Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
ECE Proposed 2nd Year Syllabus
Încărcat de
pranics3695Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ECE Proposed 2nd Year Syllabus
Încărcat de
pranics3695Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Syllabus for B.
Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
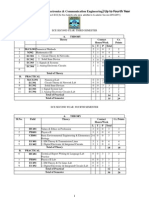
ECE SECOND YEAR: THIRD SEMESTER
Sl.No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 B. 7 8 9 10 11
Field
A. Theory
THEORY Contact Hours/Week L T P Total 2 0 0 2 3 1 0 4 3 3 3 3 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 4 3 3 4 20 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 3 3 3 3 2 3 3 3 3 14 34 Cr. Points 2 4 4 3 3 4 20 1 2 2 2 2 9 29
M(CS)301 Numerical Methods M302 Mathematics-III 1. Circuit Theory & Networks EC301 2. Solid State Device EC302 EC303 1. Signals & Systems EC304 2. Analog Electronic Circuits Total of Theory PRACTICAL Nunerical Lab M(CS)391 Circuit Theory & Network Lab EC391 Solid State Devices EC392 1. Signal System Lab EC393 2. Analog Electronic Circuits Lab EC394 Total of Practical Total of Semester
ECE SECOND YEAR: FOURTH SEMESTER
Sl.No. 1 2 3 4 5 B. 6 7 8 9
Field HU401 PH401 CH401 EC401 EC402 PRACTICAL HU491 PH491 EC491 EC492
Contact Cr. Points Hours/Week L T P Total Values & Ethics in Profession 3 0 0 3 3 Physics-II 3 1 0 4 4 Basic Environmental Engineering & Elementary 2+1 0 0 3 3 Biology 1. EM Theory & Transmission Lines 3 1 0 4 4 2. Digital Electronic Circuits 3 1 0 4 4 Total of Theory 18 18 Communication Skill & Report Writing Physics-II Lab 1. EM Theory & Tx Lines Lab 2. Digital Electronic Circuits Lab Total of Practical Total of Semester 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 12 30 2 2 2 2 8 26
A. THEORY Theory
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
SEMESTER - III Theory NUMERICAL METHODS Code : M(CS) 301 Contacts : 2L Credits :2 Approximation in numerical computation: Truncation and rounding errors, Fixed and floating-point arithmetic, Propagation of errors. (4) Interpolation: Newton forward & backward interpolation, Lagranges and Newtons divided difference Interpolation. Numerical integration: Trapezoidal rule, Simpsons 1/3 rule, Weddles rule. (5) (3)
Numerical solution of a system of linear equations: Gauss elimination method, Matrix inversion, LU Factorization method, Gauss-Jacobi and Gauss-Seidel iterative methods. (6) Numerical solution of Algebraic equation: Bisection method, Secant method, Regula-Falsi method, Newton-Raphson method. (4) Numerical solution of ordinary differential equation: Taylors series method, Eulers method, Runge-Kutta methods, Predictor-Corrector methods and Finite Difference method. (6) Text Books: 1. 2. 3. 4. References: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
C.Xavier: C Language and Numerical Methods. Dutta & Jana: Introductory Numerical Analysis. J.B.Scarborough: Numerical Mathematical Analysis. Jain, Iyengar , & Jain: Numerical Methods (Problems and Solution).
Balagurusamy: Numerical Methods, Scitech. Baburam: Numerical Methods, Pearson Education. N. Dutta: Computer Programming & Numerical Analysis, Universities Press. Soumen Guha & Rajesh Srivastava: Numerical Methods, OUP. Srimanta Pal: Numerical Methods, OUP.
MATHEMATICS Code: M 302
Contacts: 3L +1T = 4 Credits: 4 Note 1: The whole syllabus has been divided into five modules. Note 2: Structure of the question paper There will be three groups in the question paper. In Group A, there will be one set of multiple choice type questions spreading the entire syllabus from which 10 questions (each carrying one mark) are to be answered. From Group B, three questions (each carrying 5 marks) are to be answered out of a set of questions covering all the three modules. Three questions (each carrying 15 marks) are to be answered from Group C. Each question of
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
Group C will have two or three parts covering not more than two modules. Sufficient questions should to be set covering the whole syllabus for alternatives.
Module I Fourier Series: Introduction, Periodic functions, Even and odd functions, Special waveforms, Eulers formulae for Fouriers coefficients, Dirichlets conditions and sum of the Fourier series, Half range Fourier series, Parsevals identity (Statement only). Fourier Transform: Fourier Transform and its properties, Inverse Fourier Transform (Statement only), Fourier Transform of derivatives (Statement only), Convolution (8L) theorem (Statement only). Related problems.
Module II Calculus of Complex variable: Functions, Limit and Continuity, Analytic functions, Cauchy-Riemann equations ( Statement only) and related problems, Analytic continuation, Complex integration and Cauchys theorem (Statement only), Cauchys integral formula ( Statement only), Taylors and Laurent series, Zeros of an analytic function, Poles, Essential singularities, Residue theorem ( Statement only) and its application to evaluation of definite integrals (Elementary cases only), Introduction to Conformal Mapping. Module III Probability: Axiomatic definition of probability, Conditional probability, Independent events, Related problems, Bayes theorem ( Statement only) & its application. One dimensional random variable, Probability distributions-discrete and continuous, Expectation, Binomial, Poisson, Uniform, Exponential and Normal distribution, Problems on Binomial, Poisson and Normal distribution only. (12L) (12L)
Module IV Partial Differential Equations: Solution of one dimensional wave equation, One dimensional heat-conduction equation, Laplace equation in two dimension by the methods of 1: Separation of variables 2: Integral Transforms (Laplace and Fourier Transforms) ( 6L) Module V Series solution of Ordinary Differential equation: Introduction, validity of series solution of an ordinary differential equation, general method to solve equation of the type: Poy// + P1y/+P2y = 0, related problems, Bessels equation, properties of Bessels function, Recurrence formula for Bessels function of first kind, Legendres equation, Legendre function; Recurrence formula for Legendre function (Pn(x)); Orthogonality relation. ( 10L)
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
Text Books: 1. Brown J.W and Churchill R.V: Complex Variables and Applications, McGraw-Hill. 2. Das N.G.: Statistical Methods, TMH. 3. Grewal B S: Higher Engineering Mathematics, Khanna Publishers. 4. James G.: Advanced Modern Engineering Mathematics, Pearson Education. 5. Lipschutz S., and Lipson M.L.: Probability (Schaum's Outline Series), TMH.
References: 1. Bhamra K. S.: Partial Differential Equations: An introductory treatment with applications, PHI 2. Dutta Debashis: Textbook of Engineering Mathematics, New Age International Publishers. 3. Kreyzig E.: Advanced Engineering Mathematics, John Wiley and Sons. 4. Potter M.C, Goldberg J.L and Aboufadel E.F.: Advanced Engineering Mathematics, OUP. 5. Ramana B.V.: Higher Engineering Mathematics, TMH.
Code : EC 301 Module# 1.
CIRCUIT THEORY & NETWORKS Contacts : 3L +1T =4hrs
Credits :4 Hrs 4
2.
3.
4.
5. 6. 7.
Content Resonant Circuits: Series and Parallel Resonance, Impedance and Admittance Characteristics, Quality Factor, Half-Power Points, Bandwidth, Resonant voltage rise, Transform diagrams, Solution of Problems Mesh Current Network Analysis: Kirchoffs Voltage Law, Formulation of Mesh Equations, Solution of mesh equations by Cramers rule and matrix method, Driving point impedance, Transfer impedance, Solutions of Problems with DC and AC sources Node Voltage Network Analysis: Kirchoffs Current Law, Formulation of node equations and solutions, Driving point admittance, Transfer admittance, Solutions of Problems with DC and AC sources Network Theorems: Definition and implications of Superposition Theorem, Thevenins Theorem, Nortons Theorem, Reciprocity Theorem, Compensation Theorem, Maximum Power Transfer Theorem, Millmans Theorem, Star-Delta transformations, Solutions and Problems with DC and AC sources Graph of Network: Concept of Tree Branch, Tree link, junctions, Incident matrix, Tie-set matrix, Cut-set matrix, determination of loop current and node voltages. Coupled Circuits: Magnetic Coupling, polarity of coils, polarity of induced voltage, concept of self and mutual inductance, coefficient of coupling, Solution of Problems Circuit Transients: DC Transient in R-L & R-C circuits with and without initial charge, R-L-C circuits, AC transients in sinusoidal R-L, R-C, & R-L-C circuits, solution of problems Laplace Transform: Concept of complex frequency, transformation of f(t) into F(s), transformation of step, exponential, overdamped surge, critically damped surge, damped sine, undamped sine functions, properties of Laplace Transform, linearity, real-differentiation, realintegration, Initial Value Theorem and Final Value Theorem, Inverse Laplace Transform, applications in circuit analysis, Partial Fractions expansion, Heavisides Expansion Theorem, solution of problems SPICE: Introduction, model statement, elementary DC and small-signal analysis. Text Books: 1. Valkenburg M. E. Van, Network Analysis, Prentice Hall./Pearson Education 2. Hayt Engg Circuit Analysis 6/e Tata McGraw-Hill 3. D.A.Bell- Electrical Circuits- Oxford
4 2 4
8.
