Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Yearly Plan Science Year 5
Încărcat de
Aceley JainuddinDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Yearly Plan Science Year 5
Încărcat de
Aceley JainuddinDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
SK SEKSYEN 7 BANDAR BARU BANGI
PANITIA SAINS 2008
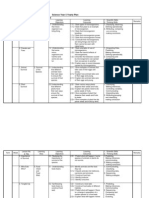
SK SEKSYEN 7 BANDAR BARU BANGI SCIENCE YEARLY PLAN : YEAR 5 SEMESTER 1 WEEK LEARNING AREAS LEARNING OBJECTIVES THEME : INVESTIGATING LIVING THINGS 1 1. Microorganism 1.1 Understanding that microorganism is a living thing. 2 3 1.2 Understanding that some microorganism are harmful and some are useful. 2. Survival of the species 2.1 Understanding that different animals have their own ways to ensure the survival of their species. 2.2 Understanding that different plants have their own ways to ensure the survival of their species. LEARNING OUTCOMES 1.1.1 State types of microorganisms. 1.1.2 State that yeast is an example of microorganism. 1.1.3 State that microorganism breathes. 1.1.4 State that microorganism grows. 1.1.5 State that microorganism moves. 1.1.6 Conclude that microorganisms are living things and most of them cannot be seen with naked eyes. 1.2.1 State examples of use of microorganisms. 1.2.2 State the harmful effects of microorganisms. 1.2.3 Describe that diseases caused by microorganisms can spread from one person to another. 1.2.4 Explain ways to prevent diseases caused by microorganisms. 2.1.1 Give examples of animals that take care of their eggs and young. 2.1.2 Explain how animals take care of their eggs and young. 2.1.3 Explain why animals take care of their eggs and young. 2.2.1 State various ways plants disperse their seeds and fruits. 2.2.2 Explain why plants need to disperse seeds or fruits. 2.2.3 Give examples of plant that disperse seeds and fruits by water. 2.2.4 Give examples of plant that disperse seeds and fruits by wind. 2.2.5 Give examples of plant that disperse seeds and fruits by animals. 2.2.6 Give examples of plant that disperse seeds and fruits by explosive mechanism. 2.2.7 Relate characteristics of seeds and fruits to the ways they are dispersed.
PANITIA SAINS 2008
SK SEKSYEN 7 BANDAR BARU BANGI 7 8 3. Food Chain and Food chains. 2.3 Realising the importance of survival of the species. 3.1 Understanding food chains. 2.3.1 Predict what will happen if some species of animals or plants do not survive. 3.1.1 Identify animals and the food they eat. 3.1.2 Classify animals into herbivore, carnivore and omnivore. 3.1.3 Construct food chain. 3.1.4 identify producer. 3.1.5 identify consumer. LEARNING OUTCOMES 3.2.1 Construct a food web. 3.2.2 Construct food webs of different habitats. 3.2.3 Predict what will happen if there is a change in population of a certain species in a food web. 3.2.4 Explain what will happen to a certain species of animals if they eat only one type of food. THEME : INVESTIGATING FORCE AND ENERGY 1. Energy. 1.1 Understanding the uses 1.1.1 Explain why energy is needed. of energy. 1.1.2 Give examples where and when energy is used. 1.1.3 State various sources of energy. 1.2 Understanding that 1.2.1 State the various forms of energy. energy can be 1.2.2 State that energy can be transformed. transformed from one 1.2.3 Give examples of appliances that make use of energy form to another. transformation. 1.3 Understanding 1.3.1 State what renewable energy is. renewable and non1.3.2 State what non-renewable energy is. renewable energy. 1.3.3 List renewable energy resources. 1.3.4 List non-renewable energy resources. 1.3.5 Explain why we need to use energy wisely. 1.3.6 Explain why renewable energy is better than non-renewable energy. 3
WEEK 9 10
LEARNING AREAS
LEARNING OBJECTIVE 3.2 Synthesizing food chains to construct food web.
