Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Endocrine System
Încărcat de
Ellaine PateñoDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Endocrine System
Încărcat de
Ellaine PateñoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
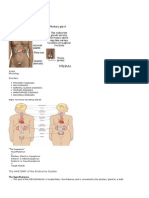
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM * Integrates body function by the synthesis and release of hormone * Functions are interrelated with the
nervous system * Secretes their products directly into the blood stream Composed of an interrelated complex of glands Pituitary adrenal thyroid parathyroid islets of langerhans of the pancreas ovaries and testes (gonads) FUNCTION : * chemical communication and coordination system that enables: > reproduction growth, development and maturation regulation of energy PITUITARY GLAND located at the sella turcica at the base of the brain composed of three lobes a. ANTERIOR LOBE secrets tropic hormones that stimulates target glands to produce hormone such as: ACTH (adenocorticoid hormone)* stimulates Adrenal glands to produce corticosteroids responsible for stress response TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) * stimulates thyroid glands to release thyroid hormones (T4,T3 and calcitonin ) thyroxine T4, triiodothyronine (T3) T3 AND T4 regulates metabolic rate( carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism) aid in regulating physical and mental growth and development
THYROCALCITONIN lower serum calcium by increasing bone deposition FSH and LH ( follicle stimulating and luetenizing hormone) * stimulates Ovaries, breast and testes for growth, maturation and function of secondary sex organs b. INTERMEDIATE LOBE secretes MSH (melanocyte stimulating hormone) affect skin pigmentation c. POSTERIOR LOBE stores and releases ADH (anti diuretic hormone) and oxytocin in the hypothalamus ADH - stimulates reabsorption of water and decreases urine output OXYTOCIN - stimulates uterine contraction during delivery - stimulates the release of milk in lactation DISORDERS OF THE PITUITARY GLAND ANTERIOR PITUTIARY GLAND: Hypopituitaryism hyperpituitaryism POSTERIOR PITUTIARY GLAND: Diabetis Insipidus SIADH HYPOPITUITARYISM MAIN PROBLEM: hypofunction of the APG resulting in deficiencies of the hormones secreted by APG and target glands CAUSES: tumor trauma- causing inadequate blood supply to the gland infection or inflammation SHEEHAN SYNDROME:
Massive bleeding post partum causing atrophy of the APG manifested by no breast milk production, no menstruation despite not pregnant SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS: Headache varying symptoms due to hormonal deficiency ( lack of hormone leads to loss of function in the gland or organ that it controls) ACTH DEFICIENCY: causing deficiency in mineralocorticcoid, glucorticoid and sex hormone sodium level in the blood BP potassium level in the blood blood sugar level energy level ability to handle stress and infection skin color TSH DEFICIENCY: causing deficiency in T4, T3 and calcitonin rate of metabolism weight persitalsis heart rate heat production intolerant to hair nails movement/ energy level cholesterol level water retention face mood / mental function calcium level bone FSH and LH DEFICIENCY: causing deficiency in sex hormone, growth hormone sex hormone: - secondary sexual characteristics ( breast, penis, testis, body hair, libido, menstruation, body frame in male, voice, sperm production, lactation growth hormone deficiency: - DWARFISM * ACHONDROPLASIA ( NANUS SYNDROME) AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT DWARFISM: hyposecretion of growth hormone; occurs before maturity height is below normal
body proportions normal retarded bone/tooth development delayed sexual maturity DIAGNOSTIC TEST: 1. skull x-rays,/CT scan 2. plasma hormone levels may be decreased depending on specific hormones undersecreted ( cortisol level, potassium, sodium, blood sugar, T3, T4, TSH, growth hormone, calcium level) NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Body image disturbance Fluid and electrolyte imbalance activity intolerance altered nutrition NURSING INTERVENTIONS: 1. Care of patient undergoing Surgical removal of tumor - hypophysectomy 2. Care of patient undergoing irradiation of the gland 3. replacement of deficient hormones such as: > corticosteroids > Levothyroxine > estrogen or androgen > growth hormones HYPERPITUITARYISM MAIN PROBLEM: Hyperfunction of the APG leading to oversecretion of one or more APG hormones 2 most common hormone affected are; - prolactin - growth hormone CAUSE/S: > Tumor SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS PROLACTINOMA: a. Galactorrhea b. Menstrual disturbance c. Gynecomastia d. Decreased libido HYPERSECRETION OF GROWTH HORMONE: a. Gigantism