9.
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
Reference Books: 1. A.B.Carlson-Circuits- Cenage Learning 2. John Bird- Electrical Circuit Theory and Technology- 3/e- Elsevier (Indian Reprint) 3. Skilling H.H.: Electrical Engineering Circuits, John Wiley & Sons. 4. Edminister J.A.: Theory & Problems of Electric Circuits, McGraw-Hill Co. 5. Kuo F. F., Network Analysis & Synthesis, John Wiley & Sons. 6. R.A.DeCarlo & P.M.Lin- Linear Circuit Analysis- Oxford 7. P.Ramesh Babu- Electrical Circuit Analysis- Scitech 8. Sudhakar: Circuits & Networks:Analysis & Synthesis 2/e TMH 9. M.S.Sukhija & T.K.NagSarkar- Circuits and Networks-Oxford 10. Sivandam- Electric Circuits and Analysis, Vikas 11. V.K. Chandna, A Text Book of Network Theory & Circuit Analysis,Cyber Tech 12. Reza F. M. and Seely S., Modern Network Analysis, Mc.Graw Hill . 13. M. H. Rashid: Introduction to PSpice using OrCAD for circuits and electronics, Pearson/PHI 14. Roy Choudhury D., Networks and Systems, New Age International Publishers. 15. D.Chattopadhyay and P.C.Rakshit: Electrical Circuits New Age
SOLID STATE DEVICES
Code : EC 302 Module 1.
Contacts : 3L +9T =3hrs
Credits :3 Hrs 4
2.
Contents Energy Bands and Charge Carriers in Semiconductors- Energy bands, E-k diagram; carrier charge and concentration; carrier drift, diffusion and recombination, quasi-Fermi energy level, surface effects Transport phenomena in semiconductor junctions: Basic p-n junction and its fabrication; junction current flow,, small signal model, generation and recombination junctions with nonuniform doping, switching time, metal-semiconductor junctions and hetero-junctions Rectifier and detector diodes: Reversed-biased p-n junction, photovoltaic effect-solar cells, zener and tunnel diodes; Varactor, Gunn and Impatt diode. Bipolar Transistor: Physical mechanism, current gain, minority current distribution; Punchthrough and avalanche effect; High voltage and high power transistors; Frequency limitations, high frequency transistors; CE, CB and CC configurations, Input and output characteristics (CE only) Field Effect Transistors: JFETS, IJFETS and MOSFETs; V-I characteristics; MOS-capacitors, flat band and threshold voltages; P and N-channel MOSFETS, Semiconductor sensors and detectors. Elements of device fabrications technology. Opto-electronic Devices: Optical absorption, photo-detectors, LEDs and LCDs, Laser diode
3. 4.
5.
6 4
6.
Total: 32 hrs Text Books : 1. 2. 3. Neamen- Semiconductor Physics and Devices TMH Bhattacharya & Sharma- Solid State Electronic Devices- Oxford Maini & Agrawal- Electronics Devices and Circuits- Wiley
Reference Books : 1. Milman, Halkias & Jit- Electronics Devices and Circuits- TMH
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
Bell-Electronics Devices and Circuits-Oxford Dimitrijev- Semiconductor Devices- Oxford Singh & Singh- Electronics Devices and Integrated Circuits PHI Bogart, Bisley & Rice- Electronics Devices and Circuits- Pearson Kasap-Principles of Electronic Materials and Devices- TMH Boylestad & Nashelsky- Electronics Devices and Circuit Theory- Pearson Salivahanan, Kumar & Vallavaraj- Electronics Devices and Circuits- TMH Pierret- Semiconductor Device Fundamentals- Pearson Islam- Semiconductor Physics and Devices- Oxford SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS Code : EC 303 Contacts : 3L +0T =3hrs Credits :3 Module Topic No Introduction- Signal Representation: Continuous and discrete time signals: Classification of Signals Periodic aperiodic even odd energy and power signals Deterministic and random signals complex exponential and sinusoidal signals periodicity properties of discrete time complex exponential unit impulse unit step impulse 1. functions Transformation in independent variable of signals: time scaling, time shifting: Discrete Fourier series (DFS), Properties of the DFS, Determination of Fourier series representation of continuous time and discrete time periodic Continuous Time Signals and Systems : Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT), Properties of DFT, Two dimensional DFT, Circular Convolution; Analysis of continuous time Fourier Transform with examples; Properties of Fourier Transform , Parsevals relation and convolution in time and frequency domains. Basic properties of continuous 2. time systems: Linearity, Causality, time invariance, stability, magnitude and Phase representations of frequency response of LTI systems -Analysis and characterization of LTI systems: Computation of impulse response and transfer function. Sampling Theorem: Representation of continuous time signals by its sample - Sampling theorem Reconstruction of a Signal from its samples, aliasing discrete time processing of continuous time signals using 3. Fouriers Transform, sampling of band pass signals using DFT Z-Transforms: Basic principles of z-transform - z-transform definition region of convergence properties of ROC Properties of z-transform Poles and Zeros inverse z-transform using Contour integration - Residue 4. Theorem, Power Series expansion and Partial fraction expansion, Relationship between z-transform and Fourier transform. Total: 32 hrs Text Books: 1. A.V.Oppenheim, A.S.Willsky and S.H.Nawab -Signals & Systems, Pearson 2. S.Haykin & B.V.Veen, Signals and Systems- John Wiley 3. A.Nagoor Kani- Signals and Systems- McGraw Hill References: 1. J.G.Proakis & D.G.Manolakis- Digital Signal Processing Principles, Algorithms and Applications, PHI. 2. C-T Chen- Signals and Systems- Oxford 3. E WKamen &BS Heck- Fundamentals of Signals and Systems Using the Web and Matlab- Pearson 4. B.P.Lathi- Signal Processing & Linear Systems- Oxford 5. P.Ramesh Babu & R.Anandanatarajan- Signals and Systems 4/e- Scitech 6. M.J.Roberts, Signals and Systems Analysis using Transform method and MATLAB, TMH 7. S Ghosh- Signals and Systems- Pearson 8. M.H.Hays- Digital Signal Processing , Schaums outlines, TMH 9. Ashok Amhardar, -Analog and Digital Signal Processing- Thomson. Phillip, Parr & Riskin- Signal, Systems and Transforms- Pe
2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Hrs
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
ANALOG ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Code : EC 304 Module 1. 2. Contacts : 3L +1T =4hrs Credits :4 Hrs 4 6
Contents Filters and Regulators: Capacitor filter, -section filter, ripple factor, series and shunt voltage regulator, percentage regulation, 78xx and 79xx series, concept of SMPS. Transistor Biasing and Stability: Q-point, Self Bias-CE, Compensation techniques, h-model of transistors. Expression for voltage gain, current gain, input and output impedance, trans-resistance & trans-conductance; Emitter follower circuits, High frequency model of transistors. Transistor Amplifiers: RC coupled amplifier, functions of all components, equivalent circuit, derivation of voltage gain, current gain, input impedance and output impedance, frequency response characteristics, lower and upper half frequencies, bandwidth, and concept of wide band amplifier. Feedback Amplifiers & Oscillators: Feedback concept, negative & positive feedback, voltage/ current, series/shunt feedback, Berkhausen criterion, Colpitts, Hartleys, Phase shift, Wein bridge and crystal oscillators. Operational Amplifier: Ideal OPAMP, Differential Amplifier, Constant current source (current mirror etc.), level shifter, CMRR, Open & Closed loop circuits, importance of feedback loop (positive & negative), inverting & non-inverting amplifiers, voltage follower/buffer circuit. Applications of Operational Amplifiers: adder, integrator & differentiator, comparator, Schmitt Trigger. Instrumentation Amplifier, Log & Anti-log amplifiers, Trans-conductance multiplier, Precision Rectifier, voltage to current and current to voltage converter, free running oscillator. Power amplifiers Class A, B, AB, C, Conversion efficiency, Tuned amplifier Multivibrator Monostable, Bistable, Astable multivibrators; Monostable and astable operation using 555 timer. Special Functional Circuits: VCO and PLL.
3.
4.
5.
6.
6 4 2 2
7. 8. 9.