11 12
13
14
PANITIA SAINS 2008
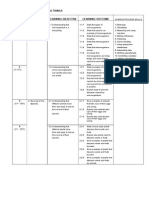
SK SEKSYEN 7 BANDAR BARU BANGI 1.3.7 Give examples on how to save energy. 1.3.8 Practise saving energy. 2.1.1 State the sources of electricity. 2.2.1 Identity the symbols of various components in a simple electric circuit. 2.2.2 Draw circuit diagrams. 2.2.3 Identify the difference in the arrangement of bulbs in series and parallel circuits. 2.2.4 Build a series circuit. 2.2.5 Build a parallel circuit. 2.2.6 Compare the brightness of the bulbs in a series and a parallel circuit. 2.2.7 Compare the effect on the bulbs when various switches in a series circuit and a parallel circuit are off. 2.3.1 Describe the danger of mishandling electrical appliances. 2.3.2 Explain the safety precautions to be taken when using electrical appliances.
15 16
2. Electricity
2.1 Knowing the sources of electricity. 2.2 Understanding a series circuit and a parallel circuit.
17
18
2.3 Understanding the safety precautions to be taken when handling electrical appliances.
PANITIA SAINS 2008
SK SEKSYEN 7 BANDAR BARU BANGI SEMESTER 2 WEEK 1 LEARNING AREAS 3. Light. LEARNING OUTCOMES 3.1.1 State that light travels in a straight line. 3.1.2 Give examples to verify that light travels in a straight line. 3.1.3 Describe how shadow is formed. 3.1.4 Design a fair test to find out what cause the size of a shadow to change by deciding what to keep the same, what to change and what to observe. 3.1.5 Design a fair test to find out what factors cause the shape of a shadow to change by deciding what to keep the same, what to change and what to observe. 3.2 Understanding that light 3.2.1 State that light can be reflected. can be reflected. 3.2.2 Draw ray diagrams to show reflection of light. 3.2.3 Give examples of uses of reflection of light in everyday life. 4. Heat. 4.1 Understanding that 4.1.1 State that when a substance gains heat it will become warmer. temperature is of 4.1.2 State that when a substance loses heat it will become cooler. indicator of degree of 4.1.3 Measure temperature using the correct technique. hotness. 4.1.4 State the metric unit for temperature. 4.1.5 State that temperature of an object or material increases as it gains heat. 4.1.6 State that temperature of an object or material decreases as it loses heat. 4.1.7 Conclude that the temperatures is an indicator to measure hotness. 4.2 Understanding the 4.2.1 State that matter expands when heated. effects of heat on matter. 4.2.2 State that matter contracts when cooled. 4.1.3 Give examples of the application of the principle of expansion and contraction in everyday life. THEME: INVESTIGATING MATERIALS 1. States of Matter 1.1 Understanding that 1.1.1 Classify objects and materials into three states of matter. matter exist in the form 1.1.2 State the properties of solid. 5 LEARNING OBJECTIVE 3.1 Understanding that light travels in a straight line.
2 3
PANITIA SAINS 2008
SK SEKSYEN 7 BANDAR BARU BANGI of solid, liquid or gas. 7 8 1.2 Understanding that matter can change from one state to another. 1.1.3 State the properties of liquid. 1.1.4 State that some liquids flow faster than others. 1.1.5 State the properties of gas. 1.2.1 State that water can change its state. 1.2.2 Conclude that water can exist in any of the three states of matter. 1.2.3 Identify the processes involved when a matter changer from one state to another. 1.2.4 Identify factors that affect the rate of evaporation of water.
WEEK 9
LEARNING AREAS
10 11
12 13
LEARNING OBJECTIVE LEARNING OUTCOMES 1.3 Understanding the water 1.3.1 Describe how clouds are formed. cycle. 1.3.2 Describe how rain is formed. 1.3.3 Explain how water is circulated in the environment. 1.3.4 Explain the importance of water cycle. 1.4 Appreciating the 1.4.1 Give reasons why we need to keep our water resources clean. importance of water 1.4.2 Describe ways to keep our water resources clean. resources. 2. Acid and Alkali. 2.1 Understanding the 2.1.1 Identify acidic, alkaline and neutral substances using litmus properties of acidic, paper. alkaline and neutral 2.1.2 Identify the taste of acidic and alkaline food. substances. 2.1.3 Conclude the properties of acidic, alkaline and neutral substances. THEME: INVESTIGATING THE EARTH AND THE UNIVERSE 1. Constellation. 1.1 Understanding the 1.1.1 State what constellation is. constellation. 1.1.2 Identify constellations. 1.1.3 State the importance of constellations. 2. The Earth, The Moon 2.1 Understanding the 2.1.1 State that the Earth rotates on its axis. and The Sun. movements of the Earth, 2.1.2 State that the Earth rotates and at the same time moves round the Moon and the Sun. the Sun. 2.1.3 State that the Moon rotates on its axis. 2.1.4 State that the Moon rotates and at the same time moves round 6
PANITIA SAINS 2008
SK SEKSYEN 7 BANDAR BARU BANGI the Earth. 2.1.5 State that the Moon and the Earth move round the Sun at the same time. 2.1.6 Describe the changes in length and position of the shadow throughout the day. 2.1.7 Conclude that the Earth rotates on its axis from west to east. 2.2.1 State that it is day time for the part of the Earth facing the Sun. 2.2.2 State it is night time for the part of the Earth facing away from the Sun. 2.2.3 Explain that day and night occur due to the rotation of the Earth on its axis. 2.3.1 State that the Moon does not emit light. 2.3.2 Explain that the Moon appears bright when it reflects sunlight. 2.3.3 Describe the phases of the Moon. 1.1.1 State the shapes of objects. 1.1.2 Identify shapes in structure. 1.2.1 Identify shapes of objects that are stable. 1.2.2 Identify the factors that affect stability of objects. 1.2.3 Explain how base area affects stability. 1.2.4 Explain how height affects stability. 1.2.5 Identify the factors that affect the strength of a structure. 1.2.6 design a model that is strong and stable.
