Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Trandate (Labetalol)
Încărcat de
E0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
3K vizualizări3 paginiLabetalol is an antianginal, 200 mg PO bid antihypertensives, beta blockers. Patients with a history of severe allergic reactions (intensity of reactions may increase), pregnancy, lactation, or children (safety not established) Common side effects Fatigue, weakness, orthostatic hypotension, impotence, aRRHYTHMIAS, BRADYCARDIA, CHF, pulmonary edema, cardiogenic (pulmonary, vascular, and uter
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Trandate (labetalol)
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentLabetalol is an antianginal, 200 mg PO bid antihypertensives, beta blockers. Patients with a history of severe allergic reactions (intensity of reactions may increase), pregnancy, lactation, or children (safety not established) Common side effects Fatigue, weakness, orthostatic hypotension, impotence, aRRHYTHMIAS, BRADYCARDIA, CHF, pulmonary edema, cardiogenic (pulmonary, vascular, and uter
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
3K vizualizări3 paginiTrandate (Labetalol)
Încărcat de
ELabetalol is an antianginal, 200 mg PO bid antihypertensives, beta blockers. Patients with a history of severe allergic reactions (intensity of reactions may increase), pregnancy, lactation, or children (safety not established) Common side effects Fatigue, weakness, orthostatic hypotension, impotence, aRRHYTHMIAS, BRADYCARDIA, CHF, pulmonary edema, cardiogenic (pulmonary, vascular, and uter
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
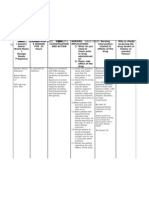
NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications Worksheets
(You will need to make additional copies of these forms)
Generic Name Trade Name Classification Dose Route Time/frequency
labetalol Normodyne, antianginals, 200 mg PO bid
Trandate antihypertensives,
Beta Blockers
Peak Onset Duration Normal dosage range
1-4 hrs 20 min-2 8-12 hrs 100 mg twice daily initially, may be increased by 100 mg
hrs twice daily q 2-3 days as needed (usual range 400-800
mg/day in 2-3 divided doses; doses up to 1.2-2.4 g/day
have been used)
Why is your patient getting this medication For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or
HTN solutions
N/A
Mechanism of action and indications Nursing Implications (what to focus on)
(Why med ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactions
Blocks stimulation of beta1 (myocardial)- and beta2 Uncompensated CHF, pulmonary edema, cardiogenic
(pulmonary, vascular, and uterine)-adrenergic shock, bradycardia or heart block. Use cautiously in:
receptor sites. Also has alpha1-adrenergic blocking Renal impairment, hepatic impairment, geriatric patients
activity, which may result in more orthostatic (increased sensitivity to beta blockers; initial dosage
hypotension. reduction recommended), pulmonary disease (including
asthma), Diabetes mellitus (may mask signs of
hypoglycemia), thyrotoxicosis (may mask symptoms).
Patients with a history of severe allergic reactions
(intensity of reactions may be increased), pregnancy,
lactation, or children (safety not established; may cause
fetal/neonatal bradycardia, hypotension, hypoglycemia, or
respiratory depression).
Common side effects
Fatigue, weakness, orthostatic hypotension, impotence,
ARRHYTHMIAS, BRADYCARDIA, CHF, PULMONARY EDEMA
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or Lab value alterations caused by medicine
herbal medicines (ask patient specifically) May cause increased BUN, serum lipoprotein, potassium,
Additive hypotension may occur with other triglyceride, and uric acid levels. May cause increased
antihypertensives (Avapro). ANA titers. May cause increase in blood glucose levels,
May cause increased serum alkaline phosphatase, LDH,
AST, and ALT levels. Discontinue if jaundice or laboratory
signs of hepatic function impairment occur.
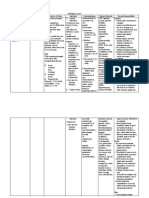
Be sure to teach the patient the following about this
medication
Instruct patient to take medication exactly as directed, at
the same time each day, even if feeling well; do not skip or
double up on missed doses. If a dose is missed, it should be
taken as soon as possible up to 8 hr before next dose.
Abrupt withdrawal may precipitate life-threatening
arrhythmias, hypertension, or myocardial ischemia. Advise
patient to make sure enough medication is available for
weekends, holidays, and vacations. A written prescription
may be kept in wallet in case of emergency. Teach patient
and family how to check pulse and blood pressure. Instruct
them to check pulse daily and blood pressure biweekly.