Total: 40 hrs Text Books: 1. Sedra & Smith-Microelectronic Circuits- Oxford UP 2. FrancoDesign with Operational Amplifiers & Analog Integrated Circuits , 3/e, McGraw Hill 3. Boylested & Nashelsky- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory- Pearson/PHI Reference Books: 1. Millman & Halkias Integrated El;ectronics, McGraw Hill. 2. Rashid-Microelectronic Circuits-Analysis and Design- Thomson (Cenage Learning) 3. Schilling & BeloveElectronic Circuit:Discrete & Integrated , 3/e , McGraw Hill 4. Razavi- Fundamentals of Microelectronic s- Wiley 5. MalvinoElectronic Principles , 6/e , McGraw Hill 6. Horowitz & Hill- The Art of Electronics; Cambridge University Press. 7. Bell- Operational Amplifiers and Linear ICs- Oxford UP 8. Tobey & Grame Operational Amplifier: Design and Applications, Mc GrawHill. 9. Gayakwad R.A -- OpAmps and Linear ICs, PHI 10. Coughlin and Driscol Operational Amplifier and Linear Integrated Circuits Pearson Education
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
Practical NUMERICAL METHODS Code : M(CS) 391 Credits :1
1. 2. 3.
Assignments on Newton forward & backward, Lagranges interpolation. Assignments on numerical integration using Trapezoidal rule, Simpsons 1/3 rule, Weddles rule. Assignments on numerical solution of a system of linear equations using Gauss elimination, Matrix inversion, Gauss-Jacobi, and Gauss-Seidel iterations.
4.
Assignments on numerical solution of Algebraic Equation by Bisection, Secant, Regular-falsi and Newton Raphson methods.
5.
Assignments on ordinary differential equation: Taylor series, Eulers, Runga-Kutta and Finite difference methods.
6.
Introduction to Software Packages: Matlab / Scilab / Labview / Mathematica.
Circuits and Networks Laboratory Code: EC391 Contacts: 3P Credits: 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Characteristics of Series & Parallel Resonant circuits Verification of Network Theorems Transient Response in R-L & R-C Networks ; simulation / hardware Transient Response in RLC Series & Parallel Circuits & Networks ; simulation / hardware Determination of Impedance (Z), and Admittance (Y) parameters of Two-port networks Generation of periodic, exponential, sinusoidal, damped sinusoidal, step, impulse, and ramp signals using MATLAB Representation of Poles and Zeros in s-plane, determination of partial fraction expansion in s-domain and cascade connection of second-order systems using MATLAB Determination of Laplace Transform, different time domain functions, and Inverse Laplace Transformation using MATLAB
Note: An Institution / college may opt for some other hardware or software simulation wherever possible in place of MATLAB Solid State Devices Laboratory Code: EC392 Contacts: 3P Credits: 2 1. Study of JFET drain and transfer characteristics. 2. JFET biasing arrangement Graphical method. 3. Build and Test JFET CS amplifier. Find performance parameters for JFET amplifier - AV, Ri, RO.
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
4. Simulation of JFET CS amplifier using multisim/spice. Find performance parameters for JFET amplifier - AV, Ri, RO and compare with theoretical and practical results. 5. Input and Output Characteristics of BJT CE configuration. Find h parameters from characteristics. 6. Build and Test BJT in CE amplifier and find performance parameters - AV, Ri, RO, AI 7. Simulation of BJT CE amplifier using multisim/spice Find performance parameters for BJT amplifier - AV, Ri, RO, AI and compare with theoretical and practical results. 8. Comparison of CE, CC, CB configurations in terms of AV, Ri, RO, AI. 9. Study of MOSFET drain and transfer characteristics 10. Frequency response - For BJT/ FET single stage amplifiers - Effect of unbypassed RE and RS. Effect of coupling and bypass capacitors on low frequency cut-off. Signals and Systems Laboratory Code: 393 Contacts: 3P Credits: 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. To study Z- transform of: a) Sinusoidal signals b) Step functions. To compare Fourier and Laplace transformations of a signal. To study convolution theorem in time and frequency domain. To Study Signal Synthesis via sum of harmonics. To study LPF &HPF, band pass and reject filters using RC circuits. To demonstrate how analog signals are sampled and how different sampling rates affect the outputs. To study sampling theorem for low pass signals and band pass signals . To determine the components of: a) Square wave b) Clipped sine wave.
Analog Electronic Circuits Laboratory Code:EC394. Contacts: 3P Credits: 2
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15.
Study of Diode as clipper & clamper Study of Zener diode as a voltage regulator Study of ripple and regulation characteristics of full wave rectifier without and with capacitor filter Study of characteristics curves of B.J.T & F.E.T . Construction of a two-stage R-C coupled amplifier & study of its gain & Bandwidth. Study of class A & class B power amplifiers. Study of class C & Push-Pull amplifiers. Realization of current mirror & level shifter circuit using Operational Amplifiers. Study of timer circuit using NE555 & configuration for monostable & astable multivibrator. Construction & study of Bistable multivibrator using NE 555. Study of Switched Mode Power Supply & construction of a linear voltage regulator using regulator IC chip. Construction of a simple function generator using IC. Realization of a V-to-I & I-to-V converter using Op-Amps. Realization of a Phase Locked Loop using Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO). Study of D.A.C & A.D.C.
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
SEMESTER - IV Theory VALUES & ETHICS IN PROFESSION HU-401 Contracts:3L Credits- 3 Science, Technology and Engineering as knowledge and as Social and Professional Activities Effects of Technological Growth: Rapid Technological growth and depletion of resources, Reports of the Club of Rome. Limits of growth: sustainable development Energy Crisis: Renewable Energy Resources Environmental degradation and pollution. Eco-friendly Technologies. Environmental Regulations, Environmental Ethics Appropriate Technology Movement of Schumacher; later developments Technology and developing notions. Problems of Technology transfer, Technology assessment impact analysis. Human Operator in Engineering projects and industries. Problems of man, machine, interaction, Impact of assembly line and automation. Human centered Technology. Ethics of Profession: Engineering profession: Ethical issues in Engineering practice, Conflicts between business demands and professional ideals. Social and ethical responsibilities of Technologists. Codes of professional ethics. Whistle blowing and beyond, Case studies. Profession and Human Values: Values Crisis in contemporary society Nature of values: Value Spectrum of a good life Psychological values: Integrated personality; mental health Societal values: The modern search for a good society, justice, democracy, secularism, rule of law, values in Indian Constitution. Aesthetic values: Perception and enjoyment of beauty, simplicity, clarity Moral and ethical values: Nature of moral judgements; canons of ethics; ethics of virtue; ethics of duty; ethics of responsibility. Books: 1. 2. 3. Stephen H Unger, Controlling Technology: Ethics and the Responsible Engineers, John Wiley & Sons, New York 1994 (2nd Ed) Deborah Johnson, Ethical Issues in Engineering, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 1991. A N Tripathi, Human values in the Engineering Profession, Monograph published by IIM, Calcutta 1996. :Physics : 3L + 1T :4
Ph 401 : Contacts Credits Modulle 1:: Mo du e 1
Vecttor Callcullus: Vect or Ca c u us: c 1..1 Physsiicall ssiigniiifiicancess off grad,, diiv,, curll. Liine iinttegrrall, ssurface iinttegrrall, vollume iinttegrrall-- physiicall examplles c a g n f c anc e o grad d v cur . L ne n e g a , urf ace n e g a , v o u me n eg a p hys ca ex amp es 1 1 Ph y h iin tthe conttextt off ellecttrriiciity and magnettiism and ssttattementtss off Sttokess ttheorrem and Gaussss ttheorrem [[No Prroof].. n h e co n e x o e ec c t y an d m ag ne s m and a emen o S oke heo em a nd Gau a m he or em N o P oof] P
10
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