14
15
2.2 Understanding the occurrence of day and night. 2.3 Understanding the phases of the Moon. THEME : INVESTIGATING TECHNOLOGY 1. Strength and Stability 1.1 Knowing the shapes of objects in structures. 1.2 Understanding the strength and stability of a structure.
16
17 18 19
PANITIA SAINS 2008
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Solar-Hydrogen Energy Systems: An Authoritative Review of Water-Splitting Systems by Solar Beam and Solar Heat: Hydrogen Production, Storage and UtilisationDe la EverandSolar-Hydrogen Energy Systems: An Authoritative Review of Water-Splitting Systems by Solar Beam and Solar Heat: Hydrogen Production, Storage and UtilisationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Document7 paginiYearly Plan Science Year 5Burhan AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biogeochemical Cycling of Mineral-Forming ElementsDe la EverandBiogeochemical Cycling of Mineral-Forming ElementsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Document5 paginiYearly Plan Science Year 5azmnqiinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scheme of Work Science Year 5Document4 paginiScheme of Work Science Year 5murniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearlyplanning Science Year5Document6 paginiYearlyplanning Science Year5Satia KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Document5 paginiYearly Plan Science Year 5wawa2006Încă nu există evaluări
- RPT Sains THN 5 - 2012Document9 paginiRPT Sains THN 5 - 2012zan75Încă nu există evaluări
- Ranc Peng Tahunan Sains Tahun 5 2014 JsuDocument8 paginiRanc Peng Tahunan Sains Tahun 5 2014 Jsunanac_2Încă nu există evaluări
- First Term Science Year 5 Yearly Plan Themes A: Investigating Living ThingsDocument24 paginiFirst Term Science Year 5 Yearly Plan Themes A: Investigating Living ThingsXgeniusXÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan STD 6 ScienceDocument3 paginiLesson Plan STD 6 ScienceVijay ManogaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Year 5 Yearly PlanDocument7 paginiScience Year 5 Yearly Plan惠鑫Încă nu există evaluări
- Theme: Investigating Living Things Learning Area Learning Objective Learning OutcomeDocument8 paginiTheme: Investigating Living Things Learning Area Learning Objective Learning OutcomewmpejonÎncă nu există evaluări
- RPT SN THN5Document10 paginiRPT SN THN5Jhoster YulongÎncă nu există evaluări
- TMK Yr2Document73 paginiTMK Yr2Rosnita Abdul WahabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Document8 paginiScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Muhammad FarisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week Learning Area Learning Objectve Learnng Outcomes Scientfc Process Skills & Thinking SkillDocument7 paginiWeek Learning Area Learning Objectve Learnng Outcomes Scientfc Process Skills & Thinking SkillDinamaniYeogesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum Specifications: Science Year 5Document20 paginiCurriculum Specifications: Science Year 5hany3688_519912007Încă nu există evaluări
- Kontrak Latihan Murid Tahun6Document2 paginiKontrak Latihan Murid Tahun6Sue Suemanie TicerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theme / Learning Area / Learning Objective EkstrapolationDocument21 paginiTheme / Learning Area / Learning Objective EkstrapolationMary Dorris JohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year Planner SC Yr 6Document8 paginiYear Planner SC Yr 6ccqwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- RPT Science Yr5 - 2011Document9 paginiRPT Science Yr5 - 2011Mohd HamedanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integrated ScienceDocument6 paginiIntegrated Scienceiteachclassroom100% (2)
- Grade 6 Science Budget of Work 1st To 4thDocument4 paginiGrade 6 Science Budget of Work 1st To 4thKristine Barredo100% (5)
- Yearly Plan 2011 Science Y5Document4 paginiYearly Plan 2011 Science Y5Mohd ZulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5 2 0 10 First SemesterDocument10 paginiScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5 2 0 10 First SemesterRaffie MuksinÎncă nu există evaluări
- RT SN PraktikumDocument3 paginiRT SN PraktikumNavamalar MuniandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Plan Year 5 Science 2008Document5 paginiYearly Plan Year 5 Science 2008marccw2000Încă nu există evaluări
- Science Competencies in 5th and 6th Grade With Table of SpecificationsDocument25 paginiScience Competencies in 5th and 6th Grade With Table of SpecificationsTerence Pelingon89% (18)