Advise patient to hold dose and contact health care
professional if pulse is <50 bpm or blood pressure changes
significantly. Advise patients to make position changes
slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension, especially
during initiation of therapy or when dose is increased.
Patients taking oral labetalol should be especially cautious
when drinking alcohol, standing for long periods, or
exercising, and during hot weather, because orthostatic
hypotension is enhanced. Caution patient that this
medication may increase sensitivity to cold. Instruct
patient to consult health care professional before taking any
OTC medications, especially cold preparations,
concurrently with this medication. Patients with diabetes
should closely monitor blood glucose, especially if
weakness, malaise, irritability, or fatigue occurs.
Medication may mask tachycardia and increased blood
pressure as signs of hypoglycemia, but dizziness and
sweating may still occur. Advise patient to notify health
care professional if slow pulse, difficulty breathing,
wheezing, cold hands and feet, dizziness, light-headedness,
confusion, depression, rash, fever, sore throat, unusual
bleeding, or bruising occurs. Instruct patient to inform
health care professional of medication regimen prior to
treatment or surgery. Advise patient to carry identification
describing disease process and medication regimen at all
times. Reinforce the need to continue additional therapies
for hypertension (weight loss, sodium restriction, stress
Nursing Process- Assessment Assessment Evaluation
(Pre-administration assessment) Why would you hold or not give this Check after giving
Monitor blood pressure and pulse med? Check frequency of refills to
frequently during dose adjustment and Signs of overdose (bradycardia, severe determine compliance.
periodically during therapy. Assess for dizziness or fainting, severe Decrease in blood pressure.
orthostatic hypotension when assisting drowsiness, dyspnea, bluish
patient up from supine position. Monitor fingernails or palms, seizures). Notify
intake and output ratios and daily weight. physician or other health care
Assess patient routinely for evidence of professional immediately if these
fluid overload (peripheral edema, signs occur. Glucagon has been used
dyspnea, rales/crackles, fatigue, weight to treat bradycardia and hypotension.
gain, jugular venous distention).
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Handout 2: Identifying Hazards and Risk Control in The Café: Step 1: Rest Step 2: Ice For Step 3: Step 4: ElevateDocument2 paginiHandout 2: Identifying Hazards and Risk Control in The Café: Step 1: Rest Step 2: Ice For Step 3: Step 4: ElevateSneha DhamijaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seroquel (Quetiapine)Document3 paginiSeroquel (Quetiapine)E100% (1)
- Supw Project Medicinal PlantsDocument7 paginiSupw Project Medicinal Plantsmehal gupta75% (4)
- Lopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgDocument2 paginiLopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgAdrianne Bazo100% (2)
- Dialysis: Hemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisDocument38 paginiDialysis: Hemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisNish Macadato BalindongÎncă nu există evaluări
- PaclitaxelDocument3 paginiPaclitaxelGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- Lamictal (Lamotrigine)Document1 paginăLamictal (Lamotrigine)E100% (1)
- Top Muscle Building and Weight Gain SecretsDocument8 paginiTop Muscle Building and Weight Gain SecretsKarl Gallagher83% (6)
- Drug Study of AminophyllineDocument6 paginiDrug Study of AminophyllineFrancis CorpuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study (Misoprostol)Document3 paginiDrug Study (Misoprostol)Danica NuevaexcijaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Keppra (Levetiracetam)Document2 paginiKeppra (Levetiracetam)E100% (1)
- Iron Deficiency Anemia PathoDocument6 paginiIron Deficiency Anemia PathoEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geodon (Ziprasidone)Document2 paginiGeodon (Ziprasidone)EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study - Nifedipine PODocument1 paginăDrug Study - Nifedipine POJet BautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digoxin Drug StudyDocument2 paginiDigoxin Drug StudyMaureen Campos-Pinera67% (3)
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 40mgDocument1 paginăProzac (Fluoxetine) 40mgEÎncă nu există evaluări
- CefiximeDocument1 paginăCefiximetaekado100% (1)
- Drug Study Delivery RoomDocument7 paginiDrug Study Delivery RoomkhleeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument6 paginiDrug StudyBrix John PortellanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TerbutalineDocument1 paginăTerbutalineRyan Paul Balot0% (1)
- CASP Case Control Study Checklist 2018 - Fillable - Form PDFDocument6 paginiCASP Case Control Study Checklist 2018 - Fillable - Form PDFEllieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neurontin (Gabapentin)Document1 paginăNeurontin (Gabapentin)E100% (3)
- RCHDocument25 paginiRCHgauravÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument6 paginiDrug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideMark ToxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument3 paginiNifedipine Drug StudyCrystal Queen MarquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study PethidineDocument2 paginiDrug Study Pethidinerica sebabillonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)Document2 paginiZosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)E67% (3)