Expressiion of grrad,, diiv,, currll and Lapllaciian iin Spherriicall and Cylliindriicall co--ordiinattess.. E xpress on of g a d d v c u a nd Lap ac an n Sph e ca an d C y n dr c a co or d na e 2L 2L Modulle 2 :: Mo du e 2 Ellecttriiciity E e c r c ty 2..1 Coullumbss llaw iin vecttorr fforrm.. Ellecttrosttattiic fiiielld and iitts curll. Gausss llaw iin iinttegrrall form and converrsiion tto 2 1 Co u umb a w n vec o o m E e c r os a c f e d an d s cur . Ga usss a w n n eg a f orm a nd co nv e s on o C E o d n diiffferrenttiiall fforrm .. Ellectttrossttattiic pottenttiiall and fiielld,, Poiissssons Eqn.. Lapllacess eqn (Appllicattion tto Carrttessiian,, d f e e n a o m E ec r o a c p o en a an d f e d P o on s Eq n Lap ace eq n (A pp i c a i on o Ca e a n e C Spheriicallly and Cylliindrriicalllly symmettrriic ssysttemss efffecttive 1D prrobllems)) Ellecttriic currrentt, driiftt vellociity,, Sp her c a y and C y nd c a y sy mme c ys e m ef e c i ve 1D p ob ems E ec r c cu ren , dr f ve o c t y c c b v currrentt densiiity,, conttiinuiitty equattiion,, sstteady currentt.. c ur e n de ns t y c on i n u y eq ua o n e a dy curr en e n 5L 5L
2..2 Diiellecttriics-conceptt of pollarriizattiion,, tthe rellattion D=00E+P,, Pollariizabiilliity.. Ellecttroniic pollariizattiion and 2 2 D e e c r c s-co nc ep of po a za on he re a i on D=0 E+ P Po ar z a b t y E ec ro n c po a r z a on an d e e + pollarriizattiion iin monoattomiic and pollyattomiic gasses... p o a z a o n n mon oa om c an d p o ya om c g a es Modulle 3:: Mo du e 3 Magnetostatiicss & Tiime Varyiing Fiielld: Ma gn et ost at c & T me Vary n g F e d: 3L 3L
3.. Lorrenttz force,, fforce on a smallll currrentt ellementt pllaced iin a magnettiic fiiielld.. Biiott--Savarrtt llaw and iitts 3 Lo en z f orce or ce on a sma c ur e n e e me n p aced n a magn e c f e d B o Sav ar aw and ss c e n B n applliicattionss,, diiverrgence off magnettiic fiielld,, vecttorr pottenttiiall, Amperress llaw iin iinttegrrall form and conversiion tto a pp c a i on d ve g enc e o ma gn e c f e d ve c o po en ia , A mpe e a w n n eg a f or m an d con vers on o v diiffferrenttiiall fforrm.. Farrada ys llaw off ellecttro-magnettiic iinducttiion iin iinttegrrall form and converrsiion tto diiffferenttiall d f e e n a o m F ar ada ys a w o e e c rro- magn e c nd uc o n n n eg a f orm an d con ve s on o d f eren i a g e forrm.. fo m 3L 3L
Modulle 4:: Mo du e 4 Ellecttromagnetiic Theory: E e c ro ma gn et c Theor y: a 4..1 Conceptt of diispllacementt currrentt Maxwelllls ffiielld equattiions,, Maxwelllss wave equattiion and iitss ssolluttiion for 4 1 Co nce p of d s p ace men cu r en M axwe s e d eq ua o ns Max we w ave eq ua o n a nd t o u on f or e a free sspace.. E..M.. wave iin a charrge frree conducttiing mediia,, Skiin depttth,, physsiicall siigniifiicance of Skiin Deptth,, E..M.. fr ee p ace E M w av e n a cha g e f ee co nd uc i n g med a Sk n de p h p hy c a s gn f c a nce of Sk n Dep h E M energy fllow,, & Poyntting Vecttor.. e nerg y f o w & Poyn i ng Vec or 6L 6L
Modulle 5:: Mo du e 5 Quantu m Mechaniics:: Qua ntu m M echa n cs u
5..1 Generralliised coordiinattes,, Lagrranges Equattiion of mottiion and Lagrrangiian,, generralliised force pottenttiall, 5 1 G ene a is e d c oord n a e s Lag ange s Eq ua o n of m o o n a nd Lag a ng an g ene a sed f orce po e n i a , g c momentta and enerrgy.. Hamiillttonss Equattiion off mottiion and Hamiillttoniian.. Prroperrttiies off Hamiiltton and Hamiillttonss mo men a a nd ene g y Ham o n Equ a on o mo on an d Ham o n an P ope e s o Ham l on an d Ham t o n d n q n p equattiion of mottion.. e qu a on of mo i on 4L 4L
11
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
Courrsse shoulld be diisscussed allong wiitth physsiicall prrobllemss off 1--D mottiion C ou e sh ou d be d c ussed a on g w h ph y c a pro b e m o 1 D m o o n o
5..2 Conceptt of prrobabiilliity and probabiilliitty densiitty,, operrattorrs,, commuttattor.. Formullattiion off quanttum mechaniicss 5 2 Co nce p of p o ba b t y a nd pro bab y d ens y op e a o s co mmu a or Formu a on o qu an um mec han c and Basiic posttullattes,, Operattorr corresspondence,, Tiime dependentt Schrdiingerrs equattiion,, fformullattion of ttiime a nd Bas c p os u a e s Op er a o corr es po nd en ce T me d epe nd en Schr d nge s eq ua o n or mu a i on of me o n iindependentt Schrrdiingerrs equattion by metthod off sseparrattiion off varriiablles,, Physiicall iintterprettattion of wave nd epe nd en S ch d ng e s e qu a i on by m e ho d o epa a o n o va ab es Ph ys ca n er pre a i on of w av e functtiion ((normalliizattiion and probabiilliitty iintterprrettattiion)),, Expecttattiion vallues,,,Appllicattiion off Schrrdiinger fu nc o n n orm a za o n a nd pro bab y n e rp e a on Ex pec a on v a u es A pp i ca on o Sc hr d n ger a o a equattiion Parrttiiclle iin an iinfiiniitte ssquare wellll pottenttiiall ((1--D and 3-D potttenttiiall wellll),, Diisscussiion on degeneratte e qu a on Pa c e n a n nf n e qu ar e w e p o e n a 1- D a nd 3-D p o e n a we ) D c uss on on de gen er a e 3 p n llevells.. ev e s 9L 9L
Module 6: Statistical Mechanics: 3.1 Concept of energy levels and energy states. Microstates, macrostates and thermodynamic probability, equilibrium macrostate. MB, FD, BE statistics (No deduction necessary), fermions, bosons (definitions in terms of spin, examples), physical significance and application, classical limits of quantum statistics Fermi distribution at zero & non-zero temperature, Calculation of Fermi level in metals, also total energy at absolute zero of temperature and total number of particles, Bose-Einstein statistics Plancks law of blackbody radiation.. 7L CH401: Basic Environmental Engineering & Elementary Biology Contacts : 3L Credits : 3 General Basic ideas of environment, basic concepts, man, society & environment, their interrelationship. 1L Mathematics of population growth and associated problems, Importance of population study in environmental engineering, definition of resource, types of resource, renewable, non-renewable, potentially renewable, effect of excessive use vis--vis population growth, Sustainable Development. 2L Materials balance: Steady state conservation system, steady state system with non conservative pollutants, step function. 1L
Environmental degradation: Natural environmental Hazards like Flood, earthquake, Landslide-causes, effects and control/management; Anthropogenic degradation like Acid rain-cause, effects and control. Nature and scope of Environmental Science and Engineering. 2L Ecology Elements of ecology: System, open system, closed system, definition of ecology, species, population,
12
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
community, definition of ecosystem- components types and function.
1L
Structure and function of the following ecosystem: Forest ecosystem, Grassland ecosystem, Desert ecosystem, Aquatic ecosystems, Mangrove ecosystem (special reference to Sundar ban); Food chain [definition and one example of each food chain], Food web. 2L
Biogeochemical Cycle- definition, significance, flow chart of different cycles with only elementary reaction [Oxygen, carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphate, Sulphur]. 1L
Biodiversity- types, importance, Endemic species, Biodiversity Hot-spot, Threats to biodiversity, Conservation of biodiversity. 2L
Air pollution and control Atmospheric Composition: Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere, Tropopause and Mesopause. 1L Energy balance: Conductive and Convective heat transfer, radiation heat transfer, simple global temperature model [Earth as a black body, earth as albedo], Problems. 1L
Green house effects: Definition, impact of greenhouse gases on the global climate and consequently on sea water level, agriculture and marine food.Global warming and its consequence, Control of Global warming. Earths heat budget. 1L
Lapse rate: Ambient lapse rate Adiabatic lapse rate, atmospheric stability, temperature inversion (radiation inversion). 2L
Atmospheric dispersion: Maximum mixing depth, ventilation coefficient, effective stack height, smokestack plumes and Gaussian plume model. 2L
Definition of pollutants and contaminants, Primary and secondary pollutants: emission standard, criteria pollutant. Sources and effect of different air pollutants- Suspended particulate matter, oxides of carbon, oxides of 2L
nitrogen, oxides of sulphur, particulate, PAN. Smog, Photochemical smog and London smog.
Depletion Ozone layer: CFC, destruction of ozone layer by CFC, impact of other green house gases, effect of ozone modification. 1L
Standards and control measures: Industrial, commercial and residential air quality standard, control measure (ESP. cyclone separator, bag house, catalytic converter, scrubber (ventury), Statement with brief reference). 1L Water Pollution and Control Hydrosphere, Hydrological cycle and Natural water.