- Chemistry Syllabus PDFDocument12 paginiChemistry Syllabus PDFMaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan Sains F1 2013Document8 paginiRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan Sains F1 2013mohd nazrul nizamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kisi-Kisi Um Ipa - For StudentsDocument2 paginiKisi-Kisi Um Ipa - For StudentsMuhammad SyahdalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Document9 paginiScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Annie GoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rancangan Tahunan Sains Tahun 5Document9 paginiRancangan Tahunan Sains Tahun 5Som Mai EmaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning Objectives 1. Animals Pupils Should LearnDocument6 paginiLearning Objectives 1. Animals Pupils Should LearnSeashellcrabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Plan SC Year 4Document16 paginiYearly Plan SC Year 4ajibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Chapter 2: Cell-The Basic Unit of LifeDocument2 paginiScience Chapter 2: Cell-The Basic Unit of LifeWan RoziahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week Topic Bil. Set Latihan Jumlah Soalan Objective StructureDocument2 paginiWeek Topic Bil. Set Latihan Jumlah Soalan Objective StructureJeevitha SubramaniamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Primary 6Document35 paginiScience Primary 6kadekspd42Încă nu există evaluări
- Learning Guide: Earth and Life Science SY: 2020-2021Document7 paginiLearning Guide: Earth and Life Science SY: 2020-2021lj BoniolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investigating Living ThingsDocument5 paginiInvestigating Living ThingsirisazreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jismo Science P3Document41 paginiJismo Science P3Astri Mustika dewiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum Specification For Year 5 Science 2011Document10 paginiCurriculum Specification For Year 5 Science 2011Aris HashimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investigating Living Things LA: 1. Interaction Among Living ThingsDocument11 paginiInvestigating Living Things LA: 1. Interaction Among Living ThingsCikgunazrisksac BasirunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jismo SCIENCE P3Document35 paginiJismo SCIENCE P3Astri Mustika dewiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ku Riku Lum Science Am T 211Document5 paginiKu Riku Lum Science Am T 211Azrai HashimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 5 Yearly PlanDocument14 paginiScience 5 Yearly PlanSri GanggaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd Grade Science SyllabusDocument6 pagini3rd Grade Science Syllabusepetadavid41Încă nu există evaluări
- Natsci 2Document4 paginiNatsci 2Angel OmlasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Course Outline: Autumn 2022 Online CompetitionDocument40 paginiScience Course Outline: Autumn 2022 Online CompetitionSherin KhairunnisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upper Primary Integrated Science Syllabus, Jan 2012 FinalDocument36 paginiUpper Primary Integrated Science Syllabus, Jan 2012 Finaldayas1979100% (4)
- RPT SN Y5Document8 paginiRPT SN Y5vargan_ramoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enabling and Enrichment Competencies For Science Melcs (Most Essential Learning Competencies)Document49 paginiEnabling and Enrichment Competencies For Science Melcs (Most Essential Learning Competencies)Zea May BiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jismo Science P5Document43 paginiJismo Science P5Astri Mustika dewiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 2: Be Friend With Nature: Theme ObjectivesDocument38 paginiGrade 2: Be Friend With Nature: Theme ObjectivessaurabhideaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignement 2.1-WPS OfficeDocument6 paginiAssignement 2.1-WPS OfficeJohn Carlo PastorÎncă nu există evaluări