b. Acromegaly GIGANTISM: - before the closure of epiphyses a. proportional growth b. tall and slender ACROMEGALY : - after the closure of the epiphyses a. disproportional growth b. enlarged hands and feet c. prominent mandible, tooth spacing widens d. large tongue e. arthritis f. cardiomegaly DIAGNOSTIC TEST: CT Scan Plasma growth hormone levels; blood sugar level NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Body image disturbance risk for injury NURSING INTERVENTIONS: Medications: Bromocriptine for prolactinoma; Octreotide for GH hypersecretion Surgery: removal of tumor; effects are irreversible Radiation therapy Diet: sodium, calories and fat Emotional support Athritis Visual problem : safety Which of these questions is appropriate for a nurse to ask a patient who is suspected of having acromegaly a. do you urinate often at night b. are you buying larger size shoes c. is your mouth frequently dry after meals d. have you had alopecia lately HYPOPHYSECTOMY partial or complete removal of the pituitary gland
indications: A. pituitary tumors b. diabetic retinopathy c. metastatic cancer surgical approach: a. craniotomy- transfrontal b. transphenoidal- mouth and nose HYPOPHYSECTOMYPOST OP CARE 1. 2. 3. 4. 1. 2. 3. 4. WOF : BLEEDING Keep patient on bed rest for 24 hours Position Maintenance of integrity of suture line Visual field testing WOF : CSF LEAK AND INFECTION Measure to prevent increase ICP Oral care but ensuring maintenance of suture line Signs of CSF leak- clear, halo ring Signs of infection 1. 2. 3. WOF : POST OP PAIN Mild analgesic narcotic analgesic Paranasal pain typically subsides when the catheters are removed after 24 to 72 hours
WOF : DIABETIS INSIPIDUS a. Due to inadequate release of ADH Usually happens 24 to 48 hours after surgery but may resolve within 72 hours b. Urine volume c. Need for water d. Urine specific gravity * I & O, daily weight monitoring, fluids, vasopressin DISORDERS OF THE POSTERIOR PITUITARY GLAND a. Diabetis Insipidus b. SIADH DIABETIS INSIPIDUS
MAIN PROBLEM: Hypofunction of the posterior pituitary gland resulting in deficiency in ADH CAUSE/S: tumor trauma inflammation pituitary surgery SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS: a. Urine b. urine specific gravity c. need for fluid d. weight e. strength f. peristalsis g. heart rate h. Blood volume and BP i. level of consciousness j. skin and mucous membrane DIAGNOSTIC TEST: a. FLUID DEPRIVATION TEST b. urine specific gravity NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Fluid volume deficit NURSING INTERVENTION: a. Maintain Fluid and sodium balance - Record I & O - Weight patient daily - maintain fluid intake - WOF for dehydration and shock - safety b. Diet sodium c. Skin care D. Medication VASOPRESSIN VASOPRESSIN a. tannate form given through IM b. refrigerate but warm to body temp before giving c. shake tannate form to ensure uniform dispersion d. Diapid given via nasal spray e. S/E: smooth muscle contraction especially arterioles and capillaries,
water intoxication, nausea, hypersensitivity SYNDROME OF INAPPROPRIATE ANTI-DIURETIC HORMONE (SIADH) MAIN PROBLEM: Excessive ADH release CAUSE/S: tumor Trauma/ Hematoma inflammation Neuro surgery SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS: a. Urine b. urine specific gravity c. need for fluid d. weight e. strength f. heart rate g. Blood volume and BP DIAGNOSTIC TEST: a. sodium level b. urine specific gravity NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Fluid volume excess Risk for injury NURSING INTERVENTION: a. Maintain Fluid and sodium balance - Record I & O - Weight patient daily - restrict fluid intake - safety b. Diet sodium C. Medication anti HPN; diuretics To which of the following nursing diagnosis would a nurse give priority when caring for a patient who has SIADH a. decreased cardiac output b. altered nutrition
c. urinary incontinence d. fluid volume excess DISORDER OF THE THYROID GLAND Hypothyroidism hyperthyroidism ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