13
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
Pollutants of water, their origin and effects: Oxygen demanding wastes, pathogens, nutrients, Salts, thermal application, heavy metals, pesticides, volatile organic compounds. 2L
River/Lake/ground water pollution: River: DO, 5 day BOD test, Seeded BOD test, BOD reaction rate constants, Effect of oxygen demanding wastes on river[deoxygenation, reaeration], COD, Oil, Greases, pH. 2L Lake: Eutrophication [Definition, source and effect]. Ground water: Aquifers, hydraulic gradient, ground water flow (Definition only) Standard and control: Waste water standard [BOD, COD, Oil, Grease], Water Treatment system [coagulation and flocculation, sedimentation and filtration, disinfection, hardness and alkalinity, softening] Waste water treatment system, primary and secondary treatments [Trickling filters, rotating biological contractor, Activated sludge, sludge treatment, oxidation ponds] tertiary treatment definition. 2L 1L 1L
Water pollution due to the toxic elements and their biochemical effects: Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, and Arsenic 1L
Land Pollution Lithosphere; Internal structure of earth, rock and soil 1L
Solid Waste: Municipal, industrial, commercial, agricultural, domestic, pathological and hazardous solid wastes; Recovery and disposal method- Open dumping, Land filling, incineration, composting, recycling. Solid waste management and control (hazardous and biomedical waste). 2L
Noise Pollution Definition of noise, effect of noise pollution, noise classification [Transport noise, occupational noise, neighbourhood noise] 1L
Definition of noise frequency, noise pressure, noise intensity, noise threshold limit value, equivalent noise level,
L10 (18 hr Index) , Ld n .
Noise pollution control. 1L
Environmental Management: Environmental impact assessment, Environmental Audit, Environmental laws and protection act of India, Different international environmental treaty/ agreement/ protocol. References/Books 1. Masters, G. M., Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science, Prentice-Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., 1991. 2. De, A. K., Environmental Chemistry, New Age International. 2L
14
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY & TRANSMISSION LINES Code : EC 401 Contacts : 3L +1T =4hrs
Credits :4
Electromagnetic Theory 1. Vector calculus orthogonal Coordinate Systems, Transformations of coordinate systems; Del operator; Gradient, Divergence, Curl their physical interpretations; Laplacian operator. [4] Coulombs law, electric field intensity, charge distribution.; Gauss law, flux density and electric field intensity. Divergence theorem. Current Densities, Conductors, Poissons & Laplaces equations, Uniqueness theorem, Biot-Savart law, Amperes law, Relation between J & H, Vector magnetic Potential, Stokes theorem. [6] Faradays law & Lenzs law, Displacement Current, J C J D Relation, Maxwells equations, Timeharmonic fields, Wave Equation, Boundary Conditions between media interface; Uniform Plane wave; Wave Propagation in Lossy Dielectric, Loss-less Dielectric, Free space. Poynting Theorem, Power flow, Poynting vector. Wave polarizations. [8] Numerical Techniques for Electromagnetic Problems- Moment Methods, Finite Difference Method, Finite Elements Method, Some case studies. [6] Transmission Lines Transmission Lines: Concept of Lump parameters and Distributed parameters, Line Parameters, Transmission line equations and solutions, Physical significance of the solutions. Propagation constant, Characteristic Impedance; Wavelength; Velocity of Propagation; Distortion-less Line, Reflection and Transmission coefficients; Standing Waves, VSWR, Input Impedance, Smith Chart Applications; Load Matching Techniques. [10] Field Analysis of Waveguides: Rectangular, Circular & Elliptical; Analysis of Resonator Applications [10]
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Text Books 1. Principles of Electromagnetics, 4th Edition, Matthew O H Sadiku, Oxford University Press. 2. Electromagnetic Field Theory & Transmission Lines, G.S.N. Raju, Pearson Education 3. Electromagnetic Waves Shevgaonkar, Tata-McGaw-Hillr R K Reference Books 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Engineering Electromagnetics, 2ed Edition - Nathan Ida, Springer India Fields & Waves in Communication Electronics, S. Ramo, J. R. Whinnery & T. Van Duzer, John Wiley Electromagnetic Theory & Applications, A. K. Saxena, Narosa Publishing House Pvt. Ltd. Electromagnetics, 2ed Edition J A Edminister, Tata-McGraw-Hill. Engineering Electromagnetics, 7thEdition-W.H.Hayt & J.A.Buck, Tata-McGraw-Hill Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission Lines- by G.Prasad, J.Prasad and J.Reddy- Scitech
15
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
Code : EC 402 Module 1.
DIGITAL ELECTRONICS & INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Contacts : 3L +1T =4hrs Credits :4
2.
3. 4. 5. 6.
7. 8.
Contents Hrs Data and number systems; Binary, Octal and Hexadecimal representation and their conversions; BCD,ASCII, EBDIC, Gray codes and their conversions; Signed binary number 5 representation with 1s and 2s complement methods, Binary arithmetic. Venn diagram, Boolean algebra; Various Logic gates- their truth tables and circuits; Representation in SOP and POS forms; Minimization of logic expressions by algebraic 6 method, K-map method and Quine-McClauskey method Combinational circuits- Adder and Subtractor circuits; Applications and circuits of Encoder, 5 Decoder, Comparator, Multiplexer, De-Multiplexer and Parity Generator. Memory Systems: RAM, ROM, EPROM, EEROM 4 Design of combinational circuits-using ROM, Programming logic devices and gate 4 arrays.(PLAs and PLDs) Sequential Circuits- Basic memory element-S-R, J-K, D and T Flip Flops, various types of Registers and counters and their design, Irregular counter, State table and state transition 6 diagram, sequential circuits design methodology. Different types of A/D and D/A conversion techniques. 4 Logic families- TTL, ECL, MOS and CMOS, their operation and specifications. 6 Total: 40 hours
Textbooks: 1. A.Anand Kumar, Fundamentals of Digital Circuits- PHI 2. A.K.Maini- Digital Electronics- Wiley-India 3. Kharate- Digital Electronics- Oxford Reference: 1. Morries Mano- Digital Logic Design- PHI 2. R.P.JainModern Digital Electronics, 2/e , Mc Graw Hill 3. H.Taub & D.Shilling, Digital Integrated Electronics- Mc Graw Hill. 4. D.Ray Chaudhuri- Digital Circuits-Vol-I & II, 2/e- Platinum Publishers 5. GivoneDigital Principles & Design, Mc Graw Hill 6. Tocci, Widmer, Moss- Digital Systems,9/e- Pearson 7. S.K.Mandal, Digital Electronics Principles and Applications- Mc Graw Hill. 4. J.Bignell & R.Donovan-Digital Electronics-5/e- Cenage Learning. 8. Leach & MalvinoDigital Principles & Application, 5/e, Mc Graw Hill 9. Floyed & Jain- Digital Fundamentals-Pearson. 10. P.Raja- Digital Electronics- Scitech Publications 11. S.Aligahanan, S.Aribazhagan, Digital Circuit & Design- Bikas Publishing Practical Communication Skill & Report Writing Code: HU491 Cr-2 Code: PH-491 Co de: PH-4 91 Conttacttss:: ((3P)) C on a c s 3 P Crrediitt:: ((2)) C ed 2 Grroup 1:: Experriimenttss on Ellecttrriiciity and Mangenttiism Gr ou p 1 Exp e men o n E ec c t y a nd Ma ng en sm c 1.. Detterrmiinattiion off diiellecttriic constttantt of a giiven diiellecttriiic matterriiall. 1 De e m na o n of d e e c r c co ns a n of a g ven d e e c r c ma e a . e d 3.. Dettermiinattion off ressiisttance off ballliisttic gallvanometter by hallf defllecttiion metthod and sttudy of 3 De er m n a i on o r e s anc e o b a ss i c ga van ome er by ha f d ef e c o n m e hod and s ud y of y h m o
16
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