- Hydralazine Drug StudyDocument2 paginiHydralazine Drug StudyErika Robella100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 paginiDrug Studyunkown userÎncă nu există evaluări
- OfloxacinDocument2 paginiOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Drug Study OxytocinDocument2 paginiDrug Study Oxytocinrica sebabillonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acyclovir Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 paginiAcyclovir Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComJanaica JuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synthroid (Levothyroxine)Document2 paginiSynthroid (Levothyroxine)E100% (2)
- DRUG STUDY - AminophyllineDocument2 paginiDRUG STUDY - AminophyllineKian Herrera100% (1)
- NEBOSH IG1 Open Book Mock Examination For Sept. 2022Document5 paginiNEBOSH IG1 Open Book Mock Examination For Sept. 2022m.naÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chlorpheniramine MaleateDocument3 paginiChlorpheniramine Maleateapi-3797941100% (1)
- Q& A DelegationDocument11 paginiQ& A DelegationFilipino Nurses CentralÎncă nu există evaluări
- SHEENA Clomid Drug StudyDocument3 paginiSHEENA Clomid Drug StudyNur SetsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chlorthalidone HygrotonDocument2 paginiChlorthalidone HygrotonLIEZEL GRACE VELAYOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study - Calcium GluconateDocument1 paginăDrug Study - Calcium GluconatemikErlhÎncă nu există evaluări
- BetamethasoneDocument3 paginiBetamethasoneMichael KuzbytÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antidiuretic DrugsDocument4 paginiAntidiuretic DrugsNavjot BrarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 paginiDrug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDanica Kate GalleonÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChlorphenamineDocument1 paginăChlorphenaminereinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study LabetalolDocument2 paginiDrug Study LabetalolJanzelvine Lee MontenegroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carboprost TromethamineDocument2 paginiCarboprost TromethamineDeathDefying DonutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 paginiDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- Drug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Document2 paginiDrug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Melinda Cariño Ballon100% (1)
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Document4 paginiChlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Nurginayah RusliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Sudy Format MethyldopaDocument3 paginiDrug Sudy Format MethyldopaBianca Marithè RejanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFDocument2 paginiDRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFMc SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument3 paginiLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Formoterol Gonzaga.Document2 paginiFormoterol Gonzaga.Sheryl Anne GonzagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole-Bactim-DSDocument4 paginiTrimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole-Bactim-DSAnika Pleños100% (1)
- THEOPHYLLINE - Drug StudyDocument2 paginiTHEOPHYLLINE - Drug Studyeric macabiogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pilocarpine (Drug Monograph)Document1 paginăPilocarpine (Drug Monograph)Muhammad ArsalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument4 paginiOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- Drug Study CaseDocument7 paginiDrug Study CaseKevin Sam AguirreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generic Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolDocument5 paginiGeneric Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolJay VillasotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument3 paginiClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsEÎncă nu există evaluări
- DS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Document2 paginiDS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Celline Isabelle ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study GuideDocument2 paginiDrug Study GuideAubrey SungaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MedroxyprogesteroneDocument5 paginiMedroxyprogesteroneunkown userÎncă nu există evaluări
- BuscopanDocument2 paginiBuscopancen janber cabrillosÎncă nu există evaluări
- CaptoprilDocument2 paginiCaptoprilJohn Louie EscardaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AminophyllineDocument9 paginiAminophyllineZaira BataloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Check The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutDocument2 paginiCheck The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutJust nowÎncă nu există evaluări
- PiroxicamDocument2 paginiPiroxicamVirginia Aira Lara MarquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- TergecefDocument2 paginiTergecefianecunar100% (3)
