Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
PWM
Încărcat de
notastudentDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
PWM
Încărcat de
notastudentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
msd 101
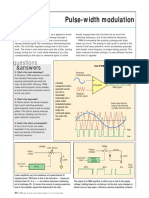
Pulse-width modulation
words, energy flows into the load not so much the switching frequency, but at the reference frequency. PWM is somewhat like pushing a playground-style merry-go-round. The energy of each push is stored in the inertia of the heavy platform, which accelerates gradually with harder, more frequent, or longer-lasting pushes. The riders receive the kinetic energy in a very different manner than how its applied.
ulse-width modulation (PWM), as it applies to motor control, is a way of delivering energy through a succession of pulses rather than a continuously varying (analog) signal. By increasing or decreasing pulse width, the controller regulates energy flow to the motor shaft. The motors own inductance acts like a filter, storing energy during the on cycle while releasing it at a rate corresponding to the input or reference signal. In other
questions &answers
Q: Whats the main advantage? A: Efficiency. PWM amplifiers run cooler than standard linear power amps, requiring substantially less heat sink mass. At about 90% efficiency, PWM makes electromagnetic motion feasible at power levels where hydraulics used to be the only option. Q: Whats the downside? A: Nature doesnt like abrupt changes; high-current switching generates electromagnetic noise as well as voltage spikes. This calls for special measures like filtering, shielding, and the use of spike-hardened components. Q: Whats the effect on bandwidth? A: As a rule of thumb, the usable bandwidth of the command signal is about one decade (10X) below the switching frequency. Command (modulating) signal
How PWM works
High
+
A simple comparator with a sawtooth carrier can turn a sinusoidal command into a pulse-width modulated output. In general, the larger the command signal, the wider the pulse.
Comparator PWM signal Low
Chopping (carrier) signal
Output stays high as long as the command is greater than the carrier. H H H H H H H
L L L High Low
Linear
Supply voltage
Pass element
PWM
Supply voltage RL Load Load Command input PWM control 50% 5% Duty cycle
Command input
Driver
95%
Linear amplifiers vary the resistance of a pass element to regulate power. Efficiency is fine at the extremes losses are minimal when R = 0 or but suffers elsewhere, bottoming out at midrange (R = RL) where the amount of energy wasted as heat in the amplifier equals that delivered to the load. 66
PTdesign www.motionsystemdesign.com October 2000
The output of a PWM amplifier is either zero or tied to the supply voltage, holding losses to a minimum. As the duty cycle changes to deliver more or less power, efficiency remains essentially constant.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Încă nu există evaluări
- Pulse-Width Modulation: QuestionsDocument1 paginăPulse-Width Modulation: QuestionsAlvaro CanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Switching Frequency Modulated DC-to-DC Converter With Reduced Spurious Noise For A RF Power Amplifier in Microwatts TransmittersDocument8 paginiA Switching Frequency Modulated DC-to-DC Converter With Reduced Spurious Noise For A RF Power Amplifier in Microwatts Transmitterssoo kimÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMI Reduction in Class-D Amplifiers by Actively Reducing PWM RippleDocument9 paginiEMI Reduction in Class-D Amplifiers by Actively Reducing PWM RippleAbhishek SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energies 13 00222 PDFDocument19 paginiEnergies 13 00222 PDFDjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of A Synchronous Rectified Switching Regulator Chip For CPU Power SupplyDocument4 paginiDesign of A Synchronous Rectified Switching Regulator Chip For CPU Power SupplysrdjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amplitude Modulator Description Application Example CircuitDocument3 paginiAmplitude Modulator Description Application Example CircuitJohanna Gwenn Taganahan LomaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequency Tracking Burst-Mode PDM-controlled Class-D Zero Voltage Soft-Switching Resonant Converter For Inductive Power Transfer ApplicationsDocument8 paginiFrequency Tracking Burst-Mode PDM-controlled Class-D Zero Voltage Soft-Switching Resonant Converter For Inductive Power Transfer ApplicationsLuis Alfonso Martinez FdezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 500-kHz Half-Bridge DC-DC ConverterDocument17 pagini500-kHz Half-Bridge DC-DC Converteratkxyz777100% (1)
- Shunt Current Sensing in 3 Phase MotorDocument8 paginiShunt Current Sensing in 3 Phase MotorHoàng Minh ĐỗÎncă nu există evaluări
- Output 2Document10 paginiOutput 2abdul shaggyÎncă nu există evaluări
- PFM - Pulse Frequency Modulation: Jaydeep ShahDocument3 paginiPFM - Pulse Frequency Modulation: Jaydeep ShahJAYDEEP SHAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geigermullerteller (Nuts and Volts 2004-01)Document5 paginiGeigermullerteller (Nuts and Volts 2004-01)Peeters GuyÎncă nu există evaluări
- WCDMA Key Technologies: ZTE University TD&W&PCS BSS Course TeamDocument42 paginiWCDMA Key Technologies: ZTE University TD&W&PCS BSS Course TeamNaman ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Test Jig Method in DFT ? - List Out Some Applications of Operational AmplifierDocument27 paginiWhat Is Test Jig Method in DFT ? - List Out Some Applications of Operational AmplifierKasu Sujith ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ni 2020Document15 paginiNi 2020tusharshharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analog Electronics Unit - 5Document66 paginiAnalog Electronics Unit - 5Rohit KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control of Reactive Power and VoltageDocument38 paginiControl of Reactive Power and VoltageKanak RaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pelletier DigitalServoAmplifierBasicsDocument32 paginiPelletier DigitalServoAmplifierBasicsJosé Juan De león JuárezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 WO - BT1002 - E01 - 1 UMTS Key Technologies-78Document78 pagini01 WO - BT1002 - E01 - 1 UMTS Key Technologies-78bilawal siddiqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- WR - bt04 - E1 - 1 Wcdma Key Technology 80Document80 paginiWR - bt04 - E1 - 1 Wcdma Key Technology 80dwaipayanchakÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 - Lecture 5 - PWMDocument13 pagini03 - Lecture 5 - PWMhoxojew752Încă nu există evaluări