variiattiion off llogariitthmiic decrementt wiith serriiess rressiisttance.. v ar a o n o o gar hm c d ecr em en w t h se e r e s anc e 4.. Detterrmiinattiion off tthe tthermo-ellecttrriic powerr att a cerrttaiin ttemperatturre off tthe giiven tthermocouplle.. 4 De e m na o n of h e hermo-e ec c p ow e a a ce a n e mper a ur e o he g ve n hermo cou p e c e h g o 5.. Detterrmiinattiion off sspeciifiic charrge (e//m) off ellecttron by J..JJ.. Thomssons metthod.. 5 De e m na o n of pe c f c cha g e ( e m) o e e c r on b y J Th om on s me ho d h Grroup 2:: Quanttum Physiicss Gr ou p 2 Qu an um Ph ys c 6.. Dettermiinattion of Pllancks conssttantt ussiing phottocellll.. 6 De er m n a i on of P a nck s c on an u n g p ho o ce . e 7.. Dettermiinattion of Landeg facttor ussiing Ellectttron spiin rressonance spettrometter.. 7 De er m n a i on of Lande g f ac or u ng E ec r o n sp n e on anc e sp e r ome er d 8.. Detterrmiinattiion off Sttefans radiiattiion consttantt 8 De e m na o n of S e f an s r ad a on co ns an o 9.. Verriiffiicattiion off Bohr s attomiic orrbiittall ttheory tthrrough Frank-Herrttz experriimentt.. 9 Ve ca o n o Bo hr s a o m c o b a h eory h o ug h Fran k- He z e xp e men a 10.. Dettermiinatttion off Rydberg conssttantt by ssttudyiing Hydrrogen// Hellium spectttrum 1 0 De e rm n a i on o R yd berg con a n by u dy n g H yd oge n He i um sp ec r u m g n Grroup 3:: Modern Physiicss Gr ou p 3 Mo der n Phys cs e 11.. Dettermiinattion of Hallll co--efffiiciientt off ssemiiconducttors.. 1 1 De er m n a i on of H a co e f c e n o em c o nd uc ors 12.. Dettermiinatttion off band gap of semiiconducttorss.. 1 2 De e rm n a i on o b an d g ap of se m cond uc or o d 13.. To sttudy currrentt--vollttage charactterriisstticss,, lload ressponse,, arreall charractterriissttiicss and specttrrall rresponsse 1 3 To s ud y cu r en vo ta ge ch ar ac e i c o ad r e po nse a e a ch a ac e ic a nd sp ec a esp on e c off photto vollttaiic sollar celllss.. o ph o o vo a c so a r c e
a) A candiidatte iis requiired tto perfform 3 experiimentts takiing one from each group.. IIniitiiattiive a) A cand d a e s re qu red t o per o rm 3 ex per men s ta k ng o ne f ro m ea ch gro up I n t a ve sshoulld be ttaken sso that mosstt of the Experiimenttss are covered iin a collllege iin tthe diissttriibuttiion hou d be a ken o th at mos of th e E xp er men are co vere d n a co e ge n he d r b u on o e o u mentiioned above.. Emphasiiss sshoulld be giiven on tthe essttiimatiion of error iin tthe datta taken.. ment o ne d abov e Emp has hou d b e g v en o n he e mat on of e rro r n he da a t aken o u n b)) IIn addiitiion a studentt shoulld perform one more experiiments where he//sshe wiilll have to b n ad d tt o n a stu den sho u d perf or m one more ex pe r me nts w here he he w l h av e to u ttransduce the outputt of any off tthe above experiimentts or the experiimentt menttiioned iin c] iinto ransd uce t he o utp u of a ny o h e a bov e ex per men s o r th e e xper men men oned n c] nt o ellecttriicall vollttage and collllect the data iin a computter ussiing phoeniix or ssiimiiillar iintterfface.. e ect r c a vo ag e a nd c o ect th e data n a co mpu er u ng phoe n x or m ar n er ace h a o c) Innovatiive experiiimentt: One more experiimentt dessiigned by the student or the concerned c) In nov at v e ex per m en : On e mo re exper ment de g ned by th e st ude nt o r t he co ncerned e tteacher or both.. eac he r or bot h Nottte:: No e i. Failure to perform each experiment mentioned in b] and c] should be compensated by two experiments mentioned in the above list. ii. At the end of the semester report should sent to the board of studies regarding experiments, actually performed by the college, mentioned in b] and c] iii. Experiment in b] and c] can be coupled and parts of a single experiment.
Recommended Textt Bookss and Reference Bookss:: Recomme nded Tex Bo ok a nd R ef ere nce Bo oks e m For Both Physiics I and IIII For Both Ph ys cs I a nd 1.. B.. Dutttta Roy (Basiic Physsiicss) 1 B D u a Roy ( Bas c Ph y c ) h 2.. R...K.. Kar (Engiineeriing Physiicss)) 2 R K K ar ( Eng n eer n g Ph ys c 3.. Manii and Mehetta ((Modern Physiicss)) 3 M an an d Meh e a Mo der n Phys cs e 4.... Arrtthur Baiisser ((Perrspecttiive & Conceptt of Modern Physiicss)) 4 Ar h ur Ba er ( Pe sp ec ve & Co nc ep of M od er n Ph ys c c & Physiicss II ((PH101//201) Ph ys c PH 10 1 20 1) Viibrrattiion and Waves V b a o n a nd Wav es 3.. Kiiingsllerr and Frey 3 K n gs e an d Fr ey
17
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
4.. 4 5.. 5 6.. 6 7.. 7 8.. 8 9.. 9 Optticss Op i c 1.. 1 2.. 2 3.. 3 4.. 4 5.. 5 6.. 6
D...P.. Roychaudhury D P Ro yc hau dh ury a N...K.. Bajjajj (Waves and Osciilllattionss)) N K B a a ( Wav es a nd Osc l a i on K... Bhatttacharya K Bha a chary a R..P.. Siingh (( Physiicss off Osciilllattions and Waves) R P S ng h Phys c o Osc a i ons and Wa ves) P y n A...B.. Guptta ((Collllege Physsiics Voll.III)) A B G up a C o eg e P hy c s V . I o Chattttopadhya and Raksshiitt (Viibrattiion,, Wavess and Acousstticss)) C ha o pa dhya a nd Rak h (V br a on Wave an d A cou i c o
Mllerr ((Physiicall Optticss)) M e Ph ys ca Op i c A...K.. Ghattak A K Gha a k E.. Hechtt (Optticss)) E H ech ( Op i c h E.. Hechtt (Schaum Seriies) E H ech ( Scha um S er e s) h F..A.. Jenkiins and H..E.. Whiitte F A Jen k ns a nd H E W h e 6.. Chiitta Ranjjan Dassguptta (( Degree Physiicss Voll 3)) 6 C h a R an a n Da gu p a ( D egr ee Phys cs Vo 3 a D y
Quanttum Physsiicss Qu an um Ph ys c 1.. Eiissberg and Ressniick 1 E berg an d R e n ck 2.. A...K.. Ghattak and S.. Lokenatthan 2 A K Gha a k an d S Lok en a h an 3.. S..N... Ghoshall (Inttrroducttorry Quanttum Mechaniicss)) 3 S N Gh osh a (I n o du c o y Qua n um M ech an c 4.. E..E..Anderrson ((Moderrn Physiicss)) 4 E E A nd e so n M od er n Ph ys c 5.. Halliida y,, Ressniick and Crrane (Physsiics voll..IIIII) 5 Ha da y R e n ck an d C a ne (P hy c s vo . I ) a n 6.. Biina ya k Dutttta Roy [Ellementtss of Quanttum Mechaniicss]] 6 B n a ya k D u a Ro y [ E e me n of Q ua n u m Me cha n c Crryssttallllography C y a o gr ap hy 1.. S..O... Piilllaii (a.. Sollliid ssttatte physiics b.. Probllem iin Sollid sttatte physiicss)) 1 S O P l a (a So d a e phys cs b Pr ob e m n So i d s a e ph ys c e 2.. A...J.. Dekkerr 2 A J De kk e 3.. Aschrrofftt and Mermiin 3 As ch o an d Mer m n 4.. Allli Omarr 4 A i O ma 5.. R..L... Siinghall 5 R L S ng ha 6.. Jak Tareen and Trn Kuttty (Bassiic courrse iin Cr ysttalllogrraphy 6 Ja k Tar een an d Tr n Ku y (Ba c c ou se n Cr ys a og a ph y a h Lasserr and Hollogrraphy La e and H o og a ph y 1.. A...K.. Ghattak and Thyagarajjan ((Lasserr) 1 A K Gha a k an d T hya gara an La e ) 2.. Tarasov (Laserr) 2 Taraso v (Lase ) a 3.. P..K.. Chakrabortty (Optttics)) 3 P K Ch akrab or y ( Op i cs K 4.. B.. Ghossh and K..G.. Majjumderr ((Opttiics) 4 B G ho h and K G M a u mde O p c s) 5.. B..B.. Laud (Laser and Non-lliinearr Optticss)) 5 B B Lau d (Laser a nd Non- ne a Op i c B 6.. Bhattttacharyya [[Engiineerriing Physsiics] Oxford 6 B ha a c hary ya En g nee ng Phy cs] O xf ord
Physiicss IIII(PH 301) Ph ys c ( PH 30 1) Cllassiicall Mechaniics ((Forr Modulle 5..1 iin PH 301) C a ss ca Mec han c s Fo Mod u e 5 1 n PH 30 1) H... Golldsstteiin H Go d e n A...K.. Roychaudhurrii A K R oy cha ud hu R..G... Takwall and P..S.. Purraniik R G Tak wa a nd P S Pu an k Rana and Joag R ana an d Jo ag M.. Speiigell ((Schaum Serriiess)) M Sp e g e Sch au m Se e u J..C... Upadhya ((Mechaniics) J C Up adh ya M ech an cs) n Ellecttrriiciiity and Magnettissm E ec c t y a nd Ma gn e i m M 3.. Reiitz,, Miilfforrd and Chrriisstty 3 R e t z M l o d and Ch y d
18
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
4.. 4 5.. 5 6.. 6
Daviid JJ.. Grriifffiitth Dav d G ff h a D... Chattttopadhya y and P..C.. Raksshiitt D Cha o pa dh ya y an d P C Rak h a a Shadowiittz ((The Ellecttrromagnettiic Fiielld)) Sh ado w z T he E ec o magne c F e d e