THYROID GLAND located at the anterior portion of the neck consist of two lobes connected by an isthmus produces thyroxine T4, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyrocalcitonin T3 AND T4 regulates metabolic rate( carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism) aid in regulating physical and mental growth and development THYROCALCITONIN lower serum calcium by increasing bone deposition HYPOTHYROIDISM MAIN PROBLEM: hypofunction of the thyroid gland with decreased thyroid hormone secretions (T3 AND T4) causing myxedema in adult and cretinism in children CAUSE/S: Primary hypothyroidism: atrophy of the gland possibly caused by an autoimmune process Secondary hypothyroidism : caused by decreased stimulation from pituitary TSH Iatrogenic: surgical removal of the gland or hypotreatment of hyperthyroidism with drugs or radioactive iodine; congenital SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS: weight persitalsis heart rate heat production intolerant to cold hair nails energy level/ activity cholesterol level water retention face
mood / mental function METABOLISM MANIFESTATION: a. altered body proportions; short stature with legs shorter than they should be in proportion to trunk b. tongue is enlarged and protrudes from mouth, resulting in breathing and feeding difficulties c. hypothermia with cool extremities d. short, thick neck e. delayed dentition f. hypotonia g. hypoactivity or well behaved baby CRETINISM MYXEDEMA COMA: In severe or untreated cases, myxedema coma may occur: a. characterized by intensification of signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism and neurologic impairment leading to coma b. precipitating factors: failure to take prescribed medications; infections; trauma; exposure to cold; use of sedatives,narcotics or anesthetics c. Management: - maintain patent airway - IV Fluid and IV thyroid hormone replacement, IV Glucose - wrap the patient ( no fast dewarming) - treat infection or underlying cause) DIAGNOSTIC TEST: a. T3 and T4 ( 70-220 ng/dl; 58.5 to 150 nmol/L b. TSH ( 0.38 to 6.15 uU/ml) c. Thyroid Scan d. Radioactive Iodine uptake test (RAIU)- measures the rate of iodine uptake the thyroid gland using iodine 123 > affected by the patients intake of iodide or thyroid hormone > assess allergy to iodine or shellfish e. Serum cholesterol NURSING DIAGNOSIS:
> Activity intolerance NURSING INTERVENTION: Thyroid supplement management of metabolism symptoms Thyroid supplement ( Synthroid synthetic levothyroxine) a. Different brands of levothyroxine may not be bioequivalent ( not to switch brand b. Take drug same time each day to maintain constant hormone levels c. Morning dosage to prevent insomia d. Monitor apical pulse and BP. Report for aggravated cardiovascular symptoms such as chest pain, dyspnea, tachycardia and nervousness) NURSING INTERVENTION: management of metabolism symptoms a. Diet : calorie, bulk, fat b. Management of constipation: c. Weight monitoring d. Mental function and activity e. Skin care f. Use of sedatives g. Environmental temperature h. WOF: thyrotoxicosis Discharge teaching: continue course of medication even if symptoms subside to prevent myxedema coma Which of the following conditions are most likely to be observed in a patient with hypothyroidism a. Brittle nails b. Heat intolerance c. Fine tremors d. Hunger HYPERTHYRODISM MAIN PROBLEM: secretion of excessive thyroid hormone in the blood causing an increase in metabolic process > Graves disease most common type of hyperthyroidism abnormal stimulation due to circulating immunoglobulin
CAUSE/S: Tumor autoimmune SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS: (Sometimes referred to as THYROTOXICOSIS) a. METABOLISM MANIFESTATION: Palpitations Heat intolerance Nervousness Insomnia Breathlessness Increased bowel movements Light or absent menstrual periods Fatigue Fast heart rate Trembling hands Weight loss Muscle weakness Warm moist skin Hair loss Staring gaze In severe untreated case can lead to thyroid storm a. THYROID STORM > uncontrolled or potentially life threatening hyperthyroidism caused by sudden and excessive release of thyroid hormone into the blood stream > precipitating factors includes stress, infection and unprepared thyroid surgery > ASSESSMENT FINDINGS: a. apprehension and restlessness b. extremely high temperature ( 40.7 C) c. tachycardia d. CHF e. respiratory distress f. delirium and coma NURSING INTERVENTIONS: a. maintain a patent airway and adequate ventilation b. administer oxygen as ordered c. administer antithyroid drugs, corticosteroids, sedative and cardiac drugs