- Amikacin Drug StudyDocument4 paginiAmikacin Drug StudyMark Angelo LorzanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study - KetoprofenDocument3 paginiDrug Study - KetoprofenThalia UyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study - CefradoxilDocument13 paginiDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- MethergineDocument2 paginiMethergineRoseben SomidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study 04-21-09Document2 paginiDrug Study 04-21-09obietobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericDocument2 paginiDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericArian May MarcosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coreg (Carvedilol)Document3 paginiCoreg (Carvedilol)EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prinivil LisinoprilDocument3 paginiPrinivil LisinoprilEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyperparathyroidism PathoDocument2 paginiHyperparathyroidism PathoEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Pancreatitis PathoDocument5 paginiAcute Pancreatitis PathoEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Influenza B PathoDocument4 paginiInfluenza B PathoEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISDocument4 paginiPyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyponatremic Dehydration PathoDocument4 paginiHyponatremic Dehydration PathoEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument4 paginiCongestive Heart FailureEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia Short PathoDocument2 paginiPneumonia Short PathoEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pancreatitis Short PathoDocument2 paginiPancreatitis Short PathoEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congestive Heart Failure-ABDocument3 paginiCongestive Heart Failure-ABEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buspar (Buspirone)Document1 paginăBuspar (Buspirone)EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theragran (Multiple Vitamins)Document3 paginiTheragran (Multiple Vitamins)EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Silvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)Document1 paginăSilvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Campral (Acamprosate Calcium)Document1 paginăCampral (Acamprosate Calcium)E100% (1)
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument1 paginăClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Document2 paginiLexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Florinef (Fludrocortisone)Document3 paginiFlorinef (Fludrocortisone)E100% (1)
- ZofranDocument1 paginăZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- FiberCon (Polycarbophil)Document1 paginăFiberCon (Polycarbophil)EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecotrin (ASA 81mg)Document3 paginiEcotrin (ASA 81mg)E100% (1)
- Solu-Cortef (Hydrocortisone)Document3 paginiSolu-Cortef (Hydrocortisone)E100% (2)
- Zocor (Simvastatin)Document3 paginiZocor (Simvastatin)E100% (1)
- Lumasiran: An Investigational Rnai Therapeutic For Primary Hyperoxaluria Type 1 (Ph1)Document1 paginăLumasiran: An Investigational Rnai Therapeutic For Primary Hyperoxaluria Type 1 (Ph1)Muhammad HaneefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessing Change in Women's Lives: A Conceptual Framework: Marty Chen Simeen MahmudDocument47 paginiAssessing Change in Women's Lives: A Conceptual Framework: Marty Chen Simeen MahmudmustafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daftar PustakaDocument37 paginiDaftar PustakaprilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MUMPSDocument14 paginiMUMPScicichepiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constructing A Nursing Budget Using A Pateint Classification SystemDocument3 paginiConstructing A Nursing Budget Using A Pateint Classification SystemRhey March100% (1)
- CDEM 17jan Complete WEBDocument24 paginiCDEM 17jan Complete WEBRicardo Jonathan Ayala GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5 First Aid and Antidotes Against Pesticides PoisoningDocument45 paginiLecture 5 First Aid and Antidotes Against Pesticides PoisoningMuhammad Shahrooz NaseerÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Right To Die: Pre-ReadingDocument8 paginiThe Right To Die: Pre-ReadingGiovanni EscobarÎncă nu există evaluări
- NBHS 1104 Topic 2Document18 paginiNBHS 1104 Topic 2hema angleÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 06Document7 paginiCH 06john mwangiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calcium CarbideDocument8 paginiCalcium CarbidetaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Errors 2Document5 paginiErrors 2Anggun rahmi PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attending Physician Statement (APS) - TPD - FamilyDocument3 paginiAttending Physician Statement (APS) - TPD - FamilyTaufik Hameed SultanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SDS 80 Fat Unsalted Butter Lactic AcidDocument8 paginiSDS 80 Fat Unsalted Butter Lactic Acidfiyan maulanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bdda2948944613921 1Document2 paginiBdda2948944613921 1info.worldwideimmigration.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSDS 681039Document9 paginiMSDS 681039toshibastabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSC Advert - 14.9.2021 2Document15 paginiPSC Advert - 14.9.2021 2Derrick Ombura NazleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lung Cap DataDocument1 paginăLung Cap DataKaren NelsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Term Paper About Alcoholic DrinksDocument7 paginiTerm Paper About Alcoholic Drinksafmzbdjmjocdtm100% (1)
- Intellectual Disability: Definition, Classification, Causes and CharacteristicsDocument13 paginiIntellectual Disability: Definition, Classification, Causes and CharacteristicsVictor BuqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gubra DIO Mouse Data FlyerDocument2 paginiGubra DIO Mouse Data FlyerGabrielaMirelaAlexeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bonderite® L-GPDocument6 paginiBonderite® L-GPLubricantes velazcresÎncă nu există evaluări