2O, fruit juice, soup to reduce risk of esophageal irritation and impaction. Education -Control lipid levels/ diet counciling Evaluation -should be monitored monthly
Fenofibrate Gemfibrozil Fibric Acid Derivatives (Fibrates)/ Lipid Lowering Agent
Tricor Lopid
Primarily to reduce high levels of plasma triglycerides (VLDLs) - GEMFIBROZIL Raise HDL cholesterol (not approved for this application) treat Hyperlipidemia
Stimulates breakdown of lipoproteins from tissues and their removal from plasma - TG 20%-50%, HDL
10%-20%
Absorption - PO (especially with food) Distribution - well, 98% protein bound Metabolism - Liver Excretion - Kidneys
Pt with liver, renal, and gallbladder disease
GI discomfort, such as nausea; Statin drugs = myopathy ab pain; and diarrhea (most Anticoagulants, such as common) warfarin (coumadin) = Rash (most common) anticoagulant effects Gallstones Hepatitis (liver injury) Muscle discomfort (myopathy)
Find if grapefruit taken Liver Function Test INR with Coumadin
Ezetimibe
Zetia
Used as adjunct to diet and exercise Hypercholesterolemia
Inhibits absorption of cholesterol from small intestine Small increase in HDL GI problems, GAS Abdominal Pain
Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitors
Absorption - PO (not affected by food) Distribution Metabolism - liver & small intestine Excretion - bile
Hepatic Impairment (dont give this drug if pt has this condition)
Myopathy Rhadbomyolysis Hepatitis Pancreatitis Thrombocytopenia (low platelets in blood)
Statins (increase liver damage Liver Function Test and myopathy) Fibrates (increase cholesterol content in bile, thus increase risk of gallstones) Bile-Acid Sequestrants (significantly decrease absorption of EZETIMIBE) Cyclosporine (greatly increase levels of EZETIMIBE)
Page 3
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cardiovascular DrugsDocument6 paginiCardiovascular Drugslhayes123488% (16)
- Assessment Info NotesDocument3 paginiAssessment Info NotesDiana DeckerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology of HypertensionDocument4 paginiPharmacology of HypertensionFlower100% (1)
- Insulin Comparison ChartDocument1 paginăInsulin Comparison Chartmaend87Încă nu există evaluări
- Family Names of DrugsDocument1 paginăFamily Names of DrugsangelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Remembering Medication ClassificationsDocument2 paginiRemembering Medication ClassificationsGVHHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology-ATI 150 Drug Cards PDFDocument4 paginiPharmacology-ATI 150 Drug Cards PDFhollyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Know Common Disease ManagementDocument14 paginiKnow Common Disease Managementcdx25Încă nu există evaluări
- Guide To Diabetes MedicationsDocument2 paginiGuide To Diabetes MedicationsJianhua ShiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary of Antidiabetic Drugs PDFDocument3 paginiSummary of Antidiabetic Drugs PDFZinc YuloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertension Drugs Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 paginiHypertension Drugs Cheat Sheet: by ViaGulzaib KhokharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Guide and Charts: AlbuminDocument16 paginiRenal Guide and Charts: AlbuminYaima JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology Important Things To RememberDocument5 paginiPharmacology Important Things To RememberHydie100% (1)
- Classification of Drugs PDFDocument15 paginiClassification of Drugs PDFmuhammad ihtisham ul hassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labs Electrolyte ChartDocument1 paginăLabs Electrolyte ChartmdcmepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heart Failure Topic DiscussionDocument11 paginiHeart Failure Topic Discussionapi-665372449Încă nu există evaluări
- @ Shopwithkey On Etsy Perfusion Drug Classification ChartDocument8 pagini@ Shopwithkey On Etsy Perfusion Drug Classification ChartSutanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DrugsDocument155 paginiDrugsAkankshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDocument5 paginiPharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDana20SÎncă nu există evaluări
- With Dr. Susan Lipsett: Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument1 paginăWith Dr. Susan Lipsett: Community Acquired PneumoniaJayantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACE InhibitorsDocument8 paginiACE InhibitorsJohn HillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartDocument5 paginiNeuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartMonica J Ortiz Pereira100% (1)
- NCLEX Review: Pharmacology Charlene Natale, BSN, RNDocument43 paginiNCLEX Review: Pharmacology Charlene Natale, BSN, RNMenly Susada100% (1)
- Kaplan Notes. ExamenSO IMPORTANTDocument145 paginiKaplan Notes. ExamenSO IMPORTANTLisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarDocument33 paginiPharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarfaizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oman Prometric Exam NotesDocument417 paginiOman Prometric Exam NotesMuhammad Amin93% (14)
- PEDIA - TachypneaDocument12 paginiPEDIA - TachypneaAlvin Germo PasuquinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Drug Stems Cheat Sheet: Drug Stem Drug Class And/or Stem Explanation ExamplesDocument2 paginiCommon Drug Stems Cheat Sheet: Drug Stem Drug Class And/or Stem Explanation ExamplesjthsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mu 002Document10 paginiMu 002chandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prefix Suffix MnemonicsDocument5 paginiPrefix Suffix MnemonicsPj MontecilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACE InhibitorsDocument26 paginiACE Inhibitorsali mohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiDocument146 paginiMechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiReynaldo RiveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug CardsDocument3 paginiDrug CardsDave HillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFDocument25 paginiDrugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFSutanya100% (2)