- VI Science Practicepaper2Document3 paginiVI Science Practicepaper2Ravi KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jismo Science Primary 5Document29 paginiJismo Science Primary 5kadekspd42100% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument1 paginăLesson PlanAceley JainuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Lesson Plan English LanguageDocument23 paginiYearly Lesson Plan English LanguageSong Ji HyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Better Tomorrow - Choral SpeakingDocument4 paginiA Better Tomorrow - Choral SpeakingNoor HayanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 paginiHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Bega 7508Document1 paginăBega 7508Hussam HarbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Holophane Prismpack II 1000W Mercury Brochure 4-76Document2 paginiHolophane Prismpack II 1000W Mercury Brochure 4-76Alan MastersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan For Light With ReflectionDocument6 paginiLesson Plan For Light With Reflectionapi-454306115Încă nu există evaluări
- Shinyu CatalogDocument2 paginiShinyu CatalogCrescendo Solusi TamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smdmark PDFDocument1 paginăSmdmark PDFThe1LegendÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 5 Las Week 3Document5 paginiScience 5 Las Week 3Carramae MasibodÎncă nu există evaluări
- RESPONDALIGHT Product Guide 2010Document12 paginiRESPONDALIGHT Product Guide 2010steve9581Încă nu există evaluări
- Examen Ambrosio 2 InglesDocument12 paginiExamen Ambrosio 2 InglesLadhy Guadalupe Feliciano FuentesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peru 120W Solar All in One V2.0Document6 paginiPeru 120W Solar All in One V2.0luciano añorgaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of A Sunlight LuminaireDocument191 paginiDevelopment of A Sunlight LuminaireFREE BUSINESS INTELLIGENCEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pole Top Luminaire IP 66: Product Data SheetDocument1 paginăPole Top Luminaire IP 66: Product Data SheetNIKIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial LightingDocument34 paginiIndustrial Lightingrsgk75100% (2)
- OphthalDocument17 paginiOphthalSanketNandaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- (The Electromagnetic Spectrum) : Using WavesDocument44 pagini(The Electromagnetic Spectrum) : Using WavesSam JordanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waves and Their Applications PDFDocument14 paginiWaves and Their Applications PDFprimalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refraction of LightDocument5 paginiRefraction of LightannmarieÎncă nu există evaluări
- AHD Camera System Quotation From PST Aurora (2017!09!22)Document15 paginiAHD Camera System Quotation From PST Aurora (2017!09!22)Galo CandelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Colour Science, Digital Colour CommunicationDocument14 paginiBasics of Colour Science, Digital Colour CommunicationalianasirgillÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHD Comprehensive Viva by Ayele Ossa LekaDocument151 paginiPHD Comprehensive Viva by Ayele Ossa Lekaayele ossaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSBS Final Syllabus Year 1 - Ver 1.0 - May 2019Document36 paginiCSBS Final Syllabus Year 1 - Ver 1.0 - May 2019skarthikpriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Miles F. Osmaston - A Particle-Tied Aether: Indications of A Deeper Foundation For Physics and RelativityDocument12 paginiMiles F. Osmaston - A Particle-Tied Aether: Indications of A Deeper Foundation For Physics and RelativityKunma050Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3 4Document84 paginiLecture 3 4misbahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pillow AssignmentDocument3 paginiPillow Assignmenthetvi joshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BY Nana Sutisna Noor Akademi Maritim CirebonDocument49 paginiBY Nana Sutisna Noor Akademi Maritim CirebonChristian Nicholas SihombingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flow Cytometry: By: Dr. Megha Gupta & Dr. Tashi AgarwalDocument116 paginiFlow Cytometry: By: Dr. Megha Gupta & Dr. Tashi Agarwalanggaririn100% (1)
- Application Manual For Raytheon/L-3 TSC4500 Thermal-Eye Thermal Security CameraDocument26 paginiApplication Manual For Raytheon/L-3 TSC4500 Thermal-Eye Thermal Security CamerahightechtalentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subluksasi LensaDocument12 paginiSubluksasi LensaDede GunawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Night Vision TechnologyDocument23 paginiNight Vision Technologydeepak18m75% (4)
- Textbooks: 1. Pallab Bhattacharya "Semiconductor Opto Electronic Devices", Prentice Hall of India PVT.Document1 paginăTextbooks: 1. Pallab Bhattacharya "Semiconductor Opto Electronic Devices", Prentice Hall of India PVT.Petrishia ArockiasamyÎncă nu există evaluări