DIAGNOSTIC TEST: a. T3 and T4 b. TSH c. Thyroid Scan d. Radioactive Iodine uptake test (RAIU)NURSING DIAGNOSIS: > Risk for injury NURSING INTERVENTION: Anti thyroid surgery RAI 131 management of metabolism symptoms NURSING INTERVENTION: Anti thyroid (PTU) - used for pregnant women and patient who refuse surgery or 131 treatment - blocks thyroid synthesis _ WOF: AGRANULOCYTOSIS LUGOLS SOLUTION - adjunct with other antithyroid drugs in preparation for thyroidectomy - inhibits the release and synthesis of thyroid hormone - decrease the vascularity of the thyroid gland - keeps the hormone inside to prevent thyroid crisis after thyroidectomy - dilute oral doses in water or fruit juices and give with meals - give through a straw to avoid tooth discoloration - force fluid to prevent deficit NURSING INTERVENTION: RAI 131: - Food may delay administration fast overnight - after treatment; patients urine and saliva are slightly radioactive for 24 hours vomitus is highly radioactive for 6-8 hours - Institute full radiation at this time ( time, distance, shielding ) - institute appropriate disposal methods when coughing and expectorating - flush toilet bowl twice after urination - pregnant personnel shouldnt take care of the patient - disposable eating utensils and linens should be used - Drink as much fluid to facilitate excretion - if patient is discharge less than 7 days after treatment with 131 dose: a. Avoid close or prolonged contact with small children b. dont sleep in the same room with spouse for 7 days after treatment
NURSING INTERVENTION: beta blockers digoxin HYPOTHYROIDISM NURSING INTERVENTION: management of metabolism symptoms a. Diet : calorie, bulk, fat b. Management of constipation: c. Weight monitoring d. Mental function and activity e. Skin care f. Use of sedatives g. Environmental temperature h. WOF: thyrotoxicosis Discharge teaching: continue course of medication even if symptoms subside to prevent myxedema coma HYPERTHYRODISM NURSING INTERVENTION: THYROIDECTOMY partial or total removal of the thyroid gland indications: subtotal thyroidectomy ( hyperthyroidism) and total thyroidectomy for thyroid cancer PRE OP NURSING INTERVENTION a. ensure client is adequately prepared for surgery such as stable CV status, weight and nutritional status are normal ( euthyroid) b. administer antithyroid drugs to suppress production and secretion of thyroid hormone and to prevent thyroid storm c. administer Lugols solution to reduce the size and vascularity of the gland and prevent hemorrhage POST OPNURSING INTERVENTION: a. monitor vital signs and I & O b. check dressing for signs of hemorrhage c. place client on semi fowlers position and support head with pillows d. observe for respiratory distress secondary to hemorrhage, edema of the glottis, laryngeal nerve damage or tetany e. keep tracheostomy set, oxygen apparatus and suction nearby
f. assess for signs of tetany due to hypocalcemia secondary to accidental removal of the parathyroid glands g. keep calcium gluconate at bedside h. encourage client to rest voice since hoarseness is common i. observe for thyroid storm due to excessive release of thyroid hormone during surgery j. administer IV fluid and analgesics 1. Which of the following is a sign of hyperthyroidism a. cold intolerance b. weight gain c. coarse tremors d. hyperactivity 2. Following a thyroidectomy the nurse carefully observe the client for signs of thyroid storm that includes: a. hypothermia b. elevated serum calcium c. sudden drop in pulse rate d. rapid heart rate and tremors DISORDERS OF THE PARATHYROID GLAND HYPOPARATHYROIDISM HYPERPARATHYROIDISM HYPOPARATHYROIDISM MAIN PROBLEM: characterized by hypocalcemia resulting from deficiency of parathromone CAUSE/S: hereditary, idiopathic caused by accidental damage to or removal of the parathyroid glands during surgery SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS 1. NEUROMUSCULAR IRRITABILITY A. tingling of fingers and around lips, painful muscle spasms, B. dysphagia, laryngospasm,seizure and cardiac arryhtmias C. Chvostek s sign D. Trousseaus sign: e. CARDIAC arrhythmia
2. personality changes, irritability and memory impairment 3. dry, scaly skin 4. hair loss 5. tooth enamel and nails DIAGNOSTIC TESTS: Serum calcium Serum phosphorus Bone density NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Risk for injury NURSING INTERVENTIONS: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Calcium supplement Diet- calcium and vitamin D Safety precaution Seizure precaution Emergency equipment and drug to manage tetany environmental control Discharge teaching:
Vitamin D and oral calcium to be taken with meals to increase absorption Because of the possibility that the parthyroid gland was accidentally removed during a radical neck dissection, the patient should be observed for which of the following signs? a. hyperventillation b. dyspnea c. facial twitching d. dysphagia HYPERPARATHYROIDISM MAIN PROBLEM: increased secretion of the PTH resulting in altered state of calcium, phosphate and bone metabolism CAUSE/S: Primary hyperparathyroidism: caused by tumor or hyperplasia of the parathyroid gland Secondary hyperparathyroidism: caused by compensatory over secretion of PTH in response to hypocalcemia from chronic disease such as rickets, ostoemalacia
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS 1. bone pain ( especially at the back), bone dimineralization, pathologic fractures 2. renal colic, kidney stones, polyuria and polydipsia 3. muscle weakness and fatigue 4. anorexia, nausea, vomiting, gastric ulcers and constipation 5. Irritability, personality changes, depression psychosis and coma 6. Cataract formation DIAGNOSTIC TESTS: Serum calcium Serum phosphorus Bone density NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Risk for injury NURSING INTERVENTIONS: Diet- calcium and vitamin D Safety precaution Surgery to remove adenoma Force fluid Strain urine 6. discharge teaching focused on: engaging in progressive ambulatory activities, increased oral fluid intake, calcium preparations 35 year old patient diagnosed with primary hyperparathyroidism is encouraged to drink at least 3 L of fluids/day. The rationale for forcing fluid is to prevent the complication of: a. hypertension and MI b. hemorrhage and hypotension c. infection and renal stones d. dropping BP and pulse ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 1. PITUITARY GLAND - ANTERIOR A. ACTH B. TSH c. FSH/LH - Intermediate ( MSH) - POSTERIOR A. ADH B. SIADH
2. THYROID GLAND - T3 AND T4 - Calcitonin 3. PARATHYROID GLAND - parathormone 4. PANCREAS - alpha cells - beta cells 5. ADRENAL GLANDS - CORTEX: a. mineralocorticoids b. glucocorticoids c. sex hormones - MEDULLA: a. epinephrine b. norepinephrine 6. SEX HORMONE - ESTROGEN - PROGESTERONE - ANDROGEN 1. PITUITARY GLAND ( Anterior) - HYPOPITUITARYISM - ACTH, TSH, FSH/LH and GROWTH HORMONE ( Dwarfism) - HYPERPITUITARYISM - ACTH, TSH, FSH/LH and Growth Hormone ( Gigantism and Acromegaly) 2. PITUITARY GLAND ( Posterior) - Diabetis Insipidus - SIADH HYPOPHYSECTOMY 2. THYROID GLAND - HYPOTHYROIDISM Myxedema Coma Cretinism
- HYPERTHYRODISM Thyroid storm Agranulocytosis 3 PARATHYROID GLAND - HYPOPARATHYROIDISM tetany - HYPERPARATHYROIDISM renal calculi 4. ADRENAL GLANDS - ADRENAL CORTEX: a. Addisons disease b. Cushings disease c. Conns Disease - ADRENAL MEDULLA: a. pheochromocytoma 5. PANCREAS - hypoglycemia - diabetis mellitus - diabetic keto acidosis - HHNK - gestational diabetis DISORDERS OF THE ADRENAL CORTEX Addisons Disease Cushings Disease Conns Disease ADDISONS DISEASE MAIN PROBLEM: hypofunction of the adrenal cortex causes decreased secretion of mineralocorticoids, glucorticoids and sex hormones CAUSE/S: 1. idiopathic athropy of the adrenal cortex due to an autoimmune process 2. destruction of the gland secondary to tuberculosis or fungal infection SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS: sodium level in the blood BP potassium level in the blood
blood sugar level energy level ability to handle stress and infection skin color DIAGNOSTIC TESTS: Serum cortisol Serum sodium Serum potassium Serum glucose NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Fluid and electrolyte Imbalance: Deficit NURSING INTERVENTION: 1. hormone replacement such as glucorticoids(cortisone) and mineralocorticoids (Florinef) 2. WOF: for shock : monitor vital signs; increase oral fluid intake; weigh daily 3. prevent exposure to infection 4. decrease stress in the environment 5. provide rest period 6. diet: calories, sodium, potassium 7. Severe infection may lead to : ADDISONIAN CRISIS