- HESI Qbank From QuizletDocument11 paginiHESI Qbank From Quizletnana100% (4)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Case StudyDocument96 paginiChronic Kidney Disease Case StudyJUDE ARIZALAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Interactions: What Is An Interaction?Document4 paginiDrug Interactions: What Is An Interaction?Leyla MajundaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs To Watch With WARFARINDocument3 paginiDrugs To Watch With WARFARINRajendra RaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 300 QuestionsDocument34 pagini300 QuestionsAhmed Assem78% (9)
- 7 Drug StudyDocument17 pagini7 Drug StudyMa. Mechile MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnxietyDocument5 paginiAnxietyJohn HolmesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beta BlockersDocument1 paginăBeta BlockersShrikant ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE AdvDocument1 paginăAntiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE Advrayooona88Încă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology FirecrackerDocument37 paginiPharmacology FirecrackerRehan Usman100% (1)
- Anticoagulants Drug TableDocument1 paginăAnticoagulants Drug TableNicole HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grapefruit Juice and Drug Interactions - 0717Document2 paginiGrapefruit Juice and Drug Interactions - 0717Asri YaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ace Inhibitors MnemonicDocument1 paginăAce Inhibitors MnemonicGirish Waru0% (2)
- Agents Causing Coma or SeizuresDocument3 paginiAgents Causing Coma or SeizuresShaira Aquino VerzosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Argus 5 1 Test CasesDocument11 paginiArgus 5 1 Test CasespponnapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti HypertensivesDocument15 paginiAnti HypertensivesFaye MillanesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vancomycin Protocol RQHRDocument15 paginiVancomycin Protocol RQHRl1o2stÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology Drug ChartDocument50 paginiPharmacology Drug ChartEssentialForLivingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insulin Chart 05032012 PDFDocument1 paginăInsulin Chart 05032012 PDFTiffany CrittendenÎncă nu există evaluări
- IV PO Conversion CAPDocument3 paginiIV PO Conversion CAPdamondouglasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharm Expansion 17 NDFDocument1 paginăPharm Expansion 17 NDFNokz M. Raki-inÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessing Abdominal Distensión After GastrectomyDocument1 paginăAssessing Abdominal Distensión After GastrectomyEunice CortésÎncă nu există evaluări
- Template Drug Card1Document1 paginăTemplate Drug Card1Kay TaylorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)Document2 paginiPharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)graycorypÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotic GuideDocument6 paginiAntibiotic GuideAnnTran100% (1)
- ATI Med Template Vitamin DDocument1 paginăATI Med Template Vitamin DHeather MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Medications UsedDocument3 paginiCommon Medications UsedRay Michael CasupananÎncă nu există evaluări
- NORADRENALINE (Norepinephrine) : Presentation DescriptionDocument3 paginiNORADRENALINE (Norepinephrine) : Presentation DescriptionMutiaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generic Name FurosemideDocument1 paginăGeneric Name FurosemideChristopher LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharm Drug Outline AdrDocument1 paginăPharm Drug Outline AdrCess Lagera YbanezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agents For Anemia, Hematopoietic, & Myeloproliferative DiseasesDocument2 paginiAgents For Anemia, Hematopoietic, & Myeloproliferative Diseaseskaylakmills_10135868Încă nu există evaluări
- 14 Fun Facts About Your Heart: Educational VersionDe la Everand14 Fun Facts About Your Heart: Educational VersionÎncă nu există evaluări
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideDe la EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandHyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Platinum Formulary 2016Document61 paginiPlatinum Formulary 2016jÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertension PDFDocument6 paginiHypertension PDFRaouf Ra'fat SolimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preparation of Extemporaneous Oral Liquid in The Hospital PharmacyDocument15 paginiPreparation of Extemporaneous Oral Liquid in The Hospital PharmacyAhmed YousefÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRUG StudyDocument43 paginiDRUG StudyNathalie Faith CotengÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIURETICSDocument40 paginiDIURETICSNiña Jean Tormis AldabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GPAT Handy NotesDocument38 paginiGPAT Handy NotescuambyahooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology ReviewerDocument28 paginiPharmacology ReviewerYuki Xairah TunayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Template ArticleDocument14 paginiTemplate ArticleLisda Amalia P. 17.010Încă nu există evaluări
- Pharma Cardio Respi and Repro NclexdocxDocument8 paginiPharma Cardio Respi and Repro NclexdocxJhayneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antihypertensive AgentDocument2 paginiAntihypertensive AgentMuhammad Naufal FadhillahÎncă nu există evaluări
- CaptoprilDocument3 paginiCaptoprilapi-3797941100% (1)
- أدوية الضغطDocument2 paginiأدوية الضغطSamalout Specialized HospitalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug ListDocument24 paginiDrug Listcicima1016Încă nu există evaluări
- Management Scorpion Sting Journal PDFDocument9 paginiManagement Scorpion Sting Journal PDFDody Tri GusnawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology ReviewerDocument21 paginiPharmacology ReviewerCzairalene QuinzonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology Made EasyDocument43 paginiPharmacology Made EasyGauthaman KarunakaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Banco de Preguntas Cardio SincDocument37 paginiBanco de Preguntas Cardio SincnoahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument8 paginiDrug StudyJohn Ronald P. RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Brief History of PharmacologyDocument6 paginiA Brief History of PharmacologyymonnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines For Avoiding Food-Drug InteractionsDocument5 paginiGuidelines For Avoiding Food-Drug InteractionslnornelasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amlodipine Captopril MetronidazoleDocument5 paginiAmlodipine Captopril Metronidazolekhrysty1506Încă nu există evaluări