- Hybrids-Simulation Using Different Model Basis For Converter Dominated Distribution GridDocument18 paginiHybrids-Simulation Using Different Model Basis For Converter Dominated Distribution Gridrajaavikhram3719Încă nu există evaluări
- Average Current Mode Control of Switching Power Supplies: Application Note U - 1 4 0Document15 paginiAverage Current Mode Control of Switching Power Supplies: Application Note U - 1 4 0Vicente CabreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Average Current Mode ControlDocument15 paginiAverage Current Mode Controlsmart2986Încă nu există evaluări
- Reactive Power ControlDocument37 paginiReactive Power Controlstrange_kid82Încă nu există evaluări
- DatashitDocument20 paginiDatashitPablo ArevaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advantage and Disadvantage PCMPWMPPM and PamDocument2 paginiAdvantage and Disadvantage PCMPWMPPM and PamJerika ToraldeÎncă nu există evaluări
- PQ ReviewDocument43 paginiPQ ReviewsanjayÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Comparative Study of Combined Unipolar and Bipolar PWM With The SVPWM For The Power Quality ImprovementDocument6 paginiA Comparative Study of Combined Unipolar and Bipolar PWM With The SVPWM For The Power Quality ImprovementDar JahangeerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of An Average Inductor-Current-Sensing CircuitDocument27 paginiDesign of An Average Inductor-Current-Sensing Circuitsoo kimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analog IC Design With Low-Dropout RegulatorsDocument373 paginiAnalog IC Design With Low-Dropout RegulatorsHoang le Huy67% (3)
- Fairchild AnDocument17 paginiFairchild AnhvhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signal Conditioning SystemsDocument20 paginiSignal Conditioning SystemsgvgfyfvicykÎncă nu există evaluări
- Load Line MeasurementDocument1 paginăLoad Line Measurementfalcon_developmentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demodulation PWM SignalDocument11 paginiDemodulation PWM SignalINDRANILÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4b - Introduction To Basic Amplifier Circuits and ParametersDocument25 pagini4b - Introduction To Basic Amplifier Circuits and Parametersfauzan putraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proportional Amplifier PVR: For Reversing DrivesDocument8 paginiProportional Amplifier PVR: For Reversing DrivesNelson Enrique Pimiento SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Features Description: D D D D DDocument41 paginiFeatures Description: D D D D DNelson OrjuelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Measurement BasicsDocument27 paginiPower Measurement BasicsSatadal GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- lt8356 1-2955993Document27 paginilt8356 1-2955993chawkigenieÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABB Taiwan Power Quality 電力品質: Jame Huang 黃昭明 Front End SalesDocument27 paginiABB Taiwan Power Quality 電力品質: Jame Huang 黃昭明 Front End SalesmypopularÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control of Boost Type Converter in Discontinuous Conduction Mode by Controlling The Product of Inductor Voltage-SecondDocument8 paginiControl of Boost Type Converter in Discontinuous Conduction Mode by Controlling The Product of Inductor Voltage-Secondseyed mohsen SalehiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance Characterization of Two Selfoscillating ControllersDocument7 paginiPerformance Characterization of Two Selfoscillating ControllersJie99Încă nu există evaluări
- Slides 03 AnalogElectronics 2Document30 paginiSlides 03 AnalogElectronics 2baraulia substationÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 WO - BT1002 - E01 - 1 UMTS Key Technologies-78Document78 pagini01 WO - BT1002 - E01 - 1 UMTS Key Technologies-78hamadashraf301Încă nu există evaluări
- CapMedPlus Copley 281plus Gradient AmpDocument8 paginiCapMedPlus Copley 281plus Gradient AmpGiovanni100% (1)
- Chapter 10Document15 paginiChapter 10Rehan ZulfiqarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guzman, Agabin Equipment ReportDocument15 paginiGuzman, Agabin Equipment ReportFloryan GorospeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slup 386Document25 paginiSlup 386AuslanderÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRANSDocument8 paginiTRANSCol. Jerome Carlo Magmanlac, ACPÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Analysis of Buck Converter Efficiency in PWM/PFM Mode With SimulinkDocument6 paginiAn Analysis of Buck Converter Efficiency in PWM/PFM Mode With SimulinkAli RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sboa 174 DDocument3 paginiSboa 174 DKrishan Kumar PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Considerations For An LLC Resonant ConverterDocument9 paginiDesign Considerations For An LLC Resonant ConverterBOLFRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Lecture NotesDocument15 pagini2 Lecture Notesankit.chandra.eee21Încă nu există evaluări
- 03 WR - bt1004 - E01 - 1 Wcdma Key Technology-80Document80 pagini03 WR - bt1004 - E01 - 1 Wcdma Key Technology-80hamadashraf301Încă nu există evaluări
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Evaluare: 2.5 din 5 stele2.5/5 (3)