Quanttum Mechaniicss Qu an um M ech an cs 7.. Eiissberg and Ressniick 7 E berg an d R e n ck 8.. A...K.. Ghattak and S.. Lokenatthan 8 A K Gha a k an d S Lok en a h an 9.. S..N... Ghoshall (Inttrroducttorry Quanttum Mechaniicss)) 9 S N Gh osh a (I n o du c o y Qua n um M ech an c 10.. E..E..Anderrson ((Moderrn Physiicss)) 10 E E A nd e so n M od er n Ph ys c 11.. Halliida y,, Ressniick and Crrane (Physsiics voll..IIIII) 11 Ha da y R e n ck an d C a ne (P hy c s vo . I ) a n 12.. Biina ya k Dutttta Roy [Ellementtss of Quanttum Mechaniicss]] 12 B n a ya k D u a Ro y [ E e me n of Q ua n u m Me cha n c Sttattissttiicall Mechaniics S a i c a Mech an c s c 1.. Searrs and Sallliinger (Kiinettiic Theor y,, Thermodynamiics and 1 Sea s and Sa l n ger ( K ne ic The or y Th er mod yn am c s and 2.. Mondall (Sttattiisstticall Physiics) 2 M on da ( S a s i ca Phys cs) 3.. S..N... Ghoshall ( Attomiic and Nucllearr Physsiics) 3 S N Gh osh a ( A o m c a nd Nu c ear Phy c s) 4.. Siingh and Siingh 4 S ng h a nd S n gh n h 5.. B..B.. Laud (Sttattiistttiicall Mechaniicss)) 5 B B Lau d (S a s ca Me cha n c B 6.. F.. Reiif (Sttattiisstticall Mechaniics) 6 F R e f ( S a i ca Mec han c s) Diiilecttrriicss D l ec c 7.. Bhattttacharyya [[Engiineerriing Physsiics] Oxford 7 B ha a c hary ya En g nee ng Phy cs] O xf ord Electromagnetic Wave and Transmission Lines Code: EC491 Contacts: 3P Credits: 2 Minimum 3 experiments from each Group. Group-A Measurement of free space wavelength, guide wavelength g and frequency f using X- band waveguide test bench. Plot vs. f & g vs. f curves. Obtain the dispersion curve (- plot) for X- band waveguide and study the phase velocity and group velocity within waveguide. Measurement of unknown impedance using shift in minima technique. Measurement of reflection co-efficient and transmission co-efficient due to a discontinuity within a waveguide. Determination of Dielectric constant of a (i) Solid material (ii) Liquid material In an X-band test bench. Sttattiisttiicall Therrmodynamiicss)) S a s ca The mo dy nam c
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Group-B Study of the filter characteristics using spectrum analyzer with tracking generator. Simulate Smith Chart on MATLAB platform. Measure VSWR for various values of ZL (load impedance). Find the position of VMAX and VMIN from the chart. 8. Study of Spectrum Analyzer. Measure frequency response of a filter using Spectrum Analyzer with tracking generator. 9. Measure ZO and of an X-band waveguide by measuring Z SC and ZOC. 10. Study the matching techniques (single -stub, double- stub and quarter wave techniques). 6. 7.
19
Syllabus for B.Tech(ECE) Second Year
Revised & Proposed Syllabus of B.Tech in ECE (To be followed from the academic session, July 2011, i.e. for the students who were admitted in Academic Session 2010-2011)
Digital Electronic & Integrated Circuits Laboratory Code: EC492 Contacts: 3P Credits: 2
1. 2. 3 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15.
Realization of basic gates using Universal logic gates. Code conversion circuits- BCD to Excess-3 and vice-versa. Four-bit parity generator and comparator circuits. Construction of simple Decoder and Multiplexer circuits using logic gates. Design of combinational circuit for BCD to decimal conversion to drive 7-segment display using multiplexer. Construction of simple arithmetic circuits-Adder, Subtractor. Realization of RS-JK and D flip-flops using Universal logic gates. Realization of Universal Register using JK flip-flops and logic gates. Realization of Universal Register using multiplexer and flip-flops. Construction of Adder circuit using Shift Register and full Adder. Realization of Asynchronous Up/Down counter. Realization of Synchronous Up/Down counter. Design of Sequential Counter with irregular sequences. Realization of Ring counter and Johnsons counter. Construction of adder circuit using Shift Register and full Adder.
20
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- EE Proposed 3rd Year Syllabus 18.05.12Document27 paginiEE Proposed 3rd Year Syllabus 18.05.12Vidit UpadhyayÎncă nu există evaluări
- AEIE Proposed 3rd Year Syllabus 22.06.12Document39 paginiAEIE Proposed 3rd Year Syllabus 22.06.12Ujaan Zidane NandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE Proposed 2nd Year Syllabus 20.01.12Document37 paginiECE Proposed 2nd Year Syllabus 20.01.12Aman KediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE Proposed 2nd Year Syllabus-15.12.11Document23 paginiEE Proposed 2nd Year Syllabus-15.12.11Kartik DebnathÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE Proposed 2nd Year Syllabus-15.12.11Document20 paginiEE Proposed 2nd Year Syllabus-15.12.11Kanika DebnathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wbut Electrical Engineering SyllabusDocument43 paginiWbut Electrical Engineering SyllabusBarun GhoraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seacom Skills University: B.Tech 2 Year 4 Semester Theory Paper Sl. No. Paper Paper Code Credit PointDocument11 paginiSeacom Skills University: B.Tech 2 Year 4 Semester Theory Paper Sl. No. Paper Paper Code Credit PointM RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eesyll PDFDocument130 paginiEesyll PDFDeepak DeepuÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE - Final - Upto - 4th - Year SyllabusDocument57 paginiECE - Final - Upto - 4th - Year SyllabusSoumyadeep GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd Sem SyllabusDocument19 pagini3rd Sem SyllabusabcÎncă nu există evaluări
- SyllabusDocument84 paginiSyllabusgjÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE Final Upto 4th Year Syllabus 6 June, 2013Document58 paginiECE Final Upto 4th Year Syllabus 6 June, 2013menilanjan89nLÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd Semester: Curriculum BookDocument19 pagini3rd Semester: Curriculum BookSai Chaitanya ChakravarthulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Be 2018 Scheme Third Semester Syllabus Ec / TCDocument119 paginiBe 2018 Scheme Third Semester Syllabus Ec / TCSanjay KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum S T R U C T U R E of S.Y.-B.Tech (Electrical Engineering) (Regularstudents)Document56 paginiCurriculum S T R U C T U R E of S.Y.-B.Tech (Electrical Engineering) (Regularstudents)Bhushan RaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Structure & Syllabus: B.Tech ProgrammeDocument57 paginiCourse Structure & Syllabus: B.Tech ProgrammekamalkantmbbsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scheme For II YearDocument37 paginiScheme For II YearShreyas S RÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.sc. Electronics Honours SyllabusDocument10 paginiB.sc. Electronics Honours Syllabussiddhartharay007Încă nu există evaluări
- 2nd Year Schem N SyllabusDocument49 pagini2nd Year Schem N SyllabusRohitha MadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 18scheme SyllDocument23 pagini18scheme SyllNk KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cou Rs E S Tructure: (3rd and 4th Semesters)Document57 paginiCou Rs E S Tructure: (3rd and 4th Semesters)Bhanu K PrakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syl 13-EE Syllabus 2012-13Document57 paginiSyl 13-EE Syllabus 2012-13kamalkantmbbsÎncă nu există evaluări
- I B Tech s-13 SyllabusDocument40 paginiI B Tech s-13 Syllabusapi-279049687Încă nu există evaluări
- Ma MSC MathsDocument42 paginiMa MSC Mathskaif0331Încă nu există evaluări
- B.SC - Maths 6th Sem FinalDocument10 paginiB.SC - Maths 6th Sem Finalबिप्लु शइकीयाÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE Final Upto 3rd Year Syllabus 13.07.12Document32 paginiEE Final Upto 3rd Year Syllabus 13.07.12Ishtiaque AnwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kerala Technological University: Master of TechnologyDocument69 paginiKerala Technological University: Master of TechnologyREVATHY RATHEESHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iit Madras Detailed SyllabusDocument14 paginiIit Madras Detailed SyllabusSuperdudeGauravÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE Final Upto 4th Year Syllabus 10.01.14Document67 paginiEE Final Upto 4th Year Syllabus 10.01.14smrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st Sem B.tech Group B 2Document14 pagini1st Sem B.tech Group B 2ANKIT CHAKRABORTYÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of PuneDocument40 paginiUniversity of PuneSopan KambleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus FOR B.Tech. Programme Civil Engineering Electrical Engineering Mechanical Engineering (First Year)Document38 paginiSyllabus FOR B.Tech. Programme Civil Engineering Electrical Engineering Mechanical Engineering (First Year)Haider HateemÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Syllabus Cse 2020 OnwardsDocument42 paginiNew Syllabus Cse 2020 OnwardsAyush ShuklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st Year Blown Up Syllabus 2016 17Document38 pagini1st Year Blown Up Syllabus 2016 17sunilsheelavantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronics and Communication EnggDocument32 paginiElectronics and Communication EnggALEX SAGARÎncă nu există evaluări
- B Tech SyllabusDocument35 paginiB Tech SyllabusRipan DeuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- KTU Thermal Science Mtech Draft SyllabusDocument82 paginiKTU Thermal Science Mtech Draft SyllabusFennÎncă nu există evaluări