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- HypocalcemiaDocument2 paginiHypocalcemiaRachel Frances SorillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HYPOPARATHYROIDISMDocument1 paginăHYPOPARATHYROIDISMPhilip Gene II MalacasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Endocrine Disorders and Diabetes MellitusDocument59 paginiPathophysiology of Endocrine Disorders and Diabetes MellitusboboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calcium Metabolism & Calcium Metabolism DisordersDocument45 paginiCalcium Metabolism & Calcium Metabolism Disorderstrisya arthaputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thyroid Diseases: Peter S. Aznar, MD, FPSP, MhpeDocument52 paginiThyroid Diseases: Peter S. Aznar, MD, FPSP, MhpeDeomicah SolanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypoparathyroidism: Low Calcium Caused by Parathyroid Gland IssuesDocument3 paginiHypoparathyroidism: Low Calcium Caused by Parathyroid Gland IssuesSharmaine Grace Florig50% (2)
- Endocrine Diseases of Newborn Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Therapeutic Options, and Outcome "Current Insights Into Disorders of Calcium and Phosphate in The NewbornDocument8 paginiEndocrine Diseases of Newborn Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Therapeutic Options, and Outcome "Current Insights Into Disorders of Calcium and Phosphate in The NewbornLuis Ruelas SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypoparathyroidism NEJM 2019 PDFDocument10 paginiHypoparathyroidism NEJM 2019 PDFalejandro toro riveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thyroid and Parathyroid Disorders: by Dr. Magdi Awad Sasi 2013Document65 paginiThyroid and Parathyroid Disorders: by Dr. Magdi Awad Sasi 2013Eidi IdhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thyroid Disorders: Hyperthyroidism HypothyroidismDocument66 paginiThyroid Disorders: Hyperthyroidism HypothyroidismGabz GabbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insulinoma and Hyperinsulinism GuideDocument13 paginiInsulinoma and Hyperinsulinism Guideaileen agustinÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Directions in The Treatment of HypoparathyroidismDocument6 paginiNew Directions in The Treatment of Hypoparathyroidismmiguel saba sabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IVMS Physiology and Pathophysiology Flash FactsDocument4.648 paginiIVMS Physiology and Pathophysiology Flash FactsMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.Încă nu există evaluări
- 6.1 Agents That Affect Bone Mineral HomeostasisDocument17 pagini6.1 Agents That Affect Bone Mineral HomeostasisAsem AlhazmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pearls and Pitfalls in Head and Neck SurgeryDocument225 paginiPearls and Pitfalls in Head and Neck SurgeryMoustafa Amin AlyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine EmergenciesDocument22 paginiEndocrine EmergenciesBen Man JunÎncă nu există evaluări
- HypocalcemiaDocument23 paginiHypocalcemiarayrrn00Încă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine SystemDocument25 paginiEndocrine Systemangel_maui100% (13)
- Parathyroid GlandDocument25 paginiParathyroid GlandJasmine Rey QuintoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blueprint B NUR104 Final 2016Document32 paginiBlueprint B NUR104 Final 2016Jen HahlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluids & Electrolyte NewDocument154 paginiFluids & Electrolyte NewMaria Visitacion100% (2)
- Epidemiology and Complications of HypoparathyroidismDocument12 paginiEpidemiology and Complications of HypoparathyroidismErika AvilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypocalcemia College PresentationDocument40 paginiHypocalcemia College PresentationClaudia IrimieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alteration in Endocrine SystemDocument215 paginiAlteration in Endocrine Systemyen1988100% (1)
- Endocrine DisordersDocument16 paginiEndocrine DisordersEiffel AnchetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Structure MusculoskeletalDocument20 paginiBone Structure MusculoskeletalLM MysÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parathyroid Diseases: Kristine Mae FernandezDocument27 paginiParathyroid Diseases: Kristine Mae Fernandeznurse_on_duty13Încă nu există evaluări
- Make Biochemistry Manual: Serum Calcium EstimateDocument3 paginiMake Biochemistry Manual: Serum Calcium Estimatehaseeb ShafaatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calcium Deficiency in The Human Body Which Causes HypocalcemiaDocument7 paginiCalcium Deficiency in The Human Body Which Causes Hypocalcemiaputrik agustinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Review of Drug Induced HypocalcemiaDocument8 paginiA Review of Drug Induced HypocalcemiaKrisna MulasimadhiÎncă nu există evaluări