- SYLLABUS First Year ECE CSE FinalDocument38 paginiSYLLABUS First Year ECE CSE FinalMir YarikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sybtech PDFDocument33 paginiSybtech PDFSonali KahreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus Mathematics 2012 13 New Scheme Existing 1Document10 paginiSyllabus Mathematics 2012 13 New Scheme Existing 1Kitti ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- K.S.Institute of Technology, Bangalore: Department of Electronics & Communication EnggDocument51 paginiK.S.Institute of Technology, Bangalore: Department of Electronics & Communication Enggchandrashekhara gÎncă nu există evaluări
- M.SC - Mathematics 3rd Sem FinalDocument11 paginiM.SC - Mathematics 3rd Sem FinalGrace HoagnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus UG With CO PDFDocument13 paginiSyllabus UG With CO PDFAditya KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nagpur University All Years SyllabusDocument31 paginiNagpur University All Years SyllabusAjit PaswanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visvesvaraya Technological University, BelgaumDocument26 paginiVisvesvaraya Technological University, BelgaumVinay DesaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.SC - Maths 3rd Sem FinalDocument10 paginiB.SC - Maths 3rd Sem FinalAsom BartaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Screenshot 2023-03-20 at 5.23.03 PMDocument77 paginiScreenshot 2023-03-20 at 5.23.03 PMLaxmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME PE Proposed 2nd Year Syllabus 06.07.11Document25 paginiME PE Proposed 2nd Year Syllabus 06.07.11Kanishka BanerjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXTC Sem 3 and Sem 4 Syllabus As Per 2012.Document46 paginiEXTC Sem 3 and Sem 4 Syllabus As Per 2012.SG CanÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.Tech 1st SemDocument15 paginiB.Tech 1st Semmrkhan.04565Încă nu există evaluări
- Calculus and Linear Algebra UG - First Semester (Common To All Branches)Document3 paginiCalculus and Linear Algebra UG - First Semester (Common To All Branches)60 - R - OP ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Punjab Technical University: Scheme & Syllabus of B. Tech. 1 & 2 Semester Batch-2011Document42 paginiPunjab Technical University: Scheme & Syllabus of B. Tech. 1 & 2 Semester Batch-2011Pankaj SainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Academic Regulations For This Program Is Same As R18 B.Tech. Academic RegulationsDocument27 paginiAcademic Regulations For This Program Is Same As R18 B.Tech. Academic RegulationsManvitha KudikalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iii & Iv: Scheme & SyllabusDocument40 paginiIii & Iv: Scheme & Syllabussrikar prahladÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st - & - 2nd - Sem - Diploma SyllabusDocument50 pagini1st - & - 2nd - Sem - Diploma Syllabusvj4249Încă nu există evaluări
- Linear Algebra and Linear Operators in Engineering: With Applications in Mathematica®De la EverandLinear Algebra and Linear Operators in Engineering: With Applications in Mathematica®Încă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Mechanics with Applications to Nanotechnology and Information ScienceDe la EverandQuantum Mechanics with Applications to Nanotechnology and Information ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Mathematics for Engineers and ScientistsDe la EverandAdvanced Mathematics for Engineers and ScientistsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- Analytical Solution Methods for Boundary Value ProblemsDe la EverandAnalytical Solution Methods for Boundary Value ProblemsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Method of Moments for 2D Scattering Problems: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsDe la EverandMethod of Moments for 2D Scattering Problems: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aqa Econ3 QP Jan12Document8 paginiAqa Econ3 QP Jan12api-247036342Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 Pneumatic and Hydraulic Actuation SystemsDocument22 paginiChapter 5 Pneumatic and Hydraulic Actuation SystemsMukhammad FauzyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.m.tech-Ece-Vlsi, Vlsi Systems, Vlsi System Design (Vlsi, Vlsis, Vlsisd) r17 Course Structure & SyllabiDocument35 pagini6.m.tech-Ece-Vlsi, Vlsi Systems, Vlsi System Design (Vlsi, Vlsis, Vlsisd) r17 Course Structure & SyllabiravibabukancharlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prepared by (Hospital Pharmacist) Primary & Secondary Healthcare DepartmentDocument11 paginiPrepared by (Hospital Pharmacist) Primary & Secondary Healthcare DepartmentwaqasÎncă nu există evaluări
- IBRO News 2004Document8 paginiIBRO News 2004International Brain Research Organization100% (1)
- "Chapter 9 - Influence Lines For Statically Determinate Structures" in "Structural Analysis" On Manifold @tupressDocument33 pagini"Chapter 9 - Influence Lines For Statically Determinate Structures" in "Structural Analysis" On Manifold @tupressrpsirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deutz Fahr Rear Axle T 7100 Workshop ManualDocument22 paginiDeutz Fahr Rear Axle T 7100 Workshop Manualcindybennettmd040595jbw100% (133)
- HK USP CompactDocument56 paginiHK USP CompactJonathan CrenshawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Components SectionDocument428 paginiMechanical Components Sectionxristo xristovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment Class X Similar Triangles: A D E B CDocument2 paginiAssignment Class X Similar Triangles: A D E B CCRPF School100% (1)
- 4.dole Regulations On Safety Standards in ConstrDocument31 pagini4.dole Regulations On Safety Standards in Constrmacky02 sorenatsacÎncă nu există evaluări
- FEED Deliverable List (Sample) : Project InformationDocument3 paginiFEED Deliverable List (Sample) : Project Informationamilasri100% (1)
- CR300 Wireless Communication ProtocolDocument130 paginiCR300 Wireless Communication ProtocolHenry Martinez BedoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5-2 Sem2 Phys ExamDocument7 pagini5-2 Sem2 Phys ExamNayLinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iso 3932 1976Document8 paginiIso 3932 1976NaveedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kyocera 1800Document2 paginiKyocera 1800gendoetzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard MissileDocument2 paginiStandard Missilemadox_3m100% (1)
- Ornament of Clear RealizationDocument11 paginiOrnament of Clear RealizationPrachi AryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paracetamol BPDocument4 paginiParacetamol BPjaimurugeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychological Factors Influencing Technology Adoption A Case S - 2021 - TechnovDocument17 paginiPsychological Factors Influencing Technology Adoption A Case S - 2021 - Technov6helmi6nauval6Încă nu există evaluări
- Cleavage in MammalsDocument51 paginiCleavage in MammalsIrfan Azram100% (4)
- Questions and Answers About Lead in Ceramic Tableware: Contra Costa Health Services / Lead Poisoning Prevention ProjectDocument4 paginiQuestions and Answers About Lead in Ceramic Tableware: Contra Costa Health Services / Lead Poisoning Prevention Projectzorro21072107Încă nu există evaluări
- Relay Identification: Example CDG31FF002SACHDocument5 paginiRelay Identification: Example CDG31FF002SACHRohit RanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Two Feasibility Study 2.0 Methods of Producing Ammonium Sulphate, ( (NH) SO)Document9 paginiChapter Two Feasibility Study 2.0 Methods of Producing Ammonium Sulphate, ( (NH) SO)Adeyoju RebeccaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 00 Calculator Techniques 02Document5 pagini00 Calculator Techniques 02Sealtiel1020Încă nu există evaluări
- Alien Magic - William Hamilton IIIDocument179 paginiAlien Magic - William Hamilton IIICarlos Rodriguez100% (7)
- Compaction - AsphaltDocument32 paginiCompaction - Asphaltrskcad100% (1)
- Foods 09 01560 PDFDocument10 paginiFoods 09 01560 PDFkim cheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design, Fabrication and Analysis of Fibonacci TurbineDocument5 paginiDesign, Fabrication and Analysis of Fibonacci TurbinearcaldartÎncă nu există evaluări
- X-Ray Radiation and Gamma RadiationDocument13 paginiX-Ray Radiation and Gamma RadiationVence MeraÎncă nu există